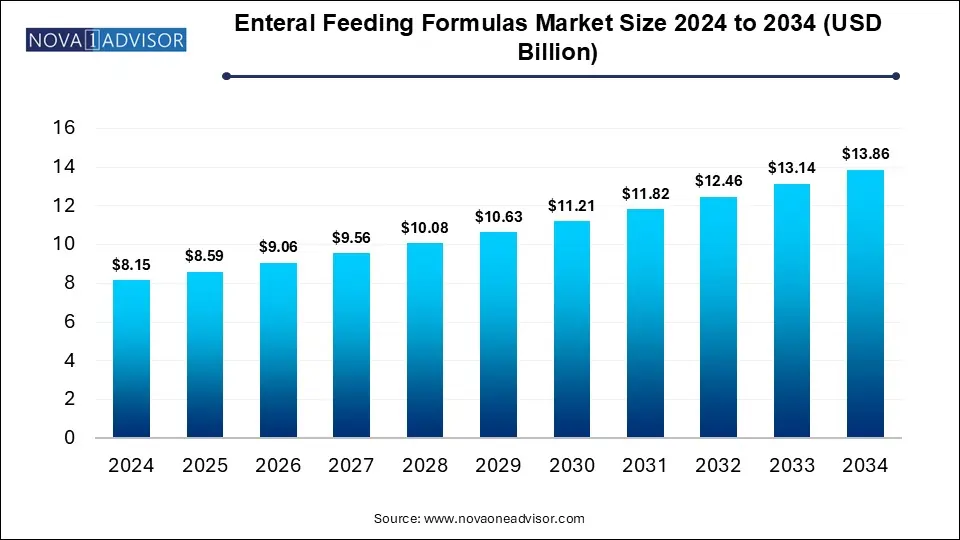
The global enteral feeding formulas market size was exhibited at USD 8.15 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 13.86 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 5.45% during the forecast period of 2025 to 2034.
Key Takeaways:
- The standard formula segment led the market with the largest revenue share of 54% in 2024.
- The intermittent feeding flow segment accounted for the largest revenue share in 2024.
- The adult segment accounted for the largest market revenue share in 2024.
- The cancer care segment accounted for the largest market revenue share in 2024
- The institutional sales segment accounted for the largest market revenue share in 2024
- The home care segment accounted for the largest market revenue share in 2024
- North America dominated the enteral feeding formulas market with the largest revenue share of 31% in 2024.
Market Overview
The Enteral Feeding Formulas Market is a critical segment within the broader clinical nutrition industry. Enteral feeding refers to the method of delivering nutrients directly into the gastrointestinal (GI) tract through a tube, bypassing oral intake. This method is essential for patients who are unable to consume food orally due to medical conditions such as neurological disorders, critical illness, gastrointestinal dysfunction, or post-surgical recovery.
Enteral feeding formulas are specialized nutritional solutions designed to meet the dietary needs of patients across different age groups and disease profiles. These formulas come in various compositions ranging from standard polymeric blends to disease-specific variants for conditions like cancer, diabetes, renal failure, and malabsorption syndromes. They are typically administered via nasogastric, gastrostomy, or jejunostomy tubes in hospitals, long-term care facilities, and increasingly, in home care settings.
As global healthcare systems shift toward value-based and home-centered care, enteral nutrition is gaining traction as a cost-effective solution for managing chronic diseases, surgical recovery, and age-related malnutrition. Coupled with the aging population, increasing prevalence of non-communicable diseases, and rising awareness about clinical nutrition, the enteral feeding formulas market is experiencing significant growth across both developed and emerging economies.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Rising Demand for Disease-Specific Formulas: Customized nutritional blends for diabetes, CKD, and oncology are gaining popularity for better clinical outcomes.
-
Growth of Home-Based Enteral Nutrition: Technological innovation and insurance support are fueling adoption in home care settings.
-
Clean Label and Natural Ingredient Movement: Consumers and caregivers are demanding formulas free of artificial additives, GMOs, and allergens.
-
Emergence of Plant-Based and Vegan Formulas: Catering to ethical, religious, and digestive needs of patients in sensitive groups.
-
Integration of Prebiotics and Probiotics: Enhancing gut health and reducing gastrointestinal complications during enteral feeding.
-
Digital Health Integration: Remote monitoring of nutrition delivery and AI-assisted meal planning are emerging adjuncts.
-
Sustainability Focus in Packaging: Manufacturers are investing in recyclable and eco-friendly packaging for medical nutrition.
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 8.59 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 |
USD 13.86 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2025 to 2034 |
CAGR of 5.45% |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2034 |
| Segments Covered |
Product, Flow Type, Stage, Indication, End-use, Sales Channel, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Central and South America; the Middle East and Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Abbott; Danone S.A; Fresenius Kabi AG; Nestlé; VICTUS; Primus Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; Meiji Holdings. Co., Ltd.; Mead Johnson & Company, LLC |
Market Driver: Increasing Prevalence of Chronic Diseases and Malnutrition
One of the strongest drivers of the enteral feeding formulas market is the rising global burden of chronic diseases such as cancer, diabetes, neurological disorders, and gastrointestinal dysfunctions. These conditions often impair a patient’s ability to chew, swallow, or absorb nutrients through conventional dietary intake. Consequently, enteral nutrition becomes a lifesaving intervention, particularly in critical care settings and post-operative recovery.
In parallel, malnutrition both undernutrition and disease-related wasting is a growing concern, particularly among the elderly and hospitalized populations. The Global Nutrition Report (2022) identified that over 30% of hospitalized patients globally are at risk of malnutrition, directly affecting their recovery, length of hospital stay, and overall prognosis. Enteral feeding formulas play a pivotal role in addressing these nutritional deficits by providing targeted, easily digestible nutrition tailored to individual metabolic needs.
Despite the clinical advantages, the enteral feeding formulas market faces significant challenges, most notably the risk of complications such as tube dislodgement, aspiration pneumonia, infections, and gastrointestinal intolerance. These complications require careful management by trained professionals, which limits the broader applicability in unsupervised or resource-limited settings.
Furthermore, specialized disease-targeted enteral formulas are often expensive, limiting access in regions with weak insurance coverage or low per capita healthcare spending. While standard polymeric formulas are relatively affordable, condition-specific products for renal, hepatic, or oncology patients can significantly increase treatment costs. Regulatory requirements for labeling, clinical validation, and manufacturing add to product development expenses, posing barriers for smaller players.
Market Opportunity: Expansion of Home Enteral Nutrition (HEN) Programs
A significant opportunity lies in the expansion of home enteral nutrition (HEN), driven by healthcare cost containment, hospital bed optimization, and patient preference for in-home recovery. Home-based care is not only more comfortable for patients but also significantly reduces costs for healthcare systems by avoiding extended hospital stays.
Technological advancements such as portable enteral pumps, ready-to-use liquid formulas, and telemonitoring tools have made it feasible to manage enteral feeding outside hospital settings. Insurance providers and governments in the U.S., Europe, and Japan are increasingly reimbursing HEN, making it a lucrative segment for manufacturers and service providers. CDMOs and logistics partners that can develop safe, shelf-stable, and patient-friendly formulas are poised for growth in this market.
Segmental Analysis
By Product
Standard formulas dominate the product segment, offering balanced nutrition with macronutrients and micronutrients suitable for patients without specific disease-related dietary restrictions. These formulas are widely used in hospitals and long-term care facilities for patients undergoing surgery, trauma recovery, or general malnutrition. They are cost-effective and suitable for long-term maintenance feeding. Their simplicity, wide applicability, and availability in both powder and liquid forms make them a staple in clinical nutrition programs.
Disease-specific formulas are the fastest-growing product category, driven by the need for targeted nutritional therapy in chronic conditions like diabetes, cancer, chronic kidney disease (CKD), and neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s. These formulas are tailored to reduce complications and improve clinical outcomes for example, low-sugar formulas for diabetic patients or renal-specific blends with restricted electrolytes. The increasing burden of lifestyle and aging-related diseases makes this a high-growth segment with opportunities for personalized nutrition innovations.
By Flow Type
Continuous feeding flow dominates this segment, especially in critical care and intensive care unit (ICU) environments where stable and consistent nutrient delivery is essential. Continuous feeding reduces the risk of gastrointestinal intolerance, improves nutrient absorption, and is easier to manage in mechanically ventilated patients. Pumps used for continuous feeding can be programmed for precise flow rates, reducing caregiver burden and enhancing safety.
Intermittent feeding flow is the fastest-growing flow type, particularly in home care and long-term care facilities. It mimics normal eating patterns, allows mobility between feeding sessions, and is preferred by patients with intact gastrointestinal function. As more patients are managed outside hospitals, intermittent feeding with or without gravity bags is becoming the norm, enhancing autonomy and quality of life.
By Stage
Adults dominate the stage segment, as most clinical nutrition interventions target adult and geriatric populations with cancer, stroke, trauma, or chronic illness. This segment covers a broad patient population from young adults recovering from surgery to elderly individuals requiring nutritional support for degenerative conditions. With global aging trends, the adult segment is expected to remain the largest and most stable revenue generator for enteral nutrition providers.
Pediatrics is the fastest-growing segment, particularly due to increasing rates of congenital disorders, neurological impairments, and premature births that require enteral nutrition. Pediatric formulas are specially designed to meet the caloric, vitamin, and mineral requirements of growing children. With advancements in neonatal and pediatric care, survival rates for critically ill children are improving, thereby boosting long-term demand for pediatric enteral formulas.
By Indication
Cancer care dominates the indication segment, owing to the high prevalence of cancer-related malnutrition, cachexia, and treatment-related feeding difficulties. Patients undergoing chemotherapy, radiation, or surgical resections often require nutritional supplementation to support recovery and reduce treatment side effects. Oncology-specific formulas with high protein, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidant content are preferred in this category.
Neurological disorders such as Alzheimer's and dysphagia are among the fastest-growing indications, reflecting the rise in neurodegenerative and age-related diseases. Enteral feeding becomes critical when these patients experience cognitive decline or impaired swallowing, and disease-specific formulas can help prevent weight loss, maintain cognition, and improve overall quality of life.
By End-use
Hospitals dominate the end-use category, particularly for acute care and post-operative nutritional support. Departments like critical care, neurology, oncology, and cardiology rely heavily on enteral nutrition to stabilize patients. Hospital-based nutrition teams typically oversee the initiation and monitoring of enteral feeding, making hospitals the largest purchasers of bulk formulas and associated devices.
Home care is the fastest-growing end-use segment, thanks to the growing preference for outpatient recovery, advances in feeding pump portability, and better caregiver training. Many developed nations now run public programs that reimburse patients for home-based enteral care, and manufacturers are introducing consumer-friendly packaging and ready-to-use formulas to support this transition.
By Sales Channel
Institutional sales dominate the market, covering direct sales to hospitals, long-term care homes, and rehabilitation centers. These bulk contracts offer volume discounts and long-term partnerships, making them a key focus for major manufacturers.
Online sales are the fastest-growing channel, especially for patients and caregivers managing long-term nutrition at home. E-commerce platforms and direct-to-consumer websites now offer customizable subscriptions, auto-replenishment, and access to disease-specific formulas. The pandemic significantly accelerated this trend, making digital access a permanent fixture of the enteral nutrition ecosystem.
Regional Analysis
North America dominates the enteral feeding formulas market, driven by a high incidence of chronic diseases, advanced healthcare infrastructure, and robust insurance coverage. The U.S. accounts for a significant share due to its aging population, presence of major manufacturers, and progressive home care models. Innovations in adult and pediatric formulas originate in North America, which also leads in clinical trials and regulatory approvals.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, fueled by increasing healthcare investments, growing awareness of clinical nutrition, and rising demand for elder care. Countries like China, India, and Japan are experiencing a surge in diabetes, cancer, and neurological disorders leading indications for enteral nutrition. Expanding hospital networks, medical tourism, and domestic production of enteral formulas are further enhancing market growth in the region.
Recent Developments
-
Nestlé Health Science (April 2025): Launched a new plant-based enteral formula line under its “Peptamen” brand for patients with digestive sensitivities and ethical dietary preferences.
-
Abbott Laboratories (March 2025): Expanded its “Ensure Plus” product range with a diabetes-specific variant targeting outpatient oncology clinics in Europe.
-
Danone Nutricia (February 2025): Introduced an AI-powered nutrition platform to personalize enteral feeding plans for hospital patients based on metabolic profiling.
-
Fresenius Kabi (January 2025): Announced a $150 million investment in a new enteral nutrition manufacturing facility in India to meet rising demand in Asia-Pacific.
-
Mead Johnson (December 2024): Collaborated with pediatric hospitals in Latin America to launch a new neonatal enteral nutrition initiative.
- Abbott
- Danone S.A
- Fresenius Kabi AG
- Nestlé
- VICTUS
- Primus Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
- Meiji Holdings. Co., Ltd.
- Mead Johnson & Company, LLC
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the global enteral feeding formulas market.
Product
- Standard Formula
- Disease-specific Formulas
-
- Alzheimer’s
- Nutrition Deficiency
- Cancer Care
- Diabetes
- Chronic Kidney Diseases
- Orphan Diseases
- Dysphagia
- Pain Management
- Malabsorption/GI Disorder/Diarrhea
- Others
Flow Type
- Intermittent Feeding Flow
- Continuous Feeding Flow
Stage
Indication
- Alzheimer’s
- Nutrition Deficiency
- Cancer Care
- Diabetes
- Chronic Kidney Diseases
- Orphan Diseases
- Dysphagia
- Pain Management
- Malabsorption/GI Disorder/Diarrhea
- Others
End-use
-
- Cardiology
- Neurology
- Critical Care (ICU)
- Oncology
- Others
- Home Care
- Long Term Care Facilities
Sales Channel
- Online Sales
- Retail Sales
- Institutional Sales
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)

