Breast Cancer Liquid Biopsy Market Size and Trends
The breast cancer liquid biopsy market size was exhibited at USD 1.34 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 2.89 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 8.0% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034. The breast cancer liquid biopsy market growth can be linked to the globally rising breast cancer cases, need for effective early detection solutions, increasing preference for non-invasive procedures, and ongoing launches of innovative liquid biopsy assays and kits.
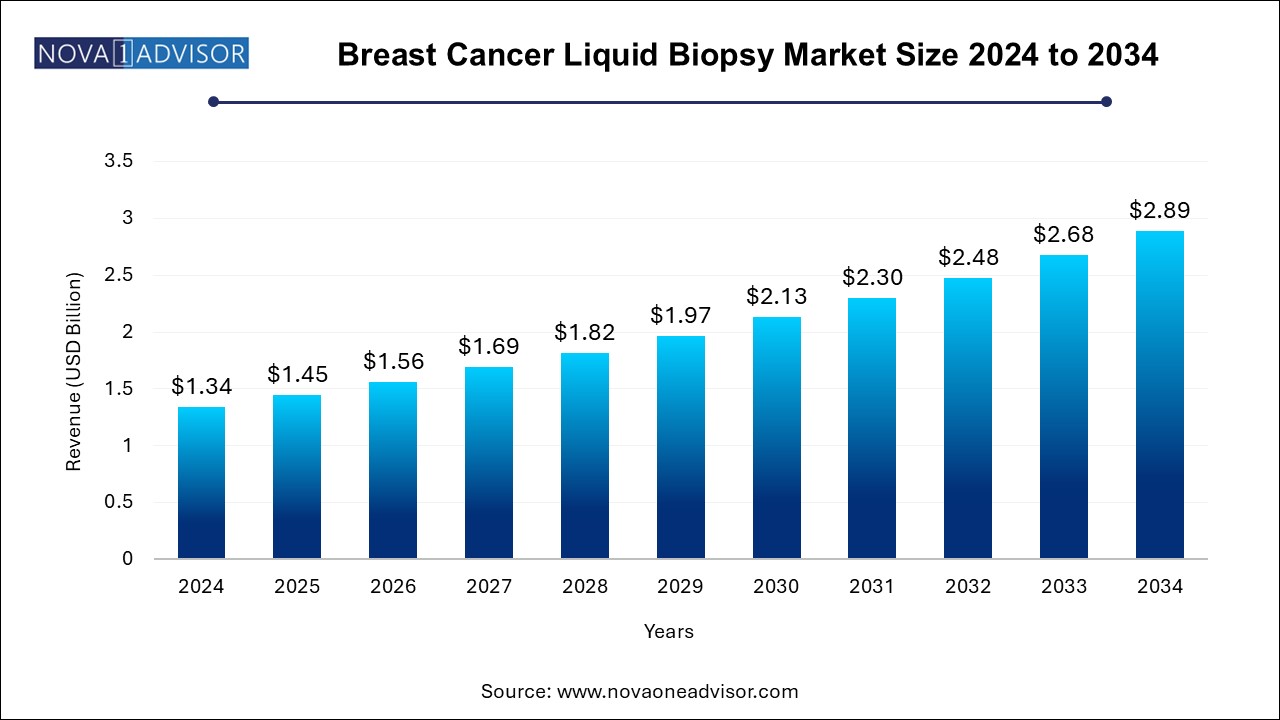
Breast Cancer Liquid Biopsy Market Key Takeaways:
- Based on circulating biomarkets, the circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA) segment led the market with the largest revenue share of 53.6% in 2024.
- The circulating tumor cells (CTCs) segment is anticipated to grow at the fastest CAGR of 9.4% over the forecast period.
- Based on application, the treatment selection segments led the market with the largest revenue share of 52.0% in 2024.
- The early detection/screening segment is expected to grow at a significant CAGR of 9.7% during the forecast period.
- North America dominated the breast cancer liquid biopsy market with the largest revenue share of 44.64% in 2024.
U.S. Breast Cancer Liquid Biopsy Market Size, Share and Trends 2024 to 2034
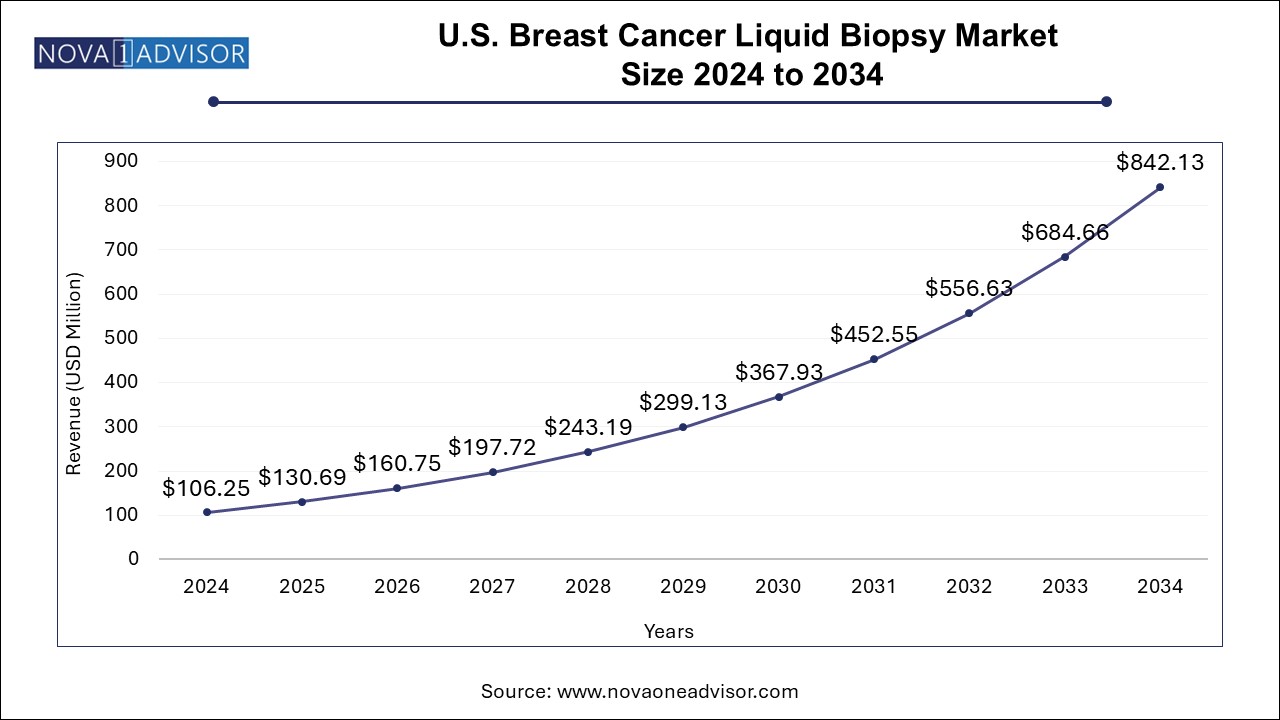
The U.S. breast cancer liquid biopsy market size was exhibited at USD 106.25 million in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 842.13 million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 23.0% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
Breast Cancer Liquid Biopsy Market By Regional Insights
North America dominated the breast cancer liquid biopsy market with the largest revenue share of 45.0% in 2024. Driven by high cancer prevalence, well-established healthcare infrastructure, early adoption of precision diagnostics, and strong regulatory support. The U.S. is home to several pioneering companies, including Guardant Health, Biocept, and Exact Sciences, which are actively developing and commercializing liquid biopsy solutions. Moreover, regulatory bodies like the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) have fast-tracked approvals for liquid biopsy tests under breakthrough device designations, accelerating market availability. Clinical adoption is further reinforced by the presence of advanced oncology centers and wide physician awareness about the benefits of non-invasive testing.
What Drives U.S. Dominance in the Breast Cancer Liquid Biopsy Market?
U.S. dominates the breast cancer liquid biopsy market in North America. The market growth is driven by the high cases of breast cancer, well-established healthcare infrastructure, continuous advancements in diagnostic technologies, increased emphasis on non-invasive diagnostic procedures and rising awareness for early detection in the population. Presence of major market players focused on implementation of go-to-market strategies such as innovative product launches, collaborations, merger & acquisition activities and gaining regulatory approvals for strengthening their businesses is contributing to the market growth. Research grants and funding provided by U.S. government agencies such as the National Institutes of Health (NIH) in liquid biopsy technologies is supporting the development of innovative liquid biopsy assays, advancing validation studies and conduction of clinical trials.
On the other hand, Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing region, owing to rising breast cancer incidence, expanding healthcare access, and increasing awareness of molecular diagnostics. Countries like China, India, and Japan are investing heavily in precision oncology, supported by government initiatives and private sector partnerships. For instance, Chinese companies such as Burning Rock Dx are gaining traction with NGS-based liquid biopsy offerings tailored for breast cancer. Meanwhile, emerging markets in Southeast Asia are witnessing a surge in demand for affordable and non-invasive diagnostic tools, making Asia Pacific a lucrative growth frontier for global and local players alike.
How is China’s Breast Cancer Liquid Biopsy Market Expanding?
China is experiencing significant growth in the breast cancer liquid biopsy market in Asia Pacific. Rising prevalence of breast cancer in China’s huge population is creating the demand for advanced, accurate and non-invasive diagnostic procedures like liquid biopsies. Rapidly evolving healthcare infrastructure, increased emphasis on R&D in genomics-based diagnostic procedures and supportive government initiatives are driving patient access to liquid biopsy technologies in China. Furthermore, increased awareness for early detection among patients and healthcare professionals and continuous advancements in liquid biopsy platforms are fuelling the market expansion.
Market Overview
The Breast Cancer Liquid Biopsy Market represents a pivotal advancement in oncology diagnostics and personalized medicine. Liquid biopsy—a minimally invasive alternative to traditional tissue biopsy—enables the detection and analysis of tumor-derived components such as circulating tumor cells (CTCs), cell-free DNA (cfDNA), and extracellular vesicles (EVs) from blood or other body fluids. In the context of breast cancer, this technology offers unprecedented potential for early detection, real-time monitoring, treatment stratification, and relapse prediction.
Breast cancer remains one of the most prevalent cancers among women globally. According to the World Health Organization, over 2.3 million women were diagnosed with breast cancer in 2020 alone. Traditional diagnostic methods like mammography and tissue biopsy, while effective, face limitations such as invasiveness, sampling errors, and delays in detection of metastasis or recurrence. Liquid biopsy addresses these gaps by offering dynamic, repeatable testing that reflects the tumor’s current genetic landscape.
The growth of this market is fueled by several factors: rising global incidence of breast cancer, increasing preference for non-invasive diagnostics, expanding clinical validation of liquid biopsy biomarkers, and supportive regulatory developments. Furthermore, advancements in next-generation sequencing (NGS) and digital PCR technologies have significantly enhanced the sensitivity and specificity of liquid biopsy platforms. As a result, the market is experiencing heightened interest from both diagnostics developers and biopharmaceutical companies, with several products receiving regulatory approval or entering clinical practice.
In essence, the breast cancer liquid biopsy market is not only transforming cancer detection and treatment but also redefining patient-centric care in oncology.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Expansion of companion diagnostics: Liquid biopsy tests are increasingly being paired with targeted breast cancer therapies to optimize treatment selection.
-
Integration of AI and machine learning for data interpretation: Advanced algorithms are enhancing the accuracy of mutation detection and resistance profiling.
-
Adoption in early-stage breast cancer: Liquid biopsy is being tested for screening and early diagnosis, especially in high-risk populations with genetic predispositions.
-
Emergence of multi-analyte panels: Companies are developing tests that assess multiple circulating biomarkers (e.g., CTCs + cfDNA) to improve diagnostic confidence.
-
Increased clinical validation: Numerous clinical trials are underway to validate liquid biopsy for monitoring therapeutic response and detecting minimal residual disease (MRD).
-
Rise in decentralized testing models: Liquid biopsy kits are being adapted for use in point-of-care or satellite laboratory settings to widen access.
-
Collaborations between diagnostics and pharma firms: Strategic partnerships are on the rise to co-develop liquid biopsy-based solutions for drug development and post-marketing surveillance.
-
Cost reduction through technological innovation: The decreasing cost of NGS and PCR platforms is helping make liquid biopsy more affordable.
-
Regulatory acceleration for breakthrough tests: Agencies such as the FDA are granting fast-track designations for promising liquid biopsy tests in oncology.
-
Personalized monitoring protocols: Real-time tracking of mutations enables personalized adjustments in treatment, particularly in HER2-positive and triple-negative breast cancer subtypes.
How Significantly AI Impacts the Breast Cancer Liquid Biopsy Market?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is improving management of breast cancer by transforming liquid biopsy tests into an efficient and reliable tool for cancer detection. Detection of cancer-related biomarkers such as circulating tumor cells (CTCs) and cell-free DNA (cfDNA) can be achieved with AI-powered liquid biopsies in early stages of breast cancer or even before symptoms appear. AI algorithms can significantly improve the diagnostic accuracy of liquid biopsy by reducing the number of false positive and false negative results, leading to evidence-based decisions. Deployment of AI models in liquid biopsy research is facilitating discovery of novel biomarkers, development of improved diagnostic tools and tailored treatment strategies.
Report Scope of Breast Cancer Liquid Biopsy Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 1.45 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 |
USD 2.89 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2025 to 2034 |
CAGR of 8.0% |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2034 |
| Segments Covered |
Circulating Biomarkers, Application, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional scope |
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, MEA |
| Key Companies Profiled |
The Menarini Group; NeoGenomics Laboratories.; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.; Myriad Genetics, Inc.; QIAGEN; Biocept, Inc.; Sysmex Corporation; Fluxion Biosciences, Inc.; Epic Sciences, Inc.; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc. |
Key Driver: Growing Preference for Non-Invasive Diagnostic Solutions
The primary driver of the breast cancer liquid biopsy market is the growing global preference for non-invasive, patient-friendly diagnostic technologies. Traditional tissue biopsies, while accurate, are associated with several limitations: they are invasive, carry procedural risks, may not always capture tumor heterogeneity, and cannot be repeated frequently for disease monitoring. In contrast, liquid biopsies offer a convenient, safer, and faster alternative that allows clinicians to assess a patient’s tumor profile in real-time through a simple blood draw.
For breast cancer patients undergoing treatment, this means dynamic disease monitoring without the need for repeated tissue excisions. For example, in metastatic breast cancer cases, where obtaining tissue from secondary tumor sites is often challenging, liquid biopsy provides a vital means to assess disease progression and treatment resistance. Furthermore, liquid biopsies can detect mutations such as PIK3CA, ESR1, and HER2, guiding clinicians in therapy selection. This shift towards patient-centric diagnostics is rapidly driving clinical and commercial interest in liquid biopsy.
Key Restraint: Lack of Standardization and Clinical Guidelines
Despite its promising clinical value, the lack of standardization across liquid biopsy platforms and the absence of universally accepted clinical guidelines remain significant restraints. Currently, different tests utilize varied methodologies for biomarker isolation, amplification, and analysis—ranging from PCR-based assays to NGS and digital droplet PCR—leading to inconsistencies in results and interpretation. Furthermore, while some assays are well-validated for certain breast cancer subtypes, others lack sufficient clinical evidence to support routine use.
The absence of harmonized protocols and thresholds also affects physician adoption. For instance, the interpretation of low variant allele frequency in cfDNA can vary based on the platform and the laboratory. Additionally, reimbursement frameworks in many regions do not yet cover liquid biopsy for all use cases, further limiting accessibility. Until standardized diagnostic algorithms and robust regulatory frameworks are established, the market’s full potential may remain constrained.
Key Opportunity: Application in Early Detection and Screening
A major growth opportunity in this market lies in the application of liquid biopsy for early breast cancer detection and population screening, especially among individuals at high genetic risk (e.g., BRCA1/2 mutation carriers). While mammography remains the frontline screening tool, its limitations—such as reduced sensitivity in dense breast tissue—necessitate adjunctive diagnostic tools.
Liquid biopsy offers the potential to detect tumor-derived mutations or epigenetic markers even before radiological changes appear. For example, studies have shown promising results in using cfDNA methylation patterns to detect early-stage breast tumors. Additionally, emerging research into extracellular vesicle cargoes, such as microRNAs, may further enhance screening sensitivity. Developing cost-effective, high-throughput liquid biopsy assays for asymptomatic individuals could revolutionize early cancer detection and significantly improve survival outcomes. Companies that successfully commercialize validated early detection panels will have a competitive edge in preventive oncology.
Breast Cancer Liquid Biopsy Market By Circulating Biomarkers Insights
Based on circulating biomarkets, the circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA) segment led the market with the largest revenue share of 53.6% in 2024. Owing to its wide applicability in mutation detection, treatment monitoring, and minimal residual disease (MRD) assessment. cfDNA-based tests are well-suited for identifying actionable mutations such as ESR1, PIK3CA, and TP53, which guide targeted therapy decisions in breast cancer patients. Moreover, technological advancements in digital PCR and NGS have improved the sensitivity and precision of cfDNA detection. The ability of cfDNA assays to offer insights into tumor heterogeneity and emerging resistance mechanisms has made them indispensable in metastatic breast cancer management.
In contrast, Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) are emerging as the fastest-growing segment within circulating biomarkers. EVs—including exosomes—carry diverse molecular information such as DNA, RNA, and proteins, reflecting the tumor’s dynamic state. Their superior stability in biofluids and capacity to convey early-stage disease signals have caught the attention of researchers and companies alike. For example, EV-derived microRNA signatures are being explored as biomarkers for triple-negative breast cancer—a subtype that lacks clear molecular targets. As EV research matures and transitions into clinical applications, this segment is expected to witness rapid growth.
Breast Cancer Liquid Biopsy Market By Application Insights
Based on application, the treatment selection segments led the market with the largest revenue share of 52.0% in 2024, Primarily because of the growing adoption of liquid biopsy to track treatment response, detect recurrence, and assess MRD. In clinical settings, serial liquid biopsy testing is increasingly being used to determine the efficacy of endocrine therapy or to detect emerging resistance mutations. Such real-time monitoring allows oncologists to tailor therapies based on evolving tumor genetics, avoiding unnecessary side effects and improving patient outcomes. Furthermore, the ability to conduct frequent, minimally invasive tests offers a major advantage in long-term surveillance of breast cancer survivors.
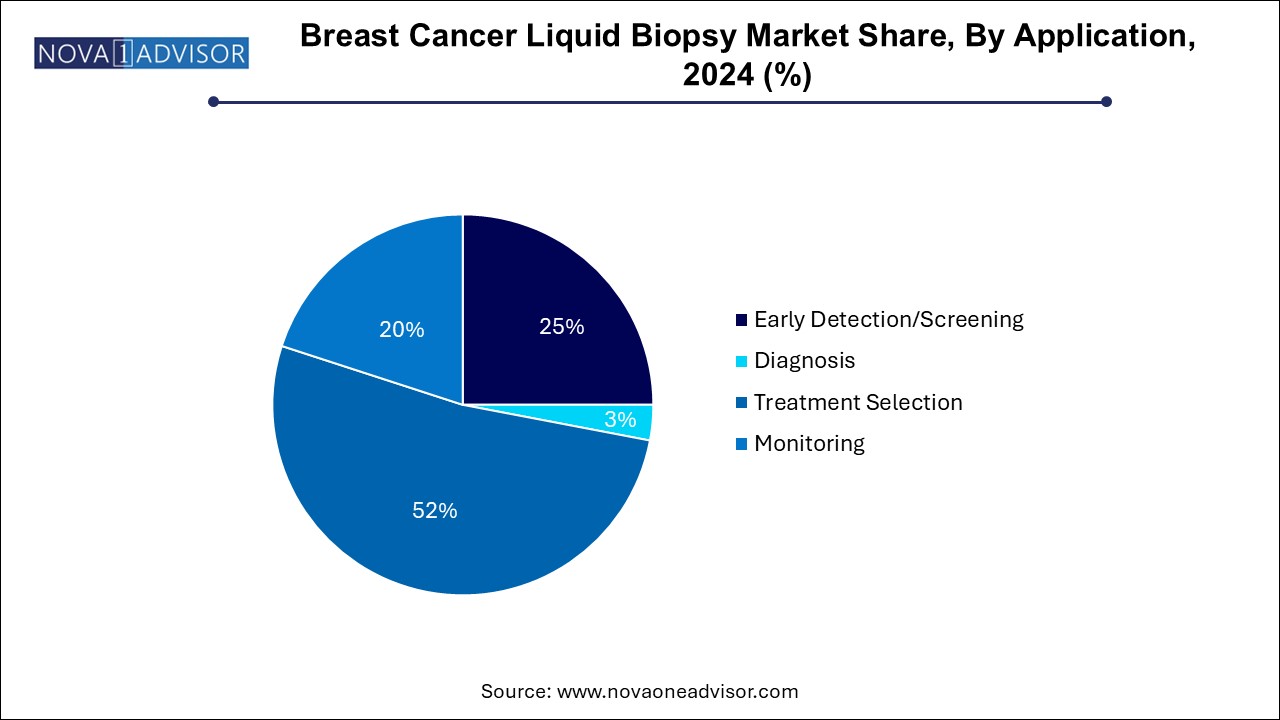
The early detection/screening segment is expected to grow at a significant CAGR of 9.7% during the forecast period, fueled by ongoing R&D efforts and clinical trials aimed at validating liquid biopsy for asymptomatic individuals or those with genetic predispositions. As mentioned earlier, methylation-based cfDNA assays and EV-based diagnostics are showing potential for early-stage detection. Additionally, public health agencies and private companies are exploring the integration of liquid biopsy into breast cancer screening programs. Once regulatory approvals and cost-effectiveness thresholds are achieved, early detection via liquid biopsy could become a game-changer in breast cancer control.
Breast Cancer Liquid Biopsy Market Recent Developments
- In June 2025, the Florida Cancer Specialists & Research Institute, LLC (FCS), introduced liquid biopsy test for the diagnosis and treatment of most common cancers, including lung, breast, colorectal, prostate cancer and cancers of the blood.
- In May 2025, England’s National Health Service (NHS) rolled out a new national scheme which will offer liquid biopsy for patients with lung and breast cancer, further paving the way for tailored cancer care and improved patient survival outcomes.
- In January 2025, The Royal Marsden National Health Service (NHS) Foundation Trust, announced expansion of its Marsden360 Liquid Biopsy Service by including the estrogen receptor alpha gene (ESR1) circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) testing for breast cancer patients in its National Genomic Test Directory.
- In October 2024, GeneCentric Therapeutics, launched the EXpressCT (Expression Signatures Through Circulating Tumor Signals) liquid biopsy platform. The company announced that is has developed liquid biopsy cell-free DNA (cfDNA) signature tests with the platform for lung, breast, pancreatic and colorectal cancers.
Some of the prominent players in the breast cancer liquid biopsy market include:
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the breast cancer liquid biopsy market
By Circulating Biomarkers
- Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs)
- Circulating Cell-free DNA (cfDNA)
- Extracellular Vesicles (EVs)
- Other Circulating Biomarkers
By Application
- Early Detection/Screening
- Diagnosis
- Treatment Selection
- Monitoring
By Regional
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa (MEA)


