Hemophilia Market Size and Research
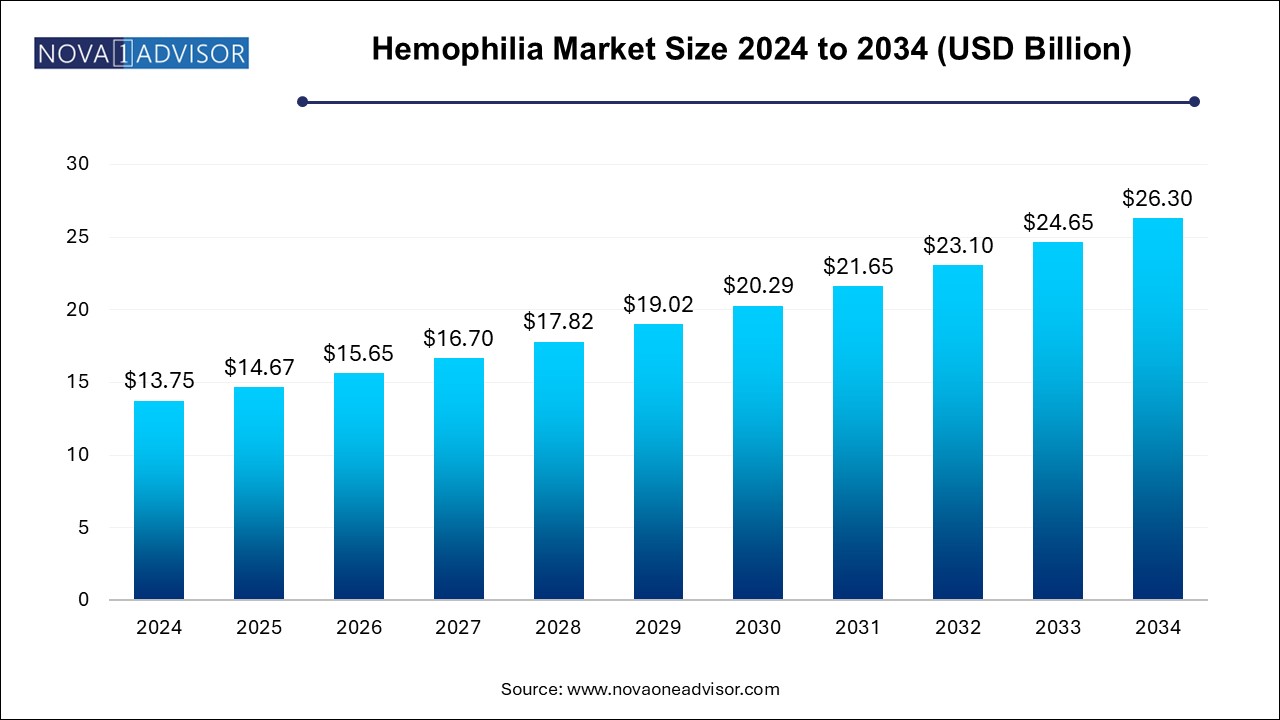
The hemophilia market size was exhibited at USD 13.75 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 26.30 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 6.7% during the forecast period 2024 to 2034.
Hemophilia Market Key Takeaways:
- Hemophilia A held the highest share of 74.16% in 2024 in the hemophilia market.
- Hemophilia B is expected to expand at a CAGR of 5.5% during the forecast period.
- The prophylaxis segment dominated the hemophilia market with a share of 48.8% in 2024.
- The cure segment is positioned to expand at the fastest CAGR of 205.8% during the forecast period
- The factor replacement therapy segment held the highest share of 61.9% in 2024 in the hemophilia market.
- The emerging gene therapy and monoclonal antibodies segment is expected to expand at a CAGR of 10.1% during the forecast period.
- The specialty pharmacies segment dominated the hemophilia market with a share of 62.0% in 2024.
- The hospital pharmacies segment is expected to expand at the fastest CAGR of 7.1% during the forecast period.
- North America was the largest revenue-generating region in the hemophilia market, with a share of 49.81% in 2024.
- Europe is expected to grow at a CAGR of 7.4% during the forecast period.
Market Overview
The global hemophilia market plays a vital role in the landscape of rare disease therapeutics, focused on managing a chronic bleeding disorder characterized by a deficiency or dysfunction of clotting factors. Hemophilia primarily manifests in two major forms: Hemophilia A (factor VIII deficiency) and Hemophilia B (factor IX deficiency). The disease significantly impairs the blood's ability to clot, resulting in prolonged bleeding episodes, both externally and internally, especially into joints and muscles.
Treatment for hemophilia revolves around factor replacement therapy, prophylactic regimens, gene therapies, and emerging monoclonal antibody technologies. Advances in recombinant factor production, extended half-life (EHL) therapies, and novel prophylactic solutions have drastically improved the quality of life for hemophilia patients over the past two decades. Additionally, groundbreaking progress in gene therapy offers hope for potential cures, reshaping the long-term treatment paradigm.
Growing awareness, improved diagnostic tools, supportive healthcare policies, and an expanding focus by biopharmaceutical giants are driving the global hemophilia market. Yet, access to advanced therapies remains a challenge in many emerging economies. As innovation and investment continue to rise, the global hemophilia market is expected to maintain robust growth trajectories over the coming years.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Emergence of Gene Therapy: Pioneering treatments targeting one-time functional cures for Hemophilia A and B.
-
Extended Half-life (EHL) Factor Products: Enhancing patient convenience by reducing injection frequency.
-
Prophylaxis Overtaking On-Demand Therapy: Increasing adoption of preventive treatment regimens to avoid spontaneous bleeding.
-
Expansion into Emerging Markets: Pharmaceutical companies targeting underdiagnosed and untreated populations.
-
Development of Non-factor Therapies: Bispecific antibodies like emicizumab offering alternatives to traditional factor replacement.
-
Home Therapy and Self-administration Trends: Empowering patients with home infusion devices and telemedicine support.
-
Growing Focus on Personalized Treatment Plans: Tailoring therapy based on pharmacokinetics (PK), severity, and lifestyle.
-
Strategic Collaborations and Licensing Deals: Increasing partnerships to accelerate gene therapy research and commercialization.
Report Scope of Hemophilia Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 14.67 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 |
USD 26.30 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2034 |
CAGR of 6.7% |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2024-2034 |
| Segments Covered |
Type; Treatment Type; Therapy; Distribution Channel; Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Covered |
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, MEA |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited; CSL Behring; Pfizer, Inc.; Bayer AG; BioMarin, Spark Therapeutics, Inc.; Sanofi; F. Hoffmann La-Roche Ltd..; Novo Nordisk A/S.; and Octapharma AG. |
Key Market Driver: Rising Approval and Adoption of Extended Half-life Therapies
The most significant driver for the hemophilia market is the rising approval and adoption of extended half-life (EHL) therapies.
Traditional factor replacement therapies require frequent infusions, often several times a week, to maintain therapeutic clotting factor levels. EHL therapies achieved through PEGylation, fusion to albumin, or Fc fragments prolong the time factor concentrates remain active in the bloodstream, allowing for reduced infusion frequency, improved patient adherence, and better bleed protection.
The success of products like Eloctate (extended half-life factor VIII) and Alprolix (extended half-life factor IX) demonstrates the shift towards more convenient, patient-friendly options. As more EHL therapies gain regulatory approval, their uptake is anticipated to replace conventional therapies rapidly, reshaping the treatment landscape globally.
Key Market Restraint: High Treatment Costs Limiting Access
A notable restraint on the global hemophilia market is the high cost of treatment, particularly advanced therapies like recombinant factors and gene therapies.
Annual treatment costs for hemophilia patients on factor replacement therapies can range from USD 150,000 to USD 300,000 or higher, depending on disease severity and regimen type. Newly introduced gene therapies are even more expensive, with single-dose costs reaching several million dollars.
Such high costs restrict therapy access to high-income countries, leaving a significant portion of the global hemophilia population in low- and middle-income regions underserved. Limited insurance coverage and inconsistent healthcare infrastructure in these regions exacerbate the accessibility gap, curbing overall market potential.
Key Market Opportunity: Breakthroughs in Gene Therapy for Potential Cure
A game-changing opportunity in the hemophilia market is the breakthrough development of gene therapy, aiming for a potential lifelong cure with a one-time treatment.
Gene therapies such as Roctavian (valoctocogene roxaparvovec) for Hemophilia A and Etranacogene dezaparvovec (Hemgenix) for Hemophilia B have already achieved regulatory approvals in the U.S. and Europe. These therapies use adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors to deliver functional copies of defective genes, restoring clotting factor production endogenously.
Widespread adoption of gene therapy, despite current cost barriers, could revolutionize disease management, substantially reduce lifetime treatment costs, and minimize patient burden. As real-world evidence of durability and safety accumulates, gene therapy has the potential to transition hemophilia treatment from chronic management to near-curative interventions.
Hemophilia Market By Type Insights
Hemophilia A dominates the type segment, accounting for around 80% of all hemophilia cases globally. Factor VIII deficiency is significantly more common than factor IX deficiency, resulting in a larger patient base for Hemophilia A therapeutics and related research.
Hemophilia B is growing fastest, fueled by advancements in factor IX replacement therapies and the approval of novel gene therapies specifically for this subtype. Additionally, emerging awareness campaigns and improved diagnostics are leading to better identification and treatment of Hemophilia B cases, accelerating market expansion.
Hemophilia Market By Treatment Insights
Prophylaxis dominates the treatment type segment, as the focus shifts from managing bleeding episodes after they occur (on-demand therapy) to preventing them altogether. Prophylactic treatment has demonstrated superiority in preserving joint function, reducing morbidity, and enhancing quality of life.
Cure-oriented approaches, particularly gene therapy, are growing fastest. Despite current affordability and access limitations, the allure of a one-time curative solution for hemophilia is driving enormous clinical and commercial interest, setting the stage for future market leadership in this segment.
Hemophilia Market By Therapy Insights
Factor replacement therapy dominates the therapy segment, historically considered the gold standard for hemophilia treatment, both in on-demand and prophylactic settings.
Gene therapy and monoclonal antibodies are growing fastest, offering transformative potential. Non-factor therapies like Roche’s Hemlibra (emicizumab) a bispecific monoclonal antibody provide bleed prevention with less frequent, subcutaneous administration. Similarly, gene therapy candidates aim to eliminate lifelong infusion requirements, representing a paradigm shift in hemophilia care.
Hemophilia Market By Distribution Channel Insights
Hospital pharmacies dominate the distribution channel segment, traditionally dispensing factor concentrates to patients undergoing acute management or surgery.
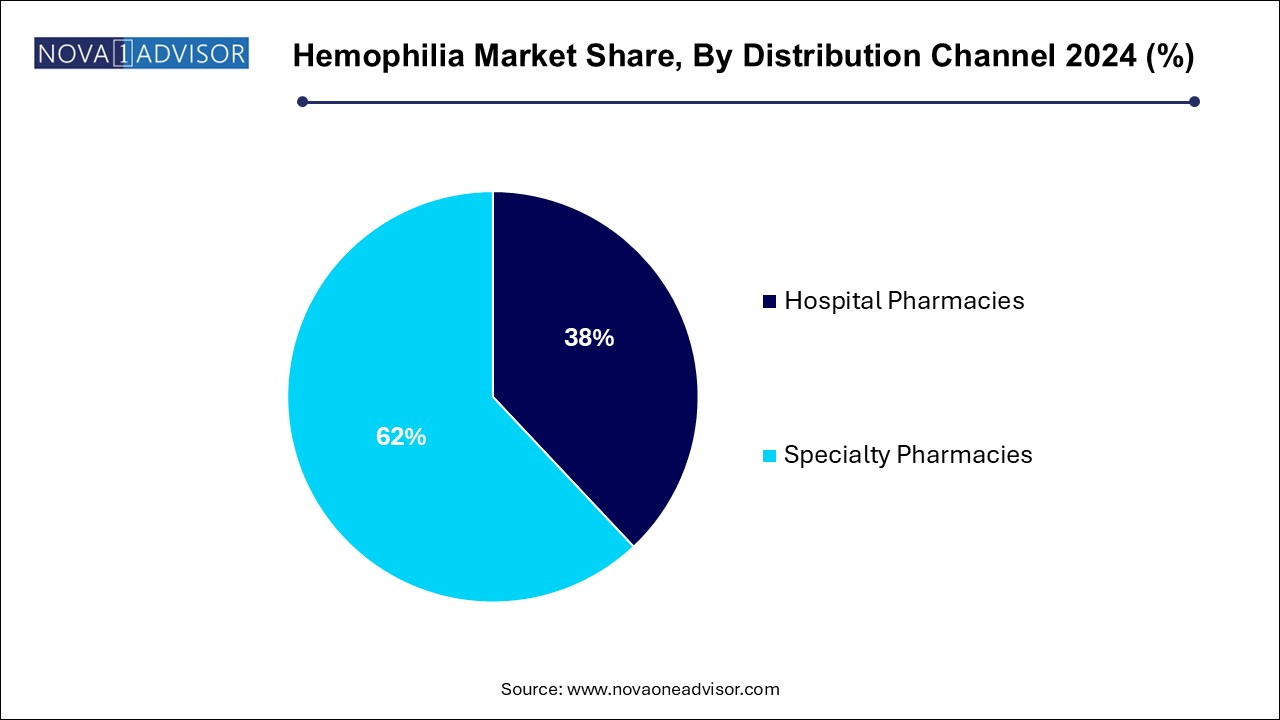
Specialty pharmacies are growing fastest, specializing in chronic disease management, providing home delivery services, patient education, and therapy adherence support. Their rising role reflects broader trends toward decentralized, patient-centered hemophilia care models.
Hemophilia Market By Regional Insights
North America holds the largest share of the hemophilia market, with the United States leading due to robust healthcare infrastructure, favorable reimbursement policies, and widespread access to advanced therapies, including gene therapies and EHL products.
Strong advocacy from organizations like the National Hemophilia Foundation (NHF), high healthcare spending, and extensive clinical trial activity contribute to sustained market leadership.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, driven by rising hemophilia awareness, improving diagnostic rates, expanding healthcare access, and increasing government support for rare diseases.
Countries like China and India, with large underdiagnosed populations, present enormous growth opportunities. International initiatives promoting affordable treatment access and collaborations between global pharmaceutical companies and local partners are accelerating market penetration in the region.
Some of the prominent players in the hemophilia market include:
- Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited
- CSL Behring
- Pfizer, Inc.
- Bayer AG
- BioMarin
- Spark Therapeutics, Inc.
- Sanofi
- F. Hoffmann La-Roche Ltd.
- Novo Nordisk A/S.
- Octapharma AG.
Recent Developments
-
March 2025: CSL Behring announced positive post-approval real-world data for Hemgenix, its gene therapy for Hemophilia B, showcasing durable factor IX expression two years post-treatment.
-
February 2025: BioMarin Pharmaceutical reported new five-year efficacy and safety data for Roctavian in Hemophilia A, demonstrating sustained factor VIII levels.
-
January 2025: Roche launched a new subcutaneous formulation of Hemlibra with a smaller volume and shorter administration time, improving patient convenience.
-
December 2024: Pfizer and Sangamo Therapeutics initiated Phase 3 trials for giroctocogene fitelparvovec, an investigational gene therapy for Hemophilia A.
-
November 2024: Takeda Pharmaceutical expanded global access initiatives for its EHL factor products, targeting underrepresented patient populations in Southeast Asia and Africa.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the hemophilia market
By Type
- Hemophilia A
- Hemophilia B
- Others
By Treatment Type
- On-demand
- Cure
- Prophylaxis
By Therapy
- Factor Replacement Therapy
-
- Plasma-derived Factor Concentrates
-
- Recombinant Factor Concentrates
-
-
- Factor VIII
- Factor VII
- Factor IX
- Desmopressin & Fibrin Sealants
- Gene Therapy & Monoclonal Antibodies
By Distribution Channel
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Specialty Pharmacies
By Regional
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa (MEA)


