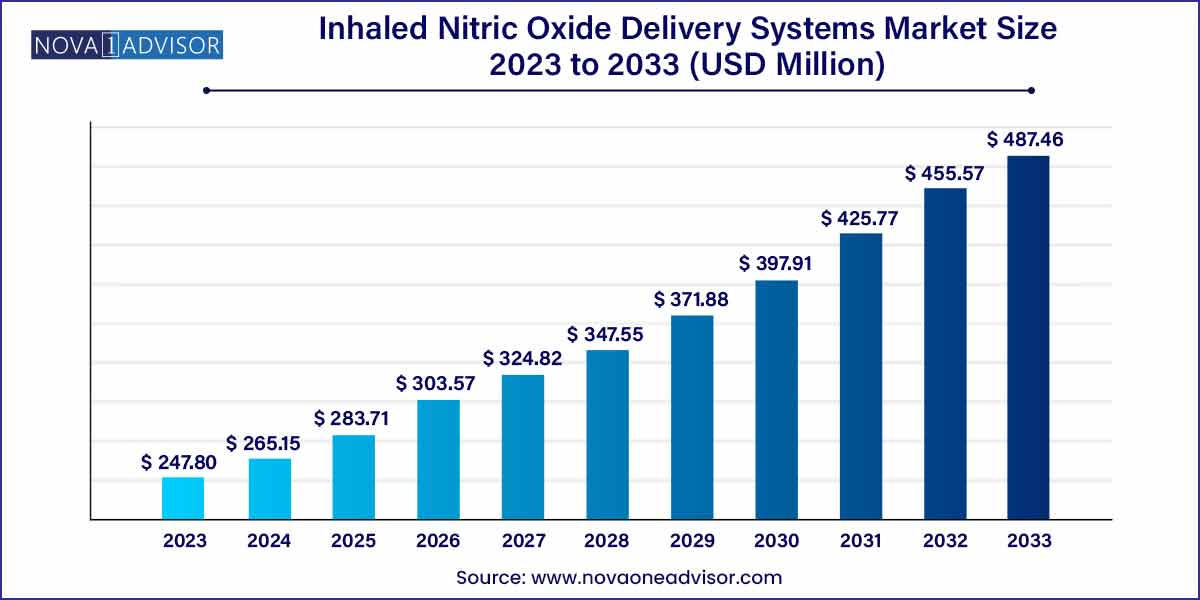
The global inhaled nitric oxide delivery systems market size was exhibited at USD 247.80 million in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 487.46 million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 7.0% during the forecast period of 2024 to 2033.
Key Takeaways:
- The pediatric segment accounted for the largest revenue share of 77.6% in 2023.
- Hypoxic Respiratory Failure (HRF) inhaled nitric oxide delivery system held the largest segment share of 80.2% in 2023.
- The disposables product segment accounted for the largest revenue share of 65.1% in 2023.
- The hospitals segment captured the highest revenue share of 88.0% in 2023.
- North America is expected to be the fastest-growing regional market, registering a CAGR of 7.84% during the forecast period.
Market Overview
The Inhaled Nitric Oxide (iNO) Delivery Systems Market represents a specialized but rapidly evolving segment within respiratory healthcare, dedicated to providing targeted pulmonary vasodilation therapy to critically ill patients. Inhaled nitric oxide is a selective pulmonary vasodilator used primarily for treating respiratory conditions such as hypoxic respiratory failure (HRF) in neonates and acute hypoxemic respiratory failure (AHRF) in adults. Its unique ability to improve oxygenation without causing systemic hypotension has made it a vital intervention in critical care settings.
Originally developed for neonatal intensive care units (NICUs), inhaled nitric oxide therapy has expanded its applications into adult critical care, especially with the rise in acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) cases. Its use surged during the COVID-19 pandemic, as clinicians sought innovative solutions to manage severe respiratory complications. As global awareness about respiratory care deepens and the burden of chronic and acute pulmonary diseases rises, demand for safe, efficient, and user-friendly inhaled nitric oxide delivery systems is expected to grow substantially.
Innovation in device design, portability, disposability, and integrated monitoring systems is fueling market expansion. Meanwhile, strategic collaborations, regulatory approvals, and investments into clinical research for new indications are further shaping the competitive landscape. With healthcare facilities emphasizing precision therapies, the inhaled nitric oxide delivery systems market is positioned to witness sustained growth over the next decade.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Expansion Beyond Neonatal Applications: Increasing use of inhaled nitric oxide therapies for adults with ARDS, pulmonary hypertension, and post-cardiac surgery complications.
-
Portable and Home-Based Delivery Systems: Development of compact, portable devices for use outside hospital settings, including emergency transport and outpatient care.
-
Increased Focus on Single-Use Disposable Products: Rising demand for disposables to minimize infection risks and improve system convenience, especially post-pandemic.
-
Integration with Ventilator and ECMO Systems: Growing need for systems compatible with advanced respiratory support technologies like extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO).
-
R&D for New Indications: Ongoing research investigating iNO therapy’s potential for treating viral infections, organ transplant support, and sepsis-related lung injury.
-
Government and Regulatory Support: FDA fast-tracking approvals during the COVID-19 pandemic highlighted regulatory bodies' recognition of iNO’s critical therapeutic role.
-
Strategic Collaborations and M&A Activity: Partnerships between device manufacturers, gas suppliers, and healthcare providers are increasing to enhance service delivery and market reach.
-
Adoption of Advanced Monitoring Technologies: Real-time monitoring of nitric oxide concentrations, oxygen saturation, and methemoglobin levels integrated into delivery systems.
Inhaled Nitric Oxide Delivery Systems Market Report Scope
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 247.80 Million |
| Market Size by 2033 |
USD 487.46 Million |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 |
CAGR of 7.0% |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered |
Type, Application, Product, End User, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Central and South America; the Middle East and Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals; Getinge; Vero Biotech; LINDE; Beyond Air; SLE; NU MED; Bellerophon Therapeutics; Air Liquide Healthcare; Circassia Pharmaceuticals. |
Key Market Driver
Growing Prevalence of Respiratory Disorders
The escalating global burden of respiratory diseases serves as a major driver for the inhaled nitric oxide delivery systems market. Conditions such as neonatal hypoxic respiratory failure, ARDS, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and pulmonary hypertension are becoming increasingly prevalent, partly due to aging populations, rising pollution levels, and infectious diseases.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), respiratory illnesses remain among the leading causes of death globally. In neonates, hypoxic respiratory failure is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality. Inhaled nitric oxide therapy offers a lifesaving intervention by improving pulmonary circulation and oxygenation without causing systemic side effects common with other vasodilators.
Moreover, the COVID-19 pandemic spotlighted respiratory failure management and the need for effective gas therapies. Studies conducted during the pandemic reinforced inhaled nitric oxide’s role in improving oxygenation in patients with severe hypoxemia, further validating its clinical utility beyond traditional neonatal applications. The increasing incidence of respiratory diseases worldwide is expected to sustain strong demand for iNO delivery systems.
Key Market Restraint
High Cost and Limited Accessibility
One of the principal restraints impacting the growth of the inhaled nitric oxide delivery systems market is the high cost associated with therapy. Inhaled nitric oxide treatment involves not only the purchase of sophisticated delivery systems but also continuous supply of medical-grade nitric oxide gas, disposables, and specialized monitoring equipment.
Furthermore, the requirement for skilled personnel to manage therapy, monitor patient response, and maintain equipment adds to operational costs. These financial burdens limit the accessibility of iNO therapy in resource-constrained settings, particularly in developing countries where budgetary limitations impact critical care provisioning.
Additionally, competition from alternative therapies like high-frequency oscillatory ventilation, surfactant replacement, and extracorporeal life support systems sometimes restrict the uptake of inhaled nitric oxide, especially where reimbursement structures are not supportive. To unlock broader adoption, innovations focused on cost reduction, portable delivery systems, and simplified user interfaces are critical.
Key Market Opportunity
Expansion into Adult Critical Care and New Indications
A major growth opportunity for the inhaled nitric oxide delivery systems market lies in expanding therapeutic applications into adult critical care settings. While traditionally associated with neonatal hypoxic respiratory failure, emerging research suggests that inhaled nitric oxide can improve outcomes in adults with conditions like ARDS, right heart failure, post-operative complications in cardiac surgery, and even severe sepsis.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, clinical studies indicated that iNO therapy improved oxygenation in intubated COVID-19 patients, spurring renewed interest in its broader application. Moreover, investigations into the use of inhaled nitric oxide for organ transplant recipients (to reduce ischemia-reperfusion injury) and in pulmonary embolism are ongoing.
Expanding label indications, supported by robust clinical trials and regulatory approvals, could significantly increase the patient pool eligible for iNO therapy, offering lucrative opportunities for device manufacturers and gas suppliers alike.
Type Insights
The Pediatrics segment dominated the inhaled nitric oxide delivery systems market, primarily due to the established efficacy of iNO therapy in treating hypoxic respiratory failure in neonates. Pediatric applications account for the bulk of iNO usage worldwide, especially in neonatal intensive care units (NICUs). The targeted use of iNO improves oxygenation, reduces the need for extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), and increases survival rates in neonates with pulmonary hypertension or meconium aspiration syndrome.
Hospitals and tertiary care centers routinely invest in pediatric-specific delivery systems, ensuring optimized dosing and monitoring tailored to neonatal needs. Leading device manufacturers focus heavily on pediatric modules with safety alarms, precision dosing, and integrated methemoglobin monitoring to mitigate risks.
On the other hand, the Adult segment is anticipated to grow at the fastest rate. The surge in ARDS cases during the COVID-19 pandemic, the increasing incidence of acute hypoxemic respiratory failure among adults, and the broader acceptance of iNO therapy for postoperative pulmonary complications are key factors driving this growth. Expanding clinical trials and regulatory approvals targeting adult indications are expected to bolster this trend.
Application Insights
Hypoxic Respiratory Failure (HRF) remained the largest application segment in the inhaled nitric oxide delivery systems market, driven by the therapy’s proven effectiveness in improving oxygenation in neonates and select adult patient populations. HRF, characterized by inadequate oxygenation despite maximal respiratory support, often necessitates adjunct therapies like iNO to achieve adequate blood oxygen levels without increasing ventilator pressures, which can damage delicate lung tissues.
The American Academy of Pediatrics endorses the use of inhaled nitric oxide as a rescue therapy for term and near-term infants with severe hypoxic respiratory failure, further cementing HRF as the primary driver of current market demand.
Meanwhile, Acute Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure (AHRF) is projected to be the fastest-growing application. AHRF often arises in adults due to conditions such as pneumonia, sepsis, and trauma-induced lung injury. The COVID-19 crisis heightened awareness and demand for therapies that could rapidly improve oxygenation without exacerbating lung injury, a role that inhaled nitric oxide therapy filled effectively. Future research and regulatory approvals aimed at adult AHRF management are expected to significantly expand market opportunities.
Product Insights
The Systems segment led the product category, encompassing the full delivery mechanisms—including gas cylinders, flow control devices, integrated ventilators, and monitoring systems—required to administer inhaled nitric oxide safely and effectively. Hospitals prioritize full-system purchases to ensure precision delivery, patient safety, and regulatory compliance. Vendors like Mallinckrodt and Bellerophon Therapeutics offer advanced systems integrated with automated alarms, fail-safes, and diagnostic capabilities.
However, Disposables are gaining momentum as the fastest-growing product category. Increasing focus on infection control, cost efficiency, and ease of use has led to the adoption of single-use, disposable cartridges, tubing sets, and sensors. Especially in post-pandemic healthcare environments, minimizing cross-contamination risks is driving hospitals and clinics to transition toward disposable products integrated into iNO therapy workflows.
End-user Insights
Hospitals accounted for the largest end-user share, being the primary centers equipped with intensive care units (ICUs) and neonatal intensive care units (NICUs) where inhaled nitric oxide therapy is administered. Hospitals invest heavily in comprehensive iNO delivery systems, gas supply contracts, and trained respiratory therapists capable of managing critical patients requiring complex therapies.
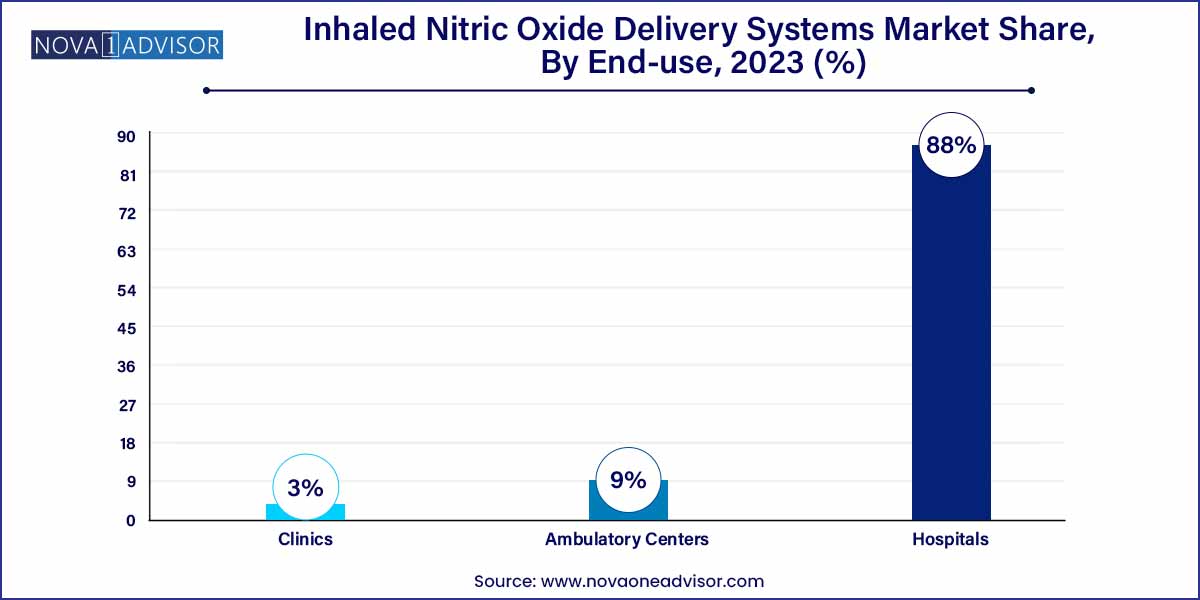
Large hospitals and academic medical centers also lead clinical research efforts evaluating new indications for iNO therapy, further reinforcing their dominance in the market.
Meanwhile, Ambulatory Centers are projected to grow at a rapid pace. The rise of outpatient surgical centers, emergency medical transport services (where portable iNO systems are valuable), and specialized pulmonary care clinics are contributing to broader use of inhaled nitric oxide beyond traditional hospital settings.
Regional Insights
North America dominated the inhaled nitric oxide delivery systems market, driven by advanced healthcare infrastructure, high adoption rates of innovative respiratory therapies, favorable reimbursement policies, and extensive clinical research activities. The U.S., in particular, witnessed increased utilization of inhaled nitric oxide during the COVID-19 pandemic, with FDA emergency use authorizations boosting market expansion.
Major players such as Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals and VERO Biotech are headquartered in North America, ensuring strong supply chains, market penetration, and continuous product innovation. Collaborations with hospitals, research institutions, and regulatory agencies further reinforce the region’s leadership.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing market, fueled by rising awareness about advanced respiratory therapies, expanding neonatal and adult critical care infrastructure, and increasing healthcare expenditure. Countries like China, India, Japan, and Australia are witnessing rising incidence rates of respiratory disorders, fueling demand for advanced treatment options like inhaled nitric oxide.
Government initiatives aimed at reducing infant mortality rates, healthcare modernization programs, and growing investments from international device manufacturers seeking to expand into emerging markets are key factors driving regional growth.
Some of the prominent players in the inhaled nitric oxide delivery systems market include:
- Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals
- Getinge
- Vero Biotech
- LINDE
- Beyond Air
- SLE
- NU MED
- Bellerophon Therapeutics
- Air Liquide Healthcare
- Circassia Pharmaceuticals
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the global inhaled nitric oxide delivery systems market.
Type
Application
- Hypoxic Respiratory Failure (HRF)
- Acute Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure (AHRF)
- Others
Product
End-user
- Hospitals
- Ambulatory Centers
- Clinics
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)


