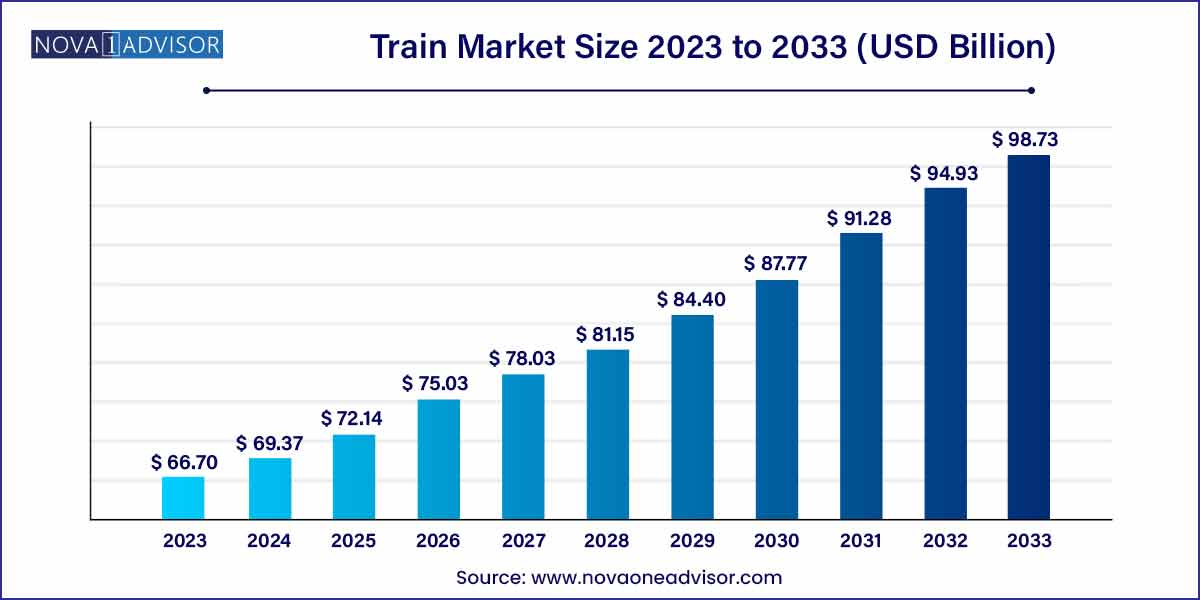
The global train market size was exhibited at USD 66.70 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 98.73 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 4% during the forecast period of 2024 to 2033.
Key Takeaways:
- Asia Pacific held more than 52.0% revenue share and dominated the global market, in 2023.
- The offline channel occupied 71.0% of the global train market during 2023.
Market Overview
The global train market represents a foundational pillar of public transportation and cargo logistics systems worldwide. Trains offer a reliable, efficient, and environmentally sustainable mode of transit, especially in a world grappling with climate change, urban congestion, and the need for mass mobility solutions. Spanning passenger services, freight hauling, high-speed rail, metro systems, and light rail transit (LRT), the train industry integrates advanced engineering with infrastructure development and smart city planning.
Across continents, rail transport is undergoing a major transformation. Traditional diesel-powered locomotives are gradually being phased out in favor of electric and hydrogen-powered units. Simultaneously, the integration of digital systems, such as predictive maintenance technologies, AI-powered signaling, and IoT-enabled fleet management, is enhancing operational safety, efficiency, and reliability. Major investments in smart rail infrastructure and high-speed rail corridors such as those in China, Japan, France, and now even India are reshaping connectivity, reducing travel times, and expanding economic opportunities in both urban and rural areas.
The global push toward decarbonization has placed trains at the forefront of clean mobility agendas. Governments, backed by international climate policies, are heavily funding rail infrastructure projects. According to International Energy Agency (IEA) projections, railways consume only 2% of total transport energy but move 8% of the world’s passengers and 7% of freight, underscoring their efficiency. As a result, trains are becoming not just a transportation solution, but a strategic investment for sustainable and inclusive growth. The market is becoming increasingly diversified with regional lines, long-distance high-speed rail, intermodal freight trains, and autonomous metro systems all contributing to a vibrant and evolving ecosystem.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Electrification of Rail Networks: Countries are rapidly converting diesel lines to electric to reduce emissions and operational costs.
-
Emergence of Hydrogen Trains: Hydrogen-powered trains are gaining momentum as an alternative in regions where electrification is expensive or impractical.
-
High-Speed Rail Expansion: New HSR projects are underway in the U.S., India, and Africa, replicating models from China and Europe.
-
Smart Train Technologies: Use of AI and IoT for predictive maintenance, automated controls, and real-time passenger information.
-
Urban Transit Integration: Metro and light rail systems are increasingly integrated with buses, e-bikes, and ride-hailing services.
-
Rail-as-a-Service (RaaS): Operators are shifting towards outcome-based service models supported by subscription pricing and integrated ticketing.
-
Digital Ticketing and Online Distribution: Rapid digitization of train booking systems, especially via mobile apps and online platforms.
-
Freight Intermodality: Freight trains are being optimized to work seamlessly with ports, warehouses, and last-mile delivery systems.
Train Market Report Scope
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 66.70 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 |
USD 98.73 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 |
CAGR of 4.0% |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered |
Type, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Distribution Channel, Region |
| Regional Scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Central and South America; the Middle East and Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Deutsch Bahn AG; SNCF Group; MTR Corporation Limited’ Amtrak Corporation; Via Rail Canada Inc.; Korea Railroad Corporation; China State Railway Co. Ltd.; ÖBB Group; Central Japan Railway Company; NSW Train link. |
Train Market Dynamics
- Technological Advancements Driving Innovation:
The train market dynamics are heavily influenced by continuous technological advancements, contributing to significant innovation within the industry. The transition from traditional steam locomotives to electric and diesel-powered trains marked a pivotal shift, enhancing efficiency and reducing environmental impact. Moreover, the development of high-speed rail technologies and magnetic levitation (Maglev) systems has redefined the capabilities of train transportation. The integration of smart technologies, such as real-time tracking and predictive maintenance, not only improves operational efficiency but also enhances safety.
- Sustainability as a Core Driving Force:
A fundamental dynamic shaping the train market is the increasing emphasis on sustainability. Trains have emerged as eco-friendly alternatives, aligning with global efforts to reduce carbon emissions and promote environmentally conscious transportation. The shift towards electrification, coupled with the adoption of energy-efficient technologies, reflects the industry's commitment to sustainability. Governments and private entities are investing in the development of electric and hybrid train systems, positioning rail transportation as a key player in the broader sustainable mobility landscape.
Train Market Restraint
- Infrastructure Investment Challenges:
One significant restraint affecting the train market pertains to the challenges associated with infrastructure investments. The development and maintenance of an extensive rail network require substantial financial commitments. Governments and private entities often face hurdles in securing funding for large-scale projects, hindering the timely expansion and modernization of rail infrastructure. Insufficient investment in rail infrastructure can lead to bottlenecks, reduced operational efficiency, and an inability to meet growing transportation demands.
- Competition from Alternative Transportation Modes:
The train market contends with stiff competition from alternative modes of transportation, such as automobiles and airplanes. The convenience and flexibility offered by personal vehicles and the speed of air travel pose challenges to the rail industry, especially in regions where well-established road and air networks exist. To remain competitive, the train market must continuously innovate, offering cost-effective, time-efficient, and sustainable transportation solutions.
Train Market Opportunity
- High-Speed Rail Expansion in Emerging Economies:
An enticing opportunity within the train market lies in the expansion of high-speed rail networks, particularly in emerging economies. As these regions experience rapid urbanization and economic development, the demand for efficient and fast transportation solutions is on the rise. Implementing high-speed rail projects presents a substantial opportunity for both government and private entities to capitalize on the growing need for connectivity.
- Elevated Focus on Urban Mobility Solutions:
The increasing focus on urban mobility solutions presents a significant opportunity for the train market, particularly in densely populated urban areas. Integrated public transportation systems, where trains play a central role, are becoming imperative for alleviating traffic congestion and reducing environmental impact. Governments and city planners are recognizing the potential of trains to serve as efficient, sustainable, and mass transit solutions. Capitalizing on this opportunity involves developing and modernizing urban rail networks, promoting seamless interconnectivity, and enhancing the overall efficiency of public transportation systems to meet the evolving needs of urban populations.
Train Market Challenges
- Regulatory Complexities and Standardization:
One of the primary challenges facing the train market revolves around regulatory complexities and the need for standardization. Different regions and countries often have varied regulatory frameworks and safety standards, posing obstacles to seamless international rail operations. The lack of standardized protocols can impede interoperability between different rail systems, hindering the development of globally connected rail networks.
- Competition from Alternative Transportation Modes:
The train market encounters significant competition from alternative modes of transportation, such as automobiles and airplanes, and emerging technologies like hyperloop systems. The convenience, speed, and door-to-door connectivity offered by these alternatives pose challenges for traditional rail systems. To address this competition, the train market must innovate to enhance its speed, efficiency, and overall customer experience. Strategic marketing and education campaigns may also be necessary to promote the environmental benefits and cost-effectiveness of rail travel compared to other modes.
Segments Insights:
Distribution Channel Insights
Offline channels dominated the train market, particularly in terms of high-value infrastructure contracts and B2B procurement. Governments, transit agencies, and freight operators typically engage in long-term, high-cost contracts negotiated through direct channels involving in-person meetings, technical demonstrations, tender submissions, and compliance reviews. These interactions are crucial for the sale of rolling stock, railcars, signaling equipment, and station infrastructure. Major OEMs like Siemens Mobility, CRRC, and Alstom rely heavily on offline engagement through trade expos, government tenders, and public-private partnerships (PPPs) to secure multi-year projects. This trend is especially dominant in Europe, Asia, and the Middle East.
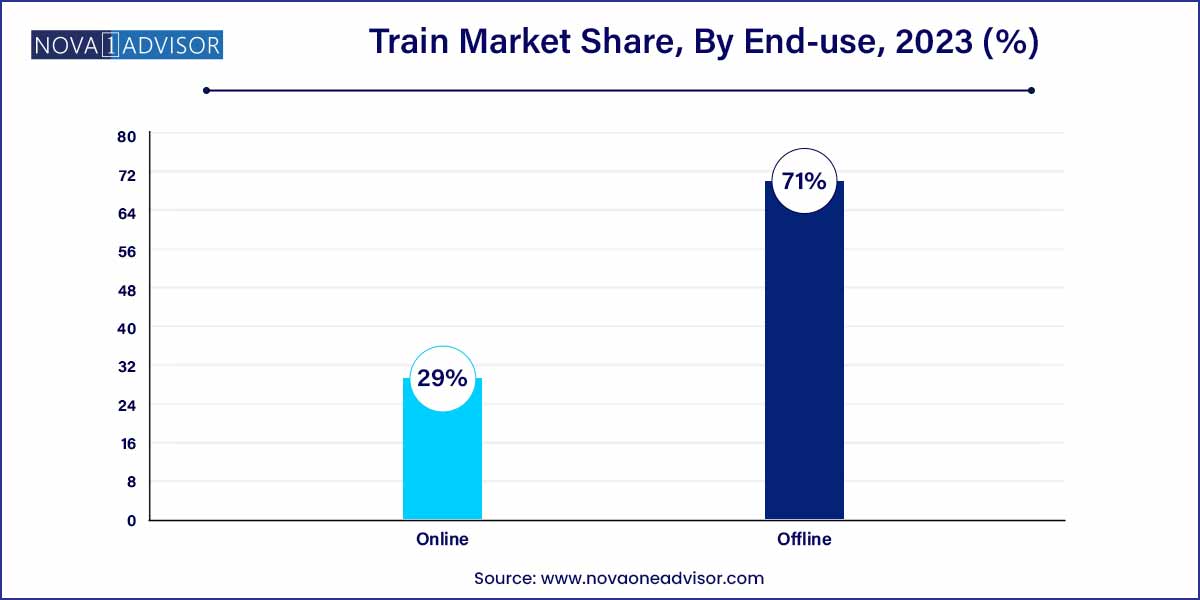
However, online distribution is the fastest-growing channel, particularly in consumer-facing services such as passenger booking, freight scheduling, and aftermarket services. Platforms like IRCTC in India, Deutsche Bahn’s DB Navigator, and Amtrak’s mobile app have revolutionized how passengers interact with train services. In 2024, SNCF (France) launched an AI-based trip planner integrated into its app, allowing passengers to plan intermodal journeys combining train, bike, and e-scooter travel. Moreover, OEMs and parts suppliers are increasingly digitizing procurement for MRO (maintenance, repair, and overhaul) components via online platforms, reducing lead times and improving supply chain transparency.
Regional Insights
Europe remains the dominant region in the global train market, driven by decades of investment in rail infrastructure, high-speed networks, and urban transit systems. Countries like France, Germany, Spain, and Switzerland have extensive electrified rail networks, and the European Union actively supports cross-border connectivity under the Trans-European Transport Network (TEN-T) initiative. European OEMs such as Siemens Mobility, Alstom, and Stadler Rail lead in technology innovation, sustainability, and manufacturing excellence. The region also hosts key global rail trade events like InnoTrans, reinforcing its position as a global hub for rail innovation. Additionally, Europe is at the forefront of hydrogen train adoption and autonomous metro deployment.
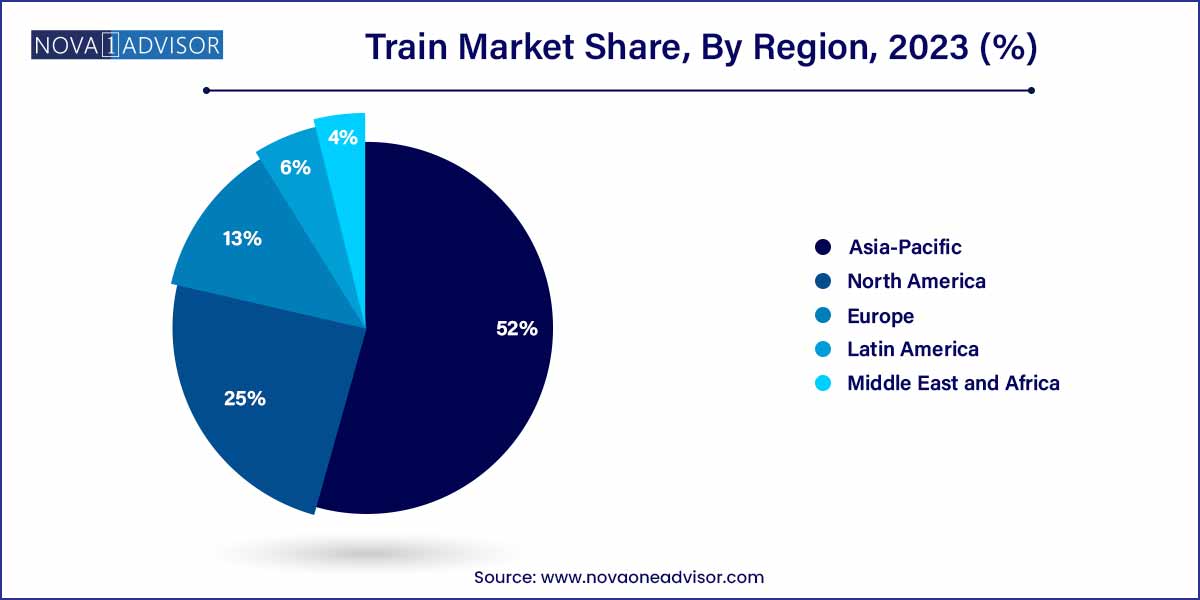
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, particularly due to rapid urbanization, expanding middle-class populations, and significant government-backed infrastructure development. China leads the world in high-speed rail, operating over 40,000 kilometers of HSR track. Japan continues to innovate with its Shinkansen bullet trains, while India is rapidly upgrading its legacy rail network with electric lines, semi-high-speed corridors, and dedicated freight corridors. Southeast Asian nations such as Thailand, Vietnam, and the Philippines are investing in metro rail systems to address urban congestion. Furthermore, local manufacturing capabilities, public financing support, and technology transfers are enabling regional OEMs to meet increasing demand cost-effectively.
Some of the prominent players in the train market include:
- Deutsch Bahn AG
- SNCF Group
- MTR Corporation Limited
- Amtrak Corporation
- Via Rail Canada Inc.
- Korea Railroad Corporation
- China State Railway Co. Ltd.
- ÖBB Group
- Central Japan Railway Company
- NSW Train link
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the global train market.
Distribution Channel
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)



