Animal Drug Compounding Market Size and Growth
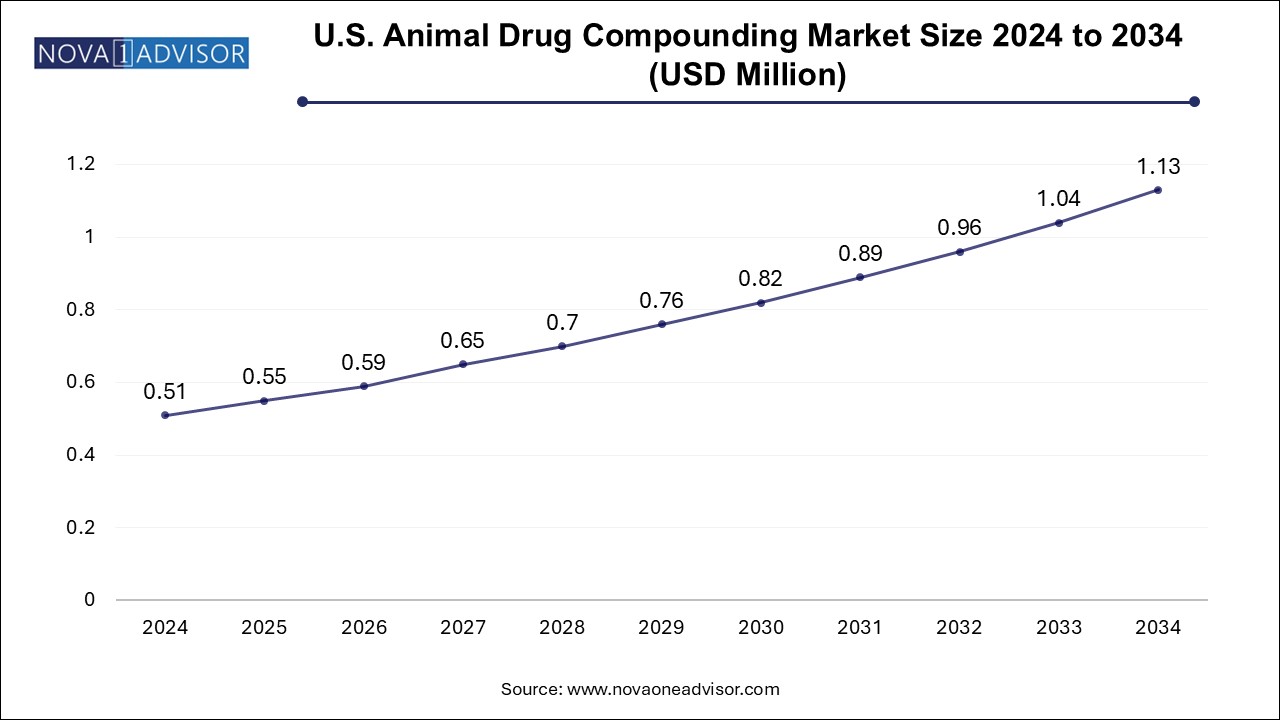
The animal drug compounding market size was exhibited at USD 1.65 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 3.66 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 8.29% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
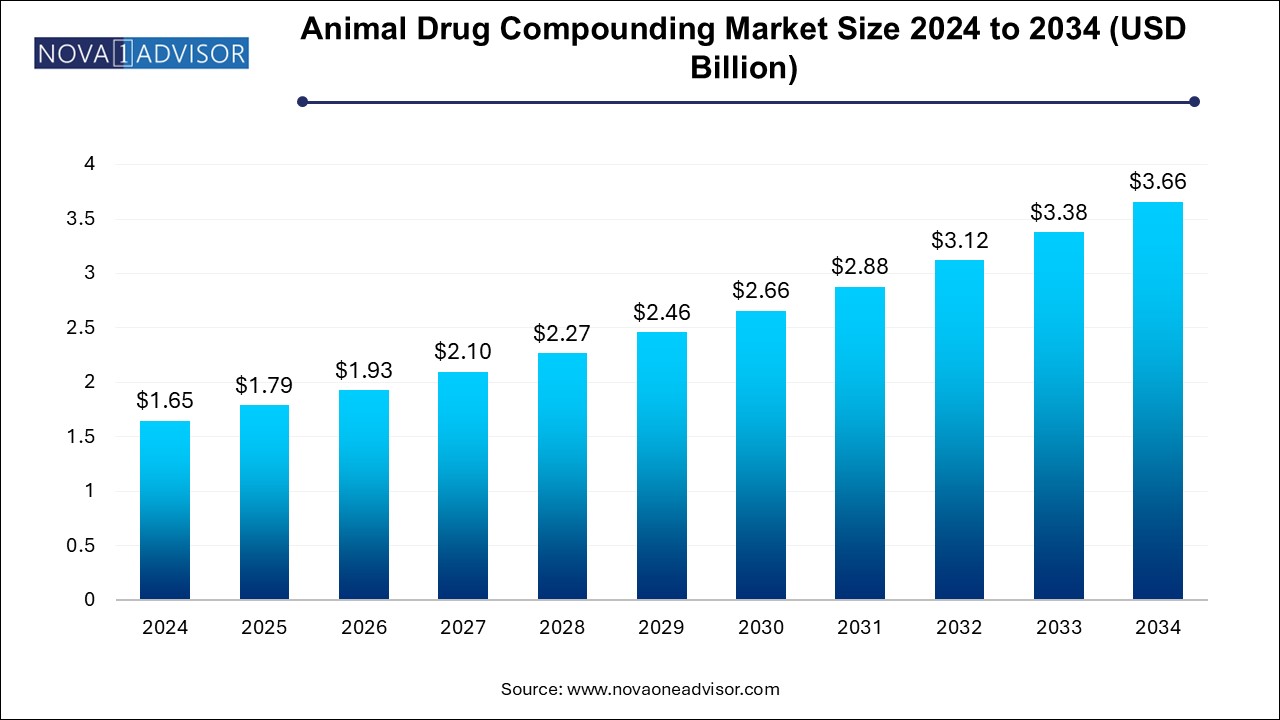
U.S. Animal Drug Compounding Market Size and Growth 2025 to 2034
The U.S. animal drug compounding market size is evaluated at USD 0.510 million in 2024 and is projected to be worth around USD 1.13 million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 7.5% from 2025 to 2034.
North America dominates the global animal drug compounding market due to a well-established veterinary infrastructure, high pet ownership rates, and supportive regulations that recognize the clinical value of compounded veterinary medications. The United States, in particular, has a large network of compounding pharmacies licensed to produce animal-specific medications. The American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA) and the FDA provide guidance that ensures safe compounding practices, promoting trust among veterinarians and pet owners.
High expenditure on pet care—coupled with rising demand for customized therapies in equine sports medicine, chronic disease management, and exotic pet care—further supports market expansion. For example, specialized compounding pharmacies in states like Florida and Texas serve thousands of veterinary clinics and animal hospitals. Moreover, the rising trend of tele-veterinary services in North America has enabled broader access to compounded drugs through e-prescriptions and direct-to-door delivery.
Asia Pacific is emerging as the fastest-growing region in the animal drug compounding market. The region’s rising pet ownership, expanding middle-class population, and increasing awareness of veterinary health are driving demand. Urbanization in countries like India, China, and Southeast Asia has led to lifestyle shifts, where companion animals are becoming integral family members. This has elevated spending on tailored pet care, including specialty medications.
Furthermore, the region’s robust livestock industry—spanning poultry, dairy, and aquaculture—has prompted interest in customized pharmaceutical interventions to boost animal health, productivity, and export standards. Veterinary service providers are gradually adopting compounding practices for herd-specific treatments. Government initiatives in animal health infrastructure, veterinary education, and public-private partnerships are expected to support long-term market growth.
Market Overview
The animal drug compounding market is steadily gaining prominence as veterinary healthcare providers and pet owners seek personalized pharmaceutical solutions tailored to the specific needs of individual animals. Compounding involves the custom preparation of medications by licensed pharmacists or veterinarians to suit particular dosage forms, strengths, or combinations not available in commercially manufactured drugs. This market addresses a critical gap in animal care where off-the-shelf medications are unsuitable, unavailable, or discontinued.
In both companion and livestock animal care, compounded medications are increasingly being used to ensure therapeutic efficacy, improve compliance, and enhance patient safety. These drugs are essential in scenarios where pets are allergic to inactive ingredients in standard drugs, require unique dosing due to weight variations, or need flavored forms to facilitate administration. As the global pet population rises, with increasing expenditure on pet wellness, the demand for customized veterinary medications has followed suit.
Moreover, the increasing complexity of veterinary care—spanning dermatology, endocrinology, oncology, neurology, and chronic pain management—has amplified the need for tailored therapeutics. The growing trend of animal humanization and an expanding network of compounding pharmacies globally continue to support market expansion. While regulations around animal drug compounding are still evolving in many countries, their broader acceptance is paving the way for structured growth through 2034.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Rising Pet Ownership and Humanization of Companion Animals Fueling Demand for Customized Medications
-
Increased Use of Flavor-Enhanced and Palatable Dosage Forms to Improve Animal Compliance
-
Technological Advancements in Compounding Equipment for Precision Dosing and Sterility
-
Regulatory Revisions Driving Safe and Standardized Practices in Veterinary Compounding
-
Growing Popularity of Hormonal Compounds for Equine and Reproductive Health Management
-
Expansion of Specialty Veterinary Clinics and Mobile Animal Health Services
-
Increased Demand for Anti-infective and Pain Management Solutions in Companion Animals
-
Emerging Use of Compounded Medications in Exotic and Non-traditional Pets
-
Rise of E-pharmacies and Online Veterinary Consultations Offering Compounded Options
-
Globalization of Veterinary Practices and Rising Livestock Exports Boosting Custom Drug Demand
Report Scope of Animal Drug Compounding Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 1.79 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 |
USD 3.66 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2025 to 2034 |
CAGR of 8.29% |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2034 |
| Segments Covered |
Product, Animal Type, Route of Administration, Dosage Form, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA |
| Key Companies Profiled |
WEDGEWOOD PHARMACY; Vimian; Pharmaca; Akina Animal Health; Triangle Compounding; Davis Islands Pharmacy and Compounding Lab; Custom Med Compounding Pharmacy; Central Compounding Center South; Wellness Pharmacy of Cary; Miller's Pharmacy |
Market Driver: Expanding Companion Animal Population and Associated Healthcare Expenditure
One of the most significant drivers of the animal drug compounding market is the rapid growth of the companion animal population worldwide, coupled with rising pet healthcare expenditure. Pet ownership is not only increasing in developed regions like North America and Europe but also expanding swiftly in urban centers across Asia and Latin America. This surge has been paralleled by heightened awareness among pet owners regarding preventive care, disease management, and quality of life improvements.
As veterinary care becomes more sophisticated, the one-size-fits-all approach of standard medications often falls short. For instance, dogs suffering from chronic arthritis may require long-term, titrated anti-inflammatory regimens, while cats with hyperthyroidism may benefit from transdermal hormonal gels when oral tablets are not tolerated. In such scenarios, compounding pharmacists can tailor the dosage, form, and combination of medications to suit specific animal needs, thereby driving market growth.
Market Restraint: Regulatory Ambiguity and Compliance Challenges
Despite its clinical benefits, the lack of harmonized regulatory frameworks governing animal drug compounding continues to restrain the market's expansion. In many regions, compounded animal drugs fall under loosely defined or ambiguous regulatory categories, leading to inconsistencies in quality, oversight, and safety standards. For example, while the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has issued guidelines for veterinary compounding, enforcement varies and depends heavily on practitioner discretion.
This uncertainty limits the confidence of veterinarians and pet owners in compounded products, especially in countries where veterinary pharmacy is still emerging. Moreover, the complexity of ensuring sterile environments, precise dosing, and contamination-free preparation adds logistical and operational hurdles for compounding pharmacies. These challenges, compounded by a lack of standardized training in veterinary pharmacology, often restrict widespread adoption and raise concerns about medication efficacy and safety.
Market Opportunity: Technological Innovations in Compounding for Specialized Veterinary Applications
The increasing integration of automation, robotics, and digitalization in pharmaceutical compounding offers a compelling opportunity to improve the scalability, accuracy, and safety of animal drug compounding. Innovations such as 3D printing of animal dosage forms, automated dose-dispensing machines, and cloud-based compounding software are reshaping how personalized medications are developed for veterinary use.
These technologies allow for precision dosing based on species, breed, weight, and metabolic profile, which is crucial in animals with narrow therapeutic indices or unique pharmacokinetics. Moreover, advanced delivery mechanisms—such as slow-release implants, buccal films, or transdermal gels—are being developed for more effective long-term therapies, particularly in horses, senior dogs, and cats with chronic diseases. As investment in animal health tech accelerates, compounding pharmacies can leverage these tools to expand their capabilities and reach new clinical domains.
Animal Drug Compounding Market By Product Insights
The CNS agents segments led the market with the largest revenue share of 34% in 2024, These include antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, and antiparasitics that are critical for treating wound infections, post-surgical complications, respiratory diseases, and systemic infections. In both companion and livestock animals, infectious disease management is a top priority, and compounding enables the creation of palatable, dose-specific formulations, especially for smaller or exotic species.
The hormones & substitutes segment is anticipated to grow at the fastest CAGR of 9.63% during the forecast period, The increased demand stems from hormonal therapies for endocrine disorders like hypothyroidism in dogs, hyperthyroidism in cats, and reproductive management in horses. For example, compounded levothyroxine in flavored suspensions offers an alternative to standard tablets, especially in pets with swallowing difficulties. The rise in hormonal imbalances due to age-related degeneration and environmental factors has expanded the clinical need for compounded hormone therapies, propelling this segment forward.
Animal Drug Compounding Market By Animal Type Insights
Based on animal type, the companion animal segment led the market with the largest revenue share of 74% in 2024 and is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR of 8.50% during the forecast period. Dogs represent the largest sub-segment, as they often require tailored therapies for allergies, joint pain, seizures, and post-operative recovery. Cats, known for their selective eating behavior and stress during pill administration, are commonly prescribed flavored liquid or transdermal compounded medications.
Meanwhile, the livestock animal segment is emerging as a high-growth area, particularly in regions with large-scale poultry, swine, and cattle farming. While compounding is traditionally associated with companion animals, the growing focus on animal welfare, organic meat certification, and responsible antibiotic use is encouraging customized, dosage-optimized treatments in farm settings. For instance, targeted anti-infective therapies or nutritional supplements in liquid suspension forms are increasingly being used to enhance livestock productivity and health outcomes.
Animal Drug Compounding Market By Route Of Administration Insights
The oral route remains the most dominant method of drug administration in the animal drug compounding market, owing to ease of delivery, availability of a wide variety of compounded dosage forms, and high compliance when flavored or disguised in food. Tablets, capsules, pastes, and flavored suspensions are widely prescribed across all animal types for acute and chronic conditions alike.
However, the topical route is witnessing rapid growth. Topical gels, creams, and transdermal patches offer an alternative for animals that resist oral medications or have gastrointestinal issues. For example, transdermal methimazole gel is preferred in feline hyperthyroidism, as it avoids first-pass metabolism and improves compliance. The demand for topical solutions is also increasing in dermatological disorders, post-surgical wound care, and pain management, particularly in horses and older pets.
Suspensions are the most commonly compounded dosage form due to their adaptability across species and conditions. They allow for flexible dosing and can be easily flavored to suit animal preferences. Veterinary suspensions are particularly favored for pediatric pets, elderly animals, and exotic species where tablets are impractical.
Meanwhile, solutions are the fastest-growing dosage form category. Their rapid onset of action and bioavailability make them ideal for emergency care and acute conditions. Injectable solutions are being increasingly compounded for parenteral administration in veterinary surgeries, livestock vaccinations, and emergency room settings. Additionally, flavored oral solutions for anti-infectives and anti-inflammatory drugs are gaining popularity due to improved taste masking and administration convenience.
Some of the prominent players in the animal drug compounding market include:
Animal Drug Compounding Market Recent Developments
-
March 2025: Wedgewood Pharmacy, a leading U.S. compounding pharmacy, expanded its product line to include transdermal behavioral medications for cats, offering greater convenience for pet owners and reducing stress on animals.
-
February 2025: Covetrus Inc. launched a cloud-based compounding prescription platform in partnership with veterinary clinics across North America to streamline the prescribing process and reduce dispensing errors.
-
January 2025: Patterson Veterinary invested in robotic compounding technology for its veterinary pharmacy division to improve dosing precision and efficiency in high-demand states.
-
December 2024: Triangle Compounding Pharmacy introduced a new series of equine hormone therapies in gel form, designed for easier administration in field conditions for competitive horses.
-
November 2024: Bova Aus (Australia) announced plans to expand its presence in Southeast Asia with compounding solutions for small animals and exotic pets, catering to a growing veterinary services market.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the animal drug compounding market
By Product
- Anti-infective Agents
- Anti-inflammatory Agents
- Hormones & Substitutes
- CNS Agents
- Other Products
By Animal Type
By Route of Administration
- Oral
- Injectable
- Topical
- Other Routes
By Dosage Form
- Suspensions
- Solutions
- Capsules
By Regional
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa (MEA)


