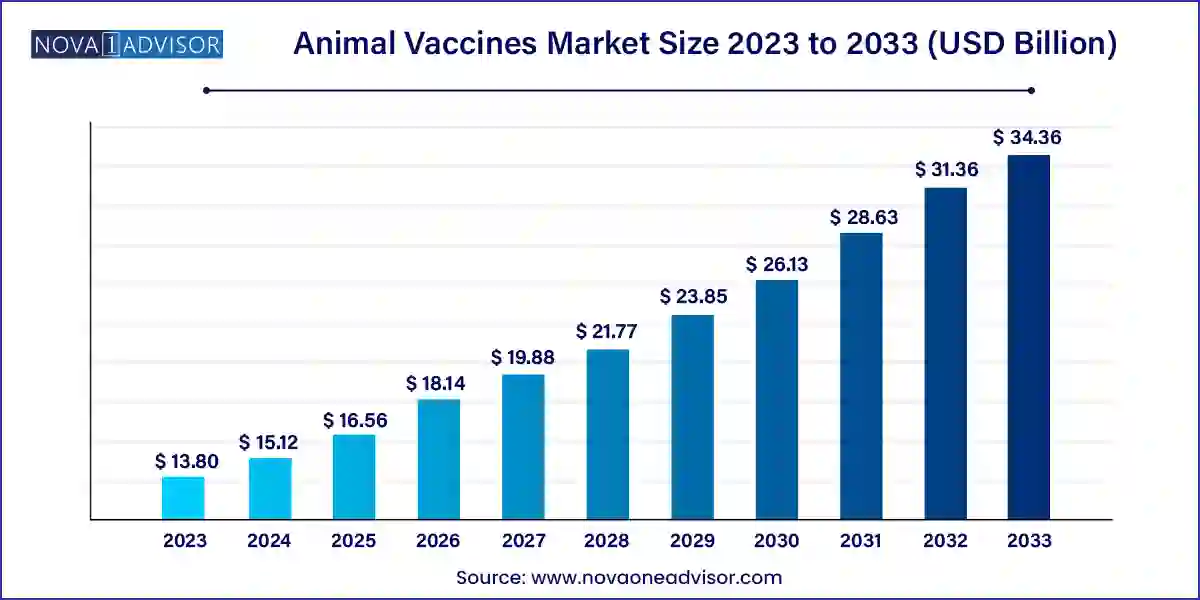
The global animal vaccines market size was exhibited at USD 13.80 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 34.36 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 9.55% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
Key Takeaways:
- North America dominated the market and accounted for a revenue share of over 26.0% in 2023.
- Asia Pacific, the market is expected to register the fastest growth rate during the forecast period.
- The attenuated live vaccines segment dominated the market for animal vaccines and accounted for a revenue share of over 35.0% in 2023.
- The livestock segment dominated the market with the highest revenue share in 2023.
- The companion segment is expected to exhibit the fastest growth rate during the forecast period.
- The subcutaneous segment dominated the market for animal vaccines with a revenue share of over 41.0% in 2023.
- The intranasal segment is expected to exhibit the fastest growth rate of over 10.0% during the forecast period.
Market Overview
The global animal vaccines market has emerged as a critical component in the veterinary healthcare ecosystem, playing an essential role in the prevention of infectious diseases in both livestock and companion animals. With the growing incidence of zoonotic diseases and the increased importance of food safety and animal welfare, the demand for effective immunization programs has accelerated significantly. The market is driven by robust advancements in biotechnology and vaccine production methods, which have led to the development of innovative formulations such as recombinant and DNA-based vaccines. Additionally, the surge in pet adoption and the increasing humanization of animals have contributed to the expansion of the companion animal vaccine segment.
The animal vaccines industry, valued in billions of dollars, continues to grow due to the dual influence of rising commercial livestock production driven by global food demand and increasing awareness about preventive healthcare for pets. Government-backed vaccination campaigns, strict animal health regulations, and the emergence of diseases like African swine fever and avian influenza have further underlined the importance of veterinary vaccines. With the One Health initiative gaining momentum, which links human, animal, and environmental health, the focus on animal immunization is expected to expand significantly over the next decade.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Rise of recombinant and DNA-based vaccines: Biotechnological innovations have enabled the development of highly specific and safe vaccines, reducing risks associated with traditional live-attenuated vaccines.
-
Increased focus on zoonotic disease control: With over 60% of infectious diseases in humans being zoonotic in origin, governments and organizations are investing more in animal vaccination programs to prevent disease transmission.
-
Adoption of precision livestock farming: Advanced monitoring and health tracking technologies allow timely vaccinations, contributing to improved productivity and reduced disease outbreaks.
-
Growing pet ownership and pet insurance: Particularly in developed regions, this has driven demand for vaccines against diseases like rabies, parvovirus, and feline leukemia.
-
Development of needle-free and oral vaccines: These alternatives offer less invasive delivery and ease of administration, especially in mass livestock vaccination programs.
-
Public-private partnerships and government initiatives: These collaborations aim to enhance access to vaccines in low-income economies, especially for livestock immunization.
-
Shift towards customized vaccines: Increasing demand for strain-specific vaccines tailored to regional disease prevalence is leading to product diversification.
Report Scope of The Animal Vaccines Market
| Report Coverage |
Details
|
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 15.12 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 |
USD 34.36 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 |
CAGR of 9.55% |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered |
Product, Animal Type, Route of Administration, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Central and South America; the Middle East and Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Zoetis; Ceva Santé Animale; Merck & Co., Inc.; Vetoquinol S.A.; Boehringer Ingelheim; Gmbh; Elanco; Virbac; Heska; Dechra Pharmaceuticals Plc; Idexx; Laboratories, Inc.; Norbrook Inc. |
Key Market Driver: Rising Global Livestock Population
A significant driver for the animal vaccines market is the rising global livestock population, particularly in developing countries. As the global population increases, so does the demand for animal-derived food products such as meat, milk, and eggs. Countries like China, India, and Brazil are significantly expanding their livestock industries to meet food security goals. However, the high density of animals increases the risk of contagious diseases, leading to devastating losses in productivity and trade. In this context, preventive vaccination becomes vital. Vaccines minimize disease outbreaks, maintain herd health, and enable farmers to meet international export standards, which often mandate vaccination documentation. Governments are also incentivizing the adoption of vaccines through subsidies and awareness campaigns, reinforcing their position as a primary tool in animal health management.
Key Market Restraint: High Costs of Vaccine Development
One of the major challenges facing the animal vaccines industry is the high cost and complexity of vaccine development. Unlike human vaccines, which benefit from massive global funding and centralized procurement, animal vaccine development often requires significant R&D investments with limited returns, particularly in low-margin livestock markets. The need to cater to a wide variety of species and pathogens further complicates vaccine design and production. Additionally, rigorous regulatory requirements, extensive field trials, and cold-chain logistics increase the overall cost burden. For smaller players, entering the market remains a formidable challenge, and for farmers in low-income regions, affording high-quality vaccines can be difficult without government support.
Key Market Opportunity: Emerging Demand in Asia-Pacific
The Asia-Pacific region presents a significant growth opportunity for animal vaccine manufacturers due to its vast livestock base, growing pet population, and rising per capita income. Countries like India, China, and Indonesia are witnessing increased livestock production for both domestic consumption and export. Simultaneously, urbanization and Western lifestyle influences are accelerating the adoption of pets, fueling demand for preventive veterinary care. Governments in the region are also ramping up investments in animal healthcare infrastructure, disease eradication programs, and public awareness campaigns. Companies entering these markets with cost-effective and easy-to-administer vaccines, especially those suitable for tropical climates and extensive animal populations, stand to gain substantial market share.
Segments:
Animal Vaccines Market By Product Insights
Attenuated live vaccines currently dominate the animal vaccines market owing to their high efficacy and long-lasting immunity. These vaccines contain a weakened form of the pathogen that stimulates a strong immune response with minimal doses. They are widely used in the poultry and swine industries to prevent viral infections like Newcastle disease and classical swine fever. The cost-effectiveness and established manufacturing processes make them a preferred choice in mass vaccination campaigns, especially in resource-constrained settings. For example, live vaccines have played a crucial role in the eradication of rinderpest, showcasing their impact in large-scale animal health initiatives.
On the other hand, DNA vaccines are witnessing the fastest growth, driven by advancements in molecular biology and regulatory acceptance in countries like the U.S. and Japan. These vaccines offer several benefits, including high specificity, safety, and the ability to induce both humoral and cell-mediated immunity. The successful application of DNA vaccines in aquaculture, particularly against infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHNV) in salmon, has paved the way for broader adoption across livestock and companion animals. Their scalability and potential for rapid development against emerging threats give them an edge in addressing future challenges in animal health.
Animal Vaccines Market By Animal Type Insights
The livestock segment, particularly poultry and swine, accounts for the largest share of the animal vaccines market. With poultry being a major source of protein globally, vaccines against avian influenza, Newcastle disease, and infectious bronchitis are in high demand. Swine vaccines have also gained prominence due to the outbreaks of African swine fever and porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome. Large-scale commercial farming operations increasingly rely on scheduled vaccination programs to maintain production efficiency and meet export requirements. Moreover, the emphasis on sustainable farming practices has boosted the adoption of preventive rather than curative healthcare strategies.
Conversely, the companion animal segment, especially canine vaccines, is the fastest-growing. Rising pet adoption, particularly in urban areas, has been accompanied by increased spending on veterinary care. Vaccines for rabies, distemper, and parvovirus are standard components of preventive pet healthcare. The feline segment is also witnessing growth, albeit at a slower pace, driven by rising awareness about cat-specific diseases like feline leukemia virus (FeLV). As pet parents increasingly view their animals as family members, the demand for innovative, pain-free, and long-acting vaccines is expected to surge.
Animal Vaccines Market By Route of Administration Insights
Subcutaneous administration is the most common route used for animal vaccines, especially in livestock. This method ensures systemic immunity and is preferred due to its ease of application, safety, and effectiveness. Subcutaneous injections are widely used in routine immunization programs, particularly on farms, where large numbers of animals need to be vaccinated quickly. Training programs for farmers and technicians have further simplified the procedure, making it the go-to method across continents.
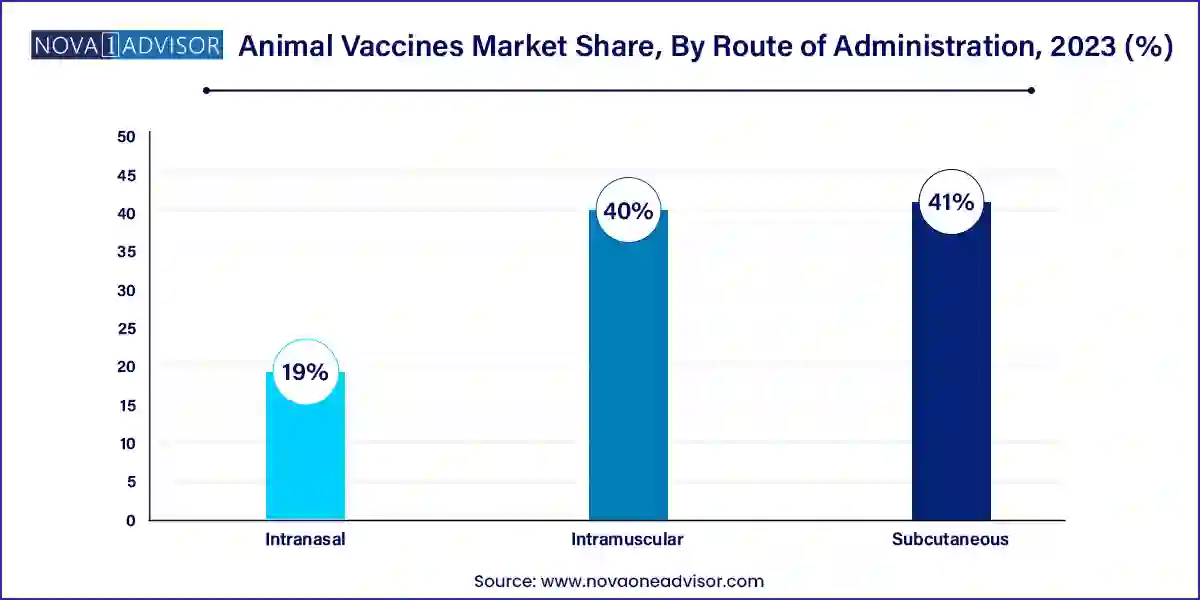
However, intranasal vaccines are gaining popularity, especially in the companion animal space. Intranasal delivery offers a stress-free alternative for pets and allows for mucosal immunity, which is critical in preventing respiratory infections like kennel cough. In livestock, researchers are exploring this route for mass vaccination due to its non-invasive nature and potential for automation, especially in poultry farming. Although still a niche segment, the growing focus on animal welfare and ease of administration is expected to drive demand for intranasal vaccine delivery in the coming years.
Animal Vaccines Market By Regional Insights
North America remains the dominant region in the animal vaccines market, driven by robust veterinary healthcare infrastructure, high awareness, and stringent animal health regulations. The U.S. leads the regional market due to its advanced biopharmaceutical industry and active government involvement in disease control programs. Notably, the USDA's Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (APHIS) plays a critical role in overseeing vaccination strategies for livestock and monitoring disease outbreaks. Additionally, widespread pet ownership and the presence of established companies like Zoetis and Merck Animal Health have created a mature and highly competitive landscape.
North America also benefits from a strong culture of veterinary preventive care. The rise in pet insurance coverage has further increased access to vaccines for diseases such as Lyme, parvovirus, and rabies. Veterinary hospitals and clinics across the U.S. are increasingly equipped with the latest immunization technologies, contributing to high vaccine uptake among pet owners.
.webp)
The Asia-Pacific region is projected to grow at the fastest rate in the animal vaccines market due to its large animal population, increasing livestock exports, and improving awareness about animal health. Countries like India, China, and Vietnam are heavily investing in modernizing their animal husbandry practices. Government-led vaccination drives against foot-and-mouth disease and avian flu have improved vaccination penetration. Additionally, rising disposable incomes and urban lifestyles are driving the demand for companion animal vaccines, particularly in India and Southeast Asia.
Furthermore, the proliferation of animal healthcare startups and international collaborations in Asia-Pacific is boosting R&D efforts in the veterinary sector. For example, China’s increased focus on biosecurity and traceability post-COVID-19 has led to more stringent animal health protocols, increasing demand for vaccines across poultry and swine industries. The region’s strategic importance is likely to expand as global players seek to establish production and distribution bases to tap into these rapidly evolving markets.
Some of the prominent players in the Animal vaccines market include:
- Zoetis
- Ceva Santé Animale
- Merck & Co., Inc.
- Vetoquinol S.A.
- Boehringer Ingelheim Gmbh
- Elanco
- Virbac
- Heska
- Dechra Pharmaceuticals Plc
- Idexx Laboratories, Inc.
- Norbrook Inc.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the global animal vaccines market.
Product
- Attenuated Live Vaccines
- Inactivated Vaccines
- Subunit Vaccines
- DNA Vaccines
- Recombinant Vaccines
Animal Type
-
- Poultry
- Aqua
- Ruminants
- Swine
Route of Administration
- Subcutaneous
- Intramuscular
- Intranasal
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)



.webp)