Commercial Greenhouse Market Size and Growth
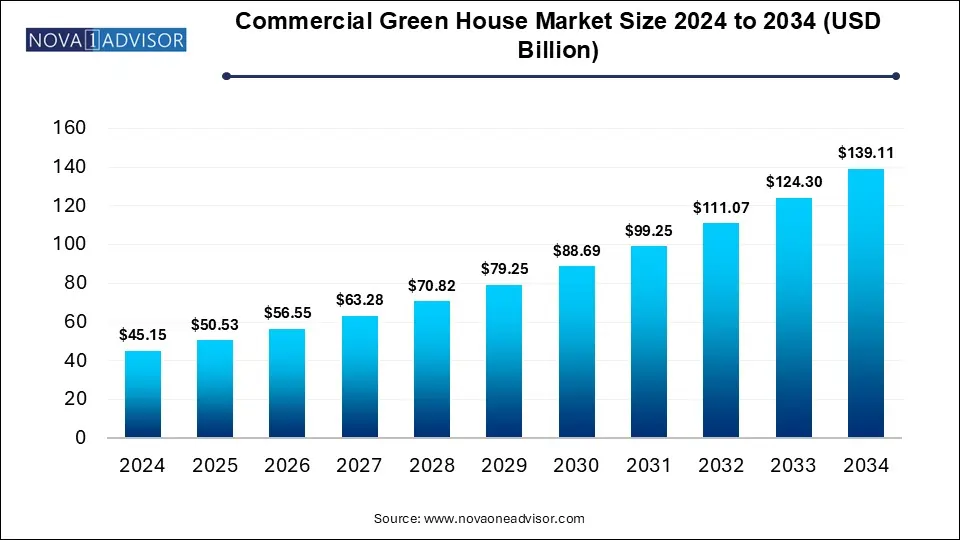
The global commercial greenhouse market was valued at USD 50.53 billion in 2025 and is projected to hit USD 139.11 billion by 2034, registering a CAGR of 11.19% from 2025 to 2034. The global commercial greenhouse market growth is attributed to the increasing demand for commercial services and solutions
Commercial Greenhouse Market Key Takeaways
- By region, North America dominated the commercial greenhouse market in 2024.
- By region, Asia Pacific is expected to grow fastest during the forecast period.
- By type insights, the glass greenhouse segment dominated the market share in 2024.
- By type insights, the plastic greenhouse segment is expected to grow fastest during the forecast.
- By application insights, the fruits and vegetables segment dominated the commercial greenhouse market in 2024.
- By application insights, the flowers and ornaments segment is expected to grow fastest during the forecast period.
Commercial Greenhouse Market Overview
The commercial greenhouse market deals with a controlled environment designed for the cultivation of plants, typically used for agricultural production on a huge amount, whereas factors such as light, humidity, and temperature are regulated to improve plant growth and yield. The market is witnessing rapid technological transformation through the integration of smart greenhouse solutions and precision agriculture. Advanced automation systems incorporating machine learning and artificial intelligence are being deployed to optimize resource management, predict disease outbreaks, and analyze crop health.
The adoption of IoT sensors for monitoring soil moisture, temperature and humidity is enabling real-time data-driven decisions for optimal crop growth and has become increasingly prevalent in controlled environment agriculture. With a growing emphasis on renewable energy integration and water conservation sustainability initiatives are further driving the commercial greenhouse market. Companies are implementing geothermal energy solutions, wind turbines, and solar panels to power commercial greenhouse operations while reducing carbon footprints, which further drives the market growth.
Commercial Greenhouse Market Trends
- Strategic initiatives: as companies seek to enhance their technological capabilities and market presence, strategic partnerships and industry consolidation are becoming increasingly prevalent as companies seek, which may drive market growth.
- Decrease in agricultural land: The continuous decline in global agricultural land has emerged as a major factor for the commercial greenhouse market. This trend is especially evident in emerging regions.
- Increased demand for food: The increasing food demand due to the changing dietary preferences and rapid urbanization are further expected to drive market growth
Report Scope of Commercial Greenhouse Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 50.53 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 |
USD 139.11 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2025 to 2034 |
CAGR of 11.19% |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2034 |
| Segments Covered |
By Type, Application and Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Priva Group (Netherlands), Hoogendoorn Growth Management (Netherlands), Ridder Group (Netherlands), Heliospectra AB (Sweden), Signify (formerly Philips Lighting) (Netherlands), Argus Control Systems Ltd. (Canada), Certhon (Netherlands), Rough Brothers Inc. (United States), Agra Tech Inc. (United States), Nexus Corporation (United States), Cravo Equipment Ltd. (Canada), GreenTechAgro LLC (United States), Planta Corp. (Canada), Richel Group (France), Harnois Greenhouses (Canada), Van Wingerden Greenhouses (United States), Logiqs B.V. (Netherlands), Van der Hoeven Horticultural Projects B.V. (Netherlands), Stuppy Inc. (United States), Ammerlaan Construction (Netherlands), Others. |
AI-driven systems in commercial greenhouse create opportunities
The continuous advancements in Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA) technology create significant opportunities in the market. These innovations enable greenhouse operators to enhance sustainability and productivity by improving increasing conditions for crops. By minimizing resource wastage and environmental impact, AI systems contribute to more sustainable agricultural practices and boost profitability for greenhouse operators. In addition, the commercial greenhouses equipped with state-of-the-art CEA systems will further be expected to enhance the growth of the commercial greenhouse market as the technology continues to evolve.
Regulatory compliance and permitting challenges
The obtaining permits and navigating regulatory compliance for greenhouse operations and construction creates formidable challenges that restrain market expansion and growth. The intricate web of regulations can cause costly and lengthy processes, impeding the entry of new players and deterring potential investors into the commercial greenhouse market.
Segment Insights
Commercial Greenhouse Market By Type
The glass greenhouse segment dominated the commercial greenhouse market in 2024. The segment is widely favored for cultivating high-value crops such as herbs, vegetables, and flowers and is driven by advantages such as superior light transmission and durability. Whereas the plastic greenhouse segment is expected to grow fastest during the forecast period. The segment serves a diverse range of applications from commercial farming to research and educational uses and offers flexibility in terms of size and design. Due to the lower upfront costs and versatility of plastic greenhouse, they are popular among small to medium-sized growers, which may drive the segment growth.
Commercial Greenhouse Market By Application
The fruits and vegetables segment dominated the commercial greenhouse market in 2024. The segment growth in the market is driven by factors such as the increasing ability of controlled environments to improve growth conditions and the increasing demand for fresh produce year-round. In addition, the flowers and ornaments are favored for their aesthetic appeal and find extensive use in horticultural exhibitions, floral arrangements and landscaping, which is further expected to drive the segment growth in the global market.
Commercial Greenhouse Market By Regional
North America dominated the commercial greenhouse market in 2024. The market growth in the region is attributed to the increasing demand for locally grown produce, rising adoption rates and technological advancements in the cultivation of vegetables, fruits and high-value specialty crops, and increasing consumer preferences for sustainability and freshness. The U.S. and Canada are the dominating countries in the region.
Asia Pacific Commercial Green House Market Trends
The Asia Pacific is expected to grow fastest during the forecast period. The market growth in the region is driven by the increasing focus on export-oriented crops such as vegetables and fruits, favorable government incentives and climatic conditions, rising disposable income and increasing urbanization. China India, Japan, and South Korea are the fastest growing countries in the region.
Some of The Prominent Players in The Commercial Greenhouse Market Include:
- Priva Group (Netherlands)
- Hoogendoorn Growth Management (Netherlands)
- Ridder Group (Netherlands)
- Heliospectra AB (Sweden)
- Signify (formerly Philips Lighting) (Netherlands)
- Argus Control Systems Ltd. (Canada)
- Certhon (Netherlands)
- Rough Brothers Inc. (United States)
- Agra Tech Inc. (United States)
- Nexus Corporation (United States)
- Cravo Equipment Ltd. (Canada)
- GreenTechAgro LLC (United States)
- Planta Corp. (Canada)
- Richel Group (France)
- Harnois Greenhouses (Canada)
- Van Wingerden Greenhouses (United States)
- Logiqs B.V. (Netherlands)
- Van der Hoeven Horticultural Projects B.V. (Netherlands)
- Stuppy Inc. (United States)
- Ammerlaan Construction (Netherlands)
- Others
Commercial Green House Market Recent Breakthroughs
- In March 2025, The MSU Extension Floriculture Team is pleased to announce the launch of a new educational video series designed to help greenhouse growers transition to biological control for managing pests in spring floriculture crops.
- In March 2025, the provider of AI solutions for vegetable growers, Source.ag announced the launch of three new product tiers, making access to high-quality data and AI more affordable and accessible for growers across the globe. By integrating AI-driven solutions into daily greenhouse operations, these new offerings are designed to help growers unlock significant growth, and scale and become more profitable.
- In August 2024, The National Aeronautics and Space Administration launched a satellite carrying a greenhouse gas-tracking device into the Earth’s orbit. The aim behind his launch was to provide “actionable data” to help slash emissions that give rise to global warming, per the agency.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Commercial Greenhouse Market.
By Type
- Glass Greenhouse
- Plastic Greenhouse
- Others
By Application
- Fruits & Vegetables
- Flowers & Ornamentals
- Nursery Crops
- Others
By Regional
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa (MEA)

