Pediatric Cardiac Surgery Market Size and Growth
The global pediatric cardiac surgery market size was valued at USD 15.69 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to reach around USD 40.33 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 9.9% from 2024 to 2033.
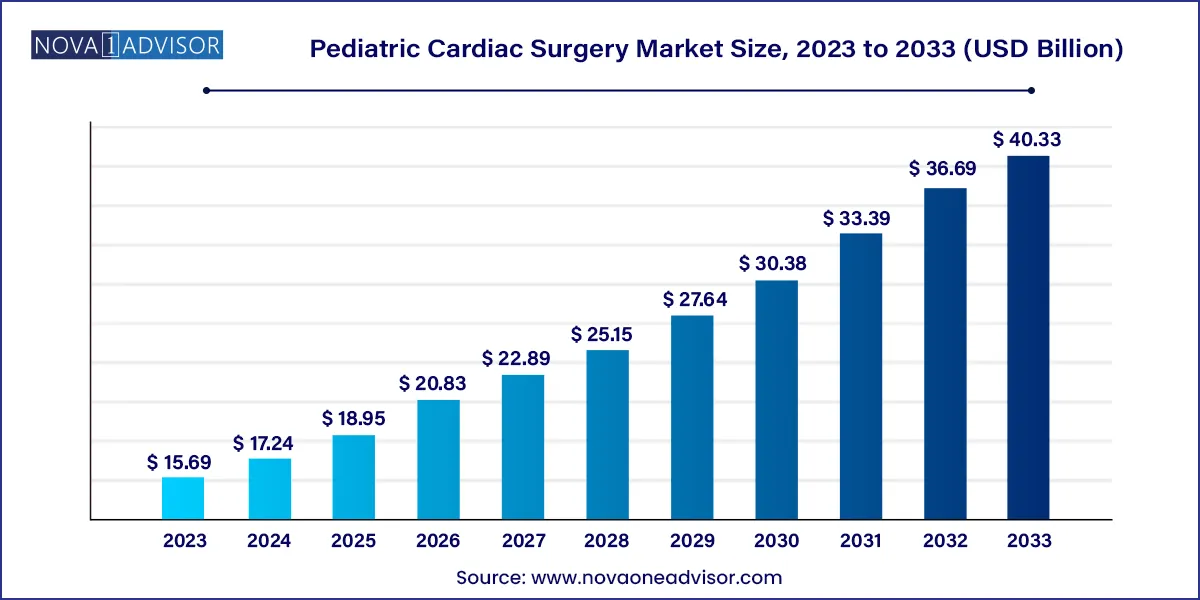
Pediatric Cardiac Surgery Market Key Takeaways
- The interventional procedures segment accounted for the largest market share of 53.87% in 2023.
- The heart rhythm management procedures segment is expected to grow at a lucrative CAGR over the forecast period.
- The hospitals segment accounted for the largest market share of 48.11% in 2023.
- Special centers are anticipated to grow at the fastest CAGR over the forecast period.
Market Overview
The Pediatric Cardiac Surgery Market plays a pivotal role in addressing congenital and acquired heart conditions in infants, children, and adolescents. This market encompasses a broad array of medical procedures, technologies, and care models aimed at correcting structural heart defects, rhythm disorders, and vascular complications in the pediatric population. With increasing global awareness of congenital heart diseases (CHDs), coupled with advancements in pediatric cardiology and surgical methods, the market is witnessing robust growth.
Congenital heart defects are among the most common birth anomalies, affecting roughly 1 in every 100 live births, and accounting for a significant proportion of neonatal and infant mortality globally. In recent years, the availability of minimally invasive techniques, real-time imaging, catheter-based interventions, and robotic surgeries has revolutionized pediatric cardiac care. These innovations reduce the need for traditional open-heart procedures and offer faster recovery, lower risk, and shorter hospital stays.
Government initiatives, philanthropic funding, and institutional investments in pediatric cardiac programs have enhanced the availability and affordability of care in both developed and developing nations. Simultaneously, the growth in pediatric intensive care units (PICUs), rising birth rates, and improved diagnostic screening for heart anomalies in utero and shortly after birth are key enablers of market expansion.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Adoption of Minimally Invasive and Hybrid Procedures: Pediatric cardiologists and surgeons are increasingly leveraging catheter-based techniques and robotic tools to reduce surgical trauma and recovery time.
-
Integration of Artificial Intelligence and 3D Printing: AI is aiding in personalized diagnostics and surgical planning, while 3D-printed heart models are used for simulation and education before complex surgeries.
-
Expansion of Pediatric Heart Centers in Emerging Markets: Countries like India, Brazil, and China are witnessing investment in dedicated pediatric heart hospitals and training programs.
-
Telemedicine and Cross-border Collaborations: Virtual consultations and international surgical collaborations are enabling access to expert care in remote and underserved regions.
-
Rise of Specialized Pediatric Cardiac Registries: Data from multicenter registries are helping clinicians benchmark outcomes, optimize care, and accelerate clinical research.
-
Focus on Post-operative Quality of Life: Emphasis is growing on long-term follow-up, neurodevelopmental outcomes, and psychosocial support post pediatric heart surgery.
-
Increased Funding for Rare Pediatric Cardiac Conditions: Non-profits and global health agencies are focusing on neglected cardiac diseases, including complex cyanotic defects and rheumatic heart disease in children.
Pediatric Cardiac Surgery Market Report Scope
| Report Attribute |
Details |
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 17.24 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 |
USD 40.33 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 |
CAGR of 9.9% |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024 to 2033 |
| Segments Covered |
Procedure, end-use, region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage |
Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Cedars-Sinai Medical Center; NYU Langone; Hospitals; Mount Sinai Hospital; Stanford Health Care-Stanford Hospital; Heart Center Hirslanden Zurich; Medical University of Vienna, Department of Cardiology; University Medical Center Hamburg; Columbia Asia Hospitals; Brigham and Women’s Hospital; Saint Luke’s Mid America Heart Institute |
Key Market Driver: Increasing Prevalence of Congenital Heart Defects (CHDs)
A major driver fueling the growth of the pediatric cardiac surgery market is the rising prevalence of congenital heart defects globally. CHDs represent one of the most common and serious birth defects, accounting for significant morbidity and mortality in infants and children. According to the CDC and other global health organizations, CHDs affect around 1.35 million newborns annually worldwide, with a higher burden in regions with limited access to early screening and intervention.
As neonatal intensive care capabilities advance, more infants born with severe cardiac malformations are surviving the perinatal period, thus requiring early surgical intervention. Procedures to correct atrial septal defects (ASDs), ventricular septal defects (VSDs), patent ductus arteriosus (PDA), and Tetralogy of Fallot are becoming increasingly routine in specialized pediatric centers.
Additionally, improvements in fetal echocardiography and prenatal screenings allow for early diagnosis and pre-birth planning, significantly increasing the chances of successful postnatal surgical outcomes. These factors collectively contribute to sustained demand for pediatric cardiac surgery.
Key Market Restraint: Shortage of Pediatric Cardiac Surgeons and Specialized Facilities
Despite technological advancements, the market faces a critical restraint in the form of a limited number of trained pediatric cardiac surgeons and specialized hospitals, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. Pediatric cardiac surgery requires high expertise, multidisciplinary teams, and advanced post-operative care capabilities, which are not universally available.
Even in developed countries, wait times for complex pediatric surgeries can be long due to workforce shortages and logistical bottlenecks. For example, rural and underserved communities in the U.S. face access issues due to the concentration of pediatric cardiac services in urban academic centers.
In regions like Sub-Saharan Africa and parts of Southeast Asia, the disparity is even starker, with some countries lacking a single pediatric heart surgeon per million population. This imbalance restricts the global availability of timely and high-quality care, leading to preventable deaths and suboptimal outcomes in many parts of the world.
Key Market Opportunity: Technological Integration in Surgical Planning and Execution
A transformative opportunity lies in the integration of cutting-edge technology such as robotic surgery, AI-guided diagnostics, 3D printing, and virtual reality simulations into pediatric cardiac surgical workflows. These technologies offer precise, patient-specific planning and execution of complex interventions, thereby improving success rates and reducing complications.
For instance, 3D printing enables surgeons to replicate the patient’s heart anatomy, helping them rehearse surgeries and plan incisions with precision. AI tools can assist in image analysis, risk stratification, and outcome prediction, enabling proactive and personalized surgical approaches. Robotic-assisted techniques, though currently used more in adult cardiology, are gradually being adapted for pediatric cases as devices become smaller and more responsive.
By investing in these technologies, hospitals and surgical centers can optimize resource use, enhance training, and reduce intraoperative and post-operative risks, thereby making advanced care more accessible and sustainable.
Pediatric Cardiac Surgery Market By Procedure Insights
Interventional procedures dominated the market, primarily due to their minimally invasive nature, shorter recovery periods, and increasing use for conditions such as atrial septal defects, coarctation of the aorta, and pulmonary valve stenosis. Catheter-based interventions, including balloon angioplasty, device closures, and stenting, are increasingly preferred for moderate defects and post-surgical corrections. These procedures can often be performed in outpatient settings or with shorter hospital stays, improving cost-effectiveness and patient comfort.
Heart rhythm management procedures are the fastest-growing segment, owing to the increasing diagnosis of pediatric arrhythmias and the rising use of pacemakers and implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) in children with congenital or post-operative rhythm disorders. Advancements in pediatric electrophysiology, including leadless pacing and cryoablation, are driving this segment forward. Specialized electrophysiology labs and improved diagnostic mapping tools are enabling more accurate interventions in this complex area.
Pediatric Cardiac Surgery Market By End-use Insights
Hospitals dominated the end-use segment, especially tertiary care and academic institutions with dedicated pediatric cardiac units. These facilities have the infrastructure, multidisciplinary teams, and intensive care capacity required for comprehensive pediatric heart surgery. Most high-risk and complex surgeries are performed in hospital settings where post-operative monitoring and emergency interventions can be readily managed. Teaching hospitals also serve as referral centers for surrounding regions, driving patient volume and research initiatives.
Specialty centers are the fastest-growing end-use category, particularly freestanding pediatric cardiology clinics and dedicated children’s hospitals. These centers offer focused expertise, integrated diagnostic and therapeutic services, and increasingly, outpatient-based surgical interventions. In the U.S. and Europe, the model of comprehensive specialty heart centers is gaining popularity, offering families coordinated, patient-centric care across diagnostics, surgery, and rehabilitation under one roof.
Pediatric Cardiac Surgery Market By Regional Insights
North America leads the pediatric cardiac surgery market, underpinned by its advanced healthcare infrastructure, high diagnosis rates, and early adoption of innovative surgical technologies. The U.S. is home to some of the world’s leading pediatric cardiac centers such as Boston Children’s Hospital, Texas Children’s Hospital, and Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, which serve as centers of excellence and research innovation.
Government-funded programs, strong private insurance coverage, and public awareness drive early diagnosis and intervention. Additionally, the region benefits from the presence of global device manufacturers and frequent FDA approvals for pediatric-specific surgical tools and implants.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing market, driven by population growth, increasing congenital disease burden, and expanding healthcare access. Countries like India, China, and Indonesia are investing in public and private cardiac centers that include pediatric surgery units. NGOs and global partnerships have also accelerated the establishment of low-cost, high-quality surgical programs in this region.
Innovative cost-containment strategies, increasing insurance penetration, and telemedicine are facilitating access to pediatric cardiac care in both urban and semi-urban areas. With continued economic growth and government support, Asia-Pacific is set to witness a rapid expansion in pediatric cardiac surgical capacity over the next decade.
Pediatric Cardiac Surgery Market Top Key Companies:
The following are the leading companies in the pediatric cardiac surgery market. These companies collectively hold the largest market share and dictate industry trends.
- Cedars-Sinai Medical Center
- NYU Langone Hospitals
- Mount Sinai Hospital
- Stanford Health Care-Stanford Hospital
- Heart Center Hirslanden Zurich
- Medical University of Vienna, Department of Cardiology
- University Medical Center Hamburg
- Columbia Asia Hospitals
- Brigham and Women’s Hospital
- Saint Luke’s Mid America Heart Institute
Pediatric Cardiac Surgery Market Report Segmentation
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Pediatric Cardiac Surgery market.
By Procedure
- Interventional Procedures
- Peripheral Vascular Procedures
- Heart Rhythm Management Procedures
By End-use
- Hospitals
- Specialty Centers
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)

