AI In Healthcare Market Size and Research 2026 to 2035
The AI in healthcare market size was exhibited at USD 37.09 billion in 2025 and is projected to hit around USD 861.04 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 36.95% during the forecast period 2026 to 2035.
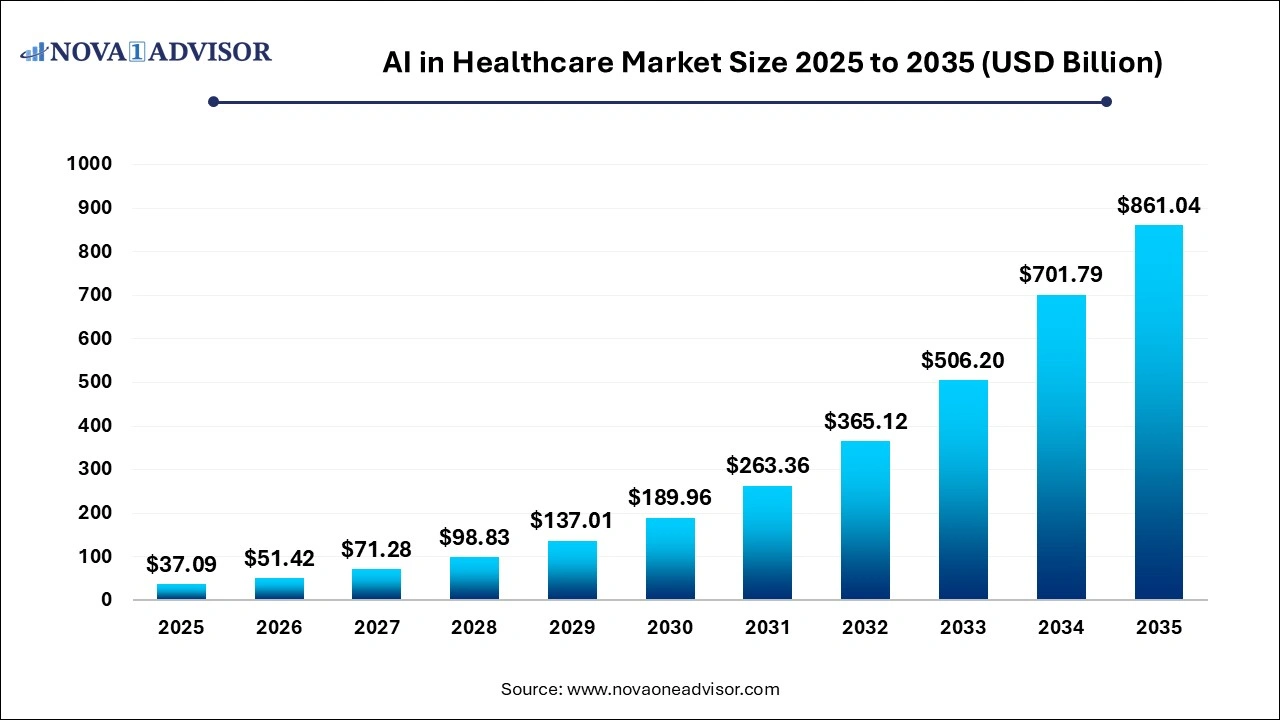
Key Takeaways:
- Based on component, the software solution segment dominated the market with the largest revenue share of over 47% in 2025.
- Based on application, the robot-assisted surgery segment dominated the market in 2025 with the largest revenue share of over 14%.
- Based on technology, the machine learning segment held the largest market share of over 36% in 2025.
- Based on end use, healthcare companies dominated the market with the largest revenue share of over 31% in 2025.
- North America AI in healthcare industry dominated the global market and accounted for the largest revenue share of over 55% in 2024.
AI In Healthcare Market Market Overview
The Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Healthcare market represents a transformative shift in how the global medical ecosystem operates. Leveraging advanced algorithms, machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), and computer vision, AI technologies are revolutionizing diagnostics, treatment planning, administrative efficiency, patient monitoring, and drug discovery. The healthcare industry, historically labor-intensive and cost-sensitive, is now embracing AI to enhance accuracy, reduce costs, and improve patient outcomes.
In 2025, the AI in healthcare market witnessed exponential growth driven by the rising burden of chronic diseases, increased digitization of health records, and a global emphasis on improving accessibility and quality of care. AI-based platforms are being utilized across hospitals, outpatient facilities, research centers, and even at the patient level via wearables and home monitoring devices. The emergence of smart assistants for elderly care, AI-powered robotic surgeries, and intelligent data management systems is further elevating the role of AI from auxiliary support to a central operational pillar.
Leading organizations and governments are investing heavily in AI to reshape public health policies and infrastructure. For instance, the UK's National Health Service (NHS) launched the AI Lab in 2020 to fund projects focusing on cancer diagnosis and stroke care. Similarly, in the U.S., the FDA has approved over 500 AI-enabled medical devices by 2024, signaling strong regulatory momentum. These developments, coupled with technological advancements, are pushing the AI in healthcare market toward an unprecedented trajectory.
Major Trends in the AI In Healthcare Market
-
Integration of AI with Electronic Health Records (EHRs) to enable predictive analytics and early intervention strategies.
-
Increased adoption of AI-powered robotic surgery systems, enhancing precision and reducing procedural time.
-
Expansion of AI-based remote patient monitoring (RPM) and virtual care platforms for chronic disease management.
-
Rise in cloud-based AI deployments to facilitate scalable solutions across diverse healthcare settings.
-
Use of NLP in administrative workflows, including automated medical coding, claims processing, and patient documentation.
-
Implementation of computer vision for image-based diagnostics, including MRI, CT scans, and pathology.
-
AI-driven drug discovery platforms reducing R&D costs and time-to-market for new therapies.
-
Use of AI algorithms in wearables and fitness apps, personalizing wellness and early disease detection.
-
Proliferation of cybersecurity solutions powered by AI to counter rising threats to healthcare data systems.
-
Growing interest in explainable AI (XAI) for ethical and transparent medical decision-making.
Report Scope of AI In Healthcare Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2026 |
USD 51.42 Billion |
| Market Size by 2035 |
USD 861.04 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2026 to 2035 |
CAGR of 36.95% |
| Base Year |
2025 |
| Forecast Period |
2026 to 2035 |
| Segments Covered |
Component, Application, Technology, End use, and Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (USD Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Microsoft; IBM; NVIDIA Corporation; Intel Corporation; Itrex Group; GE Healthcare; Google; Medtronic; Oracle; Medidata; Merck; IQVIA |
Market Driver: Rising Need for Operational Efficiency in Healthcare
One of the strongest drivers behind the AI in healthcare market is the pressing need to enhance operational efficiency while managing costs. Healthcare systems globally are grappling with a shortage of skilled professionals, an aging population, and rising treatment costs. Administrative tasks—ranging from billing to scheduling consume up to 25% of hospital budgets. AI steps in as a powerful tool to automate these tasks, optimize resource utilization, and streamline workflows.
For instance, administrative workflow assistants using NLP can transcribe clinical notes in real time, freeing physicians to focus on patient care. AI-driven triage systems reduce unnecessary emergency room visits by guiding patients toward appropriate care settings. In logistics, predictive AI models can forecast equipment maintenance needs and optimize inventory. These efficiencies translate to improved patient throughput, reduced burnout among staff, and overall cost savings establishing AI as a fundamental enabler of value-based healthcare.
Market Restraint: Data Privacy and Ethical Concerns
Despite its advantages, the AI in healthcare market faces notable challenges, primarily centered around data privacy, security, and ethics. Healthcare data is highly sensitive, and breaches can have severe legal and reputational consequences. Moreover, AI systems trained on biased or incomplete datasets may produce skewed outcomes, especially for underrepresented populations.
There are also ethical concerns regarding consent, accountability, and transparency. Patients and clinicians may hesitate to rely on algorithms for decisions involving life and death, particularly when the rationale behind AI predictions isn’t explainable. Additionally, cross-border data sharing for AI training purposes faces regulatory friction due to varying international data protection laws like HIPAA, GDPR, and others. These limitations must be addressed through robust compliance frameworks, data anonymization technologies, and the development of explainable AI models.
Market Opportunity: AI in Personalized and Precision Medicine
An outstanding opportunity within this market is the application of AI in personalized and precision medicine. Tailoring treatment plans based on a patient’s genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors holds enormous potential in improving outcomes while minimizing side effects. However, this requires complex analysis of large datasets something AI excels at.
Machine learning algorithms can sift through genomic sequences, clinical data, and treatment histories to recommend therapies most likely to succeed for a specific patient. AI tools are being used in oncology, cardiology, and neurology to guide immunotherapy, gene therapy, and targeted drugs. For example, IBM Watson Genomics partners with pathologists to identify mutations in a tumor that can be matched to clinical trials. As sequencing costs drop and data availability rises, AI will be the catalyst enabling mainstream adoption of precision medicine.
AI In Healthcare Market Segmental Analysis
By Component Analysis
Software solutions accounted for the largest share of the AI in healthcare market, as they serve as the core engines for diagnostics, data interpretation, and decision support. From NLP-enabled documentation platforms to AI algorithms analyzing CT scans, software solutions are central to all AI applications. The proliferation of cloud-based platforms like Google Health and Microsoft Azure Health Data Services has further boosted access to high-performance AI engines without needing significant on-premise infrastructure.
The services segment is witnessing the fastest growth, especially in areas of deployment, integration, and compliance management. As healthcare organizations transition to AI-enabled operations, they require specialized support for integrating tools with legacy systems, training staff, and ensuring compliance. Consulting services are also in demand to assess workflow suitability and ROI for AI investments. These services are critical in translating theoretical AI capabilities into tangible outcomes in diverse clinical environments.
By Application Analysis
Medical imaging and diagnostics is the dominant application area, primarily due to the sheer volume of radiological data and the proven capability of AI in improving accuracy. Tools like Aidoc and Zebra Medical Vision can detect anomalies like brain hemorrhages, lung nodules, or breast cancer signs faster and with greater precision than traditional methods. Hospitals are increasingly relying on AI to triage critical findings, reduce radiologist workload, and prevent diagnostic errors.
Lifestyle management and remote patient monitoring is the fastest-growing application, driven by an aging population, chronic disease prevalence, and the rise of digital health. AI integrated into wearables, mobile apps, and home monitoring systems can track vital signs, detect early anomalies, and alert caregivers. For instance, Apple Watch’s AFib detection and Fitbit’s sleep score algorithms are widely adopted tools. The COVID-19 pandemic further accelerated the demand for RPM solutions, with AI becoming the backbone of scalable, contactless care.
By Technology Analysis
Machine learning continues to dominate the AI healthcare technology segment, encompassing both supervised and unsupervised learning methods. These models are widely used for predictive analytics, treatment recommendation systems, and workflow optimization. Supervised learning, in particular, has seen success in diagnostics and triage, while reinforcement learning is being explored in robotic surgeries and personalized drug dosing.
Computer vision is the fastest-growing technology, fueled by its application in image-intensive areas like pathology, radiology, dermatology, and ophthalmology. AI models now surpass human-level performance in tasks like identifying diabetic retinopathy from retinal scans. Tools like PathAI and Paige are revolutionizing cancer diagnosis through digital pathology. As imaging hardware becomes more accessible and high-quality datasets expand, computer vision will play an increasingly central role in diagnostic workflows.
By End Use Analysis
Healthcare providers remain the leading end users, encompassing hospitals, outpatient facilities, and integrated care networks. Providers use AI across diagnostics, operations, clinical decision-making, and patient engagement. EHR-based AI tools offer predictive alerts for sepsis or readmission risks, helping clinicians make timely interventions. Robotic surgery, AI triage, and administrative bots are streamlining both clinical and back-office functions.
The patient segment is gaining traction rapidly, thanks to consumer-friendly AI in wearables, mobile apps, and telehealth platforms. Patients are now active participants in their health journeys, empowered by AI tools that monitor glucose levels, detect cardiac irregularities, or assist in mental wellness. Virtual assistants like Ada Health and Babylon AI offer medical insights directly to users. As digital literacy improves, patients will increasingly drive demand for personalized AI health solutions.
Regional Analysis
North America, led by the United States, dominates the global AI in healthcare market, thanks to strong technological infrastructure, high healthcare spending, and a vibrant ecosystem of startups, tech giants, and academic research. The U.S. boasts the highest number of FDA-approved AI medical devices and is home to leaders like IBM Watson, Microsoft, and NVIDIA. Healthcare providers in North America have aggressively adopted AI in EHR management, radiology, robotic surgeries, and virtual care platforms.
The region benefits from public-private partnerships, ample venture capital, and progressive regulatory environments. For instance, Canada’s Pan-Canadian AI Strategy and the U.S. ONC’s interoperability initiatives are laying the groundwork for seamless data exchange and AI deployment. Strong reimbursement models for digital health services further accelerate adoption.
Asia Pacific is experiencing the fastest growth in the AI in healthcare market, fueled by large populations, rising chronic disease burden, and government investments in digital health infrastructure. Countries like China and India are launching AI-driven telemedicine platforms to bridge healthcare gaps in rural areas. China's government has declared AI a national priority, leading to rapid commercialization in diagnostics and imaging.
Japan and South Korea are investing in AI robotics for eldercare, while Singapore and Australia are focusing on AI in population health management. The region’s strength lies in its ability to leapfrog traditional systems and adopt cloud-native, mobile-first AI models. Combined with rising disposable incomes and improving digital literacy, APAC offers unmatched growth potential for AI healthcare innovations.
Some of The Prominent Players in The AI in healthcare market Include:
Recent Developments
-
March 2025: Google Health announced the expansion of its AI mammography screening system to hospitals in India and South Africa through partnerships with regional NGOs.
-
January 2025: Microsoft introduced a GenAI-powered virtual assistant for hospitals, capable of summarizing clinical notes and supporting real-time physician queries.
-
November 2024: NVIDIA launched Clara Holoscan MGX a medical-grade AI computing platform designed for real-time surgical guidance and diagnostics.
-
September 2024: IBM Watson Health, rebranded as Merative, rolled out an AI-based patient engagement platform aimed at improving chronic care outcomes.
-
June 2024: Babylon Health secured contracts with multiple African governments to deploy AI triage and virtual consultation platforms in remote clinics.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2026 to 2035. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Operating room equipment market
By Component
-
-
- MPU (memory protection unit)
- FPGA (Field-programmable gate array)
- GPU (Graphics processing unit)
- ASIC (Application-specific integrated circuit)
-
-
- Adapter
- Interconnect
- Switch
-
-
- Application Program Interface (API)
- Machine Learning Framework
-
- Deployment & Integration
- Support & Maintenance
- Others (Consulting, Compliance management etc.)
By Application
- Robot Assisted Surgery
- Virtual Assistants
- Administrative Workflow Assistants
- Connected Medical devices
- Medical Imaging & Diagnostics
- Clinical Trials
- Fraud Detection
- Cybersecurity
- Dosage Error Reduction
- Precision medicine
- Drug discovery & development
- Lifestyle management & remote patient monitoring
- Wearables
- Others (Patient engagement, etc.)
By Technology
-
- Deep learning
- Supervised
- Unsupervised
- Others (Reinforcement learning, Semi supervised)
- Natural Language Processing
-
- Smart Assistance
- OCR (Optical Character Recognition)
- Auto Coding
- Text analytics
- Speech analytics
- Classification and categorization
- Context-Aware Computing'
- Computer Vision
By End Use
- Healthcare providers (hospitals, outpatient facilities, and others)
- Healthcare payers
- Healthcare companies (Pharmaceutical, Biotechnology, Medical Devices)
- Patients
- Others
By Regional
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa (MEA)

