Portable Ultrasound Devices Market Size and Research 2026 to 2035
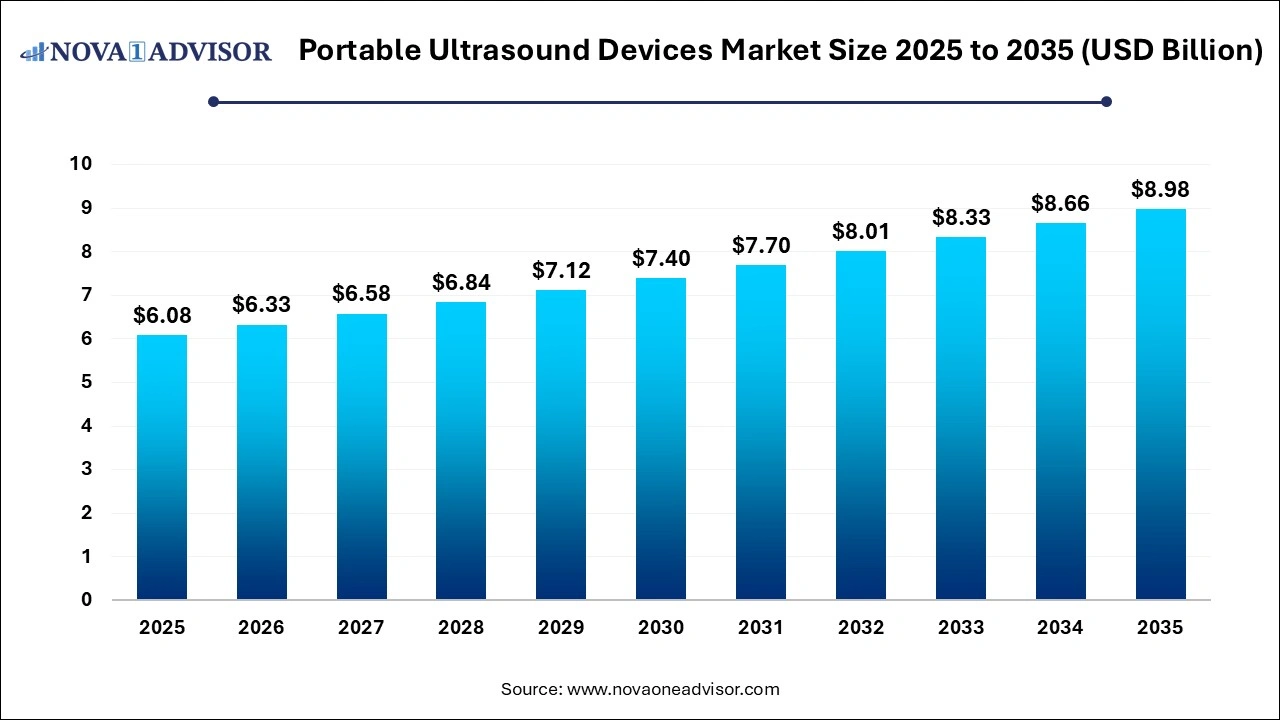
The portable ultrasound devices market size was exhibited at USD 6.08 billion in 2025 and is projected to hit around USD 8.98 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 3.98% during the forecast period 2026 to 2035. The portable ultrasound devices market expansion is driven by the rising demand for cost-effective and reliable point-of-care diagnostic technologies, shift towards decentralized healthcare, technological advancements and increased patient preference for non-invasive diagnostic procedures.
Portable Ultrasound Devices Market Key Takeaways:
- The cart/trolley segment dominated, with a market share of 65.9% in 2025.
- The handheld ultrasound devices segment is expected to grow fastest over the forecast period.
- The obstetrics/gynecology segment significantly dominated the ultrasound market, capturing a revenue share of over 46.6% in 2025.
- The cardiovascular segment is expected to grow exponentially over the forecast period.
- The Doppler portable ultrasound segment dominated the market, capturing a revenue share of over 46.8% in 2025.
- The Doppler ultrasound segment is expected to witness the fastest growth over the forecast period.
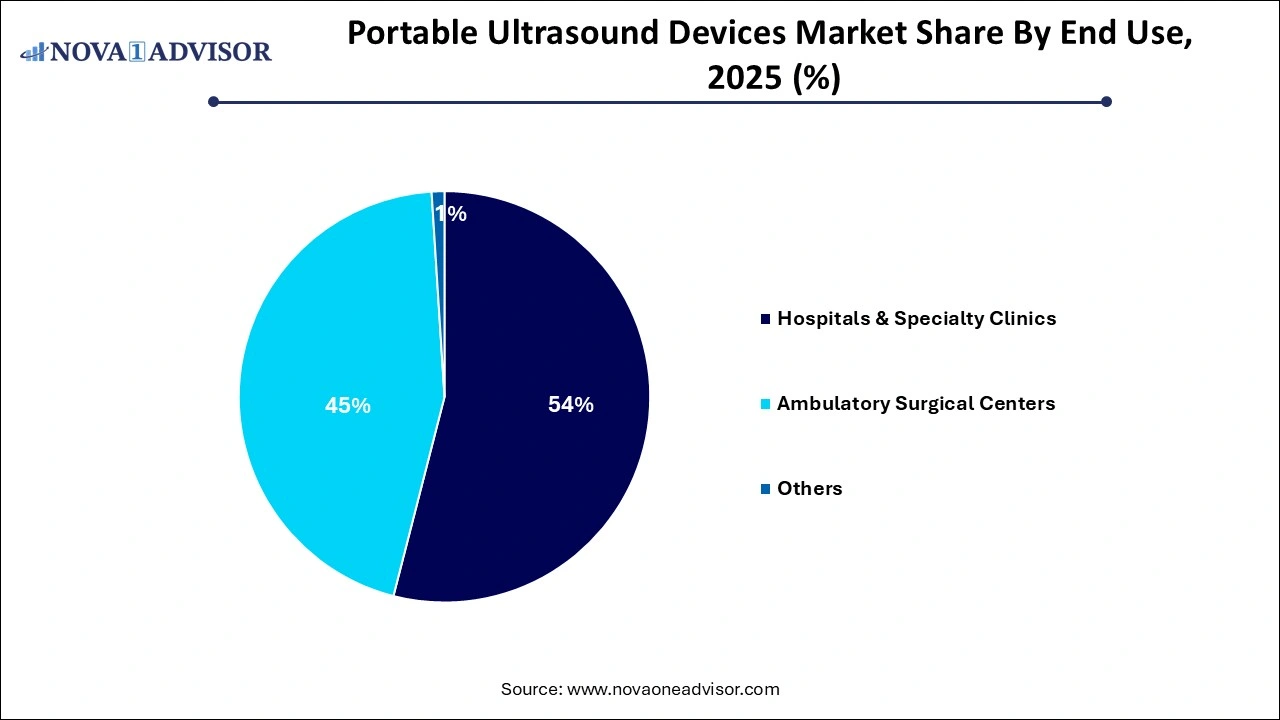
- Hospitals & specialty clinics dominated the ultrasound market and held a revenue share of over 54% in 2025.
- The ambulatory surgical centers (ASC) segment is projected to experience the fastest growth over the forecast period.
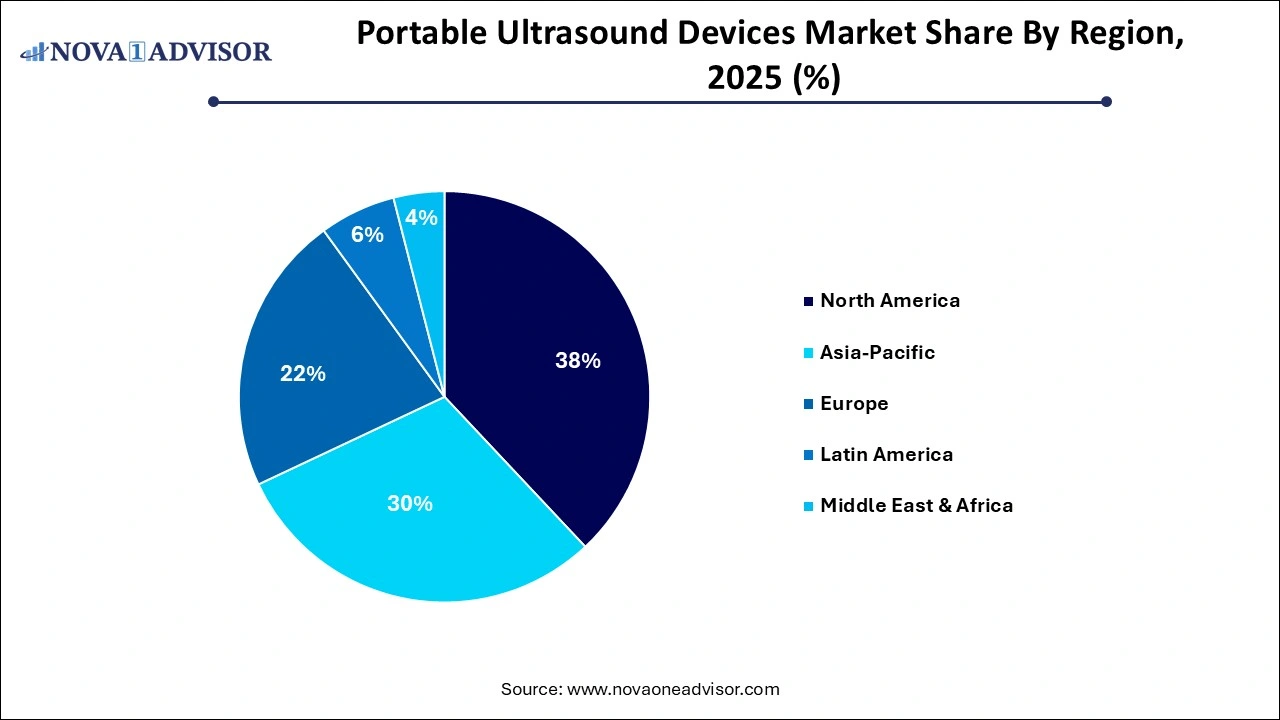
- North America portable ultrasound devices market dominated the overall global market and accounted for 38% of revenue share in 2025.
Portable Ultrasound Devices Market Overview
The portable ultrasound devices market has undergone a revolutionary transformation in recent years, emerging as one of the most dynamic segments of diagnostic imaging. Portable ultrasound systems offer non-invasive, real-time imaging in compact formats, allowing clinicians to assess, diagnose, and monitor patients at the bedside, in ambulatory settings, and even in remote or resource-limited environments. As healthcare increasingly moves toward decentralization, point-of-care diagnostics, and patient-centric care, portable ultrasound systems have become indispensable.
Traditionally limited to large hospital-based systems, ultrasound imaging is now evolving with handheld devices, compact trolleys, and wireless probes connected to smartphones and tablets. These devices are now capable of delivering high-resolution 2D, 3D, 4D, and Doppler imaging, rivaling the diagnostic performance of conventional machines. From cardiology and obstetrics to emergency care and sports medicine, their versatility is driving broader adoption across multiple specialties.
The COVID-19 pandemic further accelerated the uptake of portable ultrasound devices, particularly for lung imaging, cardiac assessment, and vascular access. Physicians and intensivists worldwide utilized these systems for bedside triage and monitoring, emphasizing their critical role in infectious and acute care scenarios. Furthermore, growing global healthcare access initiatives, particularly in rural and underserved regions, are increasing demand for affordable, portable imaging tools.
With advances in battery life, wireless connectivity, image resolution, and AI-assisted imaging, the portable ultrasound landscape is entering a new era. It not only bridges the gap between centralized and remote diagnostics but also plays a critical role in telemedicine and global health efforts. This market is poised for robust expansion, supported by shifting clinical practices, rising chronic disease prevalence, and increasing technological innovation.
Major Trends in the Portable Ultrasound Devices Market
-
Miniaturization and AI Integration: Continuous downsizing of ultrasound probes and integration with AI for auto-interpretation and anomaly detection.
-
Wireless and App-based Connectivity: Increasing use of app-controlled ultrasound probes that connect with mobile devices via Wi-Fi or Bluetooth.
-
Expansion of Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS): Surge in demand across ER, ICU, and ambulatory care for rapid diagnosis and procedural guidance.
-
Increased Use in Home Healthcare: Portable ultrasound devices are increasingly used by visiting nurses and home care providers for monitoring chronic conditions.
-
Rising Role in Sports Medicine and Orthopedics: Real-time musculoskeletal imaging is supporting injury assessment and rehabilitation planning.
-
Growing Demand in Veterinary Applications: Portable systems are gaining traction in veterinary clinics and field environments due to their mobility and affordability.
-
Government Support in Rural Health Programs: Many governments are subsidizing or procuring portable ultrasound units for maternal care and community health outreach in rural areas.
How is AI Impacting the Portable Ultrasound Devices Market?
Artificial intelligence (AI) integration is transforming point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) devices by helping clinicians to perform accurate and reliable scans, especially in resource-limited settings and remote areas. AI algorithms can provide real-time scan guidance to operators during scans and also enhance image quality for easier identification of anatomical structures and potential anomalies. Early diagnosis and detection of diseases can be achieved with the help of AI-powered models and devices, leading to improved patient outcomes. Manufactures are deploying AI models and applications for training medical professionals on properly using scanning techniques and interpretation of medical images. Expanding applications of AI such as in tele-ultrasound solutions is facilitating access to diagnostics services and remote consultations for individuals in remote locations and underserved regions.
- For instance, in June 2025, RadNet, a U.S.-based radiology organization, announced the acquisition of See-Mode Technologies Pte. Ltd., an international AI-based ultrasound imaging innovator.
Report Scope of Portable Ultrasound Devices Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2026 |
USD 6.33 Billion |
| Market Size by 2035 |
USD 8.98 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2026 to 2035 |
CAGR of 3.98% |
| Base Year |
2025 |
| Forecast Period |
2026 to 2035 |
| Segments Covered |
By Type, By Application, By Technology, By End Use |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (USD Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA |
| Key Companies Profiled |
GE HealthCare; Siemens; Koninklijke Philips N.V.; SAMSUNGHEALTHCARE.COM; FUJIFILM Holdings Corporation; Shenzhen Mindray Bio-Medical Electronics Co., Ltd.; Canon Inc.; BenQ. |
Portable Ultrasound Devices Market Dynamics
Driver
Rising Global Demand for Point-of-Care Diagnostics
A key driver accelerating the portable ultrasound devices market is the growing need for point-of-care (POC) diagnostics, especially in emergency medicine, critical care, and field applications. The ability to perform immediate, bedside imaging drastically improves clinical workflow and patient outcomes. Time-sensitive conditions such as cardiac tamponade, internal bleeding, or ectopic pregnancy require instant assessment — and POC ultrasound offers a rapid, radiation-free alternative to CT or MRI.
For instance, in emergency departments, handheld ultrasound devices are used to perform Focused Assessment with Sonography for Trauma (FAST) exams to detect internal hemorrhage. In remote or military settings, portable ultrasound is often the only feasible diagnostic imaging modality. The flexibility, cost-efficiency, and diagnostic power of POC ultrasound is a significant market driver, propelling demand across diverse clinical environments globally.
Restraint
Image Quality and User Dependency
Despite significant advancements, variability in image quality and operator dependency remains a major restraint in the widespread adoption of portable ultrasound devices. Unlike CT or MRI, ultrasound imaging requires significant skill in probe handling, anatomical orientation, and real-time interpretation. In inexperienced hands, poor technique or misinterpretation can lead to inaccurate diagnoses.
Furthermore, compact devices, especially handheld probes, often offer lower image resolution than cart-based systems, limiting their utility in certain detailed or high-risk assessments. While AI-enhanced devices are addressing this gap, variability across operators and inconsistent training standards can affect diagnostic reliability. These limitations pose significant challenges in ensuring clinical accuracy, particularly in critical or surgical decision-making contexts.
Opportunity
Integration of AI and Cloud-based Imaging Workflows
One of the most promising opportunities in the market lies in the integration of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and cloud connectivity to enhance diagnostic accuracy and streamline image management. Emerging devices now feature AI algorithms that can automatically guide probe placement, detect anomalies, and suggest potential diagnoses. This significantly reduces user dependency and facilitates adoption in primary care and low-resource settings.
Additionally, cloud-based image archiving, sharing, and analysis enables seamless collaboration across specialties, second opinions, and real-time consultation — even across geographic boundaries. For example, a rural physician can perform an ultrasound scan and instantly share images with a specialist in an urban center for interpretation. This digital infrastructure enhances portability and supports the development of scalable tele-ultrasound networks, particularly beneficial in global health and rural outreach programs.
Portable Ultrasound Devices Market Segmental Insights
By Type Insights
Cart/trolley-based portable ultrasound devices held the largest share due to their superior imaging capabilities, multi-probe support, and wider adoption across hospitals and specialty clinics. While not fully handheld, these systems are mobile enough to be moved between departments and patient bedsides, offering a balance between portability and performance. They are widely used in obstetrics, cardiology, and emergency departments for comprehensive imaging needs.
These units typically offer high-end features such as elastography, Doppler, and advanced imaging modes, making them suitable for more complex assessments. Their versatility in various clinical settings has ensured sustained demand, especially in institutions that require mobility without sacrificing diagnostic depth. Despite increasing miniaturization, cart-based units remain a staple in high-volume medical facilities.
Handheld ultrasound devices are experiencing the fastest growth, driven by increasing demand for compact, cost-effective, and user-friendly diagnostic tools. These devices, often connected to smartphones or tablets, are revolutionizing the concept of bedside and remote imaging. Their portability makes them ideal for use in ambulatory services, home care, battlefield medicine, and even rural maternal care programs.
Several startups and major players have launched app-based ultrasound probes with AI support, making them accessible to general practitioners and even paramedics. In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, handheld ultrasound was heavily used for bedside lung imaging and cardiac function monitoring. With expanding telehealth infrastructure and growing clinician acceptance, this segment is poised for exponential growth in both developed and developing markets.
By Application Insights
The obstetrics/gynecology segment significantly dominated the ultrasound market, capturing a revenue share of over 46.6% in 2025. Ultrasound is the primary tool for prenatal screening, fetal anomaly detection, gestational age estimation, and monitoring fetal growth. In many parts of the world, it is also used for intrauterine device placement, ovarian cyst monitoring, and post-menopausal evaluations.
Portable ultrasound has made maternal care more accessible, particularly in rural and underserved regions. Governments and NGOs globally deploy these devices in community outreach programs to reduce maternal and neonatal mortality. With a strong, recurring demand for reproductive health imaging, the obstetrics/gynecology segment continues to lead in adoption and revenue generation.
Musculoskeletal (MSK) ultrasound is the fastest growing application, reflecting increased use in orthopedics, sports medicine, rheumatology, and physical therapy. MSK ultrasound allows for dynamic, real-time assessment of tendons, ligaments, muscles, and joints, offering a radiation-free alternative to X-rays. It is widely used in diagnosing sprains, tears, and inflammation, guiding joint injections, and monitoring rehabilitation progress.
The compact nature of portable ultrasound makes it ideal for use in outpatient sports clinics, athletic fields, and physiotherapy centers. With the global rise in sports-related injuries and growing awareness among athletes and active individuals, this application area is witnessing rapid adoption. The emergence of AI-assisted tools and image presets tailored for MSK further accelerates market penetration in this segment.
By Technology Insights
2D ultrasound remains the most widely used technology, especially in primary care, obstetrics, and emergency diagnostics. It provides a clear, real-time two-dimensional view of anatomical structures and fluid dynamics, sufficient for a vast range of diagnostic applications. Owing to its affordability, lower power requirements, and simpler interface, 2D ultrasound continues to dominate in both hospital and field settings.
Most portable devices, including many handheld models, are primarily based on 2D imaging, offering essential diagnostic capabilities at a lower cost. Its widespread familiarity among clinicians, combined with reliability and low training thresholds, ensures its continued dominance in portable formats.
3D and 4D ultrasound technologies are growing at the fastest rate, driven by demand for enhanced anatomical visualization and patient engagement. These technologies provide volumetric imaging and real-time motion visualization, making them ideal for fetal imaging, cardiac assessments, and tumor evaluations. 4D imaging, which captures live movements, is increasingly used in obstetrics and surgical planning.
The miniaturization of 3D/4D technology into portable formats is enabling broader clinical use. For instance, many compact and trolley-based devices now offer optional 3D transducers, catering to OB/GYN clinics and imaging centers. As patient expectations for visual clarity grow and clinical applications expand, this segment is expected to continue its rapid ascent.
By End Use Insights
Hospitals & specialty clinics dominated the ultrasound market and held a revenue share of over 54.0% in 2025. Accounting for a significant portion of the market due to high procedural volumes, diverse clinical applications, and robust purchasing capacity. From emergency and intensive care units to specialized departments like cardiology and obstetrics, these institutions rely heavily on portable ultrasound for bedside and procedural imaging.
The ambulatory surgical centers (ASC) segment is projected to experience the fastest growth over the forecast period. Propelled by the healthcare shift toward outpatient procedures. ASCs use portable ultrasound for anesthesia guidance, vascular access, musculoskeletal evaluations, and postoperative monitoring. Their compact design fits well with the lean operational model of ASCs.
Portable Ultrasound Devices Market By Regional Insights
North America portable ultrasound devices market dominated the overall global market and accounted for 38% of revenue share in 2025. High adoption of innovative medical technologies, and a growing preference for point-of-care diagnostics. The U.S. has a mature portable ultrasound market, driven by high procedural volumes in cardiology, emergency care, and obstetrics. Government reimbursement policies and widespread training programs support technology dissemination across hospitals, clinics, and rural centers.
The region is also home to key industry players and several high-growth start-ups offering AI-based, smartphone-connected ultrasound systems. Academic centers and research institutions continuously evaluate and refine clinical protocols for portable ultrasound use, contributing to adoption across diverse specialties.
What Drives the Growth of the Portable Ultrasound Devices Market in U.S.?
U.S. is a major contributor to the market in North America. Increased penetration of point-of-care diagnostic technologies such as portable ultrasound in various hospital and clinical settings as well as in remote locations are enabling healthcare professionals for performing fast and real-time evaluation of patient health, further reducing the need for time-consuming and expensive imaging techniques like MRI and CT scans. Continuous technological advancements such as miniaturization of these devices enhancing portability, integration of artificial intelligence, compatibility with wireless devices like smartphones enabling remote monitoring and teleconsultations are driving the adoption of these devices. Furthermore, well-established healthcare infrastructure, increased demand for non-invasive diagnostic procedures, rising investments in R&D activities, regulatory approvals and prevalence of chronic diseases is driving the market growth.
Asia Pacific is witnessing the fastest growth, fueled by expanding healthcare access, rising chronic disease prevalence, and large population bases. Countries such as India, China, and Indonesia are seeing increased government investments in maternal care, emergency response, and rural health, where portable ultrasound plays a key role. Mobile health clinics and telemedicine programs often incorporate ultrasound devices as essential diagnostic tools.
Local manufacturers in countries like China are also developing affordable, locally adapted portable systems that meet regional clinical needs. Moreover, the growing number of skilled practitioners, medical training programs, and the rise of private diagnostic chains is fostering robust market expansion in the region.
How is China Approaching the Portable Ultrasound Devices Market?
China is expected to witness fastest growth in the Asia Pacific market over the forecast period. Rising chronic disease burden and aging demographics are driving the demand for point-of-care diagnostics like portable ultrasound devices which can be easily used in different types of settings such as hospitals, clinics and even at home. Enhanced diagnostic accuracy and availability of compact and user-friendly portable ultrasound devices with laced with advanced features are making them a reliable tool for clinicians to apply in various settings. Expansion of private healthcare sector, increased investments by the Chinese government for advancing healthcare infrastructure and rising access to medical diagnostic equipment in rural areas is fuelling the market growth.
Some of the prominent players in the portable ultrasound devices market include:
- GE HealthCare
- Siemens
- Koninklijke Philips N.V.
- SAMSUNGHEALTHCARE.COM
- FUJIFILM Holdings Corporation
- Shenzhen Mindray Bio-Medical Electronics Co., Ltd.
- Canon Inc.
- BenQ.
Portable Ultrasound Devices Market Recent Developments
- In March 2025, GE HealthCare Korea introduced its Vscan Air PT (Personal Trainer) app designed for virtually training medical professionals for its portable wireless ultrasound device, the Vscan Air series.
- In December 2024, SuperSonic Imagine introduced its fleet of handheld ultrasound devices, PocketVu designed for diagnostic medical ultrasound imaging. PocketVu is packed with features like AI-powered auto image quality adjustment, compatibility with DICOM 3.0 systems, multiple scanning modes, long battery life and is developed for supporting multitude of applications such as abdominal, cardiac, musculoskeletal, obstetric and vascular imaging.
- In September 2024, Exo Imaging, Inc., launched a new, FDA-approved, intelligent cardiac and lung scanning ultrasound application, SweepAI which will be available on the Exo Iris system.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the portable ultrasound devices market
Type
- Handheld
- Compact
- Cart/Trolley
Application
- Obstetrics/Gynecology
- Cardiovascular
- Urology
- Gastric
- Musculoskeletal
- Others
Technology
- 2D Ultrasound
- 3D & 4D Ultrasound
- Doppler Ultrasound
- High-intensity Focused Ultrasound
End Use
- Hospitals & Specialty Clinics
- Ambulatory Surgical Centers
- Others
Regional
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa (MEA)