The global neuromodulation devices market size was exhibited at USD 3.21 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 8.40 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 10.1% during the forecast period of 2024 to 2033.
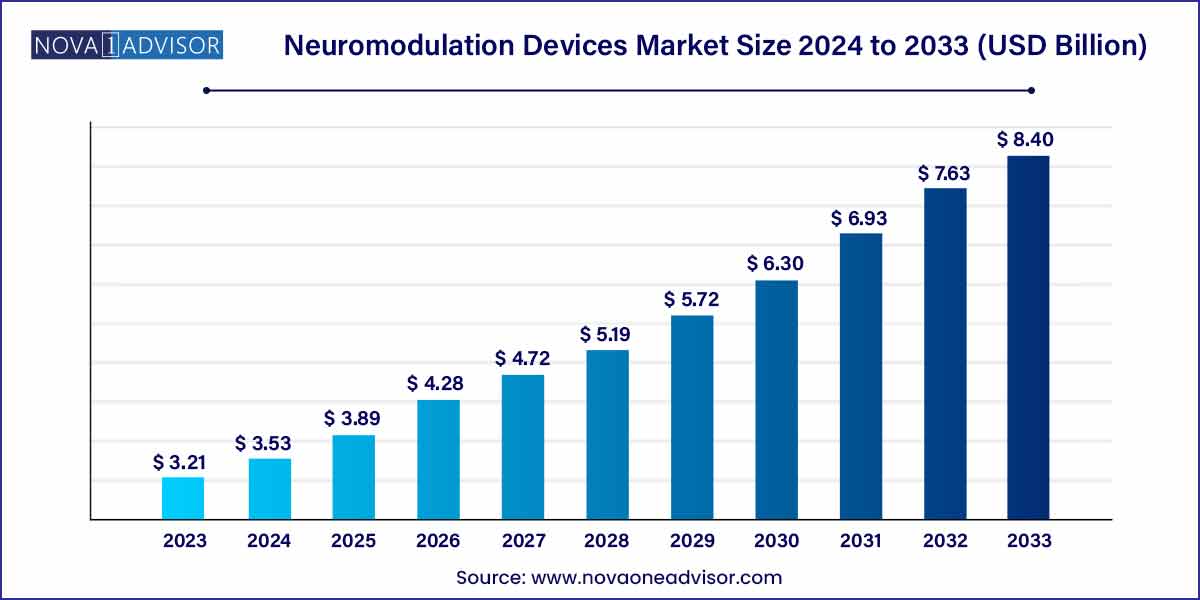
Key Takeaways:
- North America held the largest revenue share of over 46.0% in 2023.
- The spinal cord stimulators segment dominated the market with a revenue share of over 40.0% in 2023.
- In 2023, internal neuromodulation technology dominated the market with a revenue share of over 55.0%.
- Parkinson’s disease dominated the market with a revenue share of over 25.0% in 2023.
- In 2023, the metallic biomaterials segment dominated the market with a revenue share of over 45.0%.
- The hospitals and ASCs segment held the largest revenue share of above 51.0% in 2023.
Neuromodulation Devices Market: Overview
The neuromodulation devices market is witnessing rapid growth and innovation, driven by advancements in medical technology, increasing prevalence of neurological disorders, and expanding applications across various medical specialties. This overview aims to provide insights into the key dynamics, trends, and factors shaping the neuromodulation devices market landscape.
Neuromodulation Devices Market Growth
The growth of the neuromodulation devices market is propelled by several key factors. Firstly, the increasing prevalence of neurological disorders, such as chronic pain, movement disorders, epilepsy, and psychiatric conditions, is driving demand for neuromodulation therapies as alternative or adjunctive treatment options. Additionally, advancements in neuromodulation technologies, including improved electrode designs, programming algorithms, and wireless connectivity, are enhancing the efficacy, safety, and usability of neuromodulation devices, expanding their adoption across a broader patient population. Furthermore, rising investment in research and development, coupled with favorable reimbursement policies and regulatory approvals, are further stimulating market growth and innovation in the field of neuromodulation. These growth factors collectively contribute to the expansion of the neuromodulation devices market, providing patients with more effective and personalized treatment options for neurological and psychiatric conditions.
Neuromodulation Devices Market Report Scope
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 3.21 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 |
USD 8.40 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 |
CAGR of 10.1% |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered |
Product Type, Technology, Application, Biomaterial, End-use, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Central and South America; the Middle East and Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Boston Scientific Corporation; Abbott; NEVRO CORP.; Neuronetics; Medtronic. |
Neuromodulation Devices Market Dynamics
- Technological Advancements and Innovation:
A key dynamic shaping the neuromodulation devices market is the continuous advancement of technology and innovation in neuromodulation therapies. Manufacturers are constantly developing new and improved neuromodulation devices with enhanced features, such as advanced electrode designs, customizable programming options, and wireless connectivity. These technological advancements allow for more precise targeting of neural pathways, improved therapy delivery, and enhanced patient comfort and convenience. Moreover, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms into neuromodulation devices holds promise for optimizing treatment outcomes, predicting patient responses, and personalizing therapy settings based on individual patient characteristics.
- Regulatory Landscape and Reimbursement Policies:
Another significant dynamic influencing the neuromodulation devices market is the regulatory landscape and reimbursement policies governing the approval, marketing, and reimbursement of neuromodulation therapies. Regulatory bodies worldwide impose stringent requirements for the safety, efficacy, and quality of neuromodulation devices, necessitating rigorous clinical testing and documentation to obtain regulatory approvals. Moreover, navigating the complex regulatory pathways across different regions and jurisdictions poses challenges for manufacturers seeking to commercialize neuromodulation devices globally. Additionally, reimbursement policies play a crucial role in determining the accessibility and affordability of neuromodulation therapies for patients and healthcare providers.
Neuromodulation Devices Market Restraint
- High Cost of Neuromodulation Therapies:
One notable restraint in the neuromodulation devices market is the high cost associated with neuromodulation therapies. Neuromodulation devices, such as spinal cord stimulators (SCS), deep brain stimulators (DBS), and transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) devices, often involve significant upfront expenses for device implantation, programming, and follow-up care. Additionally, the ongoing maintenance and replacement costs of neuromodulation devices contribute to the overall financial burden for patients and healthcare providers. The high cost of neuromodulation therapies may pose affordability challenges for patients, particularly those without adequate insurance coverage or financial resources. Moreover, reimbursement rates and coverage policies for neuromodulation procedures vary across different payers and healthcare systems, further impacting patient access and affordability of these therapies.
- Limited Efficacy and Clinical Evidence:
Another significant restraint in the neuromodulation devices market is the limited efficacy and clinical evidence supporting the use of certain neuromodulation therapies for specific indications. While neuromodulation devices have demonstrated efficacy in managing certain neurological and psychiatric conditions, such as chronic pain, movement disorders, and depression, the clinical evidence supporting their use may vary depending on the indication and patient population. Additionally, response rates to neuromodulation therapies can vary among individuals, leading to uncertainty regarding treatment outcomes and long-term efficacy. Furthermore, the lack of standardized protocols and guidelines for patient selection, treatment optimization, and follow-up care may contribute to variability in treatment outcomes and suboptimal patient responses.
Neuromodulation Devices Market Opportunity
- Expansion of Indications and Therapeutic Applications:
One prominent opportunity within the neuromodulation devices market lies in the expansion of indications and therapeutic applications for neuromodulation therapies. While neuromodulation devices have traditionally been used to treat conditions such as chronic pain, movement disorders, and psychiatric disorders, there is growing interest in exploring their potential for addressing a broader range of neurological and neuropsychiatric conditions. Emerging areas of therapeutic interest include epilepsy, Alzheimer's disease, traumatic brain injury, addiction, and neurodevelopmental disorders. Moreover, advancements in neuromodulation technologies, such as closed-loop systems, adaptive stimulation algorithms, and targeted neural modulation techniques, offer new possibilities for precision medicine approaches and personalized treatment strategies.
- Technological Innovation and Product Development:
Another significant opportunity within the neuromodulation devices market is technological innovation and product development. Rapid advancements in neuromodulation technologies, including electrode designs, stimulation parameters, and device miniaturization, are driving innovation and enhancing the capabilities of neuromodulation devices. Moreover, the integration of advanced features such as wireless connectivity, remote monitoring, and artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms enables more personalized and adaptive neuromodulation therapies tailored to individual patient needs. Additionally, the development of non-invasive neuromodulation techniques, such as transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), offers new opportunities for expanding the reach and accessibility of neuromodulation therapies beyond traditional implantable devices.
Neuromodulation Devices Market Challenges
- Limited Understanding of Mechanisms of Action:
One notable challenge in the neuromodulation devices market is the limited understanding of the mechanisms of action underlying neuromodulation therapies. While neuromodulation devices have demonstrated efficacy in managing certain neurological and psychiatric conditions, the precise mechanisms by which they exert their therapeutic effects are not fully elucidated. This lack of mechanistic understanding hinders the optimization of treatment protocols, patient selection criteria, and stimulation parameters, leading to variability in treatment outcomes and suboptimal patient responses. Additionally, the heterogeneity of patient populations and the complexity of neurological disorders further complicate efforts to identify predictive biomarkers or therapeutic targets for neuromodulation therapies.
- Regulatory and Reimbursement Challenges:
Another significant challenge facing the neuromodulation devices market is navigating regulatory and reimbursement hurdles. Regulatory approval processes for neuromodulation devices vary across different regions and jurisdictions, necessitating comprehensive preclinical and clinical data to demonstrate safety, efficacy, and quality. Moreover, the regulatory landscape is constantly evolving, with changing requirements and standards adding complexity and uncertainty to the approval process. Additionally, reimbursement policies and coverage decisions for neuromodulation therapies vary among payers and healthcare systems, impacting patient access and affordability. Variability in reimbursement rates and coverage criteria may limit market adoption and hinder investment in research and development of innovative neuromodulation technologies.
Segments Insights:
Product Type Insights
Spinal cord stimulators (SCS) dominated the product segment in 2024. These devices are extensively used to treat chronic back and leg pain, particularly in patients who have not responded to surgery or pharmacotherapy. The popularity of SCS stems from its efficacy in reducing pain scores and enhancing mobility with relatively low complication rates. As chronic pain becomes a major public health concern, especially in aging populations, SCS devices remain a mainstay in pain management. Leading companies have also developed advanced models with rechargeable batteries and wireless control, improving both convenience and patient compliance.
Transcranial magnetic stimulators (TMS) are the fastest-growing product type. Their non-invasive nature, outpatient applicability, and growing role in psychiatric care have propelled demand. TMS is increasingly being used in mental health clinics and neurology centers to treat depression, anxiety, and even smoking addiction. Emerging portable and home-use models are also under development, which could democratize access to neuromodulation therapies beyond hospital settings. As mental health awareness rises, TMS is poised to experience a surge in clinical application.
Technology Insights
Internal neuromodulation devices held the largest share in 2024. These include implantable devices such as SCS, DBS, and VNS that provide continuous and programmable stimulation. They are typically used for long-term management of chronic or refractory conditions. Although they require surgical implantation, their precision, durability, and controlled delivery make them preferred for complex indications like Parkinson’s disease or epilepsy. Their dominance is reinforced by robust clinical evidence and long-standing adoption by specialists.
External neuromodulation devices are witnessing the fastest growth. External or non-invasive systems, such as TMS and transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulators, are gaining popularity due to their ease of use and lower procedural risk. These devices are widely used in psychiatric clinics, rehabilitation centers, and increasingly in home settings. Technological advancements have enabled portable models and cloud-based data monitoring, which appeal to younger, tech-savvy patients and enhance adherence. As the stigma around mental health treatment declines, external neuromodulation is expected to gain mainstream attention.
Application Insights
Chronic pain was the largest application area in 2024. Pain remains a global epidemic with limited effective treatments that avoid dependency and long-term side effects. Neuromodulation offers a valuable alternative by modulating pain signals in the nervous system. SCS devices are widely used for lower back pain, post-surgical neuropathic pain, and complex regional pain syndrome. Pain management specialists, neurosurgeons, and anesthesiologists continue to incorporate neuromodulation into multimodal treatment plans.
Depression is the fastest-growing application. Mental health disorders, especially treatment-resistant depression, are driving rapid adoption of TMS and VNS devices. Studies have shown that neuromodulation can provide rapid symptom relief with fewer side effects than pharmacologic therapies. With increasing global attention to mental wellness and improved reimbursement for psychiatric interventions, the depression segment is poised for dramatic growth in both clinical and outpatient settings.
Biomaterial Insights
Polymeric biomaterials held the largest share of the market. Polymers like polyurethane and silicone are commonly used in neuromodulation devices for their flexibility, durability, and biocompatibility. They are essential in creating electrode leads and casings that minimize tissue irritation. Polymeric coatings also reduce the risk of infection and improve device longevity, which is particularly important in implantable systems.
Ceramic biomaterials are growing rapidly. These materials offer superior biocompatibility and electrical insulation, making them ideal for high-precision applications in neurostimulators and TMS coils. Ceramics are also being explored for encapsulation in next-gen implants where signal fidelity is crucial. Their corrosion resistance and strength at small dimensions make them suitable for long-term implantation, especially in brain and spinal cord interfaces.
End-use Insights
Hospitals and ambulatory surgery centers (ASCs) dominated the end-use market. These facilities perform the majority of neuromodulation device implantations, particularly for DBS and SCS. With dedicated neurological and pain management departments, hospitals ensure high patient volumes and complex case handling. ASCs are increasingly performing outpatient stimulator placements due to reduced costs and improved recovery times.
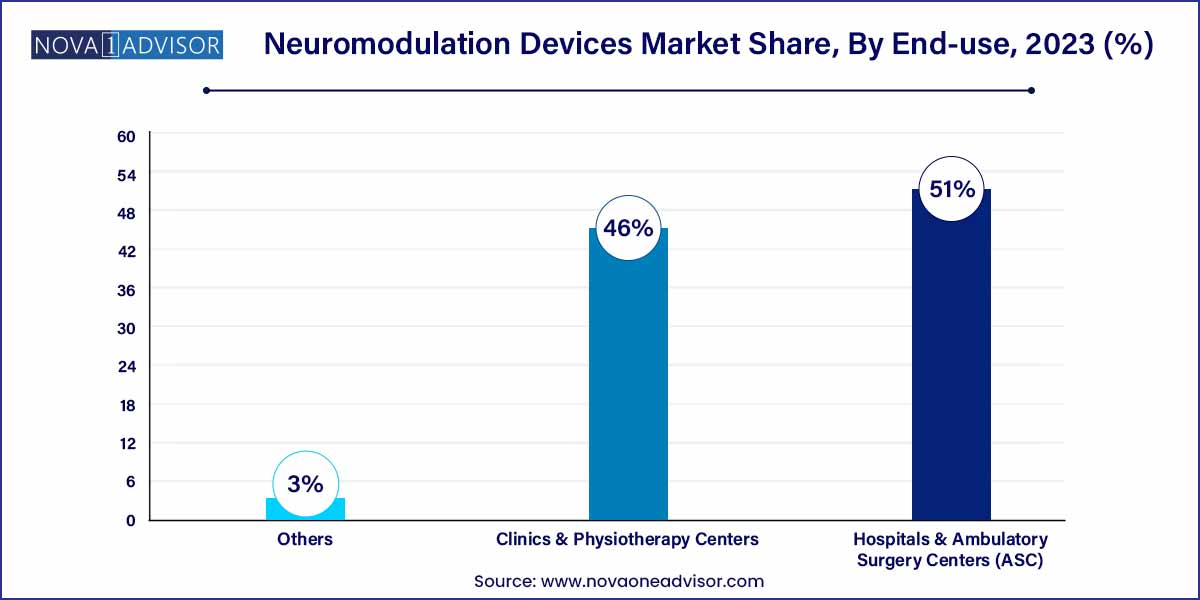
Clinics and physiotherapy centers are the fastest-growing end-use environments. TMS and non-invasive VNS devices are being deployed in standalone mental health clinics and physiotherapy centers that focus on stroke recovery, movement disorders, and pain rehabilitation. Their flexibility, low setup cost, and increasing demand from both insured and self-pay patients make them an attractive growth area for device manufacturers.
Regional Insights
North America maintained its lead in the global neuromodulation market in 2024. The region benefits from advanced healthcare infrastructure, high disease awareness, and favorable reimbursement policies for neuromodulation therapies. The U.S. alone accounts for a significant share of global implantable neurostimulator sales, particularly for SCS and DBS applications. Leading manufacturers such as Medtronic, Boston Scientific, and Nevro are headquartered in the region and have well-established clinical networks.
The rapid integration of mental health care and neurological care into mainstream treatment plans also supports TMS growth. North America’s innovation-driven regulatory system, including the FDA’s Breakthrough Device designation, further accelerates the development and approval of next-generation neuromodulation solutions.
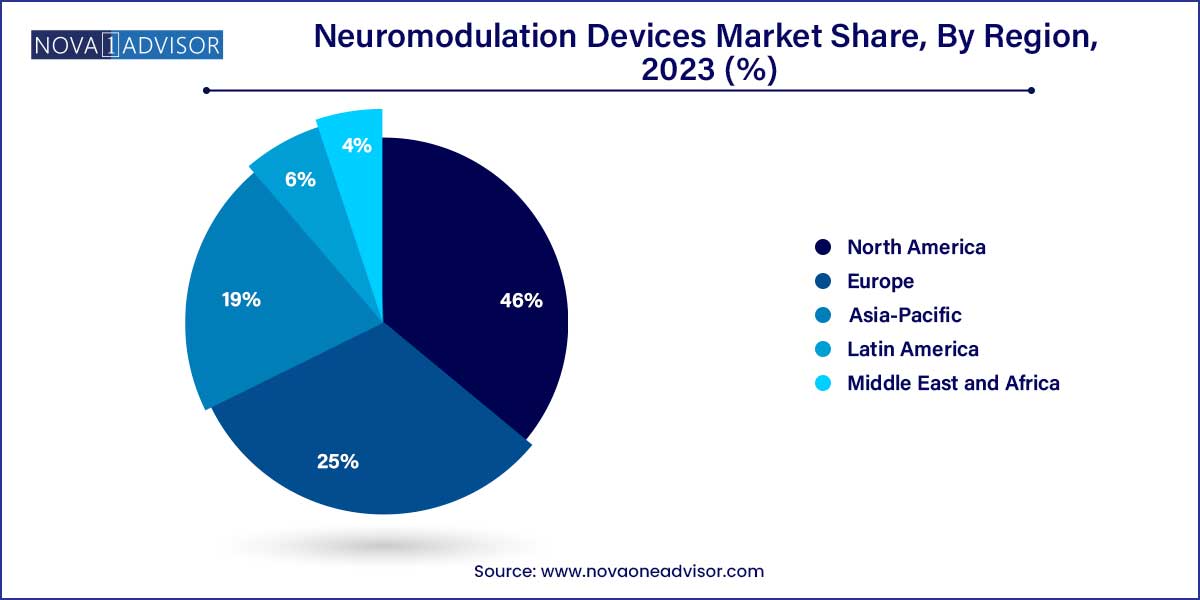
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, driven by rising healthcare expenditure, growing elderly populations, and increased awareness of neurological health. Countries like China, Japan, South Korea, and India are expanding their neurology departments and investing in neuro-rehabilitation centers. Japan, with its aging population, leads in adopting neuromodulation for Parkinson’s and stroke-related therapies.
Emerging economies in Southeast Asia are also beginning to incorporate non-invasive neuromodulation into their mental health and chronic pain management protocols. Medical tourism, favorable regulatory environments, and expanding private healthcare providers make Asia-Pacific a hotbed for future growth and innovation in this field.
Some of the prominent players in the neuromodulation devices market include:
- Boston Scientific Corporation
- Abbott
- NEVRO CORP.
- Neuronetics
- Medtronic
Recent Developments
-
Medtronic (February 2025): Received CE Mark for its Percept™ PC with BrainSense™ technology—a deep brain stimulation system that monitors brain activity to personalize treatment in Parkinson’s patients.
-
Boston Scientific (January 2025): Announced expansion of its WaveWriter Alpha™ SCS platform to Europe, offering enhanced patient control via Bluetooth-enabled remote systems.
-
Neuronetics (December 2024): Launched NeuroStar Advanced Therapy system in Japan following regulatory approval for major depressive disorder (MDD).
-
LivaNova (March 2025): Completed a successful trial for its VNS Therapy System in patients with treatment-resistant epilepsy in the U.S., paving the way for FDA approval expansion.
-
electroCore (April 2024): Announced a collaboration with the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs to deploy its gammaCore Sapphire™ non-invasive vagus nerve stimulator for PTSD and headache treatment.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2023 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the global neuromodulation devices market.
Product Type
- Spinal Cord Stimulators
- Deep Brain Stimulators
- Sacral Nerve Stimulators
- Vagus Nerve Stimulators
- Transcranial Magnetic Stimulators
- Others
Technology
Internal
External
Application
- Parkinson’s Disease
- Chronic Pain
- Migraine
- Epilepsy
- Tremor
- Depression
- Urinary & Faecal Incontinence
- Others
Biomaterial
- Polymeric Biomaterial
- Metallic Biomaterial
- Ceramic Biomaterial
End-use
- Hospitals & Ambulatory Surgery Centers (ASC)
- Clinics & Physiotherapy Centers
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)



