Autoimmune Disease Diagnostics Market Size and Trends
The autoimmune disease diagnostics market size was exhibited at USD 5.85 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 10.68 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 6.2% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.Increasing prevalence of autoimmune disorders such as type 1 diabetes in newborn babies coupled with demand for rapid diagnostics is the key driver accentuating growth.
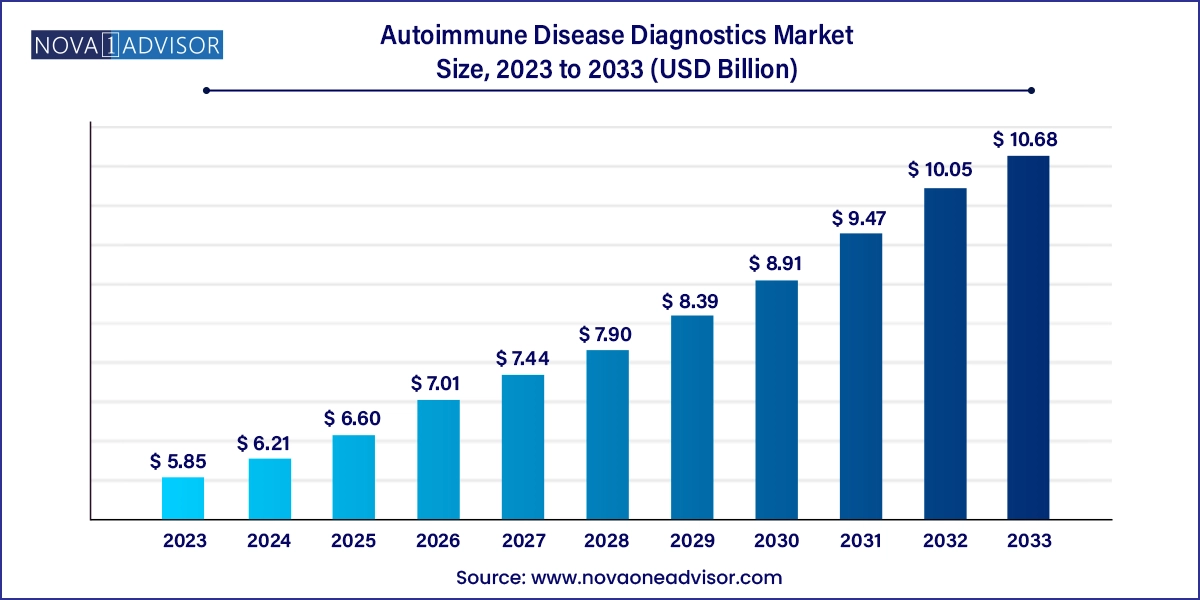
Autoimmune Disease Diagnostics Market Key Takeaways:
- Localized disease diagnostics dominated the overall market in terms of revenue in 2023.
- North America held the largest market share of over 45.0% in 2023
- The market is consolidated in nature, therefore is marked by the presence of extensive mergers and acquisitions.
Market Overview
The autoimmune disease diagnostics market plays a crucial role in modern healthcare by enabling early detection, accurate classification, and effective management of autoimmune disorders. Autoimmune diseases are conditions in which the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells and tissues, leading to chronic inflammation and organ damage. With over 100 known autoimmune diseases—including rheumatoid arthritis (RA), multiple sclerosis (MS), type 1 diabetes (T1D), and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)—diagnostic testing is essential for early intervention and improved patient outcomes.
Globally, autoimmune diseases affect an estimated 5–8% of the population, with a higher prevalence among women and older adults. The growing incidence of autoimmune conditions has intensified the demand for reliable diagnostic tools. These diagnostics include autoantibody tests, antinuclear antibody (ANA) screening, immunoassays, and molecular diagnostics. As early and precise diagnosis is pivotal for effective treatment, the market is witnessing rapid innovation in multiplexed assays, point-of-care (POC) diagnostics, and biomarker discovery.
The increasing awareness of autoimmune conditions, rise in healthcare expenditure, expansion of clinical testing infrastructure, and advancements in diagnostic technologies have contributed significantly to market growth. Furthermore, the post-pandemic healthcare landscape has emphasized precision medicine and chronic disease management, placing autoimmune diagnostics at the forefront of clinical research and product development.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Rising use of multiplexed diagnostic platforms for simultaneous detection of multiple autoantibodies.
-
Integration of AI and machine learning in interpreting complex autoimmune disease profiles and enhancing diagnostic accuracy.
-
Growing adoption of point-of-care diagnostic tests in both clinical and remote settings for faster decision-making.
-
Expansion of biomarker-based diagnostics, leading to early detection and better disease stratification.
-
Shift towards personalized medicine and companion diagnostics for autoimmune diseases like lupus and RA.
-
Surge in direct-to-consumer diagnostic testing kits, allowing patients to initiate autoimmune disease screening independently.
-
Partnerships between pharma and diagnostic companies to develop companion diagnostics for autoimmune therapies.
-
Increased government and nonprofit funding for autoimmune research, diagnostics, and awareness programs.
Report Scope of Autoimmune Disease Diagnostics Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 6.21 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 |
USD 10.68 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 |
CAGR of 6.2% |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered |
Type ,Regional |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Key Companies Profiled |
F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd; Siemens Healthineers; Abbott Laboratories; Beckman Coulter, Inc.; SQI Diagnostics; Quest Diagnostics; EUROIMMUN AG; AESKU.Diagnostics GmbH & Co. KG; INOVA Diagnostics, Inc.; Crescendo Bioscience, Inc.; bioMerieux SA; Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.; and Hemagen Diagnostics, Inc. |
Key Market Driver: Increasing Prevalence of Autoimmune Diseases Worldwide
A major driver of the autoimmune disease diagnostics market is the rising global incidence of autoimmune disorders. Factors such as genetic predisposition, environmental triggers, infections, and lifestyle changes have contributed to a growing number of autoimmune cases across all age groups. According to the American Autoimmune Related Diseases Association (AARDA), over 50 million Americans live with at least one autoimmune condition, and this number is increasing annually.
This surge in prevalence necessitates early and accurate diagnostic testing to prevent disease progression, irreversible organ damage, and long-term disability. Diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus often have nonspecific symptoms that overlap with other conditions, making diagnosis challenging. Sophisticated diagnostics are therefore essential for differential diagnosis, patient stratification, and treatment planning.
In addition, advancements in immunology have led to the identification of novel autoantibodies, enabling targeted testing and more precise disease characterization. For example, cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP) antibodies have improved early diagnosis of RA, while anti-dsDNA and anti-Sm antibodies help confirm SLE. As diagnostic techniques become more sensitive and specific, early intervention rates are improving—ultimately reducing the disease burden and healthcare costs.
Key Market Restraint: High Cost and Complexity of Advanced Diagnostic Tests
Despite the growing need for autoimmune disease diagnostics, high test costs and operational complexity remain significant market restraints. Advanced tests such as immunofluorescence assays (IFA), enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA), and multiplexed immunoassays require expensive reagents, skilled technicians, and advanced laboratory infrastructure.
In low- and middle-income countries, diagnostic accessibility remains limited due to lack of reimbursement, poorly equipped labs, and insufficient physician awareness. Even in developed regions, patients without comprehensive health insurance often face financial barriers to routine autoimmune screening. Moreover, autoimmune diseases often necessitate multiple rounds of testing for confirmation and monitoring, compounding costs.
Additionally, the heterogeneity of autoimmune diseases—manifesting differently across individuals—makes standardization of diagnostic criteria and interpretation challenging. Many patients experience delayed or incorrect diagnoses due to overlapping symptoms and inconsistent testing protocols. This diagnostic ambiguity not only delays treatment but also undermines confidence in the healthcare system.
Key Market Opportunity: Technological Advancements in Point-of-Care and Digital Diagnostics
A significant opportunity in the autoimmune disease diagnostics market lies in the rapid advancement of point-of-care and digital diagnostics. The growing need for fast, reliable, and minimally invasive testing has led to the development of compact diagnostic platforms that can be deployed in outpatient clinics, rural areas, and even home settings.
Portable immunoassay analyzers, lateral flow devices, and smartphone-integrated biosensors are now being designed to detect biomarkers associated with autoimmune diseases. These innovations dramatically reduce turnaround times, enabling same-day diagnosis and treatment planning. Moreover, remote monitoring and telehealth integration allow continuous disease surveillance—especially for patients with chronic conditions like type 1 diabetes or lupus.
Digital platforms that utilize AI algorithms to analyze test results, patient history, and symptom data are also transforming autoimmune diagnostics. These tools can flag at-risk individuals, recommend follow-up testing, and reduce human error in result interpretation. The growing market for wearable biosensors, like glucose monitors and smart patches, also hints at future convergence between chronic disease monitoring and autoimmune diagnostics.
Autoimmune Disease Diagnostics Market By Type Insights
Systemic autoimmune disease diagnostics held the largest share of the market, driven by the high prevalence and complexity of conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and ankylosing spondylitis. These disorders affect multiple organs and systems, requiring a wide range of diagnostic approaches—from serology and imaging to genetic testing. For example, RA is one of the most commonly diagnosed autoimmune diseases worldwide, often requiring tests for rheumatoid factor (RF), anti-CCP, and inflammatory markers like CRP and ESR.
SLE diagnostics have also gained traction due to the disease’s high female prevalence and complex presentation. A combination of autoantibody testing (anti-dsDNA, ANA, anti-Sm) and clinical assessments is essential for accurate diagnosis. Moreover, patients with systemic diseases often experience overlapping symptoms with other conditions, prompting the need for multiplexed testing solutions. Hospitals and specialty diagnostic labs continue to invest in systemic autoimmune testing due to the chronic nature of these diseases and the need for continuous monitoring.
In contrast, localized autoimmune disease diagnostics are the fastest-growing segment. This category includes type 1 diabetes, multiple sclerosis (MS), Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, and idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, among others. The growing number of patients with organ-specific autoimmune disorders has driven the demand for targeted diagnostics. For instance, MS diagnosis relies on oligoclonal band detection in cerebrospinal fluid along with MRI scans, while type 1 diabetes can be confirmed through autoantibody panels such as GAD and IA-2. The increasing availability of organ-specific biomarkers, along with the expansion of specialized clinics, is accelerating growth in this segment.
Autoimmune Disease Diagnostics Market By Regional Insights
North America holds the dominant share in the autoimmune disease diagnostics market, attributed to its advanced healthcare infrastructure, high awareness levels, and significant prevalence of autoimmune disorders. The U.S. leads the region, supported by widespread access to diagnostic labs, strong insurance coverage, and active government and nonprofit initiatives in autoimmune research. According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), over 23 million Americans are diagnosed with autoimmune diseases—a number that continues to rise.
Diagnostic labs in North America have also embraced automation and digitalization, allowing for high-throughput autoimmune testing. Companies such as Thermo Fisher Scientific, Bio-Rad, and Abbott Laboratories operate extensively in the region, offering a broad portfolio of diagnostic solutions. Collaborations with academic institutions and growing investment in personalized medicine further strengthen the region’s leadership.
Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing market, driven by increasing healthcare expenditure, growing autoimmune disease burden, and expanding access to diagnostic services. Countries such as China, India, Japan, and South Korea are witnessing a sharp rise in chronic conditions, including autoimmune disorders, due to urbanization, pollution, and lifestyle shifts.
Governments across the region are investing in diagnostic infrastructure, and private labs are emerging with affordable testing packages tailored to regional needs. Moreover, international diagnostic companies are forming partnerships with local players to tap into underserved markets. Increased awareness, along with mobile health initiatives and public screening campaigns, is helping reduce the diagnostic gap. As AI and telemedicine technologies penetrate Asia-Pacific, localized diagnostics for autoimmune diseases are poised for rapid adoption.
Some of the prominent players in the autoimmune disease diagnostics market include:
The market is consolidated in nature, therefore is marked by the presence of extensive mergers and acquisitions. Some key players of this market include F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd; Siemens Healthineers; Abbott Laboratories; Beckman Coulter, Inc.; SQI Diagnostics; Quest Diagnostics; EUROIMMUN AG; AESKU.Diagnostics GmbH & Co. KG; INOVA Diagnostics, Inc.; Crescendo Bioscience, Inc.; bioMerieux SA; Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.; and Hemagen Diagnostics, Inc.
Recent Developments
-
April 2025 – Thermo Fisher Scientific launched a fully automated ANA screening platform capable of processing high-throughput tests with AI-powered interpretation, targeting hospitals and large labs.
-
February 2025 – Siemens Healthineers announced its collaboration with the Lupus Research Alliance to co-develop biomarker panels for early lupus diagnosis.
-
December 2024 – Roche Diagnostics received CE Mark for its next-generation Elecsys anti-CCP assay for rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis and monitoring.
-
October 2024 – Bio-Rad Laboratories expanded its autoimmune product line with the launch of a new multiplexed assay for systemic sclerosis-related antibodies.
-
July 2024 – EUROIMMUN (PerkinElmer) launched a novel digital IFA reader for ANA and ENA detection, aimed at improving lab workflow efficiency in Europe and Asia.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the autoimmune disease diagnostics market
Type
- Systemic autoimmune disease diagnostics
-
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
- Others
- Localized autoimmune disease diagnostics
-
- Multiple sclerosis
- Type 1 diabetes
- Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
- Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
- Others
Regional
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- MEA

