Healthcare Cloud Computing Market Size and Growth
The global healthcare cloud computing market size was exhibited at USD 19.65 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 66.12 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 12.9% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
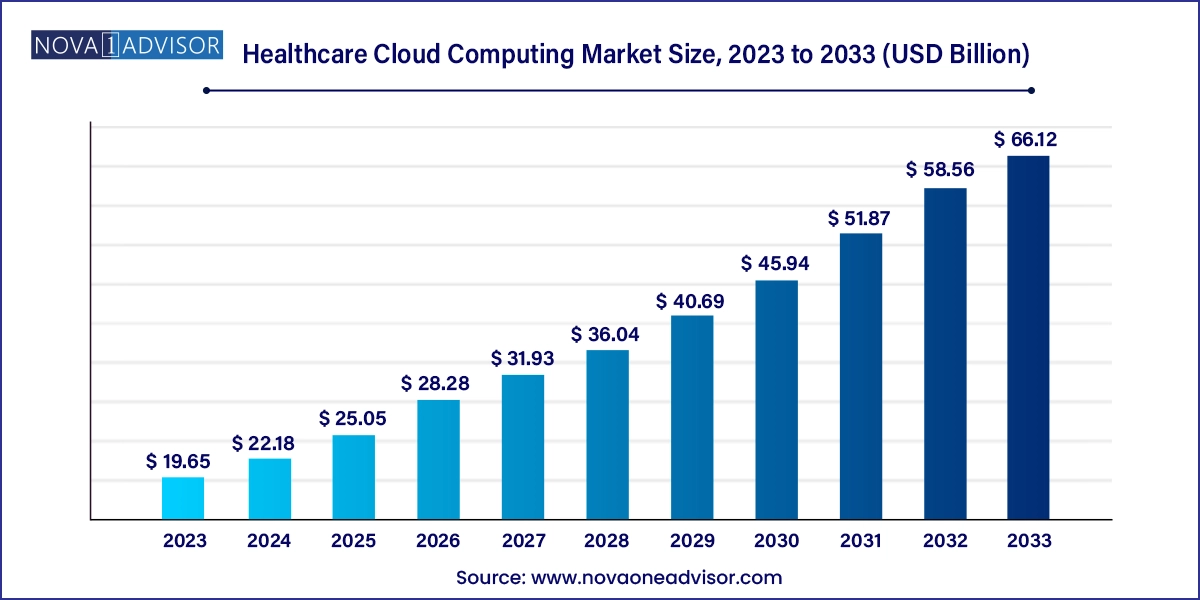
Healthcare Cloud Computing Market Key Takeaways:
- Nonclinical information systems dominated the market and accounted for a market share of 50.7% in 2023.
- The clinical information systems segment is expected to grow at a significant CAGR during the forecast period.
- Private cloud dominated the market and accounted for a market share of 37.6% in 2023.
- The hybrid cloud segment is expected to grow significantly during the forecast period.
- Pay-as-you-go dominated the market and accounted for a market share of 55.0% in 2023.
- Spot pricing segment is expected to grow at a significant CAGR during the forecast period.
- Software-as-a-service dominated the market and accounted for a market share of 45.3% in 2023.
- The infrastructure-as-a-service segment is expected to grow significantly during the forecast period.
- Healthcare providers dominated the market and accounted for a market share of 57.0% in 2023.
- The healthcare payers segment is expected to grow at a significant CAGR during the forecast period.
- North America healthcare cloud computing market dominated in 2023.
Market Overview
The global healthcare cloud computing market has emerged as one of the most transformative segments within the broader digital health ecosystem. As healthcare organizations increasingly prioritize interoperability, cost-efficiency, scalability, and real-time access to patient data, cloud computing solutions have gained prominence. Cloud computing allows healthcare providers and payers to store, process, and access vast amounts of data remotely via secure internet connections. The advantages it offers, including scalability, flexibility, lower IT infrastructure costs, and enhanced collaboration, are driving adoption across clinical and nonclinical applications.
From Electronic Medical Records (EMRs) to Population Health Management (PHM), and from billing systems to Revenue Cycle Management (RCM), healthcare organizations are increasingly leveraging cloud technologies to streamline operations, support telehealth, and facilitate data sharing. Moreover, cloud platforms are enabling precision medicine, real-time analytics, and AI-driven diagnostics, all of which require high-volume data processing capabilities.
In 2024, the global healthcare cloud computing market was valued at over USD 60 billion, and it is expected to witness a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of more than 15% through 2032. This surge is attributed to increasing healthcare digitization, growing demand for telemedicine, regulatory compliance requirements such as HIPAA and GDPR, and the integration of advanced technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), and Machine Learning (ML).
Major Trends in the Market
-
Rising Adoption of Telemedicine and Remote Patient Monitoring: Driven by the COVID-19 pandemic and post-pandemic continuity, telehealth platforms hosted on cloud infrastructure have become critical for healthcare delivery.
-
Integration of AI and Big Data Analytics: Cloud computing enables real-time data analysis for predictive healthcare, patient stratification, and diagnostic support.
-
Shift Toward Hybrid Cloud Models: To balance security and scalability, many institutions are deploying hybrid cloud strategies combining on-premise and public cloud solutions.
-
Increasing Focus on Interoperability: Cloud platforms facilitate seamless data exchange across multiple healthcare entities and EHR systems.
-
Cybersecurity Solutions Integration: With the surge in data breaches, organizations are investing in cloud-based cybersecurity tools to enhance data protection.
-
Regulatory Push for Digital Transformation: Governments globally are pushing cloud adoption through funding and mandates.
-
Rising Investment in Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS): Large health systems are migrating their infrastructure needs to cloud providers to reduce capital expenses.
Report Scope of Healthcare Cloud Computing Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 22.18 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 |
USD 66.12 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 |
CAGR of 12.9% |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered |
Type, Deployment Type, Pricing Model, Service Model, End-use, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Country scope |
U.S.; Canada; Mexico; UK; Germany; France; Italy; Spain; Denmark; Sweden; Norway; Japan; China; India; Australia; South Korea; Thailand; Brazil; Argentina; KSA; UAE; South Africa; Kuwait |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Amazon Web services, Microsoft, Google Inc, athenahealth, CareCloud, Inc., Siemens Healthineers AG, Salesforce, Inc., Oracle (Cerner Corporation), Epic Systems Corporation |
Key Market Driver
Digital Transformation and Data Interoperability Needs
One of the most powerful drivers of the healthcare cloud computing market is the pressing need for digital transformation and enhanced data interoperability. Traditional healthcare infrastructures are often fragmented, leading to information silos that hinder effective patient care. Cloud computing breaks down these barriers by offering centralized data storage, allowing different departments, providers, and even organizations to access and update patient information in real-time.
This capability is vital in today’s value-based care models where coordinated care is essential. For example, a cloud-based EHR system can be accessed simultaneously by a patient’s primary care physician, specialist, and insurance provider, enabling faster and more accurate decision-making. The push for interoperability is further backed by governmental initiatives, such as the 21st Century Cures Act in the United States, which mandates data sharing and access rights for patients.
Key Market Restraint
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
Despite its advantages, cloud computing in healthcare faces significant resistance due to data privacy and security concerns. Healthcare data is highly sensitive, and breaches can have severe consequences for both patients and providers. Regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, and other country-specific laws impose strict requirements on data handling, storage, and transmission.
Cloud environments, particularly public clouds, are often perceived as less secure compared to on-premise solutions. The risk of cyberattacks, ransomware, and unauthorized access looms large. For instance, in June 2023, a major ransomware attack on a European healthcare cloud provider compromised over 1 million patient records. Incidents like these underscore the necessity of robust cybersecurity frameworks and vendor compliance to gain the trust of stakeholders.
Key Market Opportunity
Expansion of AI and ML in Cloud-Enabled Healthcare Platforms
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are creating new growth avenues for healthcare cloud computing. These technologies require large datasets and substantial processing power, both of which are supported by cloud platforms. By hosting AI and ML algorithms in the cloud, healthcare providers can deploy intelligent diagnostic tools, automate routine tasks, and predict patient outcomes with greater accuracy.
One notable example is the use of cloud-based AI tools for radiology. These tools can scan thousands of medical images within minutes and flag abnormalities for radiologist review. In addition, cloud-hosted ML models are being used in genomics and personalized medicine, offering treatment plans tailored to individual patient profiles. The proliferation of these advanced capabilities offers a huge opportunity for cloud service providers and healthcare IT firms to collaborate on innovation.
Healthcare Cloud Computing Market By Type Insights
Clinical Information Systems (CIS), particularly Electronic Medical Records (EMRs), dominate the market by accounting for the largest revenue share. These systems are essential for digitizing patient health records, ensuring real-time access, and improving workflow efficiency. The growing need for integrated healthcare systems and real-time information exchange among caregivers is driving the adoption of cloud-based CIS. EMRs have become a cornerstone of modern healthcare delivery, particularly in large hospitals and integrated delivery networks.
Within CIS, PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication Systems) and telehealth solutions are gaining traction. PACS enables storage and access of imaging data via cloud, enhancing diagnostic efficiency and data sharing among radiologists. Telehealth, accelerated by the pandemic, continues to be adopted by rural and underserved regions where physical access to specialists is limited. Cloud-based telehealth platforms ensure continuity of care, integrate with EMRs, and support chronic disease management remotely.
Nonclinical Information Systems (NCIS) represent the fastest-growing segment in the healthcare cloud computing market. This includes Revenue Cycle Management (RCM), billing, supply chain management, and fraud detection systems. As healthcare institutions face rising costs and reimbursement challenges, optimizing administrative efficiency has become critical. Cloud-hosted NCIS solutions offer real-time analytics, cost transparency, and operational flexibility.
RCM, in particular, helps healthcare providers optimize financial processes from patient registration to final payment. Cloud-based RCM tools are increasingly integrated with clinical platforms, enabling a unified workflow that improves revenue collection and reduces administrative burden. Financial management solutions on the cloud help track expenditure, manage budgets, and generate financial insights without needing massive IT infrastructure investments.
Healthcare Cloud Computing Market By Deployment Insights
Hybrid cloud models dominate the healthcare space due to their ability to offer flexibility while maintaining control over sensitive data. This model allows institutions to store confidential patient information on private servers while utilizing public cloud for less critical applications. It supports disaster recovery, scalability, and compliance with regional regulations.
However, public cloud deployment is growing at the fastest rate. Major cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud have introduced HIPAA-compliant services that ease provider concerns. Public clouds offer cost-effective infrastructure, continuous software updates, and vast storage capabilities. The scalability of public cloud is attracting small- to medium-sized clinics and startups focused on digital health platforms.
Healthcare Cloud Computing Market By Pricing Model Insights
Pay-as-you-go pricing is the dominant model in the healthcare cloud computing market. It allows institutions to pay based on actual usage, making it financially accessible and reducing upfront capital investment. This model supports scalability and aligns costs with demand, particularly beneficial for institutions with fluctuating data loads.
Spot pricing is emerging, especially among tech-savvy startups and telehealth firms that can dynamically adjust workloads. Although it offers cost benefits, it is less predictable and may not be suitable for mission-critical applications in hospitals.
Healthcare Cloud Computing Market By Service Model Insights
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) remains the dominant service model, widely adopted due to its ease of deployment, reduced maintenance requirements, and immediate accessibility. SaaS applications span EMRs, billing systems, patient engagement platforms, and more. Vendors handle software updates and compliance, reducing the IT burden on healthcare organizations.
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) and Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) are growing segments, offering developers the flexibility to build custom healthcare applications and enabling larger organizations to migrate entire infrastructures.
Healthcare Cloud Computing Market By End-use Insights
Healthcare providers, including hospitals, clinics, and diagnostic labs, are the primary end-users of cloud computing solutions. They use cloud platforms for patient care management, imaging, scheduling, and administrative tasks. The shift toward integrated care and digital patient engagement tools continues to drive adoption among providers.
Healthcare payers are increasingly adopting cloud solutions to streamline claims processing, manage fraud detection, and provide real-time member services. Cloud-based data analytics support risk modeling and policy development, improving competitiveness and customer service.
Healthcare Cloud Computing Market By Regional Insights
North America, particularly the United States, dominates the global healthcare cloud computing market. The region benefits from advanced healthcare infrastructure, high healthcare IT spending, a favorable regulatory framework, and the presence of major technology providers such as IBM, Oracle, and Microsoft. Government incentives like the HITECH Act and stringent data protection laws have accelerated the digital transformation of healthcare in this region.
Moreover, collaborations between tech firms and healthcare institutions are common. For instance, Mayo Clinic’s partnership with Google Cloud to create an AI-powered diagnostics platform exemplifies this trend. North America's strong insurance ecosystem and increasing use of telehealth further contribute to its market leadership.
Asia Pacific is experiencing the fastest growth in the healthcare cloud computing market. Countries like China, India, Japan, and South Korea are investing heavily in healthcare IT infrastructure. The region's large population, increasing incidence of chronic diseases, and rapid urbanization are driving demand for scalable and efficient healthcare solutions.
Governments are introducing national e-health initiatives and incentivizing digital health platforms. In India, the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission is promoting cloud-based EHR adoption. Local startups, as well as global players, are launching cloud-based telemedicine and diagnostic platforms targeting underserved regions, fueling exponential growth in this market.
Healthcare Cloud Computing Market Recent Developments
-
January 2025: Microsoft Azure announced a collaboration with Epic Systems to expand its cloud capabilities for EMR systems, enabling greater interoperability and cloud-native features.
-
November 2024: Oracle Health launched a new AI-driven clinical analytics tool hosted on Oracle Cloud, aiming to enhance population health monitoring.
-
September 2024: Amazon Web Services (AWS) introduced a HIPAA-eligible imaging platform, facilitating PACS migration to the cloud with enhanced cybersecurity.
-
June 2024: IBM Watson Health expanded its Genomics Cloud Services in partnership with academic hospitals in Europe, enabling faster genetic sequencing.
Some of the prominent players in the global healthcare cloud computing market include:
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the global healthcare cloud computing market
Type
- Clinical Information Systems
-
- EMR
- PACS, VNA, and Image Sharing Solutions
- PHM
- Telehealth
- LIMS
- PIS
- RIS
- Other CIS
- Nonclinical Information Systems
-
- RCM
- Billing and Accounts Management
- Financial Management
- HIE
- Fraud Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Other NCIS
Deployment
- Private cloud
- Hybrid cloud
- Public cloud
Pricing Model
- Pay-as-you-go
- Spot Pricing
Service Model
- Software-as-a-service
- Infrastructure-as-a-service
- Platform-as-a-service
End-use
- Healthcare Providers
- Healthcare Payers
Regional
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- MEA

