Interactive Whiteboard Market Size and Trends
The interactive whiteboard market size was exhibited at USD 5.15 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 10.52 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 7.4% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
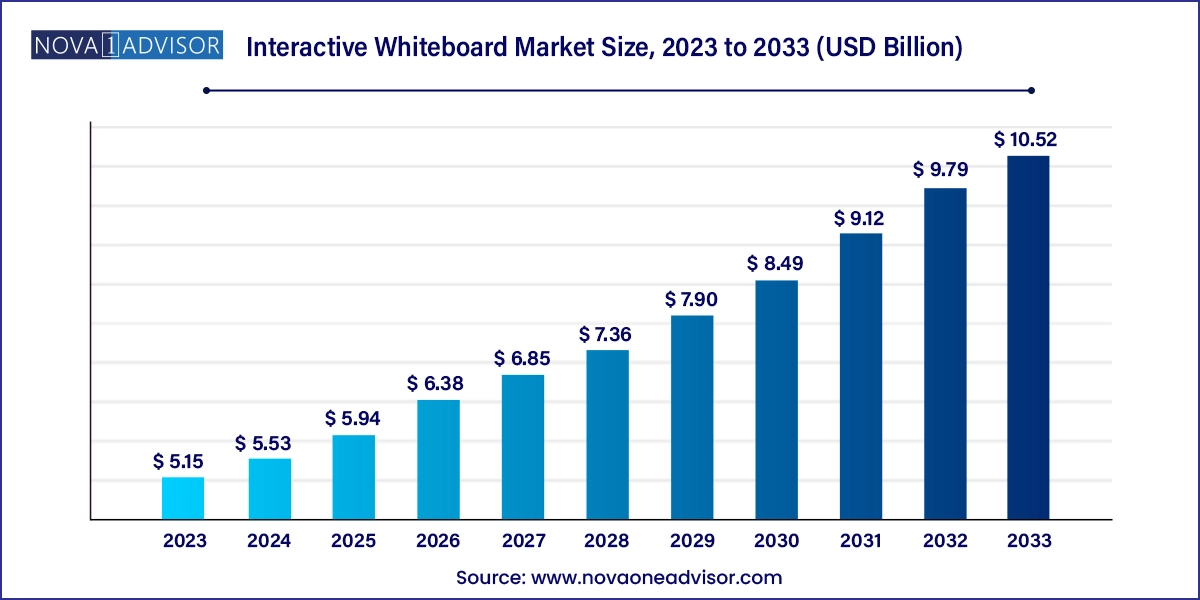
Interactive Whiteboard Market Key Takeaways:
- The resistive membrane segment accounted for the largest revenue share of over 43% in 2023.
- The capacitive segment is anticipated to expand at a CAGR of 9.1% from 2024 to 2033.
- The portable segment accounted for the largest revenue share of over 52% in 2023.
- The fixed segment is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 5.8% from 2024 to 2033.
- The front projection segment accounted for the largest market share of over 62% in 2023.
- The rear projection segment is anticipated to expand at a CAGR of 9.2% from 2024 to 2033.
- The 71-inch to 90-inch segment accounted for a significant revenue share in 2023.
- The greater than 90-inch segment is anticipated to expand significantly from 2024 to 2033.
- The education segment accounted for the largest market share of over 68% in 2023.
- The corporate sector segment is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 7.1% from 2024 to 2033.
- North America interactive whiteboard market held a significant share of over 28% of the interactive whiteboard market in 2023.
Market Overview
The Interactive Whiteboard (IWB) Market has evolved into a dynamic segment of the educational technology and collaborative digital tools ecosystem. Originally seen as a novelty within classrooms, IWBs have now matured into multifunctional platforms that combine display technology with interactive touch and writing inputs, enhancing the user experience across educational, corporate, and commercial settings. These digital whiteboards serve as a bridge between traditional writing boards and advanced visual communication tools, offering multimedia support, cloud integration, and real-time collaboration.
The transition from chalkboards to digital whiteboards aligns with broader global trends in digital transformation. In education, IWBs support hybrid learning models, encourage classroom engagement, and facilitate differentiated instruction. In corporate settings, they function as collaborative hubs for brainstorming, presentations, and remote team meetings. Government organizations, training centers, and public institutions also deploy IWBs to streamline communication and learning processes.
The market's expansion is supported by a combination of growing digital infrastructure, rising investment in EdTech, the emergence of smart offices, and post-pandemic shifts toward hybrid and remote environments. IWBs are now being integrated with AI-based features, gesture recognition, handwriting-to-text conversion, and cloud platforms like Microsoft Teams or Google Workspace—cementing their role as next-generation collaboration tools.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Integration with hybrid learning and conferencing platforms: IWBs are now designed to work seamlessly with remote teaching and meeting platforms like Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and Google Meet.
-
Rise of AI-powered whiteboards: Modern IWBs feature artificial intelligence for smart annotations, predictive suggestions, and real-time content analysis.
-
Cloud connectivity and remote collaboration: Users can access, share, and co-edit whiteboard content from any location, fostering team collaboration and distance education.
-
Growth in touchless interfaces: Post-COVID innovations have accelerated the use of gesture recognition and voice-based controls in IWBs.
-
Shift toward ultra-large displays: Increasing preference for 71-inch to 90-inch and >90-inch displays for better visibility in large classrooms and boardrooms.
-
Pen-enabled precision interfaces: Capacitive and electromagnetic pen technologies are replacing resistive touch for enhanced writing accuracy.
-
Proliferation in developing nations: Governments in Asia and Africa are investing in classroom digitization, including bulk procurement of IWBs.
-
Eco-friendly and paperless classrooms: IWBs support sustainability by reducing dependency on paper-based teaching materials.
Report Scope of Interactive Whiteboard Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 5.53 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 |
USD 10.52 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 |
CAGR of 7.4% |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered |
Technology, Form Factor, Projection Technique, Screen Size, Application, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Country scope |
U.S.; Canada; Mexico; UK; Germany; France; Italy; Spain; China; India; Japan; Australia; South Korea; Indonesia; Brazil; Argentina; UAE; Saudi Arabia; South Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled |
BenQ; Boxlight; Cisco Systems, Inc.; Epson; Google LLC; Hitachi, Ltd.; Microsoft; Newline Interactive; Panasonic Corporation; Promethean Limited; Ricoh; SAMSUNG; Sharp Corporation; SMART Technologies ULC; ViewSonic Corporation |
Key Market Driver: Increasing Adoption in the Education Sector
One of the strongest growth drivers in the interactive whiteboard market is the increasing adoption of IWBs in the education sector, particularly in K–12 and higher education institutions. As digital learning becomes mainstream, schools are investing in smart classroom infrastructure that combines digital content, real-time interaction, and visual aids. IWBs enable dynamic teaching methods by integrating audio, video, simulation, and internet resources directly into lesson plans.
In countries like China, India, the UAE, and Brazil, government-backed education modernization programs have included IWBs in public school deployments. In developed regions such as North America and Europe, private institutions are embedding IWBs into hybrid learning models where in-class and remote students can engage simultaneously. These interactive platforms foster collaborative learning, accommodate various learning styles, and promote student engagement—key priorities for educators navigating post-pandemic academic landscapes.
Key Market Restraint: High Initial Cost and Maintenance
Despite their benefits, the high initial cost and maintenance requirements of IWBs remain a significant restraint for wider adoption, especially in cost-sensitive markets and public sector institutions. Unlike traditional whiteboards, interactive boards require not just hardware but also software licensing, network integration, projector or display units, and sometimes customized furniture setups. Additionally, teacher training and IT support are necessary to ensure smooth operation, adding to the total cost of ownership.
Maintenance challenges such as calibration errors, software updates, and physical wear of touch sensors or pens—can also disrupt usage, particularly in under-resourced schools or small businesses. In regions where digital infrastructure is still developing, power supply, internet connectivity, and technical literacy further hinder IWB integration. While prices are gradually dropping and more vendors offer cost-effective alternatives, affordability continues to be a barrier for mass adoption in certain regions.
Key Opportunity: Expansion into Corporate and Hybrid Work Environments
The emergence of hybrid work models and smart office environments represents a massive opportunity for the interactive whiteboard market. As organizations embrace remote collaboration, IWBs serve as central tools for brainstorming sessions, project tracking, client presentations, and training. Their compatibility with video conferencing tools and screen-sharing platforms allows geographically dispersed teams to work together in real time.
IWBs are also being used in co-working spaces, design studios, healthcare facilities (for diagnostics visualization), and R&D departments. Businesses are increasingly opting for interactive boards that support annotation, touchscreen navigation, and multimedia sharing during meetings. The pandemic-led shift to digital collaboration has cemented the role of IWBs as integral tools for productivity in hybrid office settings. As workspaces evolve to become more flexible, connected, and digital-first, interactive whiteboards are expected to see robust demand in the commercial segment.
Interactive Whiteboard Market By Technology Insights
Infrared technology dominated the technology segment in 2024. Infrared IWBs use a grid of infrared light beams to detect touch points, offering multi-touch capabilities at relatively low costs. These are widely adopted in classrooms due to their large format compatibility, durable design, and lower operational costs. They are also easier to maintain, which appeals to schools in emerging markets. Vendors like Hitachi and Promethean frequently deploy infrared technology in education-focused models.
Capacitive technology is expected to be the fastest-growing. Capacitive IWBs, which work on the principle of detecting electrical signals from touch, offer high precision and support for multiple touch gestures. They deliver a more smartphone-like experience and are popular in high-end corporate settings and advanced classrooms. As prices fall and multi-user collaboration becomes a standard feature, capacitive IWBs are gaining traction in next-generation workspaces.
Fixed IWBs currently lead the form factor segment. These are permanently installed in classrooms, conference rooms, and training centers. Fixed boards offer high durability and seamless integration with wall-mounted displays and projectors. They are common in institutional settings where classrooms or meeting rooms are dedicated and usage is frequent.
Portable IWBs are witnessing faster growth. Designed for mobility and flexibility, portable boards are especially useful for training professionals, freelancers, and educational workshops where infrastructure is limited. Startups and SMBs also favor portable IWBs due to their plug-and-play nature and affordability. As businesses embrace mobile working and dynamic office layouts, portable IWBs are becoming popular for on-demand collaboration.
Interactive Whiteboard Market By Projection Technique Insights
Front projection dominated the market by projection type. In this setup, the projector is placed in front of the whiteboard. This method is widely used in cost-sensitive educational settings due to affordability and compatibility with existing projectors. However, it may cause shadowing when presenters stand in front of the board.
Rear projection is the fastest-growing projection technique. Rear projection eliminates shadowing and glare, providing a clear view for both presenters and audiences. Although more expensive, rear projection setups are preferred in high-end corporate environments and large auditoriums. As demand for seamless presentation experiences grows, rear projection systems are becoming more mainstream.
Interactive Whiteboard Market By Screen Size Insights
The 71–90 inch segment currently dominates the market. This size range strikes a balance between visibility and space efficiency, making it ideal for standard classrooms and mid-sized boardrooms. The screen is large enough to accommodate collaboration among multiple users while maintaining a reasonable cost.
Displays greater than 90 inches are expected to grow the fastest. With the increasing demand for immersive collaboration environments in enterprises and large academic auditoriums, ultra-large displays are in high demand. These setups are favored for group ideation sessions, engineering design reviews, and data visualization use cases.
Interactive Whiteboard Market By Applications Insights
Education remains the dominant application segment. Schools, colleges, and universities account for the largest share of interactive whiteboard adoption. IWBs are used to simplify teaching, integrate digital content, and promote collaborative learning. Government initiatives like India’s ‘Smart Classrooms’, the UK’s ‘EdTech Strategy’, and China's ‘Digital Education Plan’ are driving large-scale deployments.
The corporate sector is projected to be the fastest-growing application. As more companies adopt digital tools for team engagement and remote work, IWBs are being integrated into office ecosystems. Agile work environments, cross-functional brainstorming sessions, and real-time content collaboration are fueling IWB demand in commercial enterprises, especially within IT, finance, and consulting domains.
Interactive Whiteboard Market By Regional Insights
North America remained the largest market for interactive whiteboards in 2024. The United States and Canada lead in terms of education technology spending, digital infrastructure, and corporate digitization. The presence of key players such as SMART Technologies and Google enhances the innovation ecosystem. American classrooms, from elementary schools to universities, have adopted IWBs extensively as part of e-learning initiatives.
Additionally, North American corporations are integrating IWBs with their conference room technologies to accommodate hybrid workforces. Investment in employee training and the shift to virtual engagement across sectors has made IWBs a staple tool in North American organizations. The region’s high internet penetration, strong funding environment, and awareness levels further consolidate its leadership position.
Asia Pacific is projected to grow at the highest CAGR. Countries like China, India, South Korea, and Japan are witnessing massive digital transformation in education. China's government, under its 'Smart Education Plan', is outfitting rural schools with digital teaching tools including IWBs. India’s National Education Policy 2020 includes digital literacy and classroom modernization as key objectives, driving demand for EdTech products.
In addition to education, the booming startup ecosystem, cross-border business growth, and IT outsourcing in Asia have increased demand for collaborative tools like IWBs in corporate settings. Low-cost manufacturing capabilities and the rise of regional players also help in reducing price points, making IWBs more accessible across diverse markets in the region.
Interactive Whiteboard Market Recent Developments
-
BenQ (January 2025): Launched the RE03 Series interactive flat panels with integrated air quality sensors and AI-powered whiteboard tools aimed at smart classrooms.
-
SMART Technologies (February 2025): Announced a partnership with Google Workspace to integrate real-time cloud-based collaboration features into their IWB software ecosystem.
-
Samsung (December 2024): Expanded its Flip series with new models supporting UHD resolution, enhanced pen precision, and compatibility with Microsoft Teams.
-
Promethean (March 2025): Rolled out the ActivPanel 9 with built-in casting, biometric login, and app-based teaching tools tailored for hybrid classrooms.
-
LG Electronics (April 2024): Introduced an 86-inch IWB targeting corporate collaboration spaces, featuring 40-point touch, 4K resolution, and USB-C connectivity.
Some of the prominent players in the interactive whiteboard market include:
- BenQ
- Boxlight
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- Epson
- Google LLC
- Hitachi, Ltd.
- Microsoft
- Newline Interactive
- Panasonic Corporation
- Promethean Limited
- Ricoh
- SAMSUNG
- Sharp Corporation
- SMART Technologies ULC
- ViewSonic Corporation
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the interactive whiteboard market
Technology
- Infrared
- Resistive touch
- Electromagnetic pen
- Capacitive
- Others
Form Factor
Projection Technique
- Front Projection
- Rear Projection
Projection Technique
- Less than 50 Inch
- 50 Inch to 70 Inch
- 71 Inch to 90 Inch
- Greater than 90 Inch
Application
- Education Sector
- Corporate Sector
- Commercial Sector
- Others
Regional
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa

