North America Point Of Care Diagnostics Market Size and Research 2026 to 2035
The North America point of care diagnostics market size was exhibited at USD 21.3 billion in 2025 and is projected to hit around USD 38.71 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 6.16% during the forecast period 2026 to 2035.
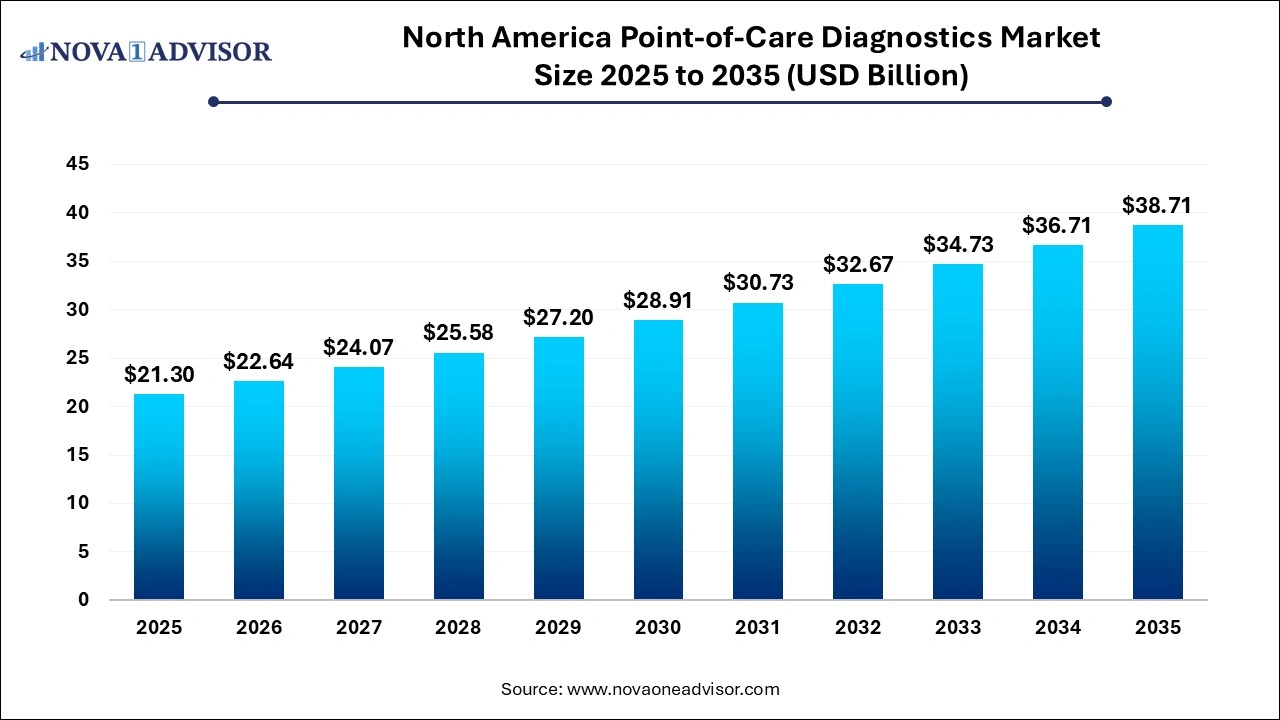
Key Takeaways:
- The infectious diseases segment accounted for 25.3% of the total market share in 2025.
- The hospitals segment dominated the North America point-of-care diagnostics market in 2025, capturing a revenue share of 37.68%..
- The POC devices that are developed have different medical diagnostic applications, such as cancer, infectious diseases, and pregnancy.
- The LDT segment is anticipated to witness the fastest growth rate in the coming years with a CAGR of 6.2%.
North America Point Of Care Diagnostics Market Overview
The North America point of care diagnostics market is experiencing a significant transformation driven by technological innovation, changing healthcare delivery models, and increasing demand for rapid, decentralized diagnostic solutions. Point-of-care diagnostics refer to medical diagnostic testing conducted at or near the site of patient care. This contrasts with conventional laboratory-based testing, enabling faster clinical decision-making, improved disease management, and increased access in both urban and rural settings.
PoC diagnostics have become indispensable tools in emergency care, primary care clinics, pharmacies, and home health monitoring, offering speed and convenience without sacrificing accuracy. Particularly in North America—where the healthcare system is under pressure from an aging population, rising chronic disease burden, and increasing patient expectations—PoC diagnostics are playing a pivotal role in reshaping healthcare pathways. From glucose testing to HbA1c monitoring, PoC devices are not only empowering patients to take control of their health but also alleviating pressure on centralized laboratory infrastructure.
The recent COVID-19 pandemic further underscored the necessity of PoC technologies. Widespread use of rapid antigen and molecular tests helped manage public health response, drive early detection, and prevent hospital overload. Post-pandemic, the market has seen a surge in self-testing, telehealth integration, and digital diagnostics, extending well beyond infectious disease applications. As a result, the North America PoC diagnostics market is entering a mature yet fast-evolving phase, with stakeholders across healthcare, retail, diagnostics, and digital health vying for market leadership.
Major Trends in the North America Point Of Care Diagnostics Market
-
Rise of Home-Based Testing and Self-collection Kits: Consumers are increasingly adopting home test kits for chronic and infectious disease monitoring.
-
Pharmacy-based Diagnostic Expansion: Retail clinics and pharmacies are integrating PoC diagnostics as a frontline triage and testing tool.
-
Digital and Connected PoC Devices: Integration with mobile apps, cloud platforms, and EHRs is enhancing data management and remote care.
-
Growing Use of HbA1c and Glucose Monitoring in Chronic Disease Management: Diabetes care is shifting toward self-monitoring and remote titration.
-
Lab-on-a-Chip Technology Evolution: Miniaturized platforms are enabling multiplex testing at the point of care.
-
Public and Private Reimbursement Expansion: CMS and private payers are widening coverage for PoC testing in clinics and home settings.
-
Shift from Laboratory Developed Tests (LDTs) to FDA-cleared Devices: Regulatory clarity is driving adoption of standardized PoC solutions.
-
CLIA-waived Diagnostic Innovations: More tests are being designed to meet CLIA-waived status, opening broader use in non-lab environments.
Report Scope of The North America Point Of Care Diagnostics Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2026 |
USD 22.64 Billion |
| Market Size by 2035 |
USD 38.71 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2026 to 2035 |
CAGR of 6.16% |
| Base Year |
2025 |
| Forecast Period |
2026-2035 |
| Segments Covered |
Product, End-use, Type, Country |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (USD Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope |
U.S., Canada |
| Key Companies Profiled |
F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG; QIAGEN; Danaher Corporation; BD; bioMérieux SA; Abbott; Siemens Healthineers A.G.; Zoetis, Inc.; Instrumentation Laboratory; Nova Biomedical; Trividia Health, Inc.; Quidel Corporation; Trinity Biotech; Sekisui Diagnostics; OraSure Technologies, Inc.; NIPRO, Spectral Medical, Inc. |
Market Driver – Increasing Prevalence of Chronic Diseases
One of the most significant drivers of the North American PoC diagnostics market is the rising burden of chronic diseases, particularly diabetes, cardiovascular conditions, and renal disorders. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), over 37 million Americans—more than 1 in 10—have diabetes, and around 96 million adults are prediabetic. The importance of timely, accessible monitoring of glucose and HbA1c levels cannot be overstated in preventing complications like kidney failure, cardiovascular events, and neuropathy.
Point-of-care glucose meters and HbA1c devices allow patients and providers to track real-time glycemic status, adjust therapies quickly, and enhance medication adherence. These tools are particularly valuable in outpatient settings, rural health clinics, and home care scenarios where laboratory access may be delayed or absent. The shift from reactive to preventive and personalized medicine is fueling rapid PoC diagnostic adoption. Furthermore, CMS initiatives promoting chronic care management and remote patient monitoring are integrating PoC diagnostics into care protocols, driving demand across the continuum of care.
Market Restraint – Regulatory and Quality Control Challenges
Despite its potential, the PoC diagnostics market in North America is constrained by regulatory hurdles and quality assurance challenges, especially in non-laboratory settings. Point-of-care tests, by their nature, are often conducted by non-laboratory professionals, including nurses, caregivers, pharmacists, or patients themselves. This raises concerns about test interpretation accuracy, operator training, result recording, and sample handling errors.
Moreover, Laboratory Developed Tests (LDTs), while instrumental during emergencies like COVID-19, often lack standardized validation protocols across institutions. The U.S. FDA has announced its intention to regulate LDTs more closely, prompting concern among smaller developers and diagnostic laboratories about compliance burdens. Additionally, CLIA-waived devices must undergo stringent usability and risk assessment, which can delay innovation timelines. This regulatory complexity, while necessary to ensure patient safety, can pose barriers to market entry and limit device scalability.
A major opportunity for the North American PoC diagnostics market lies in the integration of diagnostics with telehealth ecosystems. As virtual consultations become a mainstay in primary and chronic care management, there is growing demand for diagnostic tools that can complement telehealth workflows, especially in patient homes. Self-administered PoC tests that sync results with healthcare providers via apps or cloud-based portals are bridging the gap between virtual care and physical diagnostics.
Companies are increasingly bundling connected glucose monitors, HbA1c kits, and even multi-panel tests for cardiovascular biomarkers with remote patient monitoring services. These integrated solutions enable early intervention, titration of medications, and preventive screenings without requiring in-person visits. The U.S. federal government’s support for remote care billing codes under CMS, combined with private insurers embracing virtual care, is making this a commercially attractive space. Telehealth-compatible diagnostics are expected to redefine patient engagement and clinical efficiency, particularly for patients in rural or mobility-restricted settings.
North America Point Of Care Diagnostics Market
By Product Insights
Glucose testing dominates the product segment, representing a core application of point-of-care diagnostics in North America. With millions of Americans managing diabetes and pre-diabetes, the demand for reliable, fast, and user-friendly glucose monitors is perpetual. Devices like Dexcom G6, Abbott’s FreeStyle Libre, and OneTouch Verio have become staples in both home and clinical settings. These devices empower patients to monitor blood glucose levels in real-time, facilitating tighter glycemic control and reducing long-term complications. Many are now integrated with mobile apps, alert systems, and wearable health trackers, further embedding them into daily routines.
HbA1c testing is the fastest-growing product segment, driven by its growing role in diabetes diagnosis, treatment planning, and long-term management. HbA1c reflects average blood sugar levels over three months and is a vital tool for clinicians and patients to evaluate treatment efficacy. New PoC devices now deliver results within minutes, aiding in same-visit clinical decision-making. This has transformed how endocrinologists and primary care physicians manage diabetic care plans. Devices like Afinion 2 Analyzer (Abbott) and DCA Vantage Analyzer (Siemens Healthineers) are leading this growth, particularly in outpatient clinics, retail pharmacies, and physician offices.
By End-use Insights
Hospitals and laboratories have historically dominated the end-use segment, especially for acute and inpatient testing. Emergency departments and ICUs utilize PoC diagnostics for rapid triage and early management of critical patients. Whether assessing sepsis, cardiac events, or glycemic emergencies, the ability to deliver lab-quality results in minutes enables quicker therapeutic action. Laboratories often validate or complement PoC test results, maintaining clinical integrity in more complex cases.
Home care and self-testing are the fastest-growing end-uses, thanks to the consumerization of healthcare and expanded telehealth infrastructure. Patients with chronic illnesses or mobility limitations are increasingly managing their health from home. Glucose monitors, HbA1c kits, cholesterol tests, and even molecular diagnostics for infections are now available for doorstep delivery. Platforms like LetsGetChecked, Everlywell, and Cue Health are capitalizing on this surge by offering integrated home testing solutions backed by licensed labs and virtual consultations. Self-collection has become a critical trend, particularly post-COVID, when patients sought ways to monitor health without clinic visits.
By Type Insights
LDTs (Laboratory Developed Tests) continue to play a vital role, particularly in reference labs and large healthcare networks that need customized testing panels. Many academic institutions and hospital systems developed LDTs for COVID-19, infectious disease outbreaks, and genetic screening. Their flexibility in response to emerging needs makes them indispensable. However, regulatory uncertainty remains around standardization and FDA oversight.
Commercial PoC devices (Others) are growing faster, driven by regulatory clarity and industrial scaling. FDA-cleared, CLIA-waived PoC tests from companies like Abbott, Roche, and Bio-Rad are seeing wide adoption due to their reliability, scalability, and ease of use. These standardized tests are becoming staples in urgent care centers, pharmacies, and outpatient clinics, offering a balance of speed, accuracy, and regulatory compliance.
North America Point Of Care Diagnostics Market By Country Insights
United States
The U.S. is the dominant country in the North American point-of-care diagnostics market, accounting for the majority of revenue, innovation, and clinical adoption. The country benefits from a robust diagnostics ecosystem, with leading companies like Abbott, Danaher (Cepheid), QuidelOrtho, and Bio-Rad Laboratories headquartered here. The FDA’s Emergency Use Authorizations (EUAs) during the pandemic accelerated device approvals, while CLIA-waiver programs have enabled widespread PoC use in non-laboratory settings.
Retail pharmacies, urgent care centers, and direct-to-consumer models have all expanded significantly in the U.S., democratizing access to diagnostics. Federal programs like Medicare’s Chronic Care Management, Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) reimbursements, and Biden’s Cancer Moonshot 2.0 are promoting decentralized diagnostics and earlier detection. With healthcare shifting toward personalized, proactive care, the U.S. market for PoC diagnostics will remain a global leader.
Canada
Canada is the fastest-growing market in North America for point-of-care diagnostics, largely due to its efforts to reduce strain on primary care and improve rural access. Canadian provinces are investing in telehealth and digital diagnostics, enabling broader use of home-based and pharmacy-based testing. The Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health (CADTH) is actively reviewing PoC innovations to fast-track adoption in community clinics and rural health centers.
Increased demand for rapid COVID-19 testing also raised public awareness and institutional adoption of PoC devices. Post-pandemic, PoC solutions are being deployed for diabetes management, respiratory infections, and mental health screenings. Companies are partnering with provincial health systems to pilot diagnostic kiosks, mobile vans, and remote monitoring hubs. With favorable policy frameworks and rising consumer interest, Canada is on track for sustained PoC diagnostic growth.
Some of the prominent players in the North America point of care diagnostics market include:
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG
- QIAGEN
- Danaher Corporation
- BD
- bioMérieux SA
- Abbott
- Siemens Healthineers A.G.
- Zoetis, Inc.
- Instrumentation Laboratory
- Nova Biomedical
- Trividia Health, Inc.
- Quidel Corporation
- Trinity Biotech
- Sekisui Diagnostics
- OraSure Technologies, Inc.
- NIPRO
- Spectral Medical, Inc.
Recent Developments
-
April 2025 – Abbott launched its next-gen FreeStyle Libre 4, featuring real-time glucose tracking, AI-powered alerts, and compatibility with telehealth platforms.
-
March 2025 – Cue Health received Health Canada authorization for its COVID-19 & influenza multiplex PoC test, marking its Canadian market entry.
-
January 2025 – BD and Walgreens expanded their partnership to roll out HbA1c and cholesterol PoC tests across 1,000 retail locations in the U.S.
-
November 2024 – Siemens Healthineers introduced an AI-powered PoC analyzer for physician offices, integrating ECG, glucose, and lipid profile tests.
-
September 2024 – Bio-Rad Laboratories received FDA clearance for a new CLIA-waived PoC HbA1c analyzer designed for community health centers.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2035. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the North America point of care diagnostics market
Product
- Glucose Testing
- HbA1c Testing
End-use
- Hospitals
- Laboratories
- Home Care
-
- Self-testing
- Self-collection
-
- Physician Office
- Pharmacy & Retail Clinics
- Non-practice Clinics
- Urgent Care Clinics
- Others
-
-
- Rural Health Clinic
- Federally Qualified Health Clinic (FQHC)
Type
Country

