Pancreatic Cancer Treatment Market Size and Trends
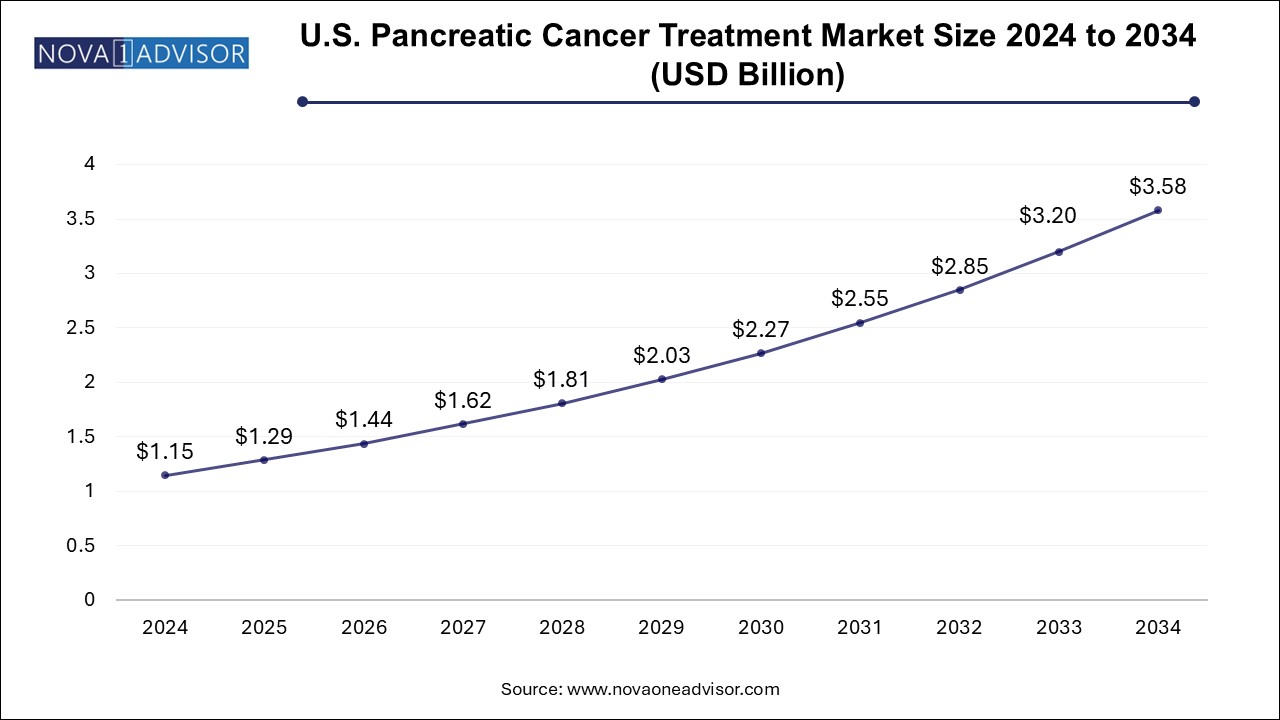
The pancreatic cancer treatment market size was exhibited at USD 3.28 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 10.47 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 12.31% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
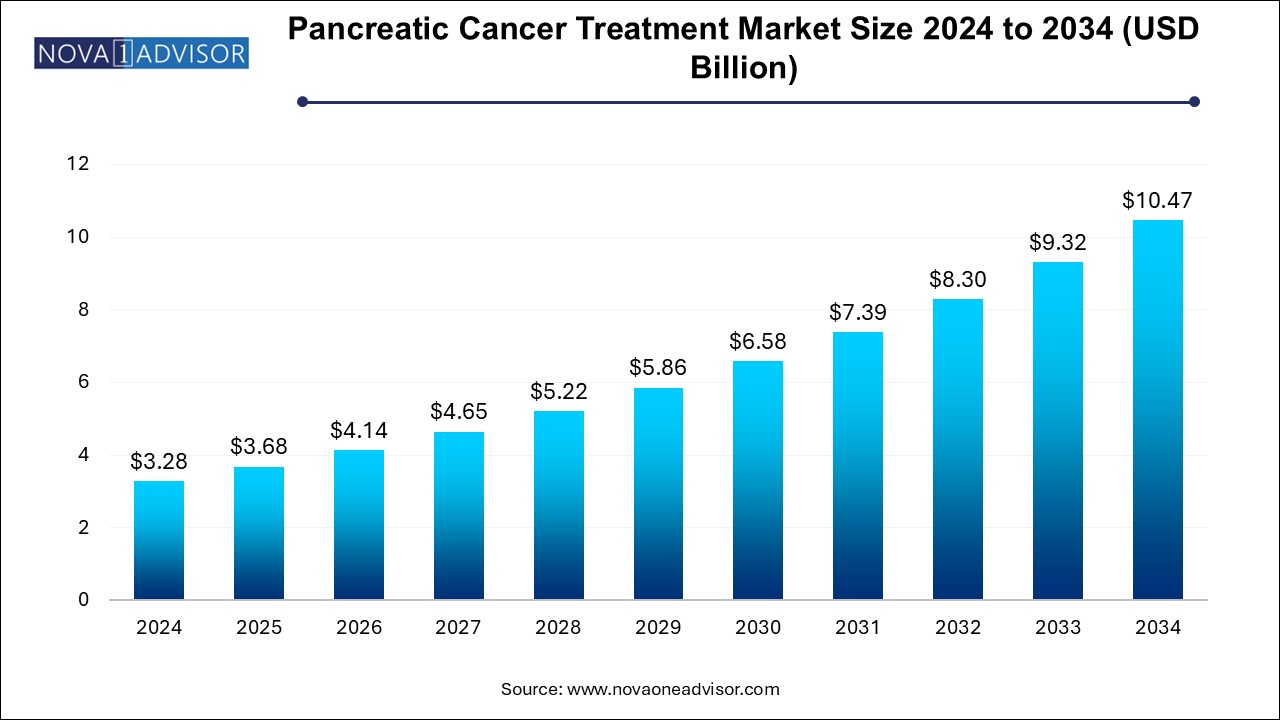
U.S. Pancreatic Cancer Treatment Market Size and Growth 2025 to 2034
The U.S. pancreatic cancer treatment market size is evaluated at USD 1.0 billion in 2024 and is projected to be worth around USD 3.1 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 10.83% from 2025 to 2034.
North America dominates the pancreatic cancer treatment market due to its advanced healthcare infrastructure, strong presence of biopharmaceutical companies, and high disease awareness. The United States, in particular, accounts for the majority of regional revenue, with extensive investment in oncology R&D, early adoption of novel therapeutics, and active clinical trial participation. Institutions like MD Anderson and Memorial Sloan Kettering lead cutting-edge pancreatic cancer research and care.
Additionally, favorable reimbursement structures, fast-track FDA designations, and growing genomic testing adoption support rapid market access for new therapies. The increasing integration of precision medicine and electronic health records (EHR) in U.S. oncology practices allows for data-driven treatment decisions, further enhancing market efficiency and patient outcomes.
Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing market, driven by rising cancer incidence, expanding healthcare infrastructure, and government focus on oncology care. Countries such as China, India, Japan, and South Korea are witnessing a surge in pancreatic cancer cases due to aging populations, lifestyle changes, and environmental exposures. Simultaneously, improvements in diagnostic capabilities and awareness campaigns are enabling earlier identification of cases.
Japan, with its universal healthcare system and strong pharmaceutical R&D base, plays a leading role in adopting new treatments. Meanwhile, China is investing heavily in local biotech innovation, clinical trial capacity, and national cancer care guidelines. Regional players are forming licensing partnerships with global drug makers to commercialize therapies faster. As affordability improves and biomarker testing becomes more prevalent, Asia Pacific is set to significantly influence the future trajectory of the pancreatic cancer treatment market.
Market Overview
The pancreatic cancer treatment market is a critical component of the global oncology therapeutics sector, reflecting both the urgency and complexity of addressing one of the most lethal malignancies. Pancreatic cancer, often diagnosed at advanced stages due to the lack of early symptoms and reliable screening methods, remains a significant clinical challenge with a five-year survival rate that continues to lag behind most other cancers. This has prompted robust research initiatives, strategic investments by pharmaceutical companies, and growing healthcare awareness efforts globally.
Pancreatic cancer can be classified primarily into two categories: exocrine tumors, which account for the vast majority of cases (over 90%), and endocrine tumors, also referred to as pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PNETs). While chemotherapy remains the cornerstone of treatment, innovations in radiation therapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and combination regimens are increasingly gaining ground. Regulatory approvals of new drug entities, companion diagnostics, and personalized treatment strategies are accelerating market evolution.
With the global burden of pancreatic cancer rising due to factors such as aging populations, smoking, obesity, and chronic pancreatitis, healthcare systems and biopharmaceutical companies are working together to bring forth novel therapeutic solutions. Strategic collaborations, clinical trial accelerations, and patient-centric drug development are expected to redefine the landscape of pancreatic cancer treatment through 2034. The market stands at a pivotal point, where unmet needs are being addressed through scientific rigor, technological integration, and enhanced clinical focus.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Rising Adoption of Combination Therapies (Chemotherapy + Targeted/Immunotherapy)
-
Increased Clinical Trial Activity for Immunotherapies and CAR-T Cell Therapies
-
Development of Biomarker-Based and Companion Diagnostic Solutions
-
Growing Pipeline of Drugs Targeting KRAS and BRCA Mutations
-
Expansion of Patient Access Programs and Reimbursement Policies in Emerging Markets
-
Use of Artificial Intelligence in Drug Discovery and Precision Oncology
-
Increased Role of Proton Therapy and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT)
-
Integration of Genomic Profiling for Personalized Treatment Approaches
-
Strategic Alliances Between Pharma and Research Institutes to Accelerate Innovation
-
Rising Demand for Outpatient Chemotherapy and Home-Based Oncology Care Models
Report Scope of Pancreatic Cancer Treatment Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 3.68 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 |
USD 10.47 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2025 to 2034 |
CAGR of 12.31% |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2034 |
| Segments Covered |
Type, Treatment, Distribution Channel, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Accuray Incorporated; AstraZeneca; Novartis AG; Pfizer Inc.; Genentech, Inc. (F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd); Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; Ipsen Pharma; Eli Lilly and Company; Siemens Healthineers AG (Varian Medical Systems, Inc.); Elekta AB |
Market Driver: High Unmet Medical Need and Rising Incidence Rates
A key driver of the pancreatic cancer treatment market is the significant unmet clinical need, combined with a rising global incidence rate. According to the Global Cancer Observatory (GLOBOCAN), pancreatic cancer was among the top ten causes of cancer-related deaths worldwide in 2022. Its silent progression and resistance to conventional treatments often result in late diagnosis and poor prognosis. This has created an urgent need for effective, safe, and accessible treatment modalities.
The increasing incidence is driven by risk factors such as aging, smoking, alcohol consumption, obesity, and diabetes. The fact that most patients are diagnosed at stage III or IV further underscores the need for systemic therapies with strong survival benefits. This urgency has translated into increased funding, fast-track drug approvals, and public-private collaborations in drug development. Pharmaceutical companies are now prioritizing pancreatic cancer in their oncology portfolios, aiming to improve progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) outcomes through new therapeutic combinations.
Market Restraint: Limited Early Detection and Therapy Resistance
Despite ongoing innovation, one of the major restraints hampering market growth is the lack of reliable early detection methods and high therapy resistance. Pancreatic cancer symptoms, such as jaundice, abdominal pain, and weight loss, often manifest only in advanced stages. Additionally, existing diagnostic modalities—like imaging and tumor markers (e.g., CA19-9)—lack sensitivity and specificity for early-stage detection.
Moreover, pancreatic tumors exhibit poor immunogenicity and are often surrounded by a dense stromal microenvironment that impedes drug penetration. Resistance to chemotherapy regimens like FOLFIRINOX and gemcitabine+nab-paclitaxel also remains a clinical hurdle. This limits the efficacy window of currently approved drugs and complicates the development of standardized protocols. Addressing this restraint requires significant advances in liquid biopsy, tumor sequencing, and drug delivery systems—areas that are still in the early adoption phase globally.
Market Opportunity: Expansion of Precision Oncology and Targeted Therapeutics
A transformative opportunity in the pancreatic cancer treatment market lies in the expansion of precision oncology and the rise of targeted therapeutics. Advances in molecular biology and genomic sequencing have identified key genetic mutations—such as KRAS, BRCA1/2, and CDKN2A—that play critical roles in pancreatic tumor development and progression. This has led to the development of novel targeted agents and companion diagnostics.
For instance, patients with BRCA mutations can now benefit from PARP inhibitors like olaparib, which delay disease progression in maintenance settings. Similarly, KRAS G12C inhibitors are showing promise in early-phase trials. Precision medicine enables oncologists to tailor treatments based on individual tumor biology, improving efficacy and minimizing toxicity. As multi-gene testing becomes more accessible and reimbursed, the integration of targeted therapy is expected to revolutionize pancreatic cancer management, particularly in the metastatic and recurrent settings.
Pancreatic Cancer Treatment Market By Type Insights
Based on type, The Exocrine pancreatic cancer, especially pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), accounts for the vast majority of diagnosed cases globally and continues to dominate the market. This subtype is characterized by aggressive behavior, early metastasis, and limited responsiveness to traditional treatment modalities. Due to its prevalence and high mortality, most clinical trials and drug development pipelines are focused on this segment. Treatments often include chemotherapy (gemcitabine, FOLFIRINOX), radiation, and, in select cases, surgical resection with adjuvant therapy.
In contrast, endocrine pancreatic tumors, while rarer, are showing the fastest growth in terms of diagnosis and treatment innovation. These tumors, also known as pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PNETs), generally have a more indolent course but may metastasize over time. Recent advances in somatostatin analogs, targeted therapies like everolimus and sunitinib, and peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) have improved the management of PNETs. Their increasing diagnosis—supported by imaging and awareness—is expanding this subsegment's market share steadily.
Pancreatic Cancer Treatment Market By Treatment Insights
Based on chemotherapy remains the standard of care and the most dominant treatment modality for pancreatic cancer. Regimens like FOLFIRINOX (5-FU, leucovorin, irinotecan, and oxaliplatin) and gemcitabine plus nab-paclitaxel are widely used for advanced-stage disease and in adjuvant settings. Despite the emergence of targeted therapies, chemotherapy continues to be the first-line treatment due to its broad applicability and survival benefit. The ease of administration and availability across geographies also supports its market dominance.
However, radiation therapy—particularly advanced techniques such as stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) and proton beam therapy—is experiencing the fastest growth. These modalities allow high-precision radiation delivery to pancreatic tumors while sparing healthy tissues. In borderline resectable and locally advanced cases, SBRT is being used in neoadjuvant settings to shrink tumors for surgical eligibility. With continued investment in radiation oncology infrastructure and clinical validation, radiation therapy is emerging as a vital component of multimodal treatment strategies.
Pancreatic Cancer Treatment Market By Distribution Channel Insights
The hospital pharmacies segment held the largest revenue share of 47.0% in 2024. The nature of these treatments—requiring clinical supervision, infusion setups, and oncologist monitoring—necessitates hospital-based delivery. Hospitals also serve as primary hubs for clinical trials, making them essential access points for investigational therapies and newly approved drugs.
However, retail pharmacies are beginning to play a growing role, especially in the distribution of oral chemotherapeutic agents and targeted therapies. As more treatments become available in pill form (e.g., capecitabine, olaparib), patients prefer the convenience of at-home medication access. This shift is particularly notable in high-income countries with established e-prescription networks and insurance coverage for specialty drugs. The expansion of patient support programs and oncology-trained pharmacists in retail settings further supports this trend.
Some of the prominent players in the pancreatic cancer treatment market include:
Pancreatic Cancer Treatment Market Recent Developments
-
March 2025: AstraZeneca announced FDA approval for the expanded use of Lynparza (olaparib) in BRCA-mutated pancreatic cancer as a maintenance therapy following first-line chemotherapy.
-
February 2025: Amgen reported promising results from its Phase II trial of sotorasib, a KRAS G12C inhibitor, in pancreatic cancer patients with resistant mutations.
-
January 2025: Roche launched a multi-center study in collaboration with Flatiron Health to explore real-world outcomes of atezolizumab in pancreatic adenocarcinoma.
-
December 2024: Bristol-Myers Squibb initiated a global trial of nivolumab plus chemotherapy in advanced pancreatic cancer, marking one of the largest immunotherapy combinations under investigation for this indication.
-
November 2024: Eisai Co., Ltd. partnered with a Singapore-based AI biotech firm to accelerate drug discovery in pancreatic and gastrointestinal cancers through computational modeling.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the pancreatic cancer treatment market
By Type
By Treatment
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation Therapy
- Others
By Channel
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Retail Pharmacies
- Others
By Regional
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa (MEA)


