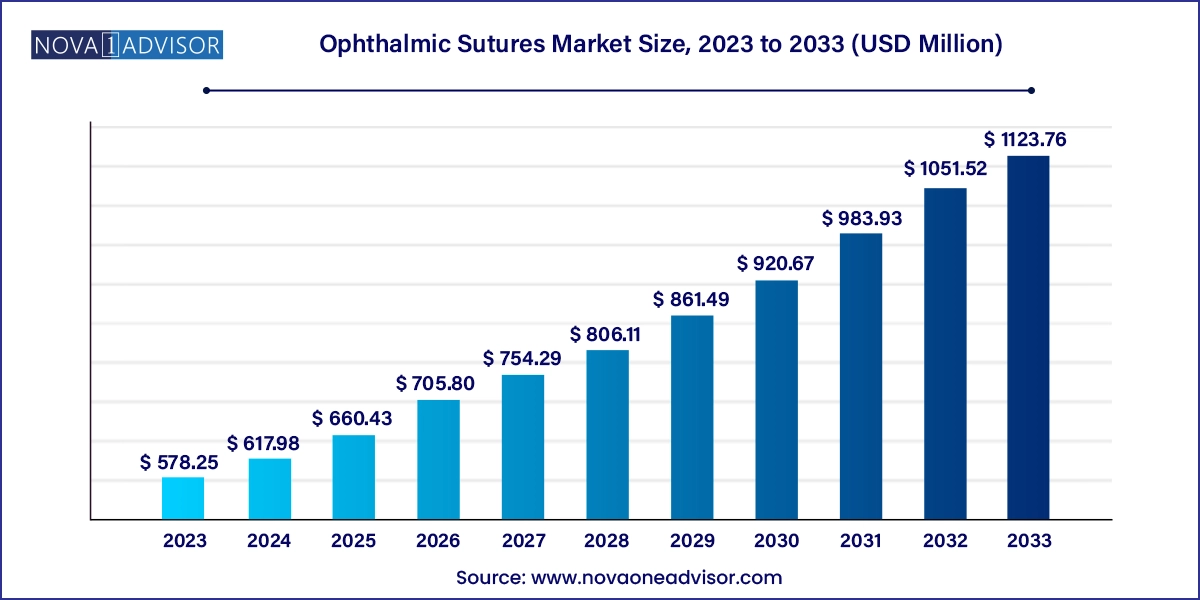
The ophthalmic sutures market size was exhibited at USD 578.25 million in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 1123.76 million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 6.87% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
The ophthalmic sutures market plays a vital role in ophthalmic surgery by providing critical closure solutions that aid in healing, maintain tissue integrity, and minimize postoperative complications. Sutures are used in various eye surgeries including corneal transplantation, cataract removal, oculoplastic procedures, vitrectomy, and iridectomy, among others. These finely engineered sutures are specifically designed for delicate eye tissue, ensuring precise handling, minimal scarring, and high tensile strength.
With the increasing global burden of vision-related disorders and a rapidly aging population, ophthalmic surgeries are on the rise. According to the World Health Organization, over 2.2 billion people globally suffer from some form of visual impairment, with cataracts and corneal diseases being among the leading causes. The increasing demand for surgical interventions in ophthalmology is a major factor driving the demand for sutures.
Moreover, advancements in suture materials, such as synthetic monofilament threads, bioresorbable sutures, and coated variants, have improved surgical outcomes and reduced the need for postoperative interventions. Surgeons are increasingly preferring sutures that offer superior handling properties, low tissue reactivity, and predictable absorption rates—particularly critical in ophthalmic procedures where precision is paramount.
The market also benefits from the global expansion of ophthalmic care centers, the growth in medical tourism (particularly for cataract and LASIK surgeries), and the rising adoption of minimally invasive techniques. While ophthalmic adhesives and laser-based closure methods are emerging alternatives, sutures remain a standard of care due to their affordability, accessibility, and versatility across surgical applications.
Increased Preference for Synthetic Sutures: Owing to better tensile strength, lower tissue reactivity, and customization options.
Adoption of Absorbable Sutures in Minimally Invasive Procedures: Surgeons increasingly prefer sutures that eliminate the need for postoperative removal.
Growth in Ophthalmic Procedures Among Geriatric Population: Age-related cataracts and retinal disorders are driving procedure volumes.
Rising Demand in Emerging Economies: Expansion of healthcare infrastructure and public health screening programs are boosting ophthalmic surgery rates.
Innovations in Micro-Sutures: Ultra-fine threads that offer higher precision in complex surgeries such as vitreoretinal and corneal transplantation.
Increased Use of Suture Coatings: Anti-bacterial and anti-inflammatory coatings are being integrated to minimize infection risks.
Integration with Robotic Microsurgery Systems: High-precision sutures compatible with robotic-assisted ophthalmic surgeries are gaining popularity.
Sustainability and Biodegradability Considerations: Focus on environmentally responsible and patient-safe suture materials.
| Report Coverage | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 617.98 Million |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 1123.76 Million |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 6.87% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered | Type, Application, End-use, Absorption Capacity, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Country scope | U.S., Canada, U.K., Germany, France, Italy, Spain, China, Japan, India, Australia, South Korea, Mexico, Brazil, Colombia, Argentina, South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE |
| Key Companies Profiled | Accutome, Inc.; Asset Medical Sarl; Alcon Inc.; Aurolab; B Braun Melsungen AG; DemeTech Corporation; FCI Ophthalmic Inc.; Medtronic Plc; Rumex International Co.; Surgical Specialties Corp; Teleflex Incorporated; Unigene |
One of the primary drivers of the ophthalmic sutures market is the escalating number of eye surgeries, particularly in aging populations. Cataract surgery remains the most common ophthalmic procedure worldwide, with millions of cases performed annually. Additionally, surgeries related to glaucoma, diabetic retinopathy, macular degeneration, and trauma-related ocular injuries are also on the rise.
The growing availability of advanced diagnostic tools and surgical technologies has led to earlier detection and treatment, thereby increasing the volume of ophthalmic procedures that require suturing. For example, corneal transplantation—a complex surgery that depends heavily on precise and biocompatible sutures—is seeing increasing demand due to higher incidence of corneal scarring and infections, particularly in developing regions.
Furthermore, the expansion of specialized ophthalmic centers and ambulatory surgical centers has improved surgical accessibility and affordability, especially in urban and semi-urban populations. These factors collectively bolster the demand for ophthalmic sutures, making it an indispensable segment in eye care.
A growing restraint in the ophthalmic sutures market is the emergence of sutureless surgical techniques. Innovations in ophthalmic adhesives, laser-assisted surgeries, and minimally invasive procedures are reducing the need for traditional sutures. For example, sutureless cataract surgeries using phacoemulsification techniques are becoming increasingly common, especially in high-income regions.
Similarly, advances in femtosecond laser technology and tissue bonding agents allow for wound closure without physical suturing, offering reduced operative time, less postoperative discomfort, and faster healing. While not universally adopted, these alternatives present a significant threat to the long-term demand for sutures, especially in developed healthcare systems focused on efficiency and cost containment.
Additionally, the risk of suture-induced infections or corneal vascularization, particularly when non-absorbable or improperly placed sutures are used, is prompting clinicians to explore alternatives, thereby limiting growth in some sub-segments.
A notable opportunity for the ophthalmic sutures market lies in the expansion of healthcare services and ophthalmic infrastructure in emerging economies. Countries such as India, Brazil, Indonesia, Nigeria, and Vietnam are witnessing increased investments in eye care programs, especially those targeting treatable blindness like cataracts and corneal diseases.
Government initiatives such as India's National Programme for Control of Blindness (NPCB) and various global partnerships with WHO and NGOs are providing low-cost or free surgeries in underserved regions. These efforts are driving procedure volumes, particularly in community outreach centers and mobile surgical camps that continue to rely on affordable and proven solutions like sutures.
Moreover, local production of ophthalmic suture materials in developing countries is improving availability while lowering costs. As these nations continue to bridge healthcare access gaps and expand universal coverage, the demand for ophthalmic surgical consumables, including sutures, is expected to rise significantly.
Synthetic sutures dominated the ophthalmic sutures market, driven by their superior physical and chemical properties compared to natural alternatives. These sutures, made from materials like polyglactin, polyglycolic acid, and polydioxanone, offer controlled absorption rates, minimal tissue reactivity, and improved tensile strength. In ophthalmic procedures, where delicate and avascular tissues are involved, these attributes are crucial for minimizing scarring, infection risk, and inflammation.
Synthetic sutures also support customization, allowing manufacturers to develop ultra-fine threads suitable for high-precision surgeries such as vitrectomy or corneal grafting. As a result, synthetic variants are becoming the go-to choice for ophthalmic surgeons across both public and private healthcare settings.
Natural sutures, such as silk or catgut, are still used in some specific applications, particularly in developing markets or where immediate cost-effectiveness is a higher priority. However, their market share is shrinking due to concerns about variable absorption rates, risk of immunogenic reactions, and reduced durability. Nonetheless, innovations in naturally derived but processed materials such as collagen-based sutures are attempting to reinvigorate this segment with better biocompatibility and performance.
Cataract surgery held the largest share of the application segment, owing to its status as the most frequently performed ophthalmic surgery worldwide. Despite growing adoption of sutureless techniques, a significant percentage of cases—especially complicated or trauma-induced cataracts—still require wound closure using fine monofilament sutures. These are critical in maintaining anterior chamber stability and preventing wound leaks.
In regions with limited access to phacoemulsification or femtosecond lasers, manual small incision cataract surgery (MSICS) continues to be the preferred method, which often involves suture placement. This solidifies the relevance of sutures in global cataract care, particularly in low-resource settings.
Corneal transplantation is the fastest-growing application segment, due to rising prevalence of corneal blindness, better availability of donor tissues, and improved surgical techniques. Corneal suturing requires ultra-fine, non-reactive, and durable sutures that can hold grafts in place while minimizing postoperative astigmatism and vascularization. The demand for 10-0 and 11-0 nylon sutures is increasing, and new materials that combine elasticity with tensile strength are under development. As corneal procedures grow in frequency and complexity, the requirement for specialized ophthalmic sutures is expected to accelerate.
Hospitals dominated the end-use segment, attributed to their comprehensive surgical capabilities, high patient volume, and access to skilled ophthalmic surgeons. Most complex surgeries such as corneal transplants and trauma repairs are conducted in hospital settings where the infrastructure supports postoperative care and complication management. Hospitals also benefit from bulk procurement systems, ensuring consistent suture supply and access to advanced variants.
Ambulatory surgical centers (ASCs) are emerging as the fastest-growing segment, especially in developed regions where outpatient surgeries like cataract extraction and oculoplastics are increasingly shifting to ASCs for cost-efficiency and faster turnover. These centers are adopting high-quality absorbable sutures to minimize follow-up visits and ensure rapid recovery. With shorter waiting times, personalized care, and improved reimbursement models, ASCs are playing a larger role in shaping ophthalmic surgical demand and suture consumption.
Non-absorbable sutures dominate the ophthalmic sutures market, particularly in surgeries where long-term tissue support and postoperative adjustability are necessary. For example, corneal transplantation surgeries often require non-absorbable nylon sutures to maintain graft integrity over months. Surgeons prefer these sutures for their strength, stability, and visibility under slit-lamp examination during follow-up.
These sutures provide the ability to be adjusted or removed based on healing patterns and patient-specific responses, offering greater control over postoperative outcomes. They are also preferred in many vitrectomy and iridectomy procedures, where prolonged healing and mechanical integrity are essential.
Absorbable sutures are the fastest-growing sub-segment, especially in cataract and oculoplastic surgeries, where natural healing can occur quickly, and suture removal may pose discomfort or infection risk. Innovations in bioresorbable materials are addressing previous limitations such as early breakdown or poor knot security. Absorbable options also reduce the need for return visits in pediatric or geriatric patients, enhancing patient compliance and satisfaction.
North America is the dominant regional market for ophthalmic sutures, driven by a well-established healthcare system, high rates of ophthalmic surgeries, and the presence of global suture manufacturers. The U.S., in particular, leads in cataract surgeries (more than 3 million annually) and corneal transplants, supported by favorable reimbursement frameworks. Advanced diagnostic and surgical tools allow for early and accurate interventions, increasing the demand for precise suture solutions.
Additionally, North American regulatory bodies like the FDA ensure strict quality and safety standards, which have prompted manufacturers to innovate suture products with advanced features such as antimicrobial coatings and reduced particulate load.
Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing regional market, propelled by a large patient pool, growing access to ophthalmic services, and national blindness control programs. India and China together perform millions of cataract surgeries each year, with governments and NGOs actively funding free surgical camps in rural and underserved areas. The expansion of medical tourism especially for eye surgeries in Thailand, Singapore, and South Korea is also supporting demand for premium ophthalmic sutures.
Domestic manufacturers in countries like India are producing cost-effective suture options tailored to local needs, contributing to rapid regional growth. Increasing awareness, improving surgical standards, and rising investments in eye care infrastructure are expected to maintain the region’s high growth trajectory.
Alcon (March 2025): Expanded its line of ophthalmic surgical tools to include next-generation 10-0 nylon sutures for corneal procedures, aiming to improve visibility and knot security.
Teleflex Medical (February 2025): Introduced a new synthetic absorbable suture line with antibacterial coating aimed at reducing postoperative endophthalmitis.
Aurolab (January 2025): Announced the launch of its new range of microsurgical sutures in India designed for affordable corneal transplant applications in developing regions.
Assut Medical Sàrl (December 2024): Began distribution of its ultra-fine synthetic ophthalmic suture line across Europe and Southeast Asia.
DemeTECH Corporation (November 2024): Partnered with Middle Eastern healthcare providers to supply high-precision non-absorbable sutures for complex ophthalmic surgeries.
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Ophthalmic Sutures Market
Type
Absorption Capacity
Application
End-use
Regional