Nanotechnology In Medical Devices Market Size and Trends
The nanotechnology in medical devices market size was exhibited at USD 4.35 billion in 2025 and is projected to hit around USD 7.87 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 6.11% during the forecast period 2026 to 2035.
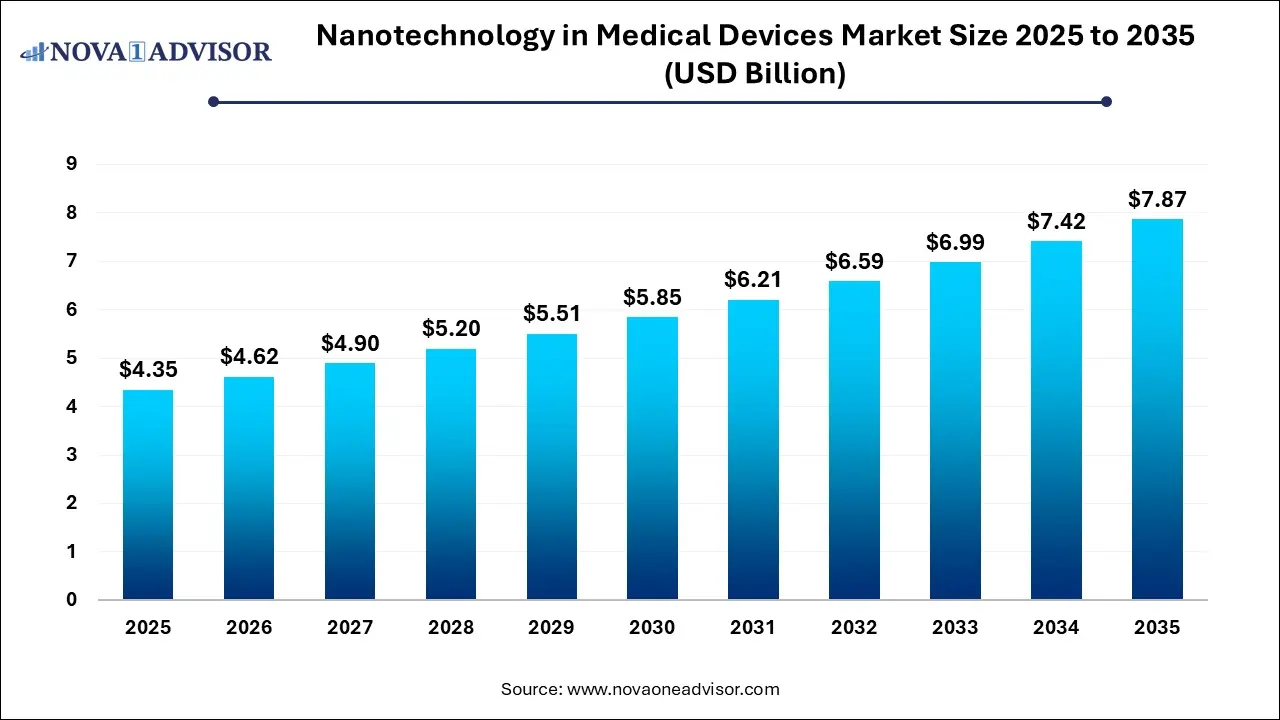
Nanotechnology In Medical Device Market Key Takeaways:
- The implantable devices segment held the largest share of 53.8% in 2025.
- The other segment is projected to grow at the fastest CAGR from 2026 to 2035.
- The orthopedics segments held the largest share of 28.0% in 2025.
- The dentistry segment is expected to grow at a significant CAGR from 2026 to 2035
- The hospitals segment held the largest share of 52.0% in 2025.
- The clinics segment is growing at the fastest CAGR of 7.0% over the forecast period.
- North America nanotechnology in medical devices market dominated the overall global market and accounted for the 35.0% revenue share in 2025.
Market Overview
The Nanotechnology in Medical Devices Market represents a groundbreaking intersection of materials science and healthcare innovation. Nanotechnology involves manipulating matter at dimensions of 1 to 100 nanometers, enabling the engineering of devices and materials with enhanced functional properties. In medical applications, this translates into miniaturized sensors, improved implant biocompatibility, targeted drug delivery, and enhanced diagnostic precision.
This market is witnessing rapid growth owing to rising demand for more effective, minimally invasive, and personalized medical treatments. The increasing prevalence of chronic conditions such as cardiovascular diseases, orthopedic disorders, and hearing loss—is also accelerating the adoption of nano-enabled implants and diagnostic tools. Devices embedded with nanomaterials exhibit superior mechanical properties, antimicrobial resistance, and improved cellular integration.
With ongoing research and commercialization of nanoscale coatings, nanoparticles, and nanostructured surfaces, medical device companies are finding new ways to differentiate their offerings. Governments and private investors alike are significantly funding nanomedicine R&D, leading to collaborations between academic institutions, startups, and multinational corporations. Regulatory support, such as FDA clearances for nanotech-enhanced devices, is also boosting credibility and market confidence.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Integration of Nanocoatings in Implants: Anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial coatings enhance device longevity and reduce infection risks.
-
Nanoparticle-based Targeted Therapies: Devices are being developed to carry nanoparticles for precise delivery to tissues or cells.
-
Bioactive Nanomaterials for Bone Regeneration: Orthopedic implants increasingly use nanocomposites for enhanced osteointegration.
-
Nano-sensors in Wearable Devices: Ultra-sensitive biosensors are enabling real-time, continuous patient monitoring.
-
Rise of 3D Nano-printing: Customized medical devices are now produced using nanoscale additive manufacturing.
-
Hybrid Nanomedicine Platforms: Devices are combining diagnostics and therapeutics (theranostics) using nanocarriers and nanoshells.
-
Regulatory Momentum for Nano-enabled Devices: Growing acceptance and clearer guidelines from FDA and EMA are fostering innovation.
Report Scope of Nanotechnology In Medical Device Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2026 |
USD 4.01 Billion |
| Market Size by 2035 |
USD 7.31 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2026 to 2035 |
CAGR of 6.11% |
| Base Year |
2025 |
| Forecast Period |
2026-2035 |
| Segments Covered |
Type, Application, End use, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Smith & Nephew PLC; Abbott Laboratories; 3M; Zimmer Biomet; Stryker; Starkey; Dentsply Sirona; Boston Scientific Corporation; LivaNova PLC; Cochlear Ltd |
Key Market Driver: Increased Demand for Minimally Invasive and Smart Medical Devices
The primary driver of this market is the rising demand for advanced, minimally invasive, and high precision medical devices, particularly in orthopedic and cardiovascular interventions. Nanotechnology enables the production of implants and catheters with superior surface properties enhancing compatibility, durability, and healing response. For instance, nano-structured titanium used in hip and knee implants offers higher osseointegration, reducing failure rates.
Moreover, hearing aids embedded with nano-sensors can detect early degeneration or fluid levels within the ear, improving prognosis. Smart wound dressings embedded with nanofibers can sense infection and release antibiotics on-demand. This shift toward intelligent, nano-enhanced medical solutions is driving both clinical outcomes and market revenue.
Key Market Restraint: Regulatory and Biocompatibility Challenges
Despite promising advancements, the market faces a critical restraint in the form of regulatory and biocompatibility challenges. The novel properties of nanomaterials pose difficulties in predicting long-term biological interactions. Questions around toxicity, degradation, and immune responses still lack definitive regulatory benchmarks in many countries.
Furthermore, standard protocols for evaluating nano-device safety are still evolving, and manufacturers often face uncertainty in approval pathways. The cost and duration of clinical trials for such devices are higher due to the requirement of long-term monitoring. These factors can delay product launches and discourage smaller innovators from entering the space, slowing market momentum.
Key Market Opportunity: Expanding Applications in Regenerative Medicine and Smart Diagnostics
A significant opportunity lies in the application of nanotechnology for regenerative medicine and real-time diagnostics. Nanostructured scaffolds are now used to mimic natural extracellular matrices for bone, nerve, and skin tissue regeneration. These devices promote cellular adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation, critical for treating complex injuries or congenital defects.
In diagnostics, nano-biosensors can detect diseases at ultra-low concentrations, enabling early diagnosis of conditions such as cancer, sepsis, or cardiovascular disorders. For instance, wearable glucose sensors using carbon nanotubes or quantum dots are enabling continuous monitoring without blood samples. The convergence of nanotechnology with bioelectronics, AI, and microfluidics is paving the way for highly personalized, non-invasive diagnostic platforms.
Nanotechnology In Medical Device Market By Type Insights
Implantable devices dominate the market, primarily due to their widespread application in orthopedics and cardiology. Orthopedic implants incorporating nanostructures—such as nanosilver, hydroxyapatite, and titanium alloys—offer enhanced bone bonding and reduced bacterial adhesion. Nanocoatings on cardiac stents improve endothelialization and prevent restenosis. Hearing aids with nanomaterials ensure reduced feedback, clearer sound processing, and smaller form factors.
Wound care is the fastest-growing segment, as nanofiber-based dressings gain traction in hospitals and clinics. These products release antibacterial agents in response to infection markers and accelerate tissue repair by mimicking natural ECM. Companies are also developing temperature-sensitive and pH-responsive nanomaterials that signal infection onset or healing stages. This responsiveness, combined with superior biocompatibility, is transforming chronic wound management.
Nanotechnology In Medical Device Market By Application Insights
Orthopedics remains the dominant application area, where nano-engineered implants help restore mobility and function in aging populations. Nano-coatings on joint replacements reduce rejection rates and improve mechanical strength, while drug-eluting nanostructures aid in post-operative recovery. Companies like Stryker and Zimmer Biomet are leading innovation in nano-enhanced orthopedic implants.
Dentistry is a rapidly growing application, driven by increasing cosmetic dentistry procedures and the need for stronger, longer-lasting materials. Nano-filled composites and adhesives provide superior wear resistance, aesthetic quality, and bonding strength. Dental fillings embedded with nanoparticles of zinc oxide or calcium phosphate reduce secondary decay and promote remineralization, offering substantial clinical benefits.
Nanotechnology In Medical Device Market By End Use Insights
Hospitals constitute the largest end-use segment, as they are primary centers for surgical implantations, emergency wound care, and hearing aid distribution. With growing patient loads and rising complexity of treatments, hospitals increasingly rely on advanced nanotechnology-integrated devices to improve surgical outcomes and reduce hospital-acquired infections.
Clinics are emerging as a fast-growing segment, especially in dentistry and hearing loss applications. Outpatient procedures are rising due to better access to miniaturized, precise instruments. Clinics benefit from the ease of integration of portable diagnostic devices and nano-dental materials that offer same-day restorations, thereby improving patient satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Nanotechnology In Medical Device Market Regional Insights
North America leads the nanotechnology in medical devices market, driven by robust R&D investments, early technology adoption, and a favorable regulatory landscape. The U.S. FDA has taken progressive steps to establish safety and efficacy frameworks for nano-enabled medical products, encouraging commercialization. Academic-industry collaborations are also prevalent, with institutions like MIT and Stanford at the forefront of nanomedicine research.
The region’s aging population, high prevalence of chronic diseases, and advanced healthcare infrastructure make it a fertile ground for innovation. Companies such as Boston Scientific, Medtronic, and Abbott Laboratories are investing heavily in nano-coatings, biosensors, and smart wound healing technologies.
Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing market, fueled by large patient populations, increasing healthcare investments, and growing local manufacturing capabilities. China, India, South Korea, and Japan are investing heavily in nanotechnology R&D for both academic and commercial purposes. Governments are also supporting startups via funding programs, especially in Japan and Singapore.
The region's demand is especially high in orthopedic and dental applications due to the rising elderly population and increasing medical tourism. Additionally, cost-sensitive innovation—such as low-cost nano-silver wound dressings and affordable nano-sensor-based wearables—is expanding access to advanced medical solutions in rural and semi-urban areas.
Some of the prominent players in the nanotechnology in medical devices market include:
Nanotechnology In Medical Device Market Recent Developments
-
March 2025: Medtronic announced successful clinical trials for its nanocoated cardiac stent designed to minimize restenosis and thrombosis risks, with anticipated FDA approval later this year.
-
February 2025: Smith & Nephew introduced a nanofiber-based wound dressing with time-release antibiotics for use in chronic wound management, targeting global diabetic populations.
-
January 2025: Stryker expanded its orthopedic portfolio with a new line of nanostructured titanium spinal implants approved in the EU, citing improved osteointegration performance.
-
December 2024: NanoHearing Aids, a U.S. startup, released a new Bluetooth-enabled hearing device enhanced with nanocoating for sweat and dust resistance, aimed at active senior users.
-
November 2024: Coltene Holding AG launched a dental adhesive incorporating nano-silica particles for enhanced longevity and wear resistance, targeting cosmetic dentistry practices in Asia.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2035. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the nanotechnology in medical devices market
By Type
-
- Orthopedic Implants
- Hearing Aids
- Cardiac Rhythm Management Devices
- Others
- Dental Filling Materials
- Wound Care
- Others
By Application
- Dentistry
- Orthopedics
- Hearing Loss
- Wound Care
- Others
By End Use
By Regional
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa (MEA)

