Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Size and Growth 2025-2034
The global tuberculosis diagnostics market size was valued at USD 3.55 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 6.42 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 6.1% from 2025 to 2034. The tuberculosis (TB) diagnostics market growth can be linked to the rising cases of TB, public awareness campaigns, supportive government initiatives, and increasing adoption of point-of-care (POC) diagnostics.
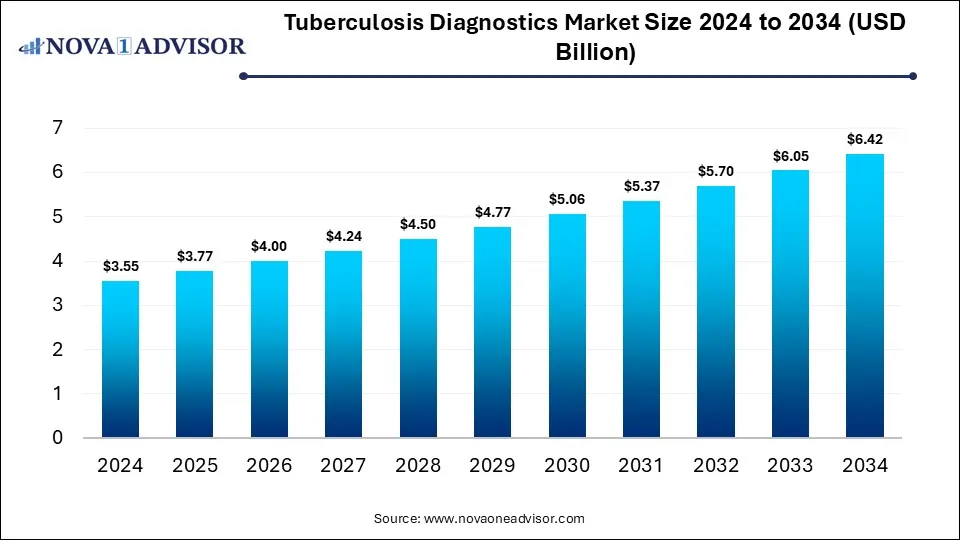
Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Key Takeaways
- The detection of Latent Infection (Skin Test & IGRA) segment dominated the market with a share of 42% in 2024.
- The detection of the Drug Resistance (DST) segment is expected to register the fastest CAGR during the forecast period.
- The diagnostic laboratories segment dominated the market with a share of 48% in 2024,
- The hospitals and clinics segment is anticipated to grow at a significant growth over the forecast period.
Market Overview
Tuberculosis (TB) remains one of the most persistent and devastating infectious diseases globally, despite decades of medical advancement and public health initiatives. The tuberculosis diagnostics market plays a crucial role in the detection, monitoring, and management of this disease, particularly in regions where the burden of TB remains high. Diagnostic tools range from conventional skin tests to sophisticated molecular diagnostics that identify drug-resistant strains and latent infections with increasing accuracy and speed.
Globally, over 10 million new TB cases are diagnosed annually, and with the resurgence of drug-resistant forms such as multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB) and extensively drug-resistant TB (XDR-TB), the need for accurate and timely diagnostics has become more pressing than ever. The World Health Organization (WHO) and national health agencies have emphasized the importance of early and reliable diagnostics to support disease surveillance, enable targeted treatment, and reduce TB-related mortality.
The global TB diagnostics market is influenced by a complex array of factors including government programs, international funding (such as from the Global Fund and USAID), emerging technologies, diagnostic automation, rising healthcare awareness, and evolving regulatory frameworks. Public-private partnerships, along with non-governmental efforts to provide cost-effective, point-of-care (POC) solutions, are significantly shaping the competitive dynamics of the market.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Shift Toward Molecular Diagnostics: Technologies such as nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs), including GeneXpert and Truenat, are replacing traditional sputum smear microscopy.
-
Rise of Point-of-Care Testing (POCT): Portable TB diagnostic tools are being deployed in resource-limited settings to increase accessibility and reduce time to diagnosis.
-
Integration of AI and Digital Tools: AI-powered radiographic analysis and digital platforms for TB image interpretation are becoming more prominent, especially in developing countries.
-
Increased Focus on Drug Resistance Detection: Advanced molecular tests are being developed to detect resistance to both first-line and second-line TB drugs in a single test.
-
Collaborative Public-Private Partnerships: Governments and global organizations are investing in partnerships to scale up diagnostics availability, especially in high-burden countries.
-
Latent TB Infection Testing (LTBI): Growing emphasis on detection of LTBI, especially in immunocompromised populations (HIV/AIDS patients, organ transplant recipients).
-
WHO End TB Strategy Support: The market is aligning with the WHO goal of a 90% reduction in TB deaths and an 80% reduction in TB incidence by 2030.
Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Report Scope
| Report Attribute |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 3.77 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 |
USD 6.42Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2025 to 2034 |
CAGR of 6.1% |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered |
Test type, End use, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage |
Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Abbott, QIAGEN, Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., BD, F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG, Hologic, Inc., Cepheid, DiaSorin S.p.A., Hain Lifescience GmbH, Oxford Immunotec |
Market Driver: Increasing Global Burden and Emergence of Drug-Resistant TB
The most significant driver of the TB diagnostics market is the persistent global burden of tuberculosis, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. According to WHO estimates, TB is the 13th leading cause of death worldwide and the second leading cause from a single infectious agent, after COVID-19. The rise of drug-resistant TB (DR-TB) has compounded the challenge, as traditional treatment and diagnosis methods are often ineffective.
MDR-TB and XDR-TB require more advanced diagnostics capable of identifying specific resistance patterns. The demand for rapid, sensitive, and scalable molecular diagnostics has led to increased adoption of PCR-based tests and automated NAAT platforms. Governments and health organizations are also focusing on strengthening laboratory capacity, supporting the expansion of TB diagnostic networks.
In response, companies like Cepheid (Danaher) have expanded their offerings with cartridge-based systems like GeneXpert MTB/RIF Ultra, which detect both TB and rifampicin resistance. The growing urgency to curb disease transmission, reduce mortality, and meet WHO goals ensures continued investment and innovation in diagnostics.
Market Restraint: High Cost of Advanced Diagnostic Technologies
While advanced molecular diagnostic tools offer higher accuracy and speed, their high cost remains a major barrier, particularly in resource-constrained settings. PCR-based systems and line probe assays can cost significantly more than conventional microscopy or skin tests, not just in equipment but also in reagents, maintenance, and training.
This cost disparity restricts widespread adoption in many developing countries, where TB prevalence is often highest. Additionally, the infrastructure requirements (such as reliable electricity, trained personnel, and controlled lab conditions) associated with sophisticated diagnostic platforms create hurdles for rural and remote deployments.
Although global health agencies and governments often subsidize these technologies, the dependence on external funding and limited local manufacturing capabilities can lead to operational disruptions. This financial barrier hinders equitable access to cutting-edge TB diagnostics across the most vulnerable populations.
Market Opportunity: Expansion of Decentralized and Point-of-Care Diagnostics
A growing opportunity in the TB diagnostics market lies in the expansion of decentralized and point-of-care (POC) testing, particularly in underserved regions. Traditional diagnostic workflows often require multiple patient visits and lengthy turnaround times, which can result in delayed treatment initiation and poor outcomes.
Innovations in portable, battery-operated devices are enabling rapid molecular testing outside central laboratories. Platforms like Molbio’s Truenat (India) and Abbott’s ID NOW are gaining traction for their ability to deliver NAAT-based results in less than an hour. These systems are revolutionizing diagnosis in primary care clinics, mobile health units, and even rural dispensaries.
Moreover, smartphone integration, cloud-based reporting, and simplified user interfaces are allowing less-trained personnel to operate these tests with minimal error. Expansion of such solutions, supported by strategic public-private partnerships and international aid, can dramatically improve diagnostic coverage and accelerate TB control.
Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market By Test Type Insights
Nucleic Acid Testing (NAT) dominates the TB diagnostics market, primarily due to its high sensitivity, specificity, and ability to detect drug resistance. Automated platforms such as Cepheid’s GeneXpert and Molbio’s Truenat are widely used in national TB programs and by global health organizations. These tests allow for simultaneous detection of TB and rifampicin resistance, offering results within 1–2 hours. NAT has become the gold standard in many high-burden countries and is favored for its integration into lab-based and point-of-care settings.
Detection of Drug Resistance is the fastest-growing segment, reflecting the increasing need for personalized treatment in response to rising DR-TB cases. Tests like line probe assays (LPAs) and next-generation sequencing (NGS) are increasingly being used to identify mutations associated with resistance to first-line (e.g., isoniazid, rifampicin) and second-line drugs. Companies like Hologic and Thermo Fisher are developing multiplex assays that offer expanded resistance panels. The speed and comprehensiveness of these tests are essential for timely therapeutic intervention, reducing disease progression and transmission.
Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market By End Use Insights
Hospitals and Clinics dominate the end-use segment, accounting for the largest share of TB diagnostics consumption. These facilities serve as the primary point of contact for symptomatic patients and often manage both inpatient and outpatient care. Hospitals are increasingly equipped with in-house laboratories and receive funding from national programs to operate advanced diagnostic tools. In countries with government-sponsored TB control efforts, clinics are integrated with diagnostic units that provide direct sputum testing, skin testing, and molecular assays.
Diagnostic Laboratories are the fastest-growing segment, propelled by rising sample outsourcing, centralized testing models, and private sector participation. In urban centers, independent labs and diagnostic chains are investing in high-throughput platforms to offer TB testing as part of broader infectious disease panels. The growth of home sample collection, online consultation platforms, and telemedicine is further boosting this segment, making TB testing more accessible and scalable.
Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market By Regional Insights
Asia-Pacific leads the global TB diagnostics market, accounting for the highest disease burden and diagnosis volume. Countries like India, China, Indonesia, and the Philippines collectively represent over 50% of global TB cases. National TB programs in these countries have adopted innovative approaches, such as deploying GeneXpert and Truenat in peripheral centers and linking patients via digital notification systems.
- For instance, in April 2025, the WHO/ Europe launched the TB-Free Central Asia initiative in Astana, Kazakhstan. The initiative focuses on providing a platform for collaborating and offering strategic guidance to the 5 central Asian countries, namely Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan for accelerating efforts to end tuberculosis (TB) by 2030.
India’s National Tuberculosis Elimination Program (NTEP), for instance, is among the world’s largest public health efforts, targeting TB elimination by 2025. The region also benefits from strong domestic manufacturing capabilities, public-private collaborations, and government support for diagnostic scaling.
China Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Trends
China is leading the tuberculosis diagnostics market in Asia Pacific, driven by the high prevalence of TB cases globally, further creating a huge demand for effective diagnostic tools for early and accurate detection of tuberculosis. The rising adoption of WHO-validated rapid diagnostic tools such as molecular assays like NAAT (Nucleic Acid Amplification Test), GeneXpert systems, and portable testing devices are improving the accuracy, speed and efficiency of diagnostic workflows. Supportive government initiatives for prioritizing TB control through national health strategies is driving investments for advancing healthcare, expansion of diagnostic infrastructure, and for implementation of advanced diagnostic technologies.
India Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Trends
India is anticipated to witness the fastest growth in the tuberculosis diagnostics market in Asia Pacific. The market growth can be attributed to the rising TB burden due to factors like crowded living conditions and pollution, increasing awareness through various government programs, focus on developing a patient-centric approach, and launch of innovative diagnostic solutions. Advanced diagnostic technologies such as drug-susceptibility testing (DST) and molecular rapid tests are contributing to the market expansion. Furthermore, increasing investments by the government and private organizations for expanding diagnostic infrastructure, as well as international support from organizations like the WHO (World Health Organization) and Global Fund are bolstering the market growth.
- For instance, in March 2025, at a summit organized on “World TB Day” at Vigyan Bhawan, Union Minister Dr. Jitendra Singh declared the completion of genome sequencing of 10,000 isolates of “Mycobacterium tuberculosis”, which is a significant genomic breakthrough transforming TB diagnosis. The genome sequencing initiative focused on data-driven research for eradicating TB is a part of the Dare2eraD TB program (Data Driven Research to Eradicate TB) and aims to sequence about 32,000 TB isolates for identification of drug resistance mutations and improving treatment outcomes.
Fastest Growing Region: Middle East & Africa (MEA)
The Middle East & Africa region is the fastest-growing TB diagnostics market, due to a combination of increasing investment, international aid, and heightened TB surveillance. Countries like South Africa face dual epidemics of TB and HIV, which has intensified diagnostic demand. WHO and the Global Fund have prioritized resource allocation to expand TB diagnostic access in sub-Saharan Africa.
Mobile testing labs, rapid molecular tools, and digitized patient tracking systems are being deployed to improve coverage. New partnerships between governments, NGOs, and diagnostic firms are facilitating equipment deployment, staff training, and long-term sustainability planning.
Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Top Key Companies:
- Abbott
- QIAGEN
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- BD
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG
- Hologic, Inc.
- Cepheid
- DiaSorin S.p.A.
- Hain Lifescience GmbH
- Oxford Immunotec
Recent Developments
- In April 2025, the World Health Organization (WHO) published the “WHO consolidated guidelines on tuberculosis. Module 3: Diagnosis”, which will support countries and technical agencies in their efforts towards strengthening tuberculosis (TB) detection.
- In March 2025, Haystack Analytics launched ‘TB One’, which is a Make-in-India solution developed for enhancing TB diagnosis by empowering any hospital or diagnostic lab with next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology. The TB One’ solution which is an all-in-one offering comprises of a pre-sequencing kit for whole genome sequencing (WGS) with access to ‘Omega TB’- HaystackAnalytics’ patented clinical reporting software, as well as on-demand access to 2GB of sequencing data.
- In April 2024, the AG Chitra TB diagnostic kit developed by the Sree Chitra Tirunal Institute for Medical Sciences and Technology (SCTIMST) and licenced to M/S Agappe Diagnostics, Kochi was launched. The kit allows detection of pulmonary tuberculosis at an early stage.
Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Report Segmentation
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Tuberculosis Diagnostics market.
By Type
- Nucleic Acid Testing
- Detection of Latent Infection (Skin Test & IGRA)
- Detection of Drug Resistance (DST)
- Other Methods
- Phage Assay
- Cytokine Detection Assay
- Diagnostic Laboratory Methods
- Radiographic Method
- Other Methods
By End Use
- Diagnostic Laboratories
- Hospitals & Clinics
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)
List of Tables
Global Level
-
Global Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Size (USD Billion), 2024–2034
-
Global Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Share by Type, 2024 & 2034
-
Global Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Share by End Use, 2024 & 2034
Regional & Country Level
North America
-
North America Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Size, by Country, 2024–2034
-
U.S. Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Size, by Type, 2024–2034
-
Canada Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Size, by Type, 2024–2034
-
Mexico Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Size, by Type, 2024–2034
-
North America Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Size, by End Use, 2024–2034
Europe
-
Europe Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Size, by Country, 2024–2034
-
Germany Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Size, by Type, 2024–2034
-
France Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Size, by Type, 2024–2034
-
U.K. Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Size, by Type, 2024–2034
-
Italy Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Size, by Type, 2024–2034
-
Rest of Europe Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Size, by Type, 2024–2034
-
Europe Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Size, by End Use, 2024–2034
Asia Pacific
-
Asia Pacific Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Size, by Country, 2024–2034
-
China Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Size, by Type, 2024–2034
-
Japan Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Size, by Type, 2024–2034
-
South Korea Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Size, by Type, 2024–2034
-
India Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Size, by Type, 2024–2034
-
Southeast Asia Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Size, by Type, 2024–2034
-
Rest of Asia Pacific Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Size, by Type, 2024–2034
-
Asia Pacific Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Size, by End Use, 2024–2034
Latin America
-
Latin America Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Size, by Country, 2024–2034
-
Brazil Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Size, by Type, 2024–2034
-
Rest of Latin America Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Size, by Type, 2024–2034
-
Latin America Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Size, by End Use, 2024–2034
Middle East & Africa
-
Middle East & Africa Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Size, by Country, 2024–2034
-
Turkey Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Size, by Type, 2024–2034
-
GCC Countries Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Size, by Type, 2024–2034
-
Africa Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Size, by Type, 2024–2034
-
Rest of Middle East & Africa Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Size, by Type, 2024–2034
-
Middle East & Africa Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Size, by End Use, 2024–2034
-
Global Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Outlook, 2024–2034 (USD Billion)
-
Global Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Share, by Type, 2024
-
Global Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Share, by End Use, 2024
-
Global Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Share, by Type, 2034
-
Global Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Share, by End Use, 2034
-
North America Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Share, by Country, 2024
-
U.S. Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Share, by Type, 2024
-
Europe Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Share, by Country, 2024
-
Germany Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Share, by Type, 2024
-
Asia Pacific Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Share, by Country, 2024
-
China Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Share, by Type, 2024
-
Latin America Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Share, by Country, 2024
-
Brazil Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Share, by Type, 2024
-
Middle East & Africa Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Share, by Country, 2024
-
GCC Countries Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Share, by Type, 2024
-
Comparative Growth Rate of Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market across Regions, 2024–2034

