Computer Aided Engineering Market Size and Growth
The global computer aided engineering market size was exhibited at USD 10176.8 million in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 32176.57 million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 12.2% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
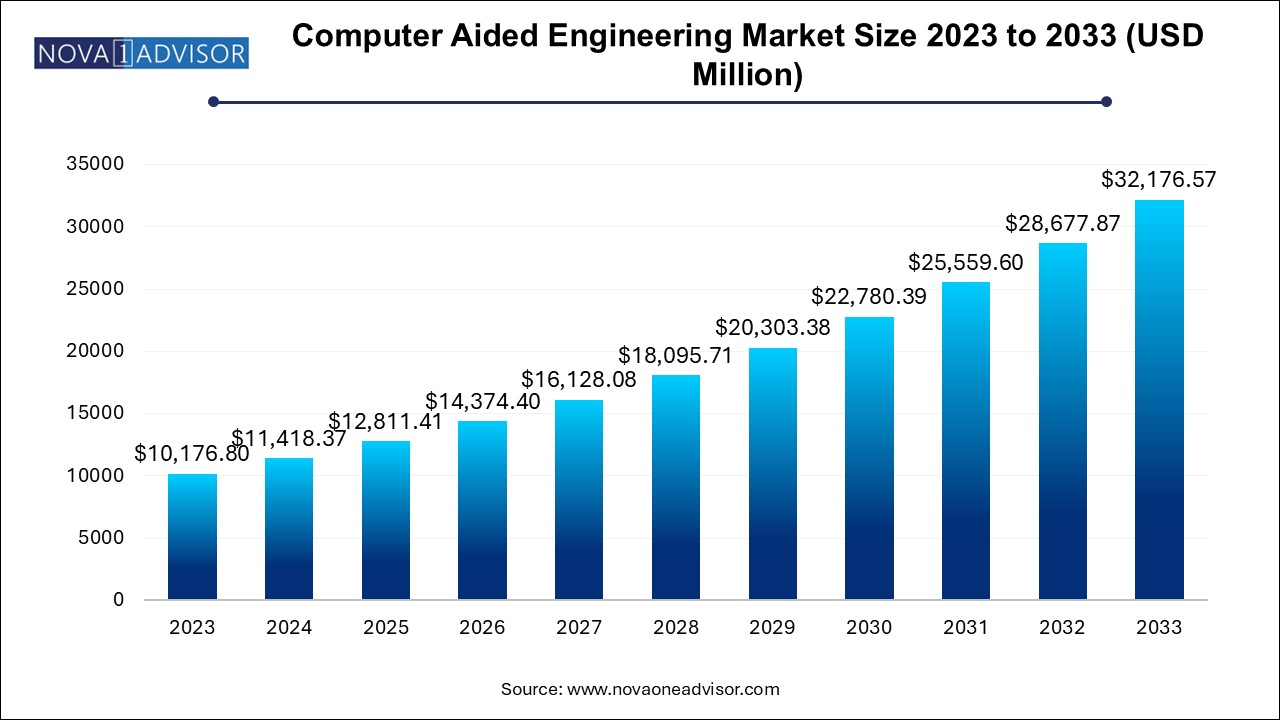
Computer Aided Engineering Market Key Takeaways:
- The software segment accounted the major market share in 2023.
- The service segment is expected to register the highest CAGR over the forecast period.
- In 2023 the on-premise segment held a market share exceeding 63% in the global market and is expected to exhibit a CAGR of nearly 10.5% from 2023 to 2030.
- In 2023, the automotive industry held the largest market share of more than 29% in the global market and expected to exhibit a significant CAGR from 2024 to 2033.
- In 2023, North America dominated the CAE market with a market share of more than 33.0% and is expected to continue its dominance over the forecast period.
- The APAC regional market is expected to witness exponential growth over the forecast period with a CAGR of 13.4%.
Market Overview
The Global Computer Aided Engineering (CAE) market is experiencing robust growth as engineering organizations increasingly prioritize virtual product development to reduce costs, accelerate time-to-market, and improve product quality. CAE encompasses a wide range of engineering simulation tools and services, including finite element analysis (FEA), computational fluid dynamics (CFD), multibody dynamics, and optimization & simulation software. These tools are critical across industries for virtual prototyping, performance validation, and failure analysis without relying entirely on expensive physical testing.
The expansion of CAE is strongly tied to the acceleration of digitization in product development lifecycles. As companies strive for more agile and efficient design processes, CAE software is being integrated with computer-aided design (CAD), computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), and product lifecycle management (PLM) systems. This integration enables end-to-end digital engineering, allowing engineers to simulate everything from fluid flow and mechanical stress to heat transfer and crashworthiness under varied operating conditions.
The rising complexity of products, particularly in automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical devices, is further necessitating advanced simulation capabilities. The push toward electric vehicles (EVs), lightweight materials, sustainable product design, and smart manufacturing technologies like digital twins has brought CAE to the forefront of innovation. Moreover, the emergence of cloud-based simulation, AI-enhanced solvers, and high-performance computing (HPC) has made CAE tools more accessible and scalable, even for mid-sized enterprises.
As industries pivot towards agile development models, CAE is becoming indispensable not just for validating design integrity but also for optimizing performance, ensuring compliance, and fostering innovation. Its role in enabling predictive engineering and model-based system engineering is set to expand dramatically in the next decade.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Cloud-Based CAE Adoption: Cloud-native platforms are enabling scalable simulation workloads with reduced IT infrastructure costs.
-
AI and Machine Learning in Simulation: AI is being integrated into solvers for intelligent mesh generation, design optimization, and real-time decision-making.
-
Integration with Digital Twin Technology: CAE forms the analytical core of digital twin models, offering real-time simulation of physical systems.
-
Multiphysics Simulation Demand: Engineers are increasingly adopting solutions that combine FEA, CFD, and thermal analysis in a unified platform.
-
Shift Toward Simulation-Driven Design: Product development is moving from prototype-test to simulate-design-manufacture workflows.
-
CAE in Additive Manufacturing: Simulation tools are being used to model residual stress, thermal distortion, and build orientation in 3D printing.
-
Industry-Specific CAE Customization: Solutions are being tailored for specific sectors like biomedical device simulation or EV battery thermal analysis.
-
Subscription-Based Licensing Models: Vendors are shifting from perpetual to SaaS-based pricing models for broader market penetration.
Report Scope of Computer Aided Engineering Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 11418.37 Million |
| Market Size by 2033 |
USD 32176.57 Million |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 |
CAGR of 12.2% |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered |
Component, Deployment Model, End-use Industry, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; South America; MEA |
| Key Companies Profiled |
ANSYS, Inc.,Altair Engineering, Autodesk, Inc., Bentley Systems, Inc., Dassault Systemes, ESI Group, Exa Corporation, Mentor Graphics Corporation (A subsidiary of Siemens AG), Hexagon AB, Siemens |
Market Driver: Increasing Product Complexity and Need for Virtual Validation
A major driver for the CAE market is the growing complexity of products across multiple industries, coupled with the imperative for virtual validation. Today’s products are becoming more sophisticated, integrating mechanical, electrical, thermal, and fluid systems. For example, an electric vehicle involves aerodynamics, battery thermal management, crash safety, and noise-vibration-harshness (NVH) all in one package. Designing such products demands simultaneous multiphysics simulation to ensure system-level performance and safety.
Virtual simulation using CAE tools allows companies to test thousands of design iterations in silico, thereby cutting down development time, reducing costs, and mitigating risk before building physical prototypes. In aerospace, CAE is used to simulate airflow, stress concentration, and structural fatigue. In consumer electronics, it helps optimize heat dissipation and shock resistance. By allowing design engineers to validate and optimize performance early in the design process, CAE tools are becoming critical enablers of rapid innovation.
While CAE tools offer enormous value, their high upfront cost and steep learning curve can act as significant barriers, particularly for small and medium enterprises (SMEs). Licensing fees for high-end FEA or CFD software can run into tens of thousands of dollars annually. In addition to software costs, organizations must invest in powerful computing infrastructure or subscription-based HPC services to handle large-scale simulations efficiently.
Moreover, CAE tools require specialized training and domain expertise. Engineers must understand both the physics of simulation and the numerical methods behind the software. Misapplication of boundary conditions or mesh setups can lead to erroneous results, making skilled workforce availability a limiting factor. Even with advancements in GUI and automation, the complexity of real-world simulations often necessitates collaboration with experienced CAE professionals or consultants.
Market Opportunity: CAE’s Role in Digital Twin and Industry 4.0 Ecosystems
An emerging opportunity lies in the integration of CAE tools into digital twin platforms and Industry 4.0 initiatives. A digital twin is a virtual representation of a physical product or system that continuously receives data from sensors, enabling real-time simulation and predictive maintenance. CAE plays a central role in the analytical engine of the digital twin, providing the simulation backbone that predicts how products will behave under actual operating conditions.
As industries invest in smart factories, connected devices, and automated processes, the demand for real-time simulation, what-if scenario planning, and failure prediction will rise. CAE is poised to expand from being a design validation tool to a real-time performance monitor, integrated with IoT platforms and machine learning analytics. This trend presents new revenue streams for software vendors, particularly those offering cloud-native, scalable solutions compatible with enterprise PLM and ERP systems.
Computer Aided Engineering Market By Component Insights
The software segment dominates the CAE market due to its central role in simulating and validating engineering processes across industries. Within software, FEA and CFD tools form the backbone of simulation-driven engineering. FEA is widely used for structural and stress analysis in mechanical components, while CFD simulates fluid flow and thermal effects. Multibody dynamics and optimization modules are gaining popularity for system-level simulations and design efficiency.
Conversely, services are growing steadily, especially training, support, and development services. As simulation tools become more advanced, organizations rely on service providers for workflow integration, customization, cloud migration, and user training. Third-party engineering consultants are also playing a key role in sectors like aerospace, where highly specialized simulations are required. Managed services and simulation process automation are emerging as key enablers for smaller firms entering the CAE space.
Computer Aided Engineering Market By Deployment Model Insights
On-premise deployment remains dominant, particularly among large enterprises and industries dealing with proprietary or highly sensitive data such as defense, automotive R&D, and aerospace. On-premise systems offer greater control, low latency, and better integration with internal IT environments, making them suitable for complex simulations requiring massive computing power and strict data security.
That said, cloud-based CAE is the fastest growing segment, driven by the increasing need for scalability, cost-efficiency, and remote access. Cloud solutions enable engineers to run simulations on demand, leveraging high-performance computing (HPC) environments without capital investment. They also simplify collaboration across distributed teams, as simulation models and results can be shared and accessed in real time. Companies like SimScale, Ansys Cloud, and Altair One are leading the transition toward cloud-first simulation.
Computer Aided Engineering Market By End-use Insights
The automotive sector dominates the CAE market, driven by the increasing use of simulation in crash testing, aerodynamics, battery performance, and NVH analysis. Automakers rely heavily on FEA and CFD to meet stringent regulatory standards while accelerating vehicle innovation. The shift toward electric mobility and autonomous vehicles has only increased the reliance on simulation tools to test software, sensors, battery cooling systems, and chassis design before physical prototyping.
Meanwhile, the medical devices segment is the fastest-growing, as companies turn to CAE to model biomechanics, simulate implant interactions, and meet regulatory compliance. With innovations like wearable sensors, robotic surgical tools, and personalized prosthetics, the need for virtual testing of structural integrity and fluid dynamics in medical products has grown. CAE is increasingly used for simulating blood flow in stents, stress testing in orthopedic implants, and real-time kinematic modeling of exoskeletons.
Computer Aided Engineering Market By Regional Insights
North America dominates the global CAE market, owing to its technological leadership, presence of major OEMs, and strong ecosystem of software vendors. The United States, in particular, is home to leading players such as Ansys, PTC, Autodesk, and Altair, which continuously innovate in CAE software offerings. The region also benefits from a well-established manufacturing sector, government-funded R&D, and the early adoption of emerging technologies such as AI, cloud computing, and digital twins.
Moreover, sectors like aerospace and defense, which are deeply embedded in North America, rely extensively on simulation to meet safety-critical and compliance-heavy product development cycles. Universities and research labs in the U.S. also contribute to advancing CAE methodologies, often in partnership with industry stakeholders.
Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing region, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing manufacturing investments, and growing demand for smart products. Countries like China, Japan, South Korea, and India are investing in domestic CAE capabilities to support local automotive, electronics, and defense industries. China, in particular, is developing indigenous CAE tools while also adopting global software to meet design and simulation demands for infrastructure, aviation, and EV sectors.
India is emerging as a CAE outsourcing hub, offering engineering simulation services to global firms in automotive and aerospace. The region’s growing emphasis on smart manufacturing, 5G integration, and AI-enhanced engineering is further fueling demand for cloud-based and AI-integrated CAE platforms. As government support for Industry 4.0 grows across the region, the CAE market is poised for long-term expansion.
Computer Aided Engineering Market Recent Developments
-
March 2024 – Ansys Inc. launched its 2024 R2 software suite, introducing enhanced CAx simulation tools with cloud-native deployment, AI-powered solvers, and extended support for digital twin integration. The update focuses on improving usability for cross-discipline simulation. [Source: BusinessWire]
-
January 2024 – Altair Engineering announced the release of Altair HyperWorks 2024, a unified CAE platform that combines generative design, meshless solvers, and cloud computing capabilities. The suite supports additive manufacturing and multi-material simulation.
-
December 2023 – Dassault Systèmes introduced BIOVIA Simulation Central, a simulation platform aimed at life sciences and medical device manufacturers, combining CAE, molecular modeling, and regulatory compliance workflows.
-
November 2023 – Siemens Digital Industries Software unveiled enhancements to Simcenter, integrating AI-based model reduction techniques to accelerate simulation cycles in automotive and aerospace applications.
-
September 2023 – Autodesk enhanced its Fusion 360 simulation workspace with new modules for thermal stress analysis and cloud-based job queueing, targeting small engineering firms and startups.
Some of the prominent players in the global computer aided engineering market include:
- ANSYS, Inc.
- Altair Engineering
- Autodesk, Inc.
- Bentley Systems, Inc.
- Dassault Systemes
- ESI Group
- Exa Corporation
- Mentor Graphics Corporation (A subsidiary of Siemens AG)
- Hexagon AB
- Siemens
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the global computer aided engineering market
Component
-
- Finite Element Analysis (FEA)
- Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)
- Multibody dynamics
- Optimization & simulation
-
- Development Service
- Training, Support & Maintenance
Deployment Model
End-use
- Automotive
- Defense & aerospace
- Electronics
- Medical devices
- Industrial equipment
- Others
Regional
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- South America
- Middle East and Africa (MEA)

