Asia Pacific Advanced Wound Care Market Size and Research
The Asia Pacific advanced wound care market size was exhibited at USD 3.01 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 4.91 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 5.6% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
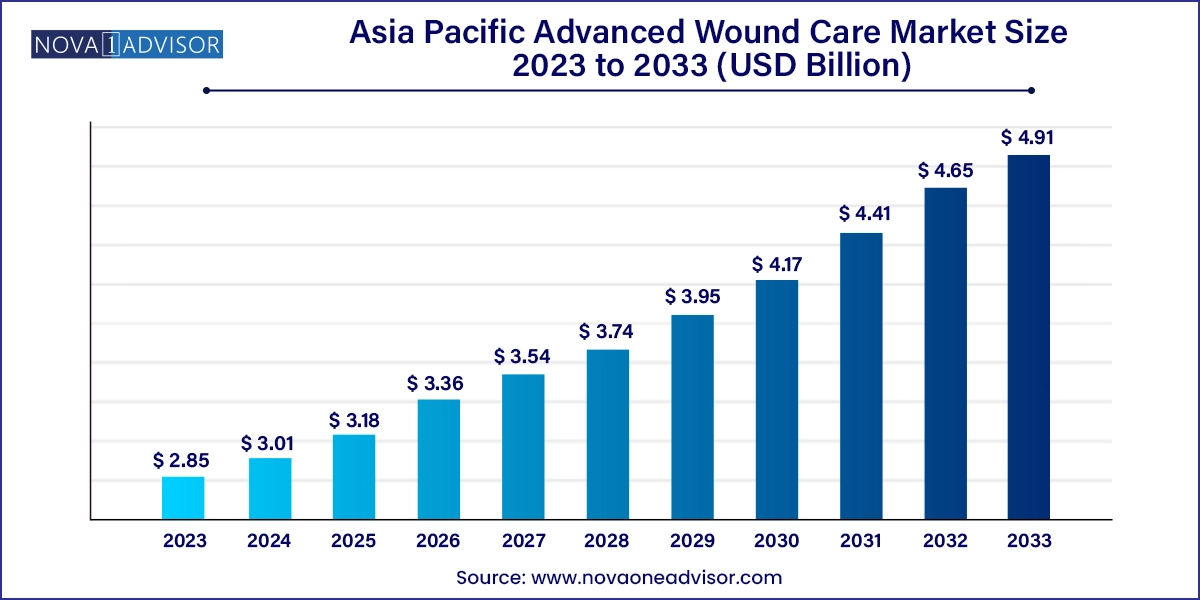
Asia Pacific Advanced Wound Care Market Key Takeaways:
- The moist segment led the market with the largest revenue share of 55.08% in 2023.
- The active segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR of 6.77% over the forecast period.
- The hospitals segment held the largest market share in terms of revenue share 49.0% in 2023.
- The home care segment is projected to grow at the fastest CAGR of 6.15% over the forecast period.
- Based on application, the chronic wounds segment accounted for the largest revenue share of 59.33% in 2023.
Market Overview
The Asia Pacific advanced wound care market is undergoing transformative growth, fueled by a combination of rising chronic disease prevalence, increased healthcare investments, an aging population, and improved access to healthcare services. Advanced wound care encompasses innovative treatment options that facilitate faster healing, minimize infection risk, and improve patient outcomes for both chronic and acute wounds. It marks a significant departure from traditional wound management techniques, offering products and systems that promote moisture balance, debridement, and tissue regeneration.
Across Asia Pacific, countries such as China, India, and South Korea are witnessing rapid urbanization and lifestyle changes that contribute to higher incidences of conditions like diabetes, vascular disease, and obesity all of which increase the risk of chronic wounds. Additionally, rising surgical procedures and road traffic accidents contribute to a growing patient population requiring acute wound management. Advanced wound care solutions ranging from hydrocolloid and foam dressings to bioengineered skin substitutes and antimicrobial therapies are increasingly preferred by clinicians due to their clinical efficacy and ability to reduce hospitalization time.
Governments and private institutions are investing in healthcare infrastructure, and there's a growing awareness among clinicians and patients about the benefits of advanced wound care. While developed markets like Australia and Singapore have established wound care protocols, emerging economies such as Vietnam and Indonesia are gradually adopting advanced solutions through public health programs and training initiatives. The market is further supported by the entry of multinational wound care companies, regional partnerships, and local manufacturing growth, particularly in cost-sensitive countries.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Shift Toward Moist and Active Dressings: Demand is increasing for dressings that maintain an optimal moist wound environment and support active healing via biomaterials and growth factors.
-
Integration of Antimicrobial Ingredients: Silver, honey, iodine, and PHMB-infused products are gaining prominence due to their efficacy against infection in chronic wounds.
-
Home-Based Wound Care Expansion: A rising geriatric population and advancements in portable wound care devices have led to a surge in home care services.
-
Government and NGO-Led Diabetic Foot Ulcer Management Campaigns: National initiatives are targeting diabetic wound care with subsidies for modern dressings and training.
-
Increased Penetration of Local Brands: Regional manufacturers are offering competitively priced foam, film, and hydrocolloid dressings, driving market penetration in tier 2 and 3 cities.
-
Adoption of Digital Wound Management Platforms: Telehealth tools and mobile apps for wound monitoring and assessment are gaining traction in hospital and outpatient settings.
-
Post-Surgical Wound Management Innovation: Growth in elective surgeries post-COVID has prompted increased use of advanced dressings for postoperative wound healing.
Report Scope of Asia Pacific Advanced Wound Care Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 3.01 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 |
USD 4.91 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 |
CAGR of 5.6% |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered |
Product, Application, End-use, Country |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Country scope |
China; India; Australia; Singapore; Vietnam; Thailand; Indonesia; South Korea; Hong Kong; Malaysia |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Mölnlycke Health Care AB; 3M; Smith & Nephew; Baxter International; Cardinal Health; Medline Industries, Inc.; ConvaTec Inc.; Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc.; Integra LifeSciences Corporation; B. Braun Melsungen AG; Coloplast Corp.; Urgo Medical |
Key Market Driver
Rising Incidence of Chronic Wounds Driven by Diabetes and Aging Population
One of the most significant drivers of the Asia Pacific advanced wound care market is the increasing prevalence of chronic wounds, particularly those linked to diabetes and aging. Diabetes is growing at an alarming rate across Asia, with India and China housing the world’s largest diabetic populations. Diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) are a leading complication of poorly managed diabetes and often result in infections, amputations, and increased mortality. Pressure ulcers and venous leg ulcers are also becoming common among the region’s elderly.
Advanced wound care solutions such as silver dressings, hydrocolloids, and negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) play a vital role in preventing infection and accelerating healing in these chronic wounds. Moreover, countries like South Korea and Singapore have implemented national programs to reduce diabetes-related hospitalizations by encouraging early detection and modern wound management protocols, further boosting market demand.
Key Market Restraint
High Cost and Unequal Access to Advanced Wound Products
Despite its potential, a major constraint in the Asia Pacific advanced wound care market is the high cost of advanced products and the unequal access to care in rural and underserved regions. While urban hospitals in countries like Australia and Singapore readily adopt foam dressings, bioactive therapies, and antimicrobial products, smaller healthcare facilities in rural areas often rely on basic gauze and traditional ointments due to budgetary and supply chain constraints.
The lack of insurance reimbursement for advanced wound care in several markets also limits patient uptake. In India and Indonesia, for example, patients often bear out-of-pocket costs, making premium wound products inaccessible to a large population. Addressing these disparities will require policy reforms, awareness campaigns, and investment in low-cost local manufacturing to enhance affordability and accessibility.
Key Market Opportunity
Expansion of Home Healthcare and Portable Wound Care Solutions
A significant opportunity lies in the expansion of home healthcare services and the growing acceptance of portable wound care solutions across Asia Pacific. The rising elderly population, along with the shift toward outpatient and remote care models, has fueled demand for easy-to-use wound dressings and mobile devices like NPWT systems suitable for home settings.
Manufacturers are responding by introducing dressings with extended wear time, self-adhesive capabilities, and infection indicators to support home-based care. In countries like Japan and South Korea, where healthcare systems are facing workforce shortages, remote wound monitoring apps and telewound consultations are enabling clinicians to guide home caregivers effectively. With rising internet penetration and wearable device adoption, this model is expected to gain traction in both developed and emerging markets.
Asia Pacific Advanced Wound Care Market By Product Insights
Moist wound dressings emerged as the dominant product segment, primarily due to their versatility, clinical efficacy, and broad application across chronic and acute wound types. Foam dressings—both adhesive and non-adhesive—lead this category, favored for their superior absorption, exudate management, and ability to create an optimal healing environment. Film, hydrocolloid, and hydrogel dressings are widely used in pressure ulcers, post-surgical wounds, and diabetic ulcers. In countries like Australia and Singapore, moist dressings are standard protocol in hospital wound care units, supported by strong clinical training programs and government-endorsed guidelines.
Meanwhile, active dressings are the fastest-growing segment, driven by rising demand for regenerative solutions. These include biomaterials such as collagen and chitosan, skin substitutes for burn victims, and growth factor-based dressings used in chronic non-healing wounds. China and South Korea are investing in bioengineered wound care technologies, while local companies in India and Thailand are entering the market with affordable alternatives. Clinical studies showing improved outcomes with active dressings are encouraging their broader adoption.
Asia Pacific Advanced Wound Care Market By End-use Insights
Hospitals remain the largest end users of advanced wound care products, accounting for a significant share of demand. Hospital-based wound care units, surgical centers, and intensive care wards rely heavily on advanced dressings and NPWT systems for treating complex and infected wounds. Multispecialty hospitals in India and China are expanding wound care programs to reduce hospital-acquired pressure ulcers (HAPUs) and improve surgical recovery outcomes. High inpatient volumes, better product availability, and trained clinical staff support this segment’s dominance.
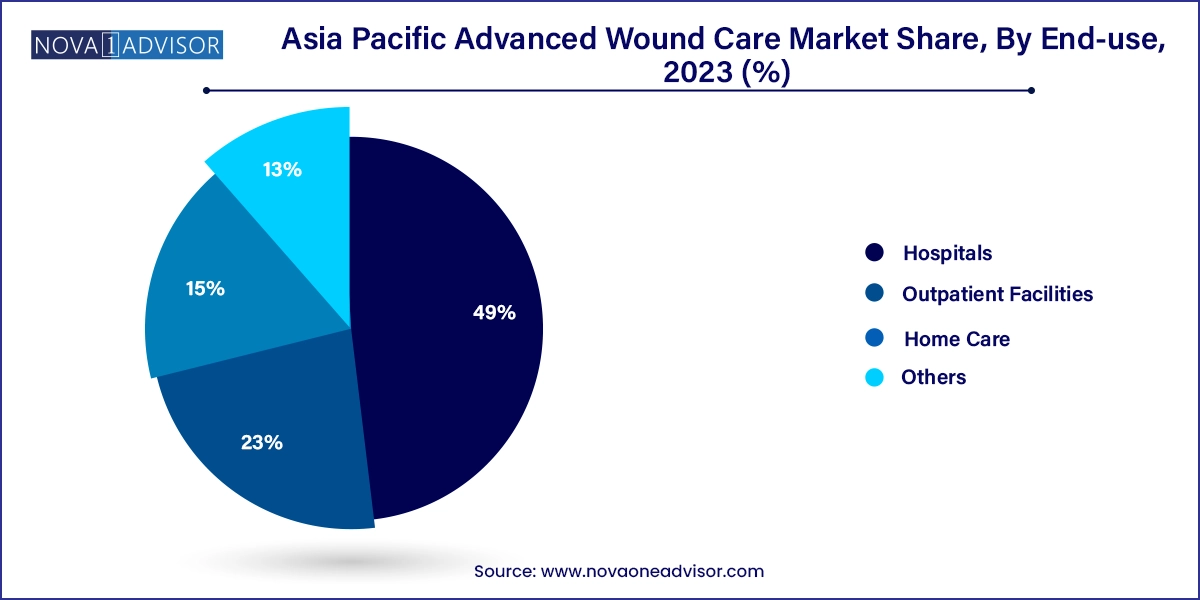
On the other hand, home care is the fastest-growing end-use segment, reflecting broader healthcare shifts across Asia Pacific. The aging population, particularly in Japan, South Korea, and Australia, is increasingly managed through community care and home nursing services. Companies are launching consumer-friendly products, including antimicrobial foam dressings and disposable wound cleansers, for home use. Additionally, partnerships between home healthcare agencies and suppliers are helping facilitate product distribution, education, and compliance, enabling patients to access quality wound care outside clinical settings.
Asia Pacific Advanced Wound Care Market By Application Insights
Chronic wounds, particularly diabetic foot ulcers and pressure ulcers, held the largest market share due to their long healing durations and higher healthcare resource consumption. The increasing diabetes burden across Asia, coupled with low awareness about foot care and delayed wound treatment, results in frequent hospitalization and infection risk. Advanced wound care products such as antimicrobial dressings and negative pressure systems are essential in preventing complications and promoting wound closure. Government diabetic screening campaigns in Malaysia and Indonesia have helped expand demand for advanced wound care in chronic settings.
Acute wounds, including surgical wounds and burns, are growing rapidly due to rising surgical volumes and accident-related trauma. First- and second-degree burns are common in rural populations with open-fire cooking practices, particularly in countries like India, Vietnam, and Indonesia. Postoperative infections are another driver for advanced wound care adoption in acute care, with antimicrobial and hydrocolloid dressings increasingly used in orthopedic and general surgeries. Educational outreach to surgeons and first responders about advanced dressing protocols has contributed to this growth.
Country Insights
China
China leads the Asia Pacific advanced wound care market due to its large population, rapid urbanization, and growing burden of chronic diseases. The expansion of healthcare infrastructure and government-backed insurance programs such as the New Rural Cooperative Medical Scheme (NRCMS) support wound care services even in rural areas. Moreover, local players like Winner Medical and Yunnan Baiyao are rapidly expanding their portfolios of foam, hydrocolloid, and antimicrobial dressings, making products more accessible and cost-effective.
India
India is emerging as a high-potential market driven by the diabetes epidemic and increasing road accident injuries. Although awareness and accessibility remain challenges in rural regions, urban hospitals are adopting advanced wound dressings and NPWT systems, particularly in surgical departments. The Indian government’s Ayushman Bharat program is expected to increase demand for modern wound care under its universal health coverage plan.
Australia
Australia has one of the most mature advanced wound care ecosystems in Asia Pacific, with government policies promoting best practices in wound prevention and management. Clinical guidelines, insurance reimbursement, and public-private partnerships have led to high adoption of antimicrobial dressings, compression therapy, and digital wound monitoring tools.
South Korea
South Korea is investing heavily in smart healthcare, and this includes innovations in wound care. Hospitals are using AI-powered imaging tools to monitor healing progress, while home care is supported through telemedicine platforms. Korean biotech companies are also developing bioactive and hydrogel dressings for commercialization in Southeast Asia.
Indonesia, Vietnam, Thailand, Singapore, Hong Kong, Malaysia
These markets are witnessing varied levels of growth. Singapore and Hong Kong show high per capita adoption of advanced wound care technologies, while Indonesia and Vietnam are benefiting from increasing public hospital investments and NGO-led diabetic foot ulcer prevention programs. Thailand’s universal healthcare system is incorporating more advanced wound products into its essential drug list.
Asia Pacific Advanced Wound Care Market Recent Developments
-
February 2025 – Smith & Nephew announced the expansion of its advanced wound care product line in Malaysia and Thailand, including silver-based antimicrobial foam dressings for diabetic wound management.
-
January 2025 – Winner Medical launched a new hydrocolloid dressing product in China targeted for pressure ulcer prevention in elderly patients.
-
November 2024 – 3M Health Care collaborated with India’s leading private hospitals to roll out an education campaign on NPWT and post-surgical wound care.
-
October 2024 – Convatec Group introduced its new wound cleanser range in South Korea and Japan, including antiseptic-based solutions and wetting agents for outpatient settings.
-
August 2024 – Mölnlycke Health Care opened a logistics hub in Singapore to streamline distribution of advanced dressings across Southeast Asia.
Some of the prominent players in the Asia Pacific advanced wound care market include:
- Mölnlycke Health Care AB
- 3M
- Smith & Nephew
- Baxter International
- Cardinal Health
- Medline Industries, Inc.
- ConvaTec Inc.
- Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc.
- Integra LifeSciences Corporation
- B. Braun Melsungen AG
- Coloplast Corp.
- Urgo Medical
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Asia Pacific advanced wound care market
Product
-
-
- Adhesive
- Non-adhesive Foam Dressings
-
- Superabsorbent Dressings
- Film Dressings
- Hydrocolloid Dressings
- Alginate Dressings
- Hydrogel Dressings
- Collagen Dressings
- Charcoals Dressings
- Wound Contact Layers
- Greasy Gauzes
- Other Advanced Dressings
-
- Silver Dressings
- Non-silver Dressings
-
-
- Honey
- Iodine
- Chitosan
- PHMB
- Others
-
- Biomaterials
- Skin-substitute
- Growth factors
-
- Wetting Agents
- Antiseptic
- Moisturizers
- Pulsed Lavage Systems
-
-
- Disposable
- Reusable
- Semi Disposable
-
- Long-Stretch Elastic Bandages
- Short-Stretch Bandages
- Multi-layer Bandages
Application
-
- Diabetic Foot Ulcers
- Pressure Ulcers
-
-
- Stage 1
- Stage 2
- Stage 3
- Stage 4
-
- Deep Tissue Injury
- Venous Leg Ulcers
- Other Chronic Wounds
-
- Surgical & Traumatic Wounds
- Burns
-
-
- 1st Degree Burns
- 2nd Degree Burns
- 3rd Degree Burns
End-use
- Hospitals
- Outpatient Facilities
- Home Care
- Others
Country
- China
- India
- Australia
- Singapore
- Vietnam
- Thailand
- Indonesia
- South Korea
- Hong Kong
- Malaysia


