U.S. Factoring Services Market Size and Growth 2026 to 2035
The U.S. factoring services market size was exhibited at USD 175.97 billion in 2025 and is projected to hit around USD 394.21 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 8.4% during the forecast period 2026 to 2035.
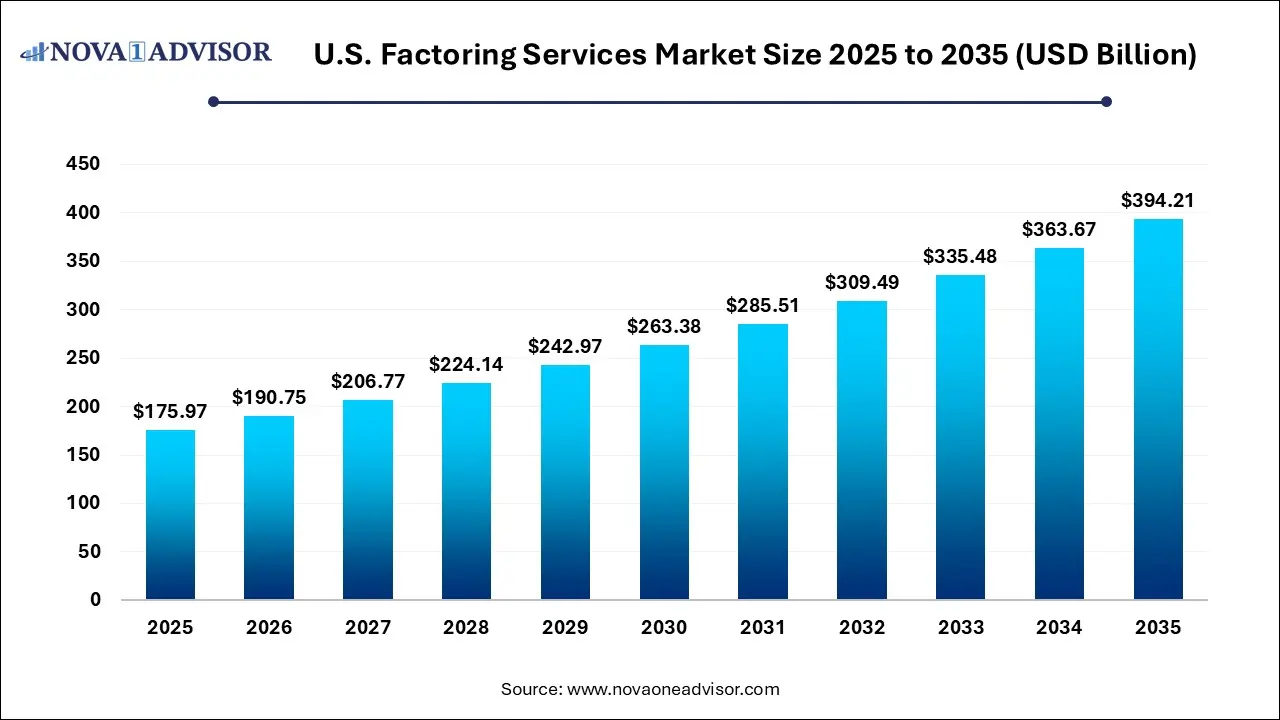
Key Takeaways:
- The domestic segment accounted for the largest market share of 80.2% in 2025.
- The international segment is expected to grow at a CAGR of 8.9% during the forecast period.
- The recourse segment accounted for the largest market share of 63.2% in 2025.
- The non-recourse segment is expected to grow at a CAGR of 8.7% during the forecast period.
- The banks segment accounted for the largest market share of 87.1% in 2025
- The Non-Banking Financial Institutions (NBFIs) segment is expected to grow at a CAGR of 9.2% during the forecast period.
- The manufacturing segment held a market share of 34% in 2025.
- The transport & logistics segment is expected to grow at a CAGR of 8.1% during the forecast period.
Market Overview
The U.S. factoring services market has matured into a critical component of business financing, playing a vital role in enabling cash flow for companies across various sectors. Factoring services involve the sale of accounts receivables (invoices) by businesses to third-party entities known as factors at a discount. This financial tool allows companies to convert outstanding invoices into immediate cash, supporting operational needs, expansion, or bridging cash flow gaps.
In a dynamic and credit-conscious environment like the United States, factoring has gained substantial traction, especially among small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that often face delays in customer payments. With a well-regulated financial ecosystem, factoring has evolved from being a last-resort funding mechanism into a mainstream financial service supported by banks, non-banking financial institutions (NBFIs), and fintech startups.
The post-COVID era further highlighted the relevance of factoring. Businesses, particularly in transportation, construction, and healthcare, experienced delayed payments while needing immediate liquidity to manage ongoing operations. Factoring provided a vital bridge for financial resilience during uncertain times. Additionally, technology adoption in this space—through digital platforms, automated invoice verification, and real-time funding—has reshaped the competitive landscape.
The U.S. market is also experiencing diversification in factoring models. From recourse to non-recourse factoring, and from domestic to international invoice financing, the sector is undergoing significant transformation. Moreover, evolving customer expectations, coupled with rising interest in alternative financing channels, are driving innovations in this industry. Companies are not only seeking cash flow solutions but also value-added services like credit protection, collections, and real-time financial analytics, turning factoring from a transactional service into a strategic tool for growth.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Digitization of factoring operations, including AI-powered invoice processing and real-time analytics.
-
Rise of non-banking financial institutions (NBFIs) and fintech firms as competitive alternatives to traditional banks.
-
Increased use of factoring by gig economy workers and independent contractors in the logistics sector.
-
Integration of factoring platforms with accounting and ERP systems for seamless operations.
-
Shift toward non-recourse factoring due to heightened credit risk concerns in volatile industries.
-
Emergence of blockchain-based invoice financing platforms offering enhanced transparency.
-
Growth in cross-border factoring fueled by international trade and global e-commerce.
-
Industry-specific customization of factoring services, especially in construction, healthcare, and media.
U.S. Factoring Services Market Report Scope
| Report Attribute |
Details |
| Market Size in 2026 |
USD 190.75 Billion |
| Market Size by 2035 |
USD 394.21 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2026 to 2035 |
CAGR of 8.4% |
| Base Year |
2025 |
| Forecast Period |
2026 to 2035 |
| Segments Covered |
Category, Type, Financial Institution, End-use |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage |
Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled |
HSBC Group; BNP Paribas; Barclays Plc; RTS Financial Services, Inc.; TCI Business Capital; Riviera Finances of Texas, Inc.; CIT Group Inc.; Triumph Business Capital; Breakout Capital, LLC; Charter Capital Holdings LP |
Market Driver: Increasing Demand for Working Capital Among SMEs
One of the most significant drivers in the U.S. factoring services market is the increasing demand for working capital, particularly among small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). These businesses often struggle with extended customer payment terms and fluctuating cash flows, making factoring a practical and accessible financing solution. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration, approximately 30% of small businesses report cash flow as their top financial challenge. Factoring bridges this gap without adding liabilities to the balance sheet, unlike traditional loans.
For example, a mid-sized logistics company in Ohio utilized domestic recourse factoring to manage delayed customer payments, which helped them meet fuel and payroll obligations without depending on credit lines. In sectors with unpredictable payment cycles—such as construction or healthcare factoring provides faster access to capital, allowing businesses to reinvest in operations, hire staff, or fund new projects. This surge in working capital requirements has bolstered the demand for factoring services and is expected to remain a primary growth driver.
Market Restraint: Risk of Client Insolvency and Fraudulent Invoices
Despite its benefits, the U.S. factoring market is challenged by the risk of client insolvency and fraudulent invoicing, especially in non-recourse factoring models where the factor assumes the default risk. While due diligence and credit assessments are standard procedures, some clients may provide falsified or non-collectible invoices, exposing the factor to financial loss. This is particularly prevalent in sectors like media and construction where project-based contracts can become complicated or face cancellations.
In 2023, several factoring companies reported increased defaults in receivables from startups in the telehealth and crypto-adjacent services sectors, which had volatile cash flow and limited payment histories. Even with modern risk mitigation tools, fraud detection remains imperfect. Factors must invest in sophisticated verification technologies, often increasing operational costs. Furthermore, sudden client bankruptcies, like the unexpected Chapter 11 filings of large retailers or tech companies, can leave factoring firms exposed to major revenue loss making risk management a critical concern.
Market Opportunity: Expansion of Factoring into Untapped Industries
An emerging opportunity for factoring services in the U.S. is the expansion into previously untapped or underpenetrated industries, such as media and entertainment, e-commerce, and telecommunication. These sectors are witnessing evolving business models, subscription-based revenues, and large receivable volumes making them ideal candidates for invoice financing solutions.
For instance, in 2024, a leading fintech-based factoring firm partnered with a California-based media production house to fund its invoice receivables from OTT platforms and streaming services. This provided immediate cash to finance ongoing production schedules without waiting for prolonged settlement cycles. Similarly, fast-growing e-commerce logistics firms are leveraging factoring to maintain inventory and shipping operations despite delayed customer payments. As factoring adapts to the nuances of new sectors and customizes its offerings—such as flexible contract lengths or dynamic discounting—it can capture a broader market base and unlock untapped revenue streams.
Segmental Analysis
By Category
Domestic factoring dominated the market in terms of volume and customer preference, owing to its lower risk profile, regulatory familiarity, and established infrastructure. Domestic factoring involves funding invoices issued within the U.S. and typically involves quicker turnaround times and simplified compliance protocols. For example, small trucking companies often factor their freight bills through domestic recourse models to obtain same-day payments. Additionally, the reliability of legal enforcement in domestic agreements makes this segment appealing for both financial institutions and customers.
Meanwhile, International factoring is emerging as the fastest-growing segment as more U.S.-based businesses expand into global markets. Companies involved in exports often face extended foreign payment terms, currency risk, and unfamiliar legal frameworks. International factoring services offer benefits such as credit protection, foreign currency support, and collections. Firms such as CIT Group and Tradewind Finance have seen increased demand for cross-border factoring, especially from U.S. manufacturers shipping goods to Latin America and Europe. The complexity of international trade and supply chain disruption is driving exporters to rely on international factoring as a secure cash flow solution.
By Type
Recourse factoring led the market due to its lower cost structure and greater acceptance among businesses. In this model, the client remains liable if the customer fails to pay, making it a safer option for factoring companies and often more affordable for businesses. Manufacturing firms with long-standing clients often choose recourse factoring, confident in the eventual payment. In 2023, over 60% of small businesses opting for factoring preferred recourse arrangements due to better fee terms and faster approvals.
On the other hand, Non-recourse factoring is witnessing rapid adoption, especially in risk-sensitive sectors like healthcare and construction, where payment defaults or disputes are more common. With non-recourse factoring, the risk of non-payment is assumed by the factor, offering added financial security to businesses. This model is also gaining traction as businesses become more risk-averse amid economic uncertainty. Fintech companies are innovating in this space by using AI to assess credit risk dynamically, enabling smarter underwriting of non-recourse transactions.
By Financial Institutions
Banks continue to dominate the factoring services market in the U.S. due to their established customer bases, credibility, and infrastructure. Many businesses prefer bank-led factoring solutions because of bundled offerings such as treasury management, business accounts, and trade finance. Major banks like Wells Fargo, JPMorgan Chase, and Bank of America have dedicated factoring divisions that offer integrated services to existing commercial clients, especially in the mid-to-large segment.
However, Non-Banking Financial Institutions (NBFIs) are growing at a faster rate, fueled by their agility, digital-first approach, and willingness to serve high-risk or underserved clients. Fintech players like BlueVine and FundThrough are disrupting the traditional factoring space by offering paperless application processes, same-day funding, and predictive analytics to assess invoice legitimacy. These firms also cater to freelancers and gig economy workers who may not qualify for traditional bank funding. Their innovation, speed, and inclusivity position them well to scale rapidly.
By End-use
Manufacturing dominated the end-use segment due to its long production and payment cycles, making factoring a crucial tool for maintaining liquidity. Manufacturers often deal with large volumes of invoices from distributors, wholesalers, and retailers with extended payment terms. Factoring enables them to fund raw material procurement, production, and labor without depending on traditional credit. In regions such as the Midwest, numerous machinery and component manufacturers rely on factoring to stabilize operations and expand output.
At the same time, Transport & Logistics has emerged as the fastest-growing sector, primarily due to the gig economy, fuel cost fluctuations, and real-time service expectations. Thousands of owner-operators and small freight companies use freight factoring daily to ensure timely fuel payments and driver wages. The rise of e-commerce and on-demand delivery services has further increased the frequency of receivables. Factoring providers now offer mobile apps, GPS integration, and instant fund transfers, making it easier for logistics firms to operate in a high-velocity business model.
Country-Level Analysis: United States
The U.S. factoring services market reflects the country’s diverse and complex business environment. With over 33 million small businesses and a thriving middle-market segment, the demand for flexible and accessible working capital solutions is higher than ever. The U.S. benefits from a robust financial infrastructure, legal enforcement mechanisms, and widespread digital adoption, all of which support the development of sophisticated factoring services.
Coastal states such as California, New York, and Florida serve as hotbeds for international factoring due to their trade exposure, while states like Texas, Illinois, and Georgia lead in domestic invoice financing for sectors like construction and transportation. Fintech penetration is strongest in tech-savvy regions like Silicon Valley and Austin, driving digital transformation in factoring platforms. Meanwhile, federal efforts to improve small business financing—such as the SBA’s alternative lender partnerships—are further fueling growth in this market.
Key Companies & Market Share Insights
- HSBC Group
- BNP Paribas
- Barclays Plc
- RTS Financial Services, Inc.
- TCI Business Capital
- Riviera Finance of Texas, Inc.
- CIT Group Inc.
- Triumph Business Capital
- Breakout Capital, LLC
- Charter Capital Holdings LP
- U.S. Factoring Services Market Segmentation
- U.S. Factoring Services Market Key Players And Regions
- Companies Profiled
- Regions Covered
Recent Developments
-
April 2025: BlueVine launched a new AI-driven factoring tool that integrates directly with QuickBooks and Xero, offering real-time invoice funding decisions for U.S.-based small businesses.
-
February 2025: CIT Group announced a strategic partnership with a leading logistics platform to offer embedded factoring services for U.S. truckers and freight brokers.
-
November 2024: FundThrough completed the acquisition of a Texas-based factoring firm to expand its customer base among manufacturing SMEs across the Southern U.S.
-
September 2024: Triumph Business Capital introduced a blockchain-based invoice verification platform aimed at reducing fraud and processing time in logistics factoring.
-
June 2024: Riviera Finance expanded its healthcare factoring portfolio by onboarding several telehealth and medical billing startups to streamline their receivables.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2035. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. Factoring Services market.
By Category
By Type
By Financial Institutions
- Banks
- Non-Banking Financial Institutions (NBFIs)
By End-use
- Manufacturing
- Transport & Logistics
- Information Technology
- Healthcare
- Construction
- Others (Media & Entertainment, Energy & Utilities, and Telecommunications)

