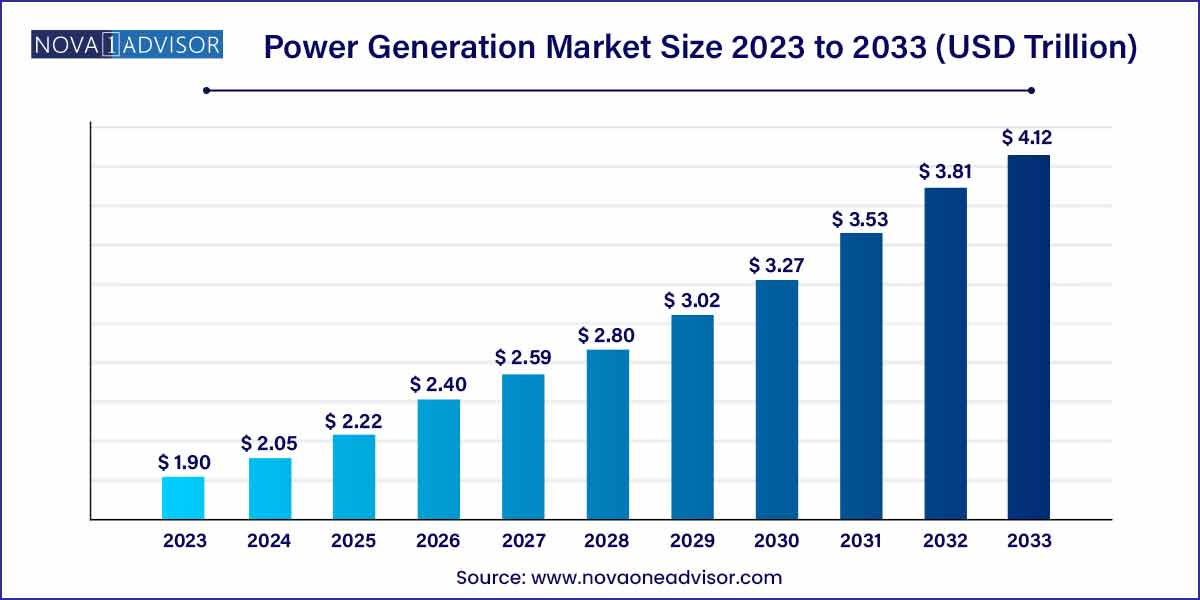
The global power generation market size was exhibited at USD 1.90 trillion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 4.12 trillion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 8.05% during the forecast period of 2024 to 2033.
Key Takeaways:
- The growth of this market has been increasing in European and North American nations
- On average, about 57% of the total share is held by the fossil fuel segment.
- The power generation market is segmented by end-user into Industrial, Commercial, Residential, and Transportation.
- Based on the source, the non-renewable source segment holds a dominant position as compared to the other source and this accounts for 70% of the total share of the global power generation market.
- Based on the type of grid used the on-grid segment has occupied the maximum market share of about 98% and it shall continue to grow during the forecast period.
Market Overview
The global power generation market serves as the backbone of modern civilization, supplying the necessary electricity to fuel economies, industries, transportation, and homes worldwide. Power generation encompasses a vast array of technologies and sources from traditional fossil fuels to rapidly expanding renewable energy platforms. As global demand for electricity continues to grow, the sector is undergoing significant transformation driven by technological innovation, decarbonization mandates, policy shifts, and changing consumer behavior.
While fossil fuel-based power generation (coal, oil, and gas) remains dominant in many parts of the world, the momentum towards cleaner, greener alternatives is unmistakable. Solar, wind, hydroelectric, and geothermal power are steadily gaining ground, bolstered by falling technology costs, government incentives, and global climate commitments like the Paris Agreement. Alongside these shifts, decentralization trends such as microgrids and off-grid renewable solutions are redefining how and where power is generated and consumed.
The growing integration of smart grids, digitization of power systems, and energy storage innovations are helping to smooth the transition towards more sustainable electricity generation. Emerging economies are investing heavily to improve access and reliability, while developed nations focus increasingly on upgrading legacy infrastructure. Together, these dynamics paint a picture of a dynamic and evolving power generation market poised for significant transformation over the coming decades.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Accelerated Transition Towards Renewable Energy Sources: Solar, wind, hydroelectric, and other renewables are rapidly increasing their share in the global energy mix.
-
Rise of Decentralized Power Systems: Off-grid solutions and microgrids are gaining traction, particularly in remote and rural areas.
-
Technological Innovations in Storage and Smart Grids: Batteries, hydrogen storage, and AI-driven smart grid systems are facilitating greater integration of intermittent renewables.
-
Phasing Out of Coal-Based Power Plants: Environmental regulations and climate goals are leading to the early retirement of coal-fired power plants in many countries.
-
Increased Investment in Nuclear Energy: Nations seeking stable baseload power without carbon emissions are reviving interest in next-generation nuclear technologies like small modular reactors (SMRs).
-
Hybrid Power Systems Development: Combining solar, wind, and battery storage in integrated solutions is becoming a standard approach to enhance energy reliability.
-
Government Subsidies and Policy Support: Favorable regulatory frameworks and incentives are propelling renewable energy adoption across regions.
-
Growing Demand for Green Hydrogen: Hydrogen produced via renewable-powered electrolysis is emerging as a significant future energy carrier, complementing renewable electricity generation.
Power Generation Market Report Scop
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 1.90 Trillion |
| Market Size by 2033 |
USD 4.12 Trillion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 |
CAGR of 8.05% |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered |
By Type, By Phases and By Distribution Channel |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Central and South America; the Middle East and Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Enel SpA, Electricite De France SA, State Power Investment Corporation, E.ON SE, Engie, Huaneng Power International, Inc., Exelon Corp, Endesa SA, Datang International Power Generation Company Limited, Inter RAO UES, Power Grid Corporation of India Limited, NTPC Limited, Tata Power, Adani Power, NHPC Limited, Guodian Corporation, Hokkaido Electric Power Company, Tohoku Electric Power Co, AGL Energy, EDF Energy, RWE, Scottish Power and Others. |
Key Market Drivers
Increase in population: The rapid increase in the population is serving as the key market driver for the power generation market. In the previous year, significant economic growth has been registered in many developing nations across the globe. The increasing population is one of the factors driving the growth of the global power generation market. Attractive growth opportunities and good potential will be provided by the nations like Mexico, Russia, Argentina, South Africa, South Korea, Indonesia, Thailand, Taiwan, China, Brazil, and India. The government policy is in these regions is supporting the growth of the global power generation market. Other favorable factors are the presence of renewable sources of energy production in most of these nations which have led to an increased amount of power generation through a sustainable source. The offered opportunities by the developing countries have given chance to future market players of the power generation market.
Rise in urbanization: The rise in urbanization in developing countries have given the speedy increase in demand for electricity, which has eventually forced the respective governments across the world to revamp various initiatives to ensure adequate power supply on their country.
Popularization of smart grid technologies: Smart grid technologies have gained popularity in the whole world due to the significant benefits in account to it efficiency and reliability. The surge in demand of smart grid has been expected as the major aspect that will affect the growth of the global power generation market in the upcoming years.
Key Market Challenges
- Old power generation infrastructure: The existing generation equipment and the system mostly rely on aging infrastructure they really struggle to meet the growing advance demand of electricity. The developing countries are especially suffering from infrastructure aging problems as the replacement requires high investment, so adding a significant inhibitor to the market.
- The decline in investment: The decline in investment in the power sectors is the biggest challenge in market growth. The investment in the coal-fired plant had already descended by 11% and the investment in gas-fired generation is affected by delays in gas-rich emerging economies.
Key Market Opportunities
- Conventional biomass combustion causes various environmental pollution and is primarily used in rural areas of most developing countries for various purposes like cooking and small agricultural activities.So to avoid the population hazards it has been the largest opportunity for the power generation market growth.
Segments Insights:
Type Insights
Fossil fuel electricity, encompassing coal, natural gas, and oil-based generation, continues to dominate the global power generation landscape. Despite mounting environmental concerns, the abundance of fossil fuel resources, existing infrastructure, and affordability have ensured their stronghold, especially in regions like Asia and Africa where electricity demand is growing rapidly. Coal-fired plants remain particularly vital in countries like China, India, and South Africa, powering industries and urban centers. Similarly, natural gas has gained favor in North America and Europe as a relatively cleaner alternative to coal, offering flexible, dispatchable power generation that complements renewable energy sources.
In contrast, Solar Electricity is witnessing the fastest growth rate among all types. Plummeting costs of photovoltaic (PV) panels, combined with increasing efficiency and favorable government policies, are fueling exponential adoption worldwide. In 2023 alone, the world added nearly 300 gigawatts (GW) of new solar capacity, according to the IEA. Countries like China, India, the U.S., and Australia are leading the surge, investing heavily in utility-scale solar farms as well as distributed rooftop installations. Solar energy’s scalability, rapid deployment, and declining costs make it a critical pillar of future global energy strategies.
End-User Insights
The industrial segment dominated the power generation market due to the sheer magnitude of electricity consumption in manufacturing, mining, petrochemicals, and heavy industries. Industrial processes often require continuous, high-capacity power supply, making industries the largest consumers of generated electricity. For instance, in the U.S., the industrial sector accounts for about 30% of total electricity consumption, driven by the production of steel, cement, chemicals, and textiles. Power generation companies prioritize industrial clients through dedicated supply contracts, captive power plants, and customized solutions like co-generation systems to ensure uninterrupted operations.
Meanwhile, the Residential Sector is expected to experience the fastest growth, fueled by urbanization, rising living standards, and the increasing penetration of electronic appliances and air conditioning systems. Residential solar panel installations have surged globally, particularly post-COVID-19 as homeowners sought greater energy independence. In emerging economies, electrification initiatives targeting rural households are dramatically expanding residential electricity consumption, creating robust demand across utility and distributed power generation platforms.
Source Insights
Conventional (non-renewable) energy sources, primarily coal, natural gas, and nuclear, have traditionally dominated global power generation. These sources provide predictable, high-capacity power generation capable of supporting baseload demand — a critical requirement for national grids. The availability of abundant natural gas reserves, especially with the advent of shale gas extraction, has also solidified non-renewable sources' importance in the power generation mix, especially in markets like the United States.
However, Renewable Sources are growing at an unprecedented pace and are projected to be the fastest-growing segment over the next decade. The global shift toward sustainability, aided by technological innovation and falling costs, has positioned renewables at the center of energy transition strategies. Notably, wind and solar combined are expected to account for over 70% of new power capacity additions worldwide through 2030, offering strong momentum for renewable energy growth.
Grid Insights
On-grid power generation systems, interconnected with centralized national grids, dominate the market due to their scalability, efficiency, and reliability. National grids facilitate large-scale distribution of electricity from power plants to end-users, supporting industries, residential areas, and commercial establishments across vast regions. Investments in smart grids, interconnection upgrades, and international energy trading also reinforce the dominance of on-grid systems.
Conversely, Off-Grid Solutions are emerging as the fastest-growing sub-segment, especially in rural and remote areas where extending national grid infrastructure is economically unfeasible. Mini-grids and stand-alone solar systems are empowering communities in Sub-Saharan Africa, South Asia, and parts of Latin America, delivering affordable electricity and unlocking socio-economic development opportunities.
Regional Insights
Asia-Pacific holds the largest share of the global power generation market, accounting for over 45% of total installed capacity. The region's burgeoning population, rapid urbanization, industrial expansion, and rising living standards are driving insatiable electricity demand. China, India, Japan, and South Korea are leading contributors, with China alone adding more renewable capacity annually than the rest of the world combined. Governments across Asia-Pacific are investing heavily in a diversified energy mix, including fossil fuels, nuclear, hydroelectricity, and renewables. The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) also accelerates cross-border power infrastructure development, boosting regional integration and supply security.
The Middle East & Africa (MEA) region is emerging as the fastest-growing market for power generation, underpinned by both economic diversification efforts and electrification needs. Oil-rich Gulf nations like Saudi Arabia and the UAE are investing billions in solar and nuclear projects to reduce reliance on hydrocarbons. Simultaneously, countries like Egypt, Kenya, and Nigeria are focusing on renewable energy projects to bridge electricity access gaps and fuel economic development. Ambitious projects such as Saudi Arabia’s NEOM city and Egypt’s Benban Solar Park highlight the scale of transformation underway in the MEA power sector.
Recent Developments
-
April 2025 – General Electric (GE) Vernova announced its plan to spin off its energy business into a separate entity focused on accelerating renewable and gas power projects globally.
-
March 2025 – Siemens Energy secured a major contract to build a 2.2 GW combined-cycle gas power plant in Egypt, enhancing the country's grid stability and supporting its growing industrial sector.
-
February 2025 – NextEra Energy revealed its investment of $10 billion into expanding its U.S. solar and battery storage projects by 2027, reinforcing its position as a renewable energy leader.
-
January 2025 – EDF Energy commenced operations at its new offshore wind farm in Scotland, adding 1.2 GW to the U.K.'s renewable energy portfolio.
-
December 2024 – Toshiba Energy Systems announced new partnerships in Southeast Asia to deploy next-generation geothermal and hydroelectric power plants.
Some of the prominent players in the power generation market include:
- Enel SpA
- Electricite De France SA
- State Power Investment Corporation
- E.ON SE
- Engie
- Huaneng Power International, Inc.
- Exelon Corp
- Endesa SA
- Datang International Power Generation Company Limited
- Inter RAO UES
- Power Grid Corporation of India Limited
- NTPC Limited
- Tata Power
- Adani Power
- NHPC Limited
- Guodian Corporation
- Hokkaido Electric Power Company
- Tohoku Electric Power Co
- AGL Energy
- EDF Energy
- RWE
- Scottish Power
- Centrica
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the global power generation market.
By Type
- Hydroelectricity
- Fossil Fuel Electricity
- Nuclear Electricity
- Solar Electricity
- Wind Electricity
- Geothermal Electricity
- Biomass Electricity
- Other Electricity
By End-User
- Industrial
- Commercial
- Residential
- Transportation
By Source
- Conventional/Non-Renewable Source
- Renewable Source
By Grid
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)

