Erectile Dysfunction Drugs Market Size and Research
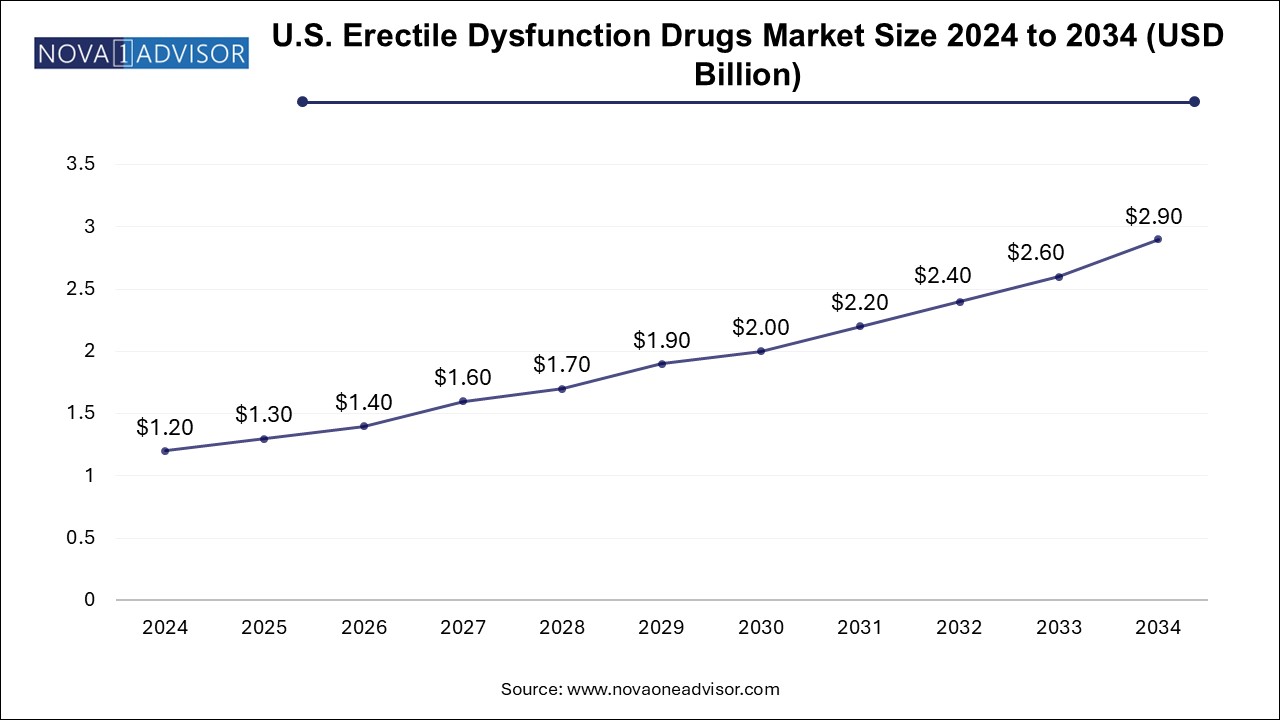
The erectile dysfunction drugs market size was exhibited at USD 3.15 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 7.55 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 9.14% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
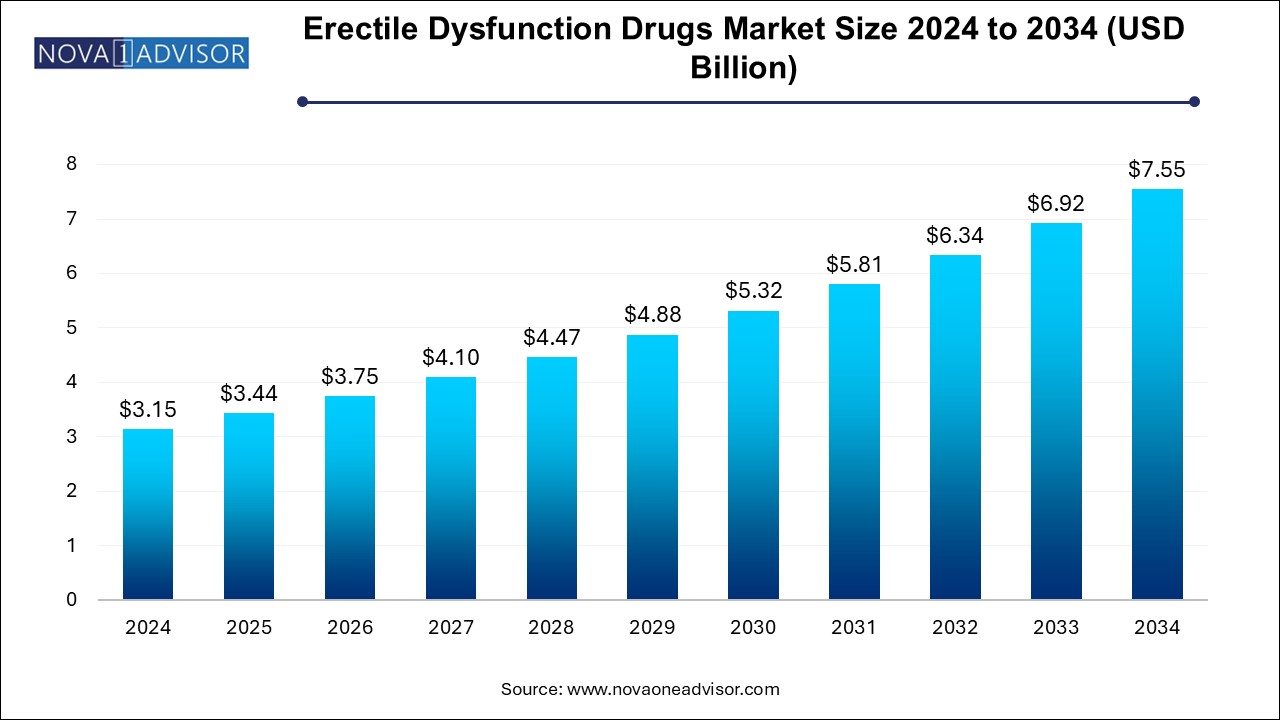
U.S. Erectile Dysfunction Drugs Market Size and Growth 2025 to 2034
The U.S. erectile dysfunction drugs market size is evaluated at USD 1.20 billion in 2024 and is projected to be worth around USD 2.90 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 8.35% from 2025 to 2034.
The erectile dysfunction drugs market in North America, led by the United States, holds the largest share of the global erectile dysfunction drugs market. This dominance is underpinned by high awareness levels, access to advanced healthcare infrastructure, and the presence of leading pharmaceutical manufacturers. The U.S. has been a pioneer in ED drug development, with the early launch and widespread adoption of Viagra, Cialis, and Levitra. The region’s mature insurance and regulatory environment, along with its high spending on prescription drugs, ensures consistent revenue for branded and generic products.
The rise of direct-to-consumer telemedicine platforms has further reshaped ED treatment in North America. Companies like Roman and Hims have normalized conversations around men’s health and expanded market access to previously untapped demographics, such as millennials and Gen Z. As clinical research continues on newer delivery mechanisms and long-acting therapies, North America is expected to remain at the forefront of ED market innovation and commercial success.
Asia Pacific is emerging as the fastest-growing market, driven by demographic factors, increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, improving economic conditions, and gradual destigmatization of sexual health. Countries such as China, India, Japan, and South Korea are witnessing an increase in ED diagnoses due to lifestyle changes, stress, diabetes, and cardiovascular disorders. As healthcare access improves and male health becomes a priority, demand for ED treatments is on the rise.
Moreover, Asia Pacific’s pharmaceutical industry is investing heavily in generic PDE5 inhibitors to serve domestic and export markets. Governments are also increasing support for public education around sexual dysfunction, while telehealth services and e-pharmacies are expanding rapidly across the region. With a large aging male population, increasing disposable incomes, and rising digital penetration, Asia Pacific is poised to be a major growth engine for the global ED drug industry over the next decade.
Market Overview
The erectile dysfunction (ED) drugs market has evolved significantly over the past two decades, transitioning from a relatively under-discussed therapeutic area to a mainstream segment of the global pharmaceutical industry. Erectile dysfunction, characterized by the consistent inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual performance, affects millions of men globally. While commonly associated with aging, ED is increasingly recognized in younger age groups due to lifestyle-related factors, psychological stress, and the prevalence of conditions such as diabetes, obesity, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease.
Pharmacological intervention remains the first-line treatment for ED, with phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitors being the most widely prescribed class of drugs. Since the introduction of sildenafil citrate (Viagra) in the late 1990s, followed by tadalafil (Cialis), vardenafil (Levitra), and avanafil (Stendra), the market has seen strong growth driven by efficacy, ease of use, and increasing awareness. The expiration of patents for leading drugs has also given rise to a robust generics market, improving accessibility in both developed and developing countries.
With a global shift toward greater openness about men's health, expanding telehealth services, and the growth of e-pharmacy platforms, the ED drugs market is poised for steady expansion. Emerging therapies, including novel delivery systems and regenerative treatments, are expected to add new dimensions to the market. Despite social stigma and regulatory complexities in some regions, increasing consumer education and technological innovation are likely to propel this market’s evolution through 2034.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Rise of Generic Versions Driving Price Competition and Market Expansion
-
Growth of Telemedicine Platforms Specializing in Men’s Sexual Health
-
Increased Demand for Fast-Acting and Long-Lasting Formulations
-
Development of Novel Delivery Modes (e.g., sublingual, nasal, topical)
-
Expansion of Over-the-Counter ED Treatments in Select Markets
-
Growing Interest in Herbal and Nutraceutical Alternatives for ED
-
Integration of ED Management in Digital Health Apps and Wearables
-
Rise in Younger ED Diagnoses Attributed to Lifestyle and Mental Health Issues
-
Strategic Collaborations Between Pharma and Direct-to-Consumer Brands
-
Emerging Research on Stem Cell Therapy and Regenerative Medicine in ED
Report Scope of Erectile Dysfunction Drugs Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 3.44 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 |
USD 7.55 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2025 to 2034 |
CAGR of 9.14% |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2034 |
| Segments Covered |
Product, Mode of Administration, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Bayer AG, Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline PLC, Petros Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Pfizer Inc., Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd, Lupin Limited, Futura Medical, Cure Pharmaceutical, 23andMe, Hims & Hers Health, Inc., RO, BlueChew, GoodRx, Inc. |
Market Driver: Rising Prevalence of Lifestyle-Associated Chronic Conditions
A prominent driver for the erectile dysfunction drugs market is the rising prevalence of chronic diseases and lifestyle-related health conditions, which are closely associated with impaired sexual function. Diabetes, cardiovascular disease, obesity, and metabolic syndrome are particularly notable for their role in damaging vascular and nerve function, both of which are essential for achieving an erection.
For instance, research shows that over 50% of diabetic men experience some degree of ED, making this population a critical target for pharmaceutical intervention. Additionally, sedentary lifestyles, smoking, excessive alcohol use, and mental health issues—particularly stress and depression—further exacerbate ED risk. As these conditions continue to climb globally, especially in aging and urbanizing populations, the need for effective ED treatment becomes more pronounced. The rising awareness of these correlations, along with the medicalization of male sexual health, is significantly boosting the demand for ED medications across all regions.
Market Restraint: Social Stigma and Cultural Taboos
Despite growing public awareness, a major barrier to market growth remains the persistent social stigma and cultural taboos surrounding sexual health, particularly in conservative societies. Men in many cultures are reluctant to seek treatment for ED due to embarrassment, fear of judgment, or concerns about masculinity. This often leads to underdiagnosis and underreporting, thereby limiting the full potential of the market.
In some regions, access to professional consultation or sexual health services is restricted due to regulatory hurdles or lack of trained personnel. Even where treatment is available, men may opt for unregulated or counterfeit medications due to privacy concerns or cost. These issues contribute to a substantial treatment gap, especially in parts of Asia, the Middle East, and Africa. Bridging this divide requires concerted efforts in public health education, privacy-driven healthcare delivery, and destigmatization campaigns that encourage open conversations about sexual dysfunction.
Market Opportunity: Growth of Direct-to-Consumer and Telehealth Models
An emerging opportunity reshaping the ED drugs market is the rapid expansion of direct-to-consumer (DTC) telehealth platforms, which enable discreet, online access to diagnosis, prescription, and home delivery of ED medications. Companies like Hims, Roman (Ro), and Lemonaid Health have created end-to-end digital experiences tailored specifically to men’s sexual health, leveraging teleconsultation models, digital marketing, and subscription services.
These platforms have successfully addressed two critical barriers in ED management: convenience and discretion. They allow patients to bypass in-person visits and avoid social stigma, while still receiving medically supervised treatment. As telehealth regulations evolve and digital literacy expands, especially in post-pandemic healthcare environments, DTC services are expected to significantly increase market penetration. This model is particularly effective among younger tech-savvy consumers who prefer digital interactions over traditional healthcare settings.
Erectile Dysfunction Drugs Market By Product Insights
The Viagra (sildenafil citrate) segment dominated the market and accounted for the largest revenue share of 57.4% in 2024. Its pioneering status, high brand recall, and extensive clinical data have established it as the most widely recognized and prescribed drug for ED. Sildenafil works by enhancing blood flow to the penis by inhibiting the PDE5 enzyme, with an onset time of 30 to 60 minutes and duration of around 4 hours, making it suitable for planned sexual activity. Generic versions of Viagra have further democratized access, particularly in developing markets, where affordability is a key concern.
The Cialis (tadalafil) is witnessing the fastest growth due to its longer duration of action—up to 36 hours—and greater flexibility for spontaneous sexual activity. Known as the "weekend pill," tadalafil is increasingly preferred by men who value sustained efficacy and convenience. It also has approval for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), providing additional therapeutic value. Its once-daily dosing formulation for continuous therapy has attracted users with chronic or severe ED, positioning Cialis as a strong contender in the evolving treatment landscape.
Erectile Dysfunction Drugs Market By Mode of Administration Insights
The oral mode segment accounted for the largest market share of 85.0% in 2024. Oral PDE5 inhibitors have become the mainstay of ED treatment, with proven safety profiles and rapid onset of action. They are easy to distribute, administer, and dose, making them suitable for a wide demographic, from elderly men to younger patients with psychogenic ED. Online retail and telehealth models also facilitate access to oral tablets, which can be discreetly ordered and consumed.
Meanwhile, injectable and other modes of administration, though currently niche, are experiencing gradual growth—particularly among patients unresponsive to oral therapies. Intracavernosal injections (e.g., alprostadil), urethral suppositories, and experimental modes like topical gels, sublingual films, and nasal sprays are expanding the delivery options available. These formulations are gaining attention for faster onset, localized action, and reduced systemic side effects. Innovation in this space, especially in combination therapies or devices, is expected to create incremental value and diversify treatment options.
Some of the prominent players in the erectile dysfunction drugs market include:
Erectile Dysfunction Drugs Market Recent Developments
-
March 2025: Pfizer Inc. launched a new low-dose version of sildenafil targeted at younger men with mild ED, to be distributed through digital prescription platforms across Europe and North America.
-
February 2025: Reckitt Benckiser acquired a stake in a U.K.-based men’s health telemedicine startup to expand its presence in the ED and wellness segments.
-
January 2025: Endo International introduced a new fast-dissolving oral strip formulation of avanafil, offering rapid onset for patients seeking immediate efficacy.
-
December 2024: Zydus Lifesciences announced the launch of its generic tadalafil and vardenafil combinations in India, focusing on affordable treatment for rural and underserved populations.
-
November 2024: Bayer AG initiated Phase II trials for a novel topical PDE5 inhibitor gel designed for patients with gastrointestinal intolerance to oral medications.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the erectile dysfunction drugs market
By Product
- Viagra (sildenafil citrate)
- Cialis (Tadalafil)
- Levitra/Staxyn (vardenafil)
- Stendra/Spedra (avanafil)
- Zydena (udenafil)
- Other Drugs
By Route of Administration
- Oral Mode of Administration
- Injectable Mode of Administration
- Other Modes of Administration
By Regional
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa (MEA)


