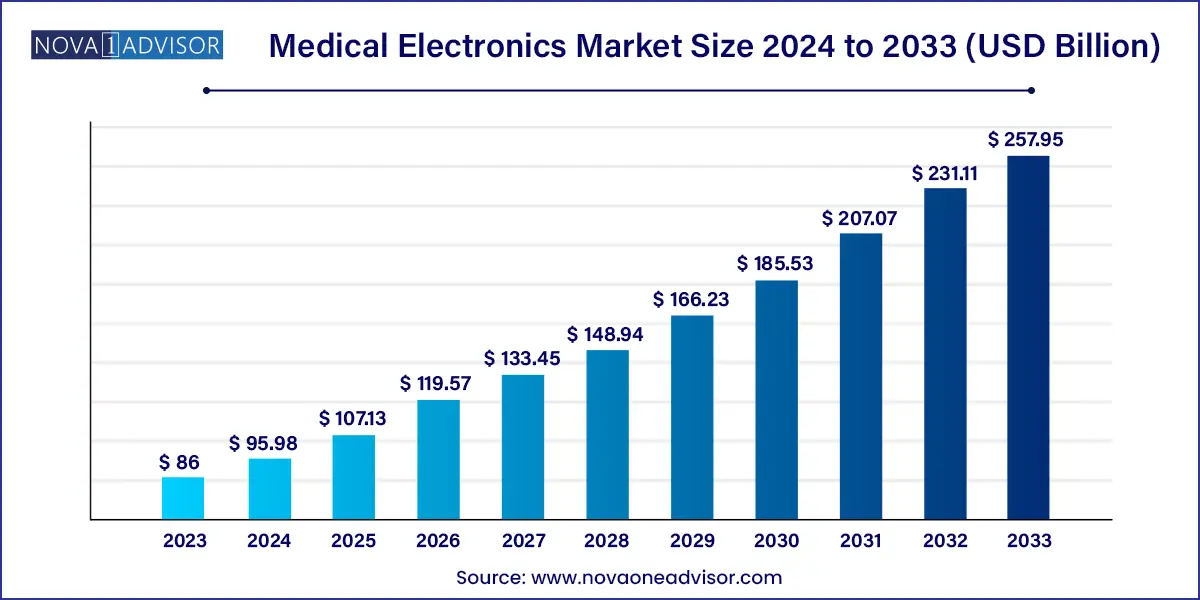
The global medical electronics market size was exhibited at USD 86.00 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 257.95 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 11.61% during the forecast period of 2024 to 2033.
Key Takeaways:
- North America led the global market with the highest market share of 45% in 2022.
- Asia-Pacific is predicted to expand at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period.
- By Product, the therapeutics segment has held the largest market share in 2022.
- By Product, the diagnostics segment is anticipated to grow at a remarkable CAGR during the projected period.
- By Application, the hospitals segment had the biggest market share of 48% in 2022.
- By Application, the homecare segment is estimated to expand at the fastest CAGR over the projected period.
Medical Electronics Market: Overview
The medical electronics market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by advancements in technology, increasing demand for minimally invasive procedures, and rising healthcare expenditures worldwide. Medical electronics encompass a wide range of devices and equipment used in healthcare settings, including diagnostic imaging systems, patient monitoring devices, therapeutic equipment, and wearable medical devices.
Growth Factors
The global medical electronics market is primarily driven by the rising prevalence of various chronic diseases and growing geriatric population across the globe. The chronic diseases such as diabetes, cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and COPD are the major factors responsible for the increasing adoption of the medical electronics. According to the United Nations, the global geriatric population was estimated at around 382 million (aged 60 years and above) in 2017 and this number is projected to reach at 2.1 billion by 2050. The geriatric people are more prone to the various chronic diseases and hence boosts the demand for various diagnostics and therapeutics medical electronic devices such as CT scanner, ultrasound, patient monitoring systems, medical implantable devices, pacemakers, and respiratory care devices. Furthermore, the rising number of ICU admissions is fueling the growth of the global medical electronics market. According to the Society of Critical Care Medicine, almost 40 to 50% of the ICU admissions require ventilators, which fosters the growth of the medical electronics. The availability of wider range of diagnostic and therapeutic devices coupled with the rising government and corporate investments to equip the hospitals with digital and electronic equipment across the globe, is a significant growth driver of the market.
The surging uses of the diagnostic devices such as ultrasound equipment, CT scanners, and X-Rays in the diagnosis of various diseases and bones related issues has significantly driven the market growth in the past. Moreover, the rising investments in the research has led to the integration of the latest technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) with the various medical electronics. The technological advancements helps the healthcare units to offer enhanced patient care services and increases the patients conveniences and results in improved customer experiences in any healthcare setting. The rising demand for the early detection and treatment of the disease among the population and rising popularity of the minimal-invasive surgeries is propelling the demand for the various medical electronics across the globe that fosters the growth of the medical electronics market.
Medical Electronics Market Report Scope
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 86.0 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 |
USD 257.95 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 |
CAGR of 11.61% |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered |
Product, Application, Geography |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Central and South America; the Middle East and Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Siemens AG, ON Semiconductor Corporation, GE Healthcare, Freescale Semiconductor Inc., Texas Instruments Incorporated, STMicroelectronics N.V., Philips Healthcare Pvt. Ltd., Tekscan, Inc., NXP Semiconductors N.V.. |
Medical Electronics Market Dynamics
In the medical electronics market, two primary dynamics play significant roles in shaping its trajectory. Firstly, technological advancements drive market growth by continuously enhancing the capabilities and efficiency of medical devices. Innovations such as miniaturization, wireless connectivity, and integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms have revolutionized medical electronics, enabling more accurate diagnoses, minimally invasive procedures, and personalized treatment options. These advancements not only improve patient outcomes but also streamline healthcare processes, reducing costs and increasing accessibility to quality care.
Secondly, the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases and the aging population worldwide contribute to the growing demand for medical electronics. Chronic conditions such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and respiratory disorders require continuous monitoring and management, driving the adoption of patient monitoring devices, wearable medical devices, and therapeutic equipment. Additionally, the rise of remote patient monitoring and telemedicine solutions further boosts the demand for medical electronics, enabling healthcare providers to monitor patients' health remotely, facilitate timely interventions, and improve overall patient care.
Medical Electronics Market Restraint
In the medical electronics market, two prominent restraints hinder its growth trajectory. Firstly, stringent regulatory requirements and lengthy approval processes pose significant challenges for manufacturers seeking to introduce new medical devices and technologies. Compliance with regulations such as FDA approvals in the United States and CE markings in Europe requires extensive testing, documentation, and validation, resulting in prolonged time-to-market and increased development costs. This regulatory burden can deter innovation and limit market entry, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) with limited resources and expertise.
Secondly, the high cost of medical electronics devices presents a barrier to adoption, particularly in developing regions with limited healthcare budgets and infrastructure. Advanced medical devices such as diagnostic imaging systems, patient monitoring devices, and therapeutic equipment often come with substantial price tags, making them inaccessible to healthcare facilities with constrained resources. Additionally, the ongoing maintenance, training, and infrastructure requirements further contribute to the total cost of ownership, posing financial challenges for healthcare providers.
Medical Electronics Market Opportunity
Within the medical electronics market, two significant opportunities emerge. Firstly, the increasing adoption of telemedicine and remote patient monitoring presents a compelling growth opportunity. Technological advancements in medical electronics, such as wearable devices, mobile health apps, and remote monitoring systems, enable healthcare providers to deliver care beyond traditional clinical settings. This trend is particularly relevant in rural and underserved areas, where access to healthcare services is limited. By leveraging telemedicine and remote monitoring solutions, healthcare providers can improve patient access to care, enhance care coordination, and reduce healthcare disparities, thereby driving market expansion.
Secondly, the rising demand for personalized healthcare solutions offers a lucrative opportunity for innovation in the medical electronics market. Advances in genomics, digital health technologies, and data analytics enable the development of personalized diagnostics, treatment plans, and interventions tailored to individual patient needs. Medical electronics devices that incorporate AI algorithms and predictive analytics can analyze vast amounts of patient data to identify trends, predict disease progression, and optimize treatment outcomes.
Medical Electronics Market Challenges
In the medical electronics market, two primary challenges present significant hurdles. Firstly, interoperability issues among different medical devices and systems hinder seamless data exchange and integration within healthcare ecosystems. The lack of standardized communication protocols and data formats often results in data silos, making it difficult for healthcare providers to access comprehensive patient information and make informed clinical decisions. Additionally, interoperability challenges can lead to inefficiencies in care coordination, fragmented workflows, and increased risk of errors.
Secondly, cybersecurity threats pose a growing concern for medical electronics devices and healthcare systems. The increasing connectivity of medical devices to networks and the internet exposes them to potential cybersecurity vulnerabilities, including malware, ransomware, and data breaches. A cybersecurity breach in medical electronics devices can compromise patient safety, expose sensitive healthcare data, and disrupt healthcare operations. Moreover, the complex and interconnected nature of healthcare networks makes them attractive targets for cyberattacks. Mitigating cybersecurity risks requires implementing robust security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and regular security audits, to safeguard medical electronics devices and healthcare systems against potential threats.
Segments Insights:
Product Insights
The diagnostics segment dominated the medical electronics market, owing to its critical role in early disease detection, condition monitoring, and clinical decision-making. Devices such as MRI scanners, CT/PET systems, ultrasound machines, X-ray equipment, and patient monitoring systems are central to both inpatient and outpatient care. Hospitals and diagnostic centers worldwide rely on these devices to diagnose a wide range of diseases—from cardiovascular and neurological conditions to musculoskeletal and oncological disorders.
For example, MRI scanners offer non-invasive, high-resolution visualization of soft tissues, proving vital in neuroimaging, musculoskeletal diagnostics, and tumor detection. CT scanners, meanwhile, are instrumental in emergency settings, trauma analysis, and pre-operative planning. Patient monitoring systems—ranging from basic vitals tracking to advanced ICU-level monitoring—ensure real-time insights during surgery and recovery.
On the other hand, therapeutics is the fastest-growing product segment. Technological advancements in implantable medical devices, such as pacemakers and neurostimulators, along with rising adoption of surgical robots, are key contributors. For instance, respiratory care devices like non-invasive ventilators saw exponential demand during the pandemic and continue to serve chronic respiratory patients at home. Furthermore, robotic surgery is gaining traction across disciplines—urology, gynecology, cardiothoracic, and orthopedics—for its precision, reduced trauma, and faster recovery. The integration of imaging with real-time robotic assistance is pushing therapeutic medical electronics into a new frontier of personalized, minimally invasive care.
Application Insights
Hospitals dominated the application segment due to their comprehensive infrastructure, skilled personnel, and capacity to house a wide array of high-end diagnostic and therapeutic electronics. From imaging diagnostics to robotic surgeries and critical care monitoring, hospitals are the primary consumers of both high-value capital equipment and consumables. Multi-specialty hospitals routinely use devices like MRI scanners, CT scanners, surgical robots, patient monitors, and implantable electronics as part of routine care.
Moreover, hospitals serve as hubs for emergency response, chronic disease management, and surgical intervention, where real-time data and precision tools are vital. With rising patient footfall, especially in tertiary care centers, hospitals invest in integrated electronics that support electronic health records (EHRs), predictive diagnostics, and automated reporting—streamlining operations and outcomes.
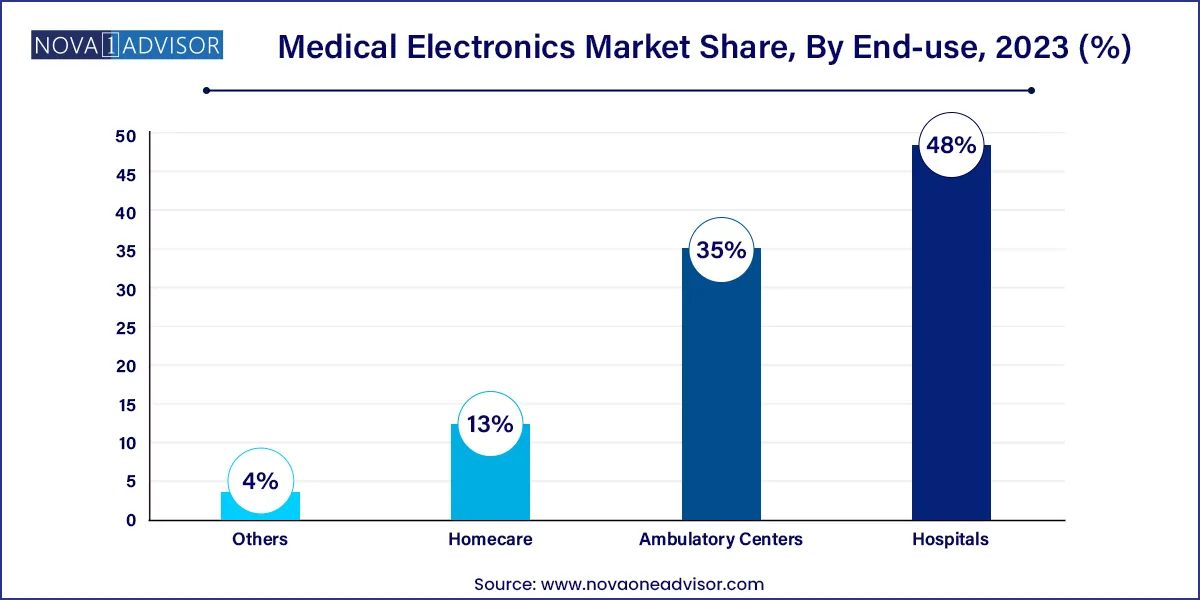
Meanwhile, homecare is the fastest-growing application segment, fueled by the dual forces of technology miniaturization and rising demand for personalized care. Patients with chronic conditions like COPD, diabetes, or heart failure benefit from portable and wearable devices that allow real-time health tracking and medication compliance. Devices such as portable ECGs, respiratory monitors, and insulin pumps now come with smartphone connectivity, cloud access, and physician alerts. Aging populations, particularly in countries like Japan, Germany, and the U.S., are accelerating this trend as elderly patients prefer aging-in-place supported by smart medical electronics.
Regional Analysis
North America led the global medical electronics market, driven by advanced healthcare infrastructure, high healthcare expenditure, and a strong presence of technology giants and medical device manufacturers. The United States, in particular, has consistently invested in state-of-the-art hospital systems, digital health integration, and AI-based diagnostic tools. Leading firms like GE Healthcare, Medtronic, and Boston Scientific are headquartered here and benefit from a highly structured regulatory and reimbursement environment.
Additionally, North America’s strong research institutions and frequent adoption of cutting-edge healthcare technologies enable early and widespread deployment of devices like robotic surgery systems, implantable cardiac devices, and cloud-connected patient monitors. The rapid growth of ambulatory surgical centers (ASCs), homecare programs, and telemedicine platforms further reinforces the region’s dominance in medical electronics.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing market, fueled by a combination of economic growth, urbanization, rising healthcare awareness, and government investment in digital health infrastructure. China and India, with their vast populations and burgeoning middle class, are aggressively expanding access to modern healthcare—creating unprecedented demand for diagnostic imaging systems, portable devices, and smart wearables.
Japan and South Korea, on the other hand, are home to cutting-edge innovation in medical robotics, imaging technology, and electronics manufacturing. Government-led programs promoting healthcare digitalization and local production of medical devices are helping bridge the urban-rural care gap. For example, India’s “Digital Health Mission” and China’s health tech expansion policies are creating favorable regulatory conditions for domestic and international players.
The region also benefits from cost-effective labor, encouraging global manufacturers to set up production and R&D facilities locally, further driving down device costs and increasing adoption.
Some of the prominent players in the Medical electronics market include:
- Renesas Electronics Corporation
- Siemens AG
- ON Semiconductor Corporation
- GE Healthcare
- Freescale Semiconductor Inc.
- Texas Instruments Incorporated
- STMicroelectronics N.V.
- Philips Healthcare Pvt. Ltd.
- Tekscan, Inc.
- NXP Semiconductors N.V.
Recent Developments
-
April 2025 – Medtronic plc launched its new Micra AV2 pacemaker, a next-generation leadless cardiac device with extended battery life and Bluetooth-based monitoring.
-
February 2025 – GE HealthCare unveiled its AI-enhanced MRI scanner “SIGNA Horizon” with adaptive imaging for faster neurological and musculoskeletal diagnostics.
-
December 2024 – Siemens Healthineers introduced a compact, mobile CT scanner tailored for intensive care units and emergency departments.
-
October 2024 – Philips Healthcare announced a strategic collaboration with Amazon Web Services (AWS) to integrate its patient monitoring systems with cloud-based AI analytics.
-
August 2024 – Intuitive Surgical received CE Mark for its latest Da Vinci SP robotic system for transoral and urologic surgeries, expanding its footprint in European and Asian hospitals.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the global medical electronics market.
By Product
-
- Implantable Medical Devices
- Surgical Robots
- Pacemakers
- Neuro stimulation Devices
- Respiratory Care Devices
-
- CT/PET Devices
- Patient Monitoring Devices
- Ultrasound Devices
- X-Ray Devices
- MRI Scanners
- CT Scanners
- Others
By Application
- Hospitals
- Ambulatory Centers
- Homecare
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)


