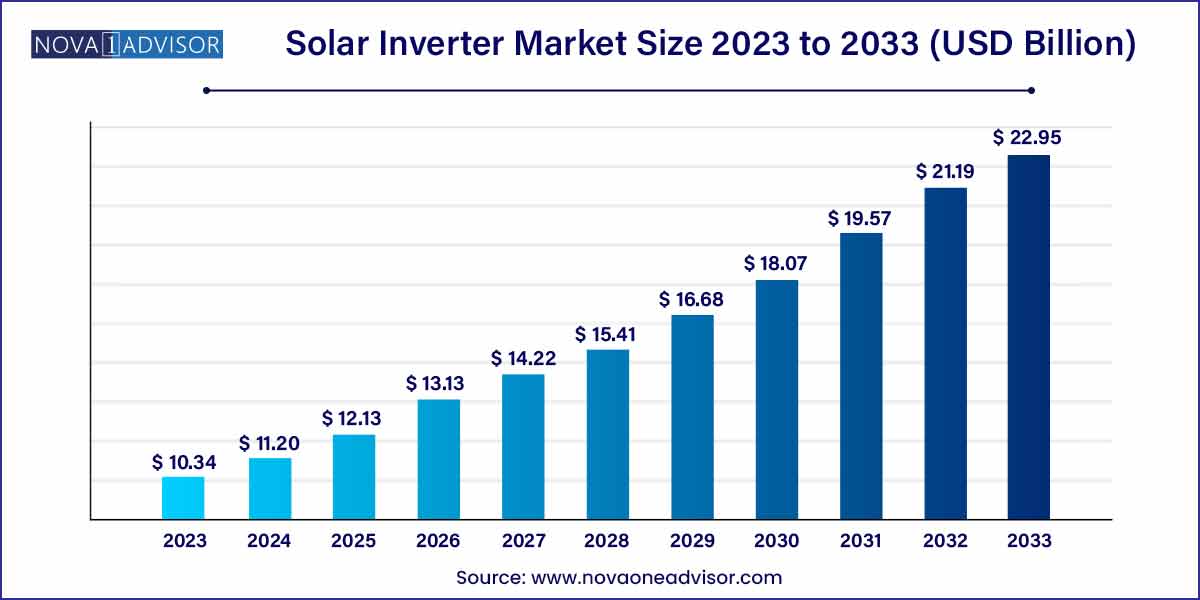
The global solar inverter market size was exhibited at USD 10.34 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 22.95 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 8.3% during the forecast period of 2024 to 2033.
Key Takeaways:
- Asia-Pacific accounted for the largest revenue share of around 44% in 2023.
- The central inverter segment dominated the market with a share of 50% in 2023.
- In 2023, the on-grid segment dominated the solar (PV) inverter market.
- The utilities segment accounted for 44% of the market share in 2023.
Growth Factors
The solar inverter helps to provide electricity in areas such as industrial, commercial, and residential. The solar (PV) inverter can be connected as on-grid or off-grid. The types of solar (PV) inverter are central inverter, string inverter, and micro inverter. The global solar (PV) inverter market is expanding due to rapid expansion of the renewable energy sector. The growing demand and need for green and clean energy are driving the growth and development of global solar (PV) inverter market over the projected period. The government of developed and developed regions is taking initiatives to curb the impact of the carbon emissions and greenhouse gas emissions.
The string solar (PV) inverter are adopted in all areas and utilities as it is effective and incurs low failure rates while operating and maintaining in large buildings. The string solar (PV) inverter is also low in cost as compared to other types of solar (PV) inverters. The implementation of solar (PV) inverter is feasible in nature as it has good power back up. Due to infrastructural development and growing number of construction and building projects, the demand for solar (PV) inverter is growing at a rapid pace. Another factor that is boosting the expansion of the global solar (PV) inverter market is the growing number of home loans and home renovation projects in developed and developing regions. Moreover, due to low cost and tax benefits provided by solar (PV) inverter, the business owners are accepting and adopting solar (PV) inverter on a large scale. As a result, all these factors are driving the demand for solar (PV) inverter in the global market.
Solar Inverter Market Report Scope
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 10.34 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 |
USD 22.95 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 |
CAGR of 8.3% |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered |
Product, Connection, Phase, End User, Nominal Power Output, Nominal Output Voltage, Geography |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Central and South America; the Middle East and Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Omron Corporation, ABB Ltd, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Siemens AG, Schneider Electric SE, SMA Solar Technology AG, Delta Electronics Inc., SunPower, Hitachi Hi-Rel Power Electronics Pvt. Ltd, Power Electronics S.L. |
Key Market Driver: Rising Demand for Renewable Energy Sources
The most significant driver of the solar inverter market is the global push towards renewable energy sources to combat climate change and reduce dependence on fossil fuels. Governments worldwide are implementing ambitious targets to increase their share of renewables in the energy mix. For instance, the European Union aims for climate neutrality by 2050, heavily relying on solar energy among other renewables. Simultaneously, developing countries like India are rapidly expanding their solar capacity under initiatives such as "Solar India Mission."
Solar inverters play a crucial role in this transition by ensuring efficient conversion, grid synchronization, and energy management. Innovations in inverter technologies, including hybrid and smart inverters, are enabling seamless integration of solar energy into traditional grids, bolstering market growth further.
Key Market Restraint: High Initial Cost of Advanced Inverter Technologies
Despite significant advancements, the solar inverter market faces a restraint in the form of high upfront costs associated with premium inverter technologies, particularly hybrid and smart inverters. While traditional inverters have become more affordable, advanced models that offer functionalities such as grid-forming capabilities, storage integration, and remote monitoring can be cost-prohibitive for residential users and small businesses.
This cost barrier is more pronounced in developing countries where economic constraints can inhibit the widespread adoption of solar technology. Although long-term savings and incentives often outweigh initial costs, the need for substantial initial investments can deter adoption rates, especially in price-sensitive markets.
Key Market Opportunity: Emergence of Energy Storage Solutions
The rapid growth of the energy storage market presents a significant opportunity for the solar inverter industry. As residential, commercial, and industrial sectors seek greater energy independence, the demand for battery-coupled solar systems is accelerating. Inverters capable of managing both solar generation and battery storage are becoming highly desirable.
Companies are developing hybrid inverter solutions that facilitate direct energy storage without the need for separate charge controllers. For example, Tesla's Powerwall combined with its proprietary inverters exemplifies the synergy between solar generation and storage, providing users with uninterrupted power even during grid outages. Such developments not only enhance market opportunities for inverter manufacturers but also align with broader trends toward decentralized energy systems.
By Product Type
Central inverters dominated the market, driven by their suitability for large-scale utility applications. Central inverters are extensively used in solar farms due to their high capacity and cost-effectiveness at large scales. Their robust designs allow for efficient management of high-voltage outputs and offer easier maintenance compared to managing numerous string inverters. A 100 MW solar farm, for instance, may rely heavily on central inverters due to their ability to handle vast quantities of power through fewer units, minimizing complexity and reducing the overall system cost.
However, micro-inverters are witnessing the fastest growth, particularly in the residential and small commercial sectors. Micro-inverters offer unique advantages such as module-level monitoring, flexibility, and higher energy yields in shaded environments. As homeowners increasingly adopt rooftop solar panels, the demand for easy-to-install and reliable micro-inverters is surging. For instance, Enphase Energy has reported significant growth in its micro-inverter shipments over recent years, reflecting this trend.
By Connection
On-grid inverters led the market, fueled by urbanization and government policies favoring grid-tied solar systems. On-grid systems are attractive due to their financial viability, where excess energy can be sold back to the utility grid under net metering programs. Countries like Germany and Australia have robust net metering frameworks, encouraging residential and commercial entities to invest in on-grid solar systems equipped with advanced inverters.
Off-grid inverters are expanding rapidly, particularly in remote and underserved regions. In countries across Africa and Southeast Asia, where grid access remains limited, off-grid solar systems offer a lifeline. These inverters, coupled with energy storage solutions, provide continuous power supply and foster socioeconomic development in rural areas.
By Phase
Three-phase inverters accounted for the largest share due to their dominance in commercial and industrial applications. Three-phase inverters are more efficient for managing high-load demands and are integral for operations in factories, shopping centers, and large buildings. For example, an industrial facility with significant machinery requires the robust and reliable performance that three-phase inverters provide.
Meanwhile, single-phase inverters are growing fast within the residential segment. Increasing rooftop solar installations across suburban homes have fueled the demand for single-phase inverters, which are better suited for lower voltage and smaller scale systems typically found in households.
By End User
Utilities remained the dominant end-user, primarily driven by extensive utility-scale solar projects. Projects such as the Noor Abu Dhabi Solar Plant, which uses centralized inverter technologies, underscore the pivotal role of utilities in market demand.
The residential sector is the fastest-growing, boosted by declining PV module costs, enhanced financing options, and a desire for energy independence. For instance, residential solar installations surged in the United States in 2024, leading to a proportional increase in residential inverter sales.
By Nominal Power Output
The 33 - 110 kW segment led the market, attributed to its application in medium to large commercial and industrial installations. Systems in this power range are prevalent in mid-sized manufacturing plants and commercial establishments like malls.
The ≤ 0.5 kW segment is growing most rapidly, driven by the boom in small residential solar applications, including home solar panels and RV solar setups.
By Nominal Output Voltage
230 - 400 V inverters dominated, given their suitability across a range of residential, commercial, and small industrial applications.
600 V systems are growing swiftly, particularly for large commercial and utility-scale projects where higher voltage enables longer string lengths, reducing system costs and increasing efficiency.
Regional Analysis
Asia-Pacific dominated the solar inverter market, owing to massive solar installations across China, India, and Australia. China alone accounted for over 35% of global solar additions in 2024, driven by aggressive renewable energy policies and technological advancements. For example, China's Belt and Road Initiative has incorporated renewable energy investments, bolstering inverter demand.
The Middle East & Africa (MEA) region is the fastest growing, propelled by new solar projects aimed at diversifying energy sources away from oil dependence. Countries like Saudi Arabia and the UAE are investing heavily in solar infrastructure. The Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum Solar Park in Dubai is a prime example, with substantial deployments of advanced solar inverters.
Key Developments
-
January 2025: Huawei Technologies launched its next-generation residential smart solar inverter series, boasting enhanced AI-driven energy management features.
-
February 2025: SMA Solar Technology announced the opening of a new research center in Germany focused on the development of hybrid inverter solutions for emerging markets.
-
March 2025: Sungrow Power Supply Co., Ltd. signed a strategic partnership with an Indian solar farm developer to deploy 200 MW of solar inverters across five Indian states.
-
April 2025: Enphase Energy expanded its micro-inverter manufacturing facility in Mexico to cater to growing North and South American demand.
Some of the prominent players in the solar inverter market include:
- Omron Corporation
- ABB Ltd
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Siemens AG
- Schneider Electric SE
- SMA Solar Technology AG
- Delta Electronics Inc.
- SunPower
- Hitachi Hi-Rel Power Electronics Pvt. Ltd
- Power Electronics S.L.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the global solar inverter market.
By Product Type
- Central Inverter
- String Inverter
- Micro Inverter
- Others
By Connection
By Phase
By End User
- Residential
- Commercial
- Industrial
- Utilities
By Nominal Power Output
- ≤ 0.5 kW
- 0.5 - 3 kW
- 3 - 33 kW
- 33 - 110 kW
- 110 kW
By Nominal Output Voltage
- ≤ 230 V
- 230 - 400 V
- 400 - 600 V
- 600 V
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)

