U.S. Deep Brain Stimulation In Parkinson’s Disease Market Size and Growth
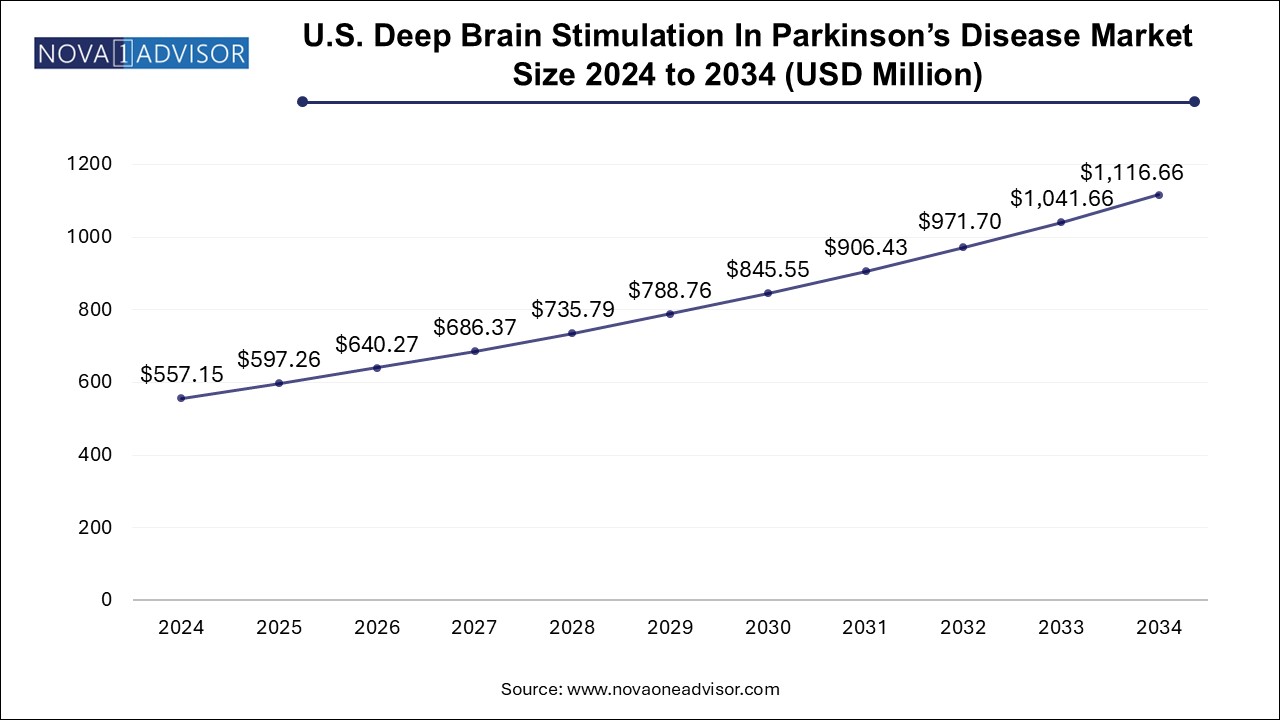
The U.S. deep brain stimulation in Parkinson's disease market size was exhibited at USD 557.15 million in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 1116.66 million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 7.2% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
Market Overview
The U.S. deep brain stimulation (DBS) market for Parkinson’s disease (PD) represents a technologically advanced and therapeutically significant domain within neuromodulation and neurological disease management. Deep brain stimulation is a neurosurgical intervention that involves implanting electrodes into specific brain regions to deliver electrical impulses that regulate abnormal neural activity—a hallmark of Parkinson’s disease progression.
Parkinson’s disease, a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia (slowness of movement), and postural instability, currently affects over one million individuals in the United States. While pharmacological therapy—especially levodopa—is the first-line treatment, many patients eventually experience motor fluctuations and dyskinesias that become refractory to medication. DBS offers a highly effective alternative for managing these advanced symptoms and improving the quality of life for PD patients.
With the growing aging population, increased awareness about surgical interventions, and enhanced precision in neurosurgical techniques, demand for DBS systems is on the rise. Technological innovations such as closed-loop stimulation, rechargeable pulse generators, and directional leads are making DBS systems more effective and patient-friendly. The U.S. remains at the forefront of this innovation landscape, supported by robust reimbursement infrastructure, clinical trial activity, and a growing network of neurosurgical centers of excellence.
In addition to standard surgical centers, academic hospitals and movement disorder specialists are driving adoption through rigorous clinical protocols and interdisciplinary care models. The market is further supported by collaborations between medtech companies, neurologists, and patient advocacy groups to improve access and outcomes in deep brain stimulation therapy.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Adoption of Directional Leads: Directional DBS leads offer more precise stimulation with reduced side effects compared to traditional omnidirectional leads.
-
Rise in Dual-Channel Devices: Increasing preference for dual-channel stimulators due to better bilateral symptom control in advanced PD.
-
Development of Closed-loop (Adaptive) DBS Systems: AI and real-time neural feedback are being integrated to optimize stimulation dynamically based on brain activity.
-
Miniaturization and Rechargeable IPGs: Long-lasting, rechargeable implantable pulse generators are gaining popularity for reducing replacement surgeries.
-
Increased Use of Robotic-Assisted Neurosurgery: Robotic tools and intraoperative MRI are improving accuracy and reducing surgical complications.
-
FDA Expedited Pathways Supporting Innovation: Breakthrough device designation and other regulatory support are accelerating DBS device development.
-
Remote Programming and Tele-DBS: Digital platforms allow for remote adjustment of stimulation parameters, improving care access for rural patients.
-
Integration with Wearables and Neuro-sensing: Patient-specific data from wearables is being used to fine-tune DBS therapy.
Report Scope of U.S. Deep Brain Stimulation In Parkinson’s Disease Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 597.26 Million |
| Market Size by 2034 |
USD 1116.66 Million |
| Growth Rate From 2025 to 2034 |
CAGR of 7.2% |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2034 |
| Segments Covered |
Product |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Key Companies Profiled |
ABBOTT; Medtronic; Boston Scientific Corporation |
Market Driver: Growing Incidence and Progression of Parkinson’s Disease
A key driver of the U.S. deep brain stimulation market for Parkinson’s disease is the rising prevalence of the condition coupled with increasing progression to advanced stages where DBS becomes a viable treatment option. Parkinson’s disease affects more than 60,000 new individuals annually in the U.S., and with life expectancy increasing, many patients are living long enough to experience complex motor complications.
Pharmacological therapies often provide good symptom control during early stages, but over time, their effectiveness wanes. Levodopa-induced dyskinesia and on-off fluctuations typically emerge after 5 to 10 years of medication use, leaving patients with debilitating symptoms. DBS has emerged as a highly effective treatment modality in such cases, particularly for patients under the age of 70 who are otherwise medically fit for surgery.
Clinical studies have demonstrated DBS’s efficacy in significantly improving tremor, rigidity, and bradykinesia, while also enhancing patient independence and reducing medication burden. The growing consensus among neurologists about its long-term benefits, coupled with patient advocacy, is fueling market growth in the U.S.
Market Restraint: High Cost and Surgical Risk
Despite its clinical effectiveness, the high cost and surgical risk associated with DBS therapy remain significant restraints. Deep brain stimulation involves complex pre-operative assessment, stereotactic surgery, and post-operative device programming—all of which can accumulate substantial healthcare costs. The average cost of a DBS system implantation can range from $50,000 to $100,000, depending on the device and hospital.
Although most insurance providers and Medicare cover DBS for Parkinson’s disease, the upfront expenses and ongoing follow-up costs may deter patients or result in delayed access. Additionally, surgical risks such as hemorrhage, infection, lead migration, and cognitive or psychiatric side effects—although rare—remain a concern for patients and caregivers. These factors can contribute to a conservative approach by some physicians, thereby limiting broader market adoption.
Market Opportunity: Expansion of Tele-DBS and Remote Programming Technologies
A promising opportunity in the U.S. DBS market is the expansion of tele-neurology and remote programming technologies, which can significantly improve post-operative care and accessibility. After DBS surgery, patients typically undergo multiple device programming sessions to optimize therapeutic outcomes. For patients living in rural areas or with limited mobility, traveling to specialized centers can be burdensome.
Tele-DBS enables neurologists to fine-tune device settings remotely using secure platforms, reducing the need for in-person visits. These capabilities have been accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic and are increasingly supported by hospital networks and insurance providers. Furthermore, remote monitoring using wearable devices and AI-driven analytics is enabling dynamic stimulation adjustment, paving the way for adaptive DBS systems.
Manufacturers that integrate digital tools into their systems and support tele-optimization will be well-positioned to capture this evolving care paradigm, particularly as virtual care becomes a staple in chronic disease management.
U.S. Deep Brain Stimulation In Parkinson’s Disease Market By Product Insights
The dual-channel segment led the market with the largest revenue share of 60.0% in 2024, driven by their ability to deliver bilateral stimulation—essential for managing the symmetrical symptoms often seen in advanced Parkinson’s disease. Dual-channel systems can independently modulate stimulation in both hemispheres of the brain, providing greater flexibility and better outcomes in patients with varying symptom patterns on each side of the body. These systems are often preferred in academic hospitals and specialized centers where patient-tailored programming is emphasized.
Moreover, many modern dual-channel systems are equipped with rechargeable batteries, directional leads, and real-time feedback capabilities, making them suitable for complex and long-term cases. The added functionality and precision, although more expensive, provide improved therapeutic benefit, justifying the cost in high-acuity cases.
Single-channel DBS devices are expected to grow moderately, especially in patients who require unilateral therapy or in early-stage bilateral cases where cost or surgical simplicity is prioritized. These devices are simpler to implant and may be selected for patients with asymmetric symptomatology. With advancements in single-lead targeting and stimulation algorithms, these systems are finding niche use in specific cohorts. However, dual-channel remains the default choice for most patients with bilateral symptom presentation.
Country-Level Analysis
In the U.S., the adoption of deep brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease is being driven by several key national factors:
-
Specialized Neurosurgical Centers: The country is home to leading DBS centers such as the Cleveland Clinic, Mayo Clinic, and Mount Sinai Hospital, which offer advanced neurosurgical care and post-operative programming services.
-
Reimbursement Support: Medicare and private insurers generally provide reimbursement for FDA-approved DBS devices in Parkinson’s disease, facilitating broader access among eligible patients.
-
Clinical Research Ecosystem: The U.S. conducts a substantial share of global clinical trials in neuromodulation. Ongoing studies explore closed-loop DBS, novel electrode configurations, and gene-therapy-DBS combinations, reinforcing innovation.
-
Patient Advocacy and Education: Organizations such as the Michael J. Fox Foundation and the Parkinson’s Foundation promote awareness, education, and clinical trial participation, helping destigmatize surgical intervention and improve patient uptake.
Some of the prominent players in the U.S. deep brain stimulation in Parkinson's disease market include:
U.S. Deep Brain Stimulation In Parkinson’s Disease Market Recent Developments
-
In February 2025, Medtronic received FDA approval for its Percept™ PC Neurostimulator with BrainSense™ technology, enabling real-time brain signal recording during DBS therapy for Parkinson’s patients in the U.S.
-
In December 2024, Abbott Laboratories announced the U.S. launch of its Infinity™ DBS System featuring remote programming capabilities via secure iOS-based platforms, allowing neurologists to adjust stimulation settings from outside the clinic.
-
In September 2024, Boston Scientific completed enrollment in its pivotal clinical trial evaluating the Vercise Genus™ DBS system in early-stage Parkinson’s disease patients, with results expected by late 2025.
-
In July 2024, the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) initiated a trial combining DBS with wearable sensors and AI algorithms to develop an adaptive stimulation model that adjusts parameters in real-time based on tremor detection.
-
In May 2024, NeuroPace, traditionally focused on epilepsy, announced plans to explore adaptive neuromodulation platforms for Parkinson’s disease, signaling growing industry convergence in neurotechnology.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. deep brain stimulation in Parkinson's disease market
By Product
- Single-channel
- Dual-channel

