Negative Pressure Wound Therapy Market Size and Trends
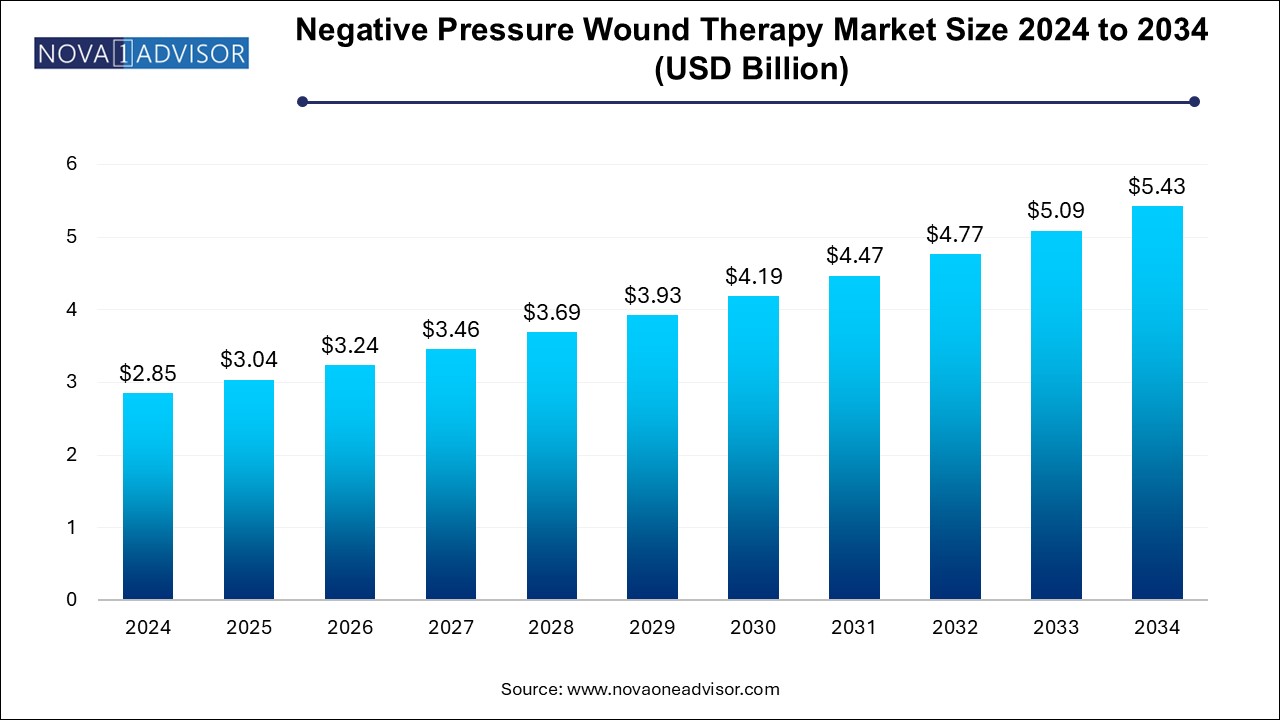
The global negative pressure wound therapy market size was exhibited at USD 2.85 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 5.43 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 6.65% during the forecast period of 2024 to 2034.
Negative Pressure Wound Therapy Market Key Takeaways:
- North America accounted for the highest market share in 2024.
- The conventional segment accounted for the largest market share of 85.0% in 2024.
- The chronic wounds segment dominated the market in 2024.
- The hospital segment dominated the market in 2024 on account of a high volume of patients due to the increasing chronic diseases globally.
Market Overview
Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT) is a transformative wound care modality that involves applying sub-atmospheric pressure to a wound site using a sealed wound dressing connected to a vacuum pump. This therapeutic approach significantly enhances wound healing by removing exudates, reducing edema, promoting perfusion, and facilitating granulation tissue formation. With increasing global awareness of advanced wound care techniques, NPWT has become an indispensable component in the management of both chronic and acute wounds.
The NPWT market has experienced robust growth over the past decade, underpinned by the rising prevalence of diabetes, a growing geriatric population prone to chronic wounds, and a surge in surgical procedures globally. According to data from the International Diabetes Federation, more than 540 million adults are living with diabetes as of 2024, a primary driver of diabetic foot ulcers one of the key applications of NPWT.
Moreover, technological advancements in single-use and portable NPWT devices have expanded accessibility beyond hospital settings to homecare environments, improving patient compliance and clinical outcomes. Countries with high surgical volume, such as the U.S., Germany, China, and India, are witnessing an increasing uptake of NPWT, driven by efforts to minimize post-operative complications and hospital readmissions.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Shift Towards Single-use and Portable NPWT Devices: Increasing demand for ambulatory care has spurred the adoption of lightweight, disposable NPWT systems that offer enhanced mobility for patients.
-
Rising Incidence of Chronic Wounds: The growing burden of chronic diseases such as diabetes and venous insufficiency continues to drive the need for long-term wound management solutions.
-
Technological Integration with Digital Health: Innovations such as remote monitoring, integrated pressure sensors, and cloud connectivity are being embedded into NPWT systems for better patient adherence and clinician oversight.
-
Growing Preference for Home Healthcare: Payers and providers are increasingly shifting wound care services to home settings, driven by cost-effectiveness and patient convenience.
-
Expansion in Emerging Markets: Asia-Pacific and Latin America are witnessing increased healthcare investments and regulatory approvals, fostering adoption of NPWT.
-
Strategic Collaborations and M&A Activities: Companies are forming alliances with hospitals and wound care centers or acquiring niche technology players to strengthen market presence.
Negative Pressure Wound Therapy Market Report Scope
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 3.04 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 |
USD 5.43 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2034 |
CAGR of 6.65% |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2024-2034 |
| Segments Covered |
Product, Wound Type, End-use, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Central and South America; the Middle East and Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled |
3M; Talley Group Ltd (Direct Healthcare Group); Smith+Nephew; Mölnlycke Health Care, Medela AG; DeRoyal Industries, Inc.; Convatec Inc. Cardinal Health; Paul Hartmann AG |
Market Driver: Rising Surgical Procedures Globally
One of the most compelling drivers propelling the NPWT market is the global increase in surgical procedures. As surgical wounds account for a significant proportion of NPWT usage, the sheer rise in inpatient and outpatient surgeries across orthopedic, cardiovascular, and plastic disciplines plays a critical role in market expansion. Surgical site infections (SSIs), which affect approximately 2-5% of patients undergoing surgery in the U.S. according to the CDC, present a major post-operative complication. NPWT has proven efficacy in reducing the risk of SSIs by maintaining a clean wound environment, thus driving adoption. Furthermore, elective surgeries that were deferred during the pandemic are resurging, adding further momentum to NPWT demand.
Market Restraint: High Cost of Advanced NPWT Devices
Despite its clinical efficacy, the high cost associated with NPWT devices and associated consumables remains a substantial market restraint, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. Conventional NPWT systems involve recurring expenses such as canisters, dressings, and maintenance, placing a financial burden on healthcare systems and patients. Reimbursement complexities in certain regions further limit access. Although single-use systems are designed to be cost-effective, they still pose affordability challenges for underinsured populations. This financial barrier restricts market penetration, especially in rural settings where budget allocations for advanced wound care are constrained.
Market Opportunity: Expansion of NPWT in Home Healthcare Settings
The transition of wound care from clinical to home settings represents a lucrative growth opportunity for NPWT providers. Home healthcare adoption is being bolstered by the aging population, healthcare decentralization, and payer incentives to reduce hospital stays. Single-use NPWT devices, which are compact and user-friendly, are particularly suited for home use. Companies that tailor NPWT systems for home application ration for monitoring wound progress remotely further amplifies the market potential in this segment.
Segments Insights:
Negative Pressure Wound Therapy Market By Product Insights
Conventional NPWT devices dominated the market in 2024, attributed to their widespread use in hospitals and surgical centers, especially for complex wounds requiring high exudate management. These systems are equipped with adjustable pressure settings and large-capacity canisters, making them ideal for inpatient care. For example, VAC therapy systems by 3M (formerly KCI) are still considered a gold standard in many healthcare facilities. The dominance of conventional systems is also rooted in their robust clinical validation across various wound types.
Conversely, the single-use NPWT devices segment is projected to witness the fastest growth during the forecast period. These devices cater to the growing preference for outpatient and home-based care. Products like Smith & Nephew’s PICO system are lightweight, canister-free, and designed for ease of use, even by non-professionals. Their expanding application in post-operative incisions and minor chronic wounds makes them increasingly popular, especially in cost-sensitive outpatient scenarios. Moreover, the reduced need for in-person dressing changes also lowers healthcare worker burden, which is highly desirable in strained healthcare environments.
Negative Pressure Wound Therapy Market By Wound Type Insights
Chronic wounds held the largest share of the market, as they require prolonged and intensive management, making them prime candidates for NPWT intervention. Diabetic foot ulcers, in particular, are a leading segment, given the rising diabetes prevalence globally. NPWT helps in controlling infection and enhancing perfusion in ischemic wound beds, making it indispensable for chronic wound therapy. Venous leg ulcers and pressure ulcers are also common in elderly and immobile populations, further reinforcing the market share of this segment.
Meanwhile, the acute wounds segment, especially surgical and traumatic wounds, is poised to grow at the highest CAGR. Increasing surgical procedures and trauma cases from road accidents and burns are central to this growth. NPWT use in acute settings is driven by evidence showing reduced wound healing time, less scarring, and better aesthetic outcomes — vital for trauma and plastic surgeries. Additionally, enhanced recovery protocols in hospitals now routinely include NPWT for post-operative care, fueling further adoption in this segment.
Negative Pressure Wound Therapy Market By End-use Insights
Hospitals dominated the end-use segment, given their advanced infrastructure, trained personnel, and access to reimbursement frameworks for NPWT procedures. Complex surgeries and critical care cases are primarily handled in hospitals, necessitating conventional NPWT systems that are monitored by specialists. Multi-disciplinary wound care teams in tertiary care centers are more likely to use NPWT as part of integrated wound management protocols.
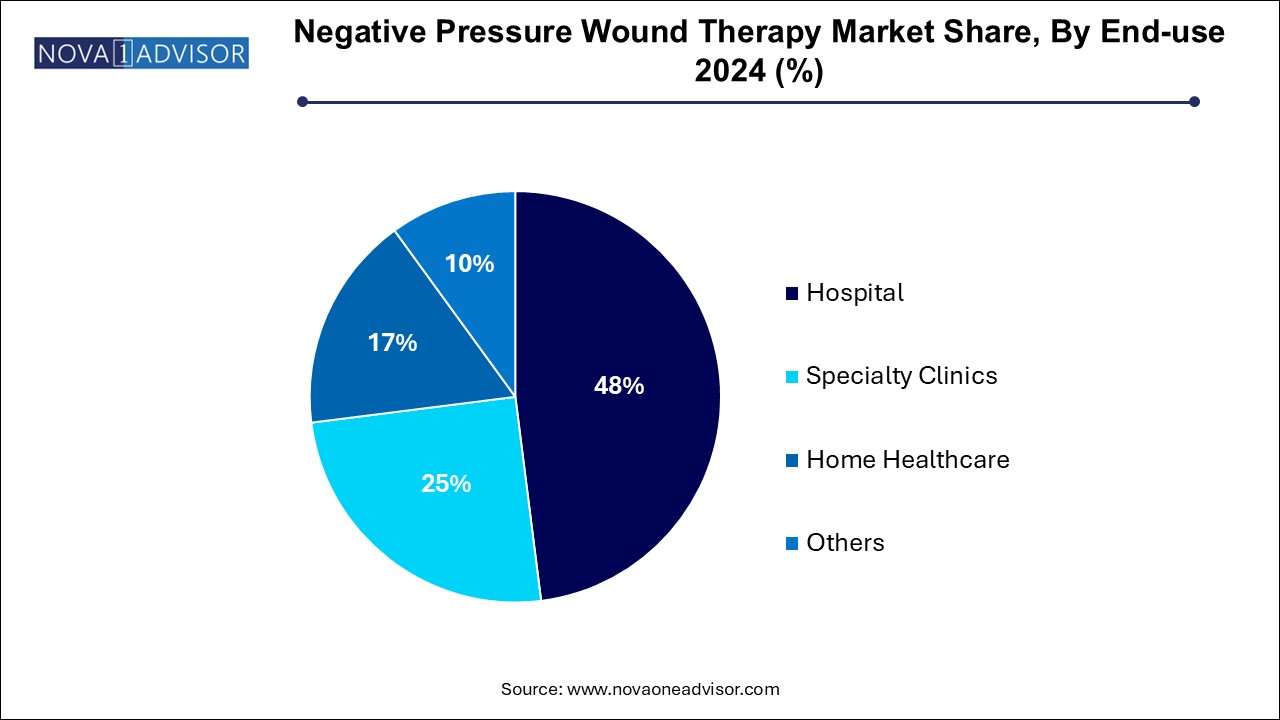
However, the home healthcare segment is expected to witness the fastest growth. This shift is fueled by both economic and patient-centric factors. As more patients are discharged early from hospitals, NPWT is being prescribed for at-home use to complete wound healing. Portable and single-use systems have made it feasible to extend wound care services to home environments without compromising efficacy. Moreover, home care agencies are increasingly investing in staff training for NPWT application, enhancing the practicality of home-based wound management.
Negative Pressure Wound Therapy Market By Regional Insights
North America remains the dominant region in the global NPWT market. The region’s well-established healthcare infrastructure, high surgical volume, favorable reimbursement systems, and strong presence of key market players like 3M and Smith & Nephew significantly contribute to its leadership. The U.S. alone accounts for a large portion of NPWT revenue due to its proactive approach toward chronic disease management and rapid adoption of innovative wound care technologies. Furthermore, initiatives such as Medicare coverage for home-based NPWT further boost usage in the region.
On the other hand, Asia-Pacific is emerging as the fastest-growing region. Rising awareness about advanced wound care, growing incidences of diabetes, and increasing healthcare expenditures are the primary drivers. Countries like China, India, and Japan are witnessing a rise in surgical procedures and chronic wounds, necessitating effective post-operative and chronic wound management. Additionally, international players are entering these markets through partnerships and distribution agreements, further stimulating market penetration. Government investments in healthcare infrastructure and favorable regulatory reforms are also catalyzing growth.
Negative Pressure Wound Therapy Market Recent Developments
-
In February 2024, Smith & Nephew launched a next-generation single-use NPWT system, PICO 7Y, with an integrated belt clip and longer wear time. This innovation is aimed at expanding use in outpatient surgical centers.
-
In October 2023, 3M received FDA clearance for an upgraded version of its V.A.C. Therapy system, featuring enhanced digital connectivity for remote monitoring by clinicians. This step was seen as a strategic move to capitalize on the telehealth trend.
-
In August 2023, Mölnlycke Health Care announced the expansion of its NPWT dressing production facility in Finland to meet rising European demand, indicating strong regional momentum.
-
In May 2023, ConvaTec launched a digital wound documentation platform in combination with its NPWT devices, integrating AI-driven wound progression analytics to support decision-making in clinical settings.
Some of the prominent players in the Negative pressure wound therapy market include:
- 3M
- Talley Group Ltd (Direct Healthcare Group)
- Smith+Nephew
- Mölnlycke Health Care
- Medela AG
- DeRoyal Industries, Inc.
- Convatec Inc.
- Cardinal Health
- Paul Hartmann AG
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the global negative pressure wound therapy market.
By Product
- Conventional NPWT Devices
- Single-use NPWT Devices
- NPWT Accessories
By Wound Type
-
- Pressure Ulcer
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer
- Venous Leg Ulcer
- Others
-
- Surgical & Traumatic Wounds
- Burns
By End-use
- Hospital
- Specialty Clinics
- Home Healthcare
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)


