Telehealth Market Size and Growth
The global telehealth market size was valued at USD 112.08 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to reach around USD 1,002.82 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 24.5% from 2024 to 2033.
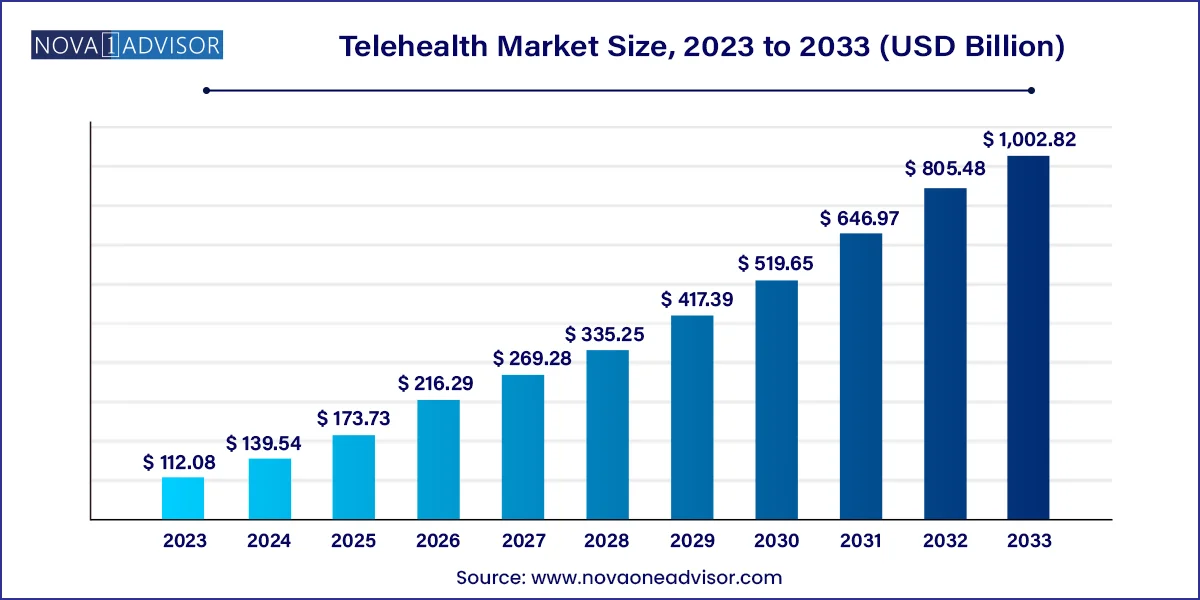
Telehealth Market Key Takeaways
- North America dominated the market in 2023 with the largest revenue share of 47.11%.
- Asia Pacific is projected to witness the fastest growth during the forecast period.
- Services segment held the largest revenue share of 48.8% in 2023.
- Software segment is anticipated to witness the fastest CAGR of 24.8% over the forecast period.
- Based on delivery mode, web-based delivery mode held the largest share in 2023.
- Cloud-based delivery segment is anticipated to witness the fastest CAGR over the forecast period.
- In 2023, radiology segment emerged as the largest segment
- Psychiatry segment is anticipated to grow at the fastest rate over the forecast period from 2024 to 2033
- Provider segment held the largest share in 2023.
- The payers segment is anticipated to witness fastest CAGR over the forecast period.
Market Overview
The Telehealth Market has evolved from a niche healthcare service model into a global healthcare delivery imperative. Defined as the remote provision of clinical and non-clinical healthcare services via digital platforms, telehealth encompasses a broad spectrum of applications such as virtual consultations, remote diagnostics, treatment follow-up, remote patient monitoring (RPM), and chronic disease management. It leverages communication technologies like smartphones, cloud computing, wearable devices, and AI-powered platforms to transcend geographical and logistical barriers in care delivery.
The growth of the telehealth market has been exponential, particularly in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, which forced rapid adoption of digital health tools. Healthcare systems worldwide turned to telehealth to ensure care continuity while minimizing the risk of virus transmission. This initial wave of adoption has since transitioned into a sustainable model driven by consumer demand for convenience, cost-effectiveness, and timely care.
Telehealth is no longer limited to general consultations. It now serves diverse specialties such as psychiatry, dermatology, endocrinology, oncology, cardiology, and even dental and gynecological care. Telehealth platforms also serve providers and payers by reducing operational costs, streamlining workflows, and enabling data-driven care. With the rise of chronic diseases, aging populations, and global healthcare access disparities, the telehealth market is positioned as a transformative force across developed and emerging economies.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Hybrid Care Models: Integration of virtual and in-person care to optimize treatment outcomes and patient engagement.
-
Expansion in Behavioral and Mental Health Services: Surge in tele-psychiatry and substance use consultations amid rising mental health awareness.
-
AI-Powered Diagnostic Tools: Use of artificial intelligence for symptom triage, radiology analysis, and treatment recommendations.
-
Wearables and IoT Integration: Enhanced data collection from home using connected devices like blood pressure meters, glucose monitors, and ECG wearables.
-
Cloud-Based Platforms Leading Growth: Secure, scalable, and interoperable cloud systems are driving long-term telehealth deployment.
-
Increased Reimbursement Support: Governments and private insurers are institutionalizing reimbursement for virtual care.
-
Focus on Specialty Telehealth: Dermatology, endocrinology, oncology, and cardiology expanding teleconsultations beyond general medicine.
-
Mobile-First Interfaces: Growing preference for app-based platforms due to accessibility and smartphone penetration.
Telehealth Market Report Scope
| Report Attribute |
Details |
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 139.54 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 |
USD 1,002.82 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 |
CAGR of 24.5% |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024 to 2033 |
| Segments Covered |
Product type, delivery mode, end-use, disease area, region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage |
Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Koninklijke Philips N.V.; GE Healthcare; Cerner Corporation (Oracle); Siemens Healthineers; Medtronic; Teladoc Health Inc.; American Well; MDLive; Doctor On Demand; Global Med |
Market Driver: Growing Prevalence of Chronic Diseases and Aging Populations
One of the strongest market drivers is the rising global burden of chronic diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular disorders, and respiratory illnesses, especially among aging populations. These conditions require ongoing care, regular monitoring, medication adherence, and lifestyle counseling needs ideally suited to the telehealth model.
In regions where in-person visits are costly, time-consuming, or unavailable, telehealth enables continuous patient engagement. A hypertensive patient in rural India or an elderly diabetic in the U.S. can receive consultations, send health data, and get prescriptions from the comfort of home. This not only improves outcomes but also reduces hospital readmissions and emergency visits.
As more health systems emphasize preventive and value-based care, telehealth serves as a cost-effective, scalable solution to manage chronic disease populations proactively.
Market Restraint: Regulatory Disparities and Data Privacy Concerns
Despite rapid growth, regulatory fragmentation and concerns about data security remain significant barriers. Each country and in some cases, each state has different laws governing telehealth delivery, licensure, cross-border consultations, and patient consent. This lack of harmonization restricts scalability, especially for multinational platforms.
Data privacy is another critical issue. Telehealth platforms handle sensitive health data, making them potential targets for cyberattacks. The industry must adhere to complex regulations such as HIPAA (U.S.), GDPR (EU), and similar frameworks elsewhere. Non-compliance can lead to legal consequences, loss of patient trust, and reputational damage.
To overcome these challenges, companies must invest in cybersecurity, build robust compliance systems, and advocate for clearer, standardized telehealth laws globally.
Market Opportunity: AI and Remote Monitoring for Personalized Virtual Care
An emerging opportunity lies in the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and remote patient monitoring (RPM) devices to deliver personalized telehealth experiences. AI-powered tools are already being used to analyze patient symptoms, recommend next steps, and assist clinicians with diagnostics. Combined with real-time data from wearable and IoT-enabled devices, these platforms can monitor vitals, detect anomalies, and trigger alerts before complications arise.
Imagine a cardiac patient with a wearable ECG patch sending data to a telecardiologist, who is then aided by AI to detect early signs of arrhythmia. Or a diabetes management platform that combines glucose readings, diet data, and predictive algorithms to adjust insulin doses.
These smart, personalized platforms not only improve care quality but also reduce clinician workload and create high-value digital therapeutics for chronic care ecosystems.
Telehealth Market By Product Type Insights
Services dominate the telehealth market, accounting for the majority of revenue. These include real-time interactions (virtual consultations), remote patient monitoring (RPM), and store-and-forward services (asynchronous data sharing like imaging or lab reports). The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the widespread acceptance of virtual visits across primary and specialty care, and health systems have integrated these into routine care models.
Software is the fastest-growing segment, particularly integrated software solutions that combine EHR systems, patient scheduling, billing, and teleconsultation capabilities. These platforms are the digital backbone of telehealth ecosystems, allowing providers to manage clinical and administrative workflows seamlessly. Standalone software also finds use in smaller practices and niche specialty applications.
Hardware remains essential, especially medical peripheral devices such as pulse oximeters, BP meters, glucose monitors, and ECG patches, all of which transmit physiological data during remote assessments. However, hardware growth is somewhat moderate due to increasing use of consumer-grade devices with smartphone connectivity.
Telehealth Market By Delivery Mode Insights
Cloud-based solutions are leading the market, offering scalability, remote accessibility, data backup, and lower infrastructure costs. Cloud-based telehealth systems are ideal for multi-site health systems and mobile-first applications, allowing seamless updates, integration, and deployment. These platforms also support AI integration and telemonitoring dashboards in real time.
Web-based delivery is growing, especially in middle-income countries, where bandwidth and device constraints make browser-based telehealth services more practical than downloadable apps. On-premises solutions, while secure and compliant, are mostly limited to large hospital systems due to higher costs and maintenance needs.
Telehealth Market By Disease Area Insights
Psychiatry leads among telehealth applications, driven by global mental health crises, stigma-free virtual access, and proven effectiveness of teletherapy. Anxiety, depression, PTSD, and substance use disorders are being treated via video and chat-based platforms with growing clinical and consumer adoption.
Dermatology and Endocrinology are rapidly expanding. Dermatology consultations often require image uploads and brief follow-ups, making them highly suited to virtual care. Similarly, diabetes and thyroid management rely on lab data and medication adjustments—tasks efficiently managed via RPM and virtual check-ins.
Other growing specialties include cardiology (remote ECGs), oncology (post-treatment care), gynecology (prenatal checkups), and neurology (Parkinson’s and seizure monitoring).
Telehealth Market By End-use Insights
Providers (hospitals, clinics, and physician networks) dominate the telehealth end-user market. They utilize telehealth platforms to extend reach, manage chronic patients, follow up with post-op cases, and conduct triage. This segment benefits from integrated software and diagnostic hardware that support clinical decision-making.
Patients are the fastest-growing segment, empowered by user-friendly apps, home monitoring devices, and access to specialty consultations. Direct-to-consumer (DTC) telehealth platforms like Teladoc and MDLIVE are reshaping how patients initiate care, particularly in mental health, dermatology, and sexual health.
Payers are increasingly investing in telehealth to reduce costs, improve outcomes, and engage members in preventive care. Insurance providers are forming alliances with telehealth firms to offer bundled or subscription services to policyholders.
Telehealth Market By Regional Insights
North America leads the telehealth market, with the U.S. at the forefront due to advanced healthcare IT infrastructure, favorable reimbursement policies, and strong consumer adoption. CMS and private payers have significantly expanded telehealth reimbursement post-COVID, fueling adoption across Medicare, Medicaid, and employer-sponsored health plans. The U.S. is also home to leading telehealth vendors and VC-backed startups driving innovation.
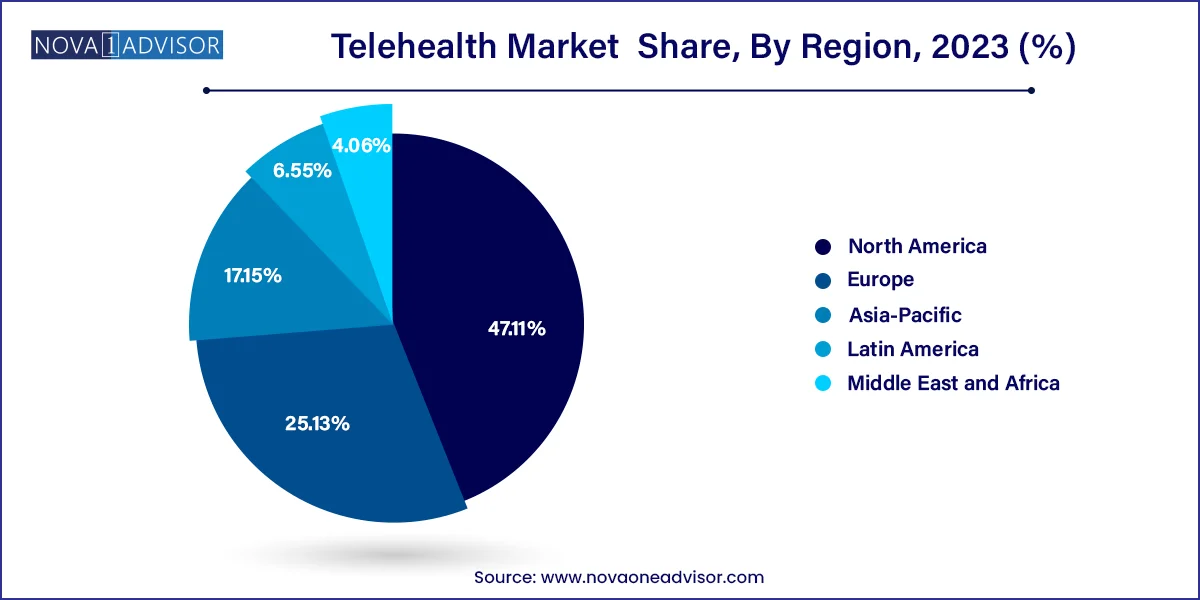
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, driven by smartphone penetration, expanding internet access, and governmental digitization initiatives. China, India, and Indonesia are seeing an explosion in teleconsultation startups, many backed by government health insurance schemes or public-private partnerships. In Japan and South Korea, aging populations are increasing demand for remote care services.
Telehealth Market Top Key Companies:
- Koninklijke Philips N.V
- GE Healthcare
- Oracle Cerner (earlier Cerner Corporation)
- Siemens Healthineers
- Medtronic
- Teladoc Health Inc
- American Well
- MDLIVE
- Doctor On Demand
- Global Med
Telehealth Market Recent Developments
-
Teladoc Health (April 2025): Announced AI-powered virtual assistant for mental health triage, aiming to reduce appointment wait times and direct patients to the right therapist.
-
Amwell (March 2025): Partnered with Epic Systems to offer fully integrated EHR-telehealth workflows to hospitals across the U.S.
-
Practo (India, February 2025): Launched a multilingual voice-based teleconsultation feature to improve rural access to doctors.
-
Ping An Good Doctor (China, January 2025): Surpassed 500 million users on its telehealth platform, expanding into digital pharmacy services.
-
MDLIVE (December 2024): Rolled out a specialty women’s health telehealth solution covering fertility, prenatal, and menopause care.
Telehealth Market Report Segmentation
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Telehealth market.
By Product Type
- Hardware
- Monitors
- Medical Peripheral Devices
- Blood Pressure Meters
- Blood Glucose Meters
- Weighing Scales
- Pulse Oximeters
- Peak Flow Meters
- ECG Monitors
- Others
- Software
- Standalone Software
- Integrated Software
- Services
- Remote Patient Monitoring
- Real-Time Interactions
- Store and Forward
- Others
By Delivery
- On-premises
- Web-based
- Cloud-based
By End-use
- Payers
- Providers
- Patients
By Disease Area
- Psychiatry
- Substance Use
- Radiology
- Endocrinology
- Dermatology
- Gastroenterology
- Neurological Medicine
- ENT
- Cardiology
- Oncology
- Dental
- Gynecology
- General Medicine
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)


