U.S. Generic Injectables Pharmaceutical Contract Manufacturing Market Size and Trends
The U.S. generic injectables pharmaceutical contract manufacturing market size was exhibited at USD 3.26 billion in 2025 and is projected to hit around USD 8.85 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 10.5% during the forecast period 2026 to 2035.
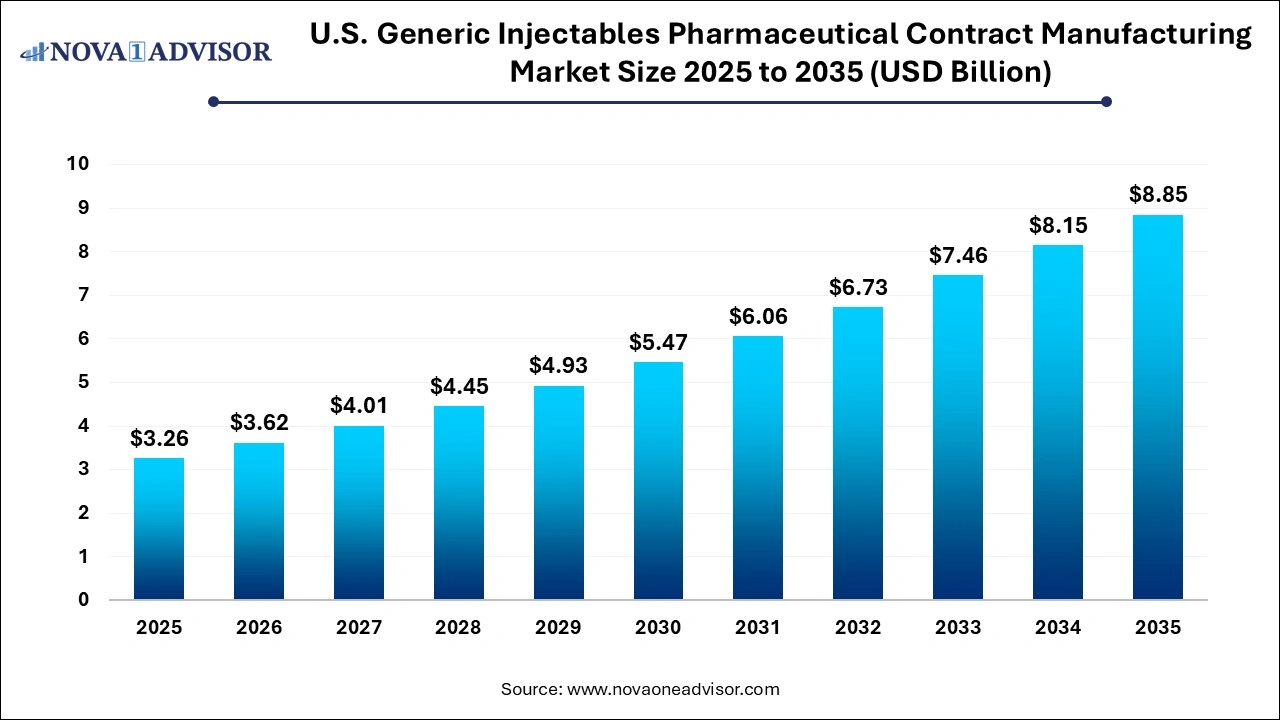
U.S. Generic Injectables Pharmaceutical Contract Manufacturing Market Key Takeaways:
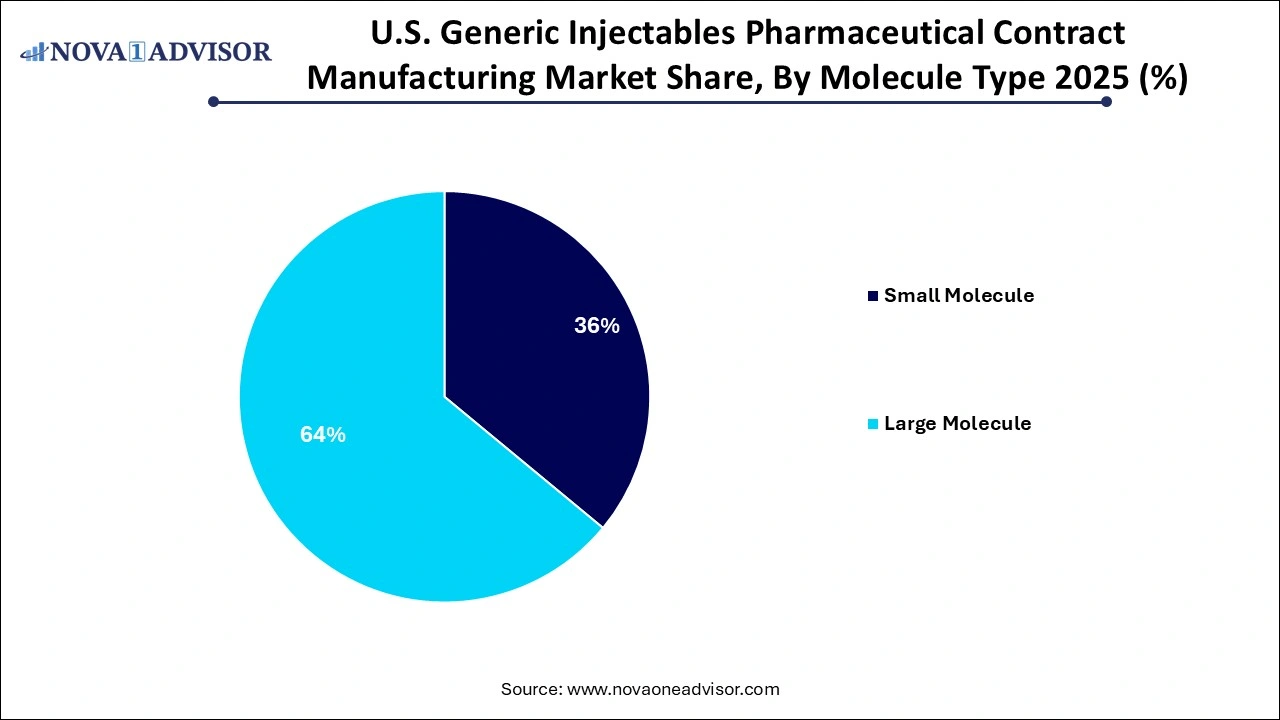
- The large molecule segment held the dominant revenue share of 64% in 2025.
- The small molecule segment is anticipated to register a stable CAGR of 10.5% during the forecast period.
- The oncology segment held the largest revenue share of 29.9% in 2025 in the U.S. generic injectables pharmaceutical contract manufacturing market.
- On the other hand, the neurology segment is expected to register the fastest CAGR of 11.3% during the forecast period.
U.S. Generic Injectables Pharmaceutical Contract Manufacturing Market Overview
The U.S. generic injectables pharmaceutical contract manufacturing market is a key segment within the broader pharmaceutical outsourcing landscape. As pharmaceutical companies increasingly focus on cost reduction, speed-to-market, and portfolio diversification, contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs) have become essential partners particularly in the complex and highly regulated injectable drug segment.
Injectable generics administered directly into the bloodstream, muscle, or tissues play a pivotal role in treating chronic and acute diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular conditions, diabetes, infections, and neurological disorders. Unlike oral generics, injectable formulations require sterile manufacturing environments, advanced filling and packaging capabilities, and compliance with stringent FDA Current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMPs).
Contract manufacturers in the U.S. are leveraging their expertise in aseptic processing, lyophilization, fill-finish services, and prefilled syringes or vials to meet rising demand. As regulatory scrutiny increases and drug development pipelines expand, pharma companies especially generic drug developers turn to CMOs to outsource complex formulation, scale production, and comply with evolving FDA requirements.
Moreover, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s efforts to accelerate generic drug approvals, coupled with an increasing number of drug patent expirations, continue to drive the growth of generic injectables and, consequently, the need for reliable CMO partnerships.
Major Trends in the U.S. Generic Injectables Pharmaceutical Contract Manufacturing Market
-
Increased demand for lyophilized (freeze-dried) injectable formulations to enhance drug stability
-
Rise of fill-finish outsourcing due to complexity and capital intensity of in-house operations
-
Growing focus on prefilled syringes and ready-to-administer formats among healthcare providers
-
Technological advancements in high-speed isolator systems and robotic aseptic filling
-
Expansion of biologics-focused CMOs entering large molecule generic injectables
-
Surging interest in dual-chamber systems and auto-injectors for patient convenience
-
Consolidation among mid-sized CMOs to enhance service breadth and geographical reach
-
Increased partnerships between generics manufacturers and U.S.-based CDMOs to reduce global supply chain dependency
Report Scope of U.S. Generic Injectables Pharmaceutical Contract Manufacturing Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2026 |
USD 3.62 Billion |
| Market Size by 2035 |
USD 8.85 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2026 to 2035 |
CAGR of 10.5% |
| Base Year |
2025 |
| Forecast Period |
2026-2035 |
| Segments Covered |
Molecule Type, Application |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (USD Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Country scope |
U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Hikma Pharmaceuticals plc; Pfizer Inc.; Fresenius Kabi; Sandoz AG; Jubilant Pharma Limited; Baxter; PCI Pharma Services; Gland Pharma Limited (USA); Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories Ltd.; Grand River Aseptic Manufacturing |
Market Driver: Rising Cost Pressure on Generics Manufacturers
One of the most important drivers of this market is the economic pressure on generic drug companies to reduce manufacturing costs while maintaining high-quality standards. As generic drugs become increasingly commoditized, price competition has intensified, particularly in the U.S. market where pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) and group purchasing organizations (GPOs) drive hard bargains.
Injectable generics are especially susceptible to these pressures due to the high fixed costs of sterile production infrastructure, including cleanrooms, validated aseptic equipment, and quality control labs. Rather than investing in costly internal capabilities, pharmaceutical firms choose to outsource to CMOs with existing sterile manufacturing lines and regulatory approvals, thereby avoiding upfront capital expenditures.
Moreover, contracting with CMOs allows drug sponsors to scale production quickly, meet fluctuating demand, and focus their internal resources on R&D or portfolio expansion. As a result, many generics companies in the U.S. have adopted a lean manufacturing strategy, increasing reliance on external partners for injectable drug production.
Market Restraint: Stringent Regulatory Compliance and Facility Qualification
Despite the clear growth potential, one significant restraint in this market is the complexity and cost of maintaining regulatory compliance, both for CMOs and their clients. Injectable drug manufacturing must adhere to stringent FDA and USP standards, including aseptic process validation, endotoxin testing, and particulate matter control.
Any deviation from sterility standards can result in costly product recalls, regulatory warning letters, or manufacturing site shutdowns. For CMOs, this means continuous investment in training, quality assurance systems, and requalification of equipment and processes, often translating into higher costs for their clients.
Additionally, for generic sponsors evaluating CMO partners, the process of auditing, certifying, and validating external facilities adds complexity and risk. Contract disputes over batch failures, delays, or regulatory noncompliance can disrupt supply chains and damage reputations, making risk-sharing models and quality assurance transparency essential for successful partnerships.
Market Opportunity: Demand Surge for U.S.-based Supply Chains and Strategic Redundancy
One of the most promising opportunities in the U.S. generic injectables contract manufacturing market is the increased demand for domestic production capabilities, driven by supply chain vulnerabilities exposed during the COVID-19 pandemic. The pharmaceutical industry and U.S. government policymakers are now prioritizing resilient, domestic drug supply chains, particularly for critical care medications and sterile injectables.
The Biden Administration’s Executive Order on America’s Supply Chains and FDA’s Essential Medicines List have identified the need to onshore manufacturing of vital medications, creating incentives for CMOs to expand capacity in the U.S. Furthermore, generic manufacturers are adopting a “China-plus-one” or “India-plus-one” sourcing strategy to mitigate geopolitical risks.
This shift presents a major growth opportunity for U.S.-based CMOs that can offer FDA-compliant, end-to-end services for fill-finish, lyophilization, prefilled syringes, and packaging of sterile injectables. Partnerships between CMOs and public-private consortia, as well as grants from BARDA and ASPR, are also fueling capacity expansion and modernization of domestic infrastructure.
U.S. Generic Injectables Pharmaceutical Contract Manufacturing Market Segmental Insights
By Molecule Type Insights
Small molecule generic injectables currently dominate the U.S. market, accounting for the majority of outsourced contract manufacturing volumes. These molecules, which include antibiotics, analgesics, antipsychotics, and cardiovascular drugs, have been off-patent for years and are well-established in terms of formulation and delivery.
CMOs supporting small molecule injectables often offer modular filling lines capable of handling multiple SKUs with relatively quick changeover times. The cost-efficiency of small molecules makes them attractive for bulk manufacturing and hospital use, especially in vial and ampoule formats.
Moreover, given the breadth of therapeutic categories covered by small molecule injectables, contract manufacturers frequently partner with multiple clients and produce a broad portfolio of products, ensuring stable utilization of production assets.
Large molecule injectables primarily biosimilars and peptide-based drugs represent the fastest-growing segment of the market. As the first wave of biologics like Remicade, Neulasta, and Avastin lose patent protection, generic companies are racing to bring biosimilar injectables to market, often outsourcing production to specialized biologics CMOs.
These complex molecules require sophisticated cell culture facilities, aseptic processing, and cold-chain packaging, making them ideal candidates for outsourcing. The growth of subcutaneous biologics in prefilled syringe formats is also driving demand for CDMOs with integrated capabilities in formulation, device assembly, and regulatory support.
CMOs capable of manufacturing both drug substance and drug product (end-to-end biologics services) are especially well-positioned to capitalize on this trend, as biosimilar sponsors seek speed, quality, and scalability.
By Application Insights
Oncology is the largest application segment for generic injectable contract manufacturing, owing to the high prevalence of cancer and the increasing availability of generic formulations of chemotherapy drugs such as cisplatin, paclitaxel, and doxorubicin. Many of these agents require lyophilization, cytotoxic handling, and specialized containment systems, which makes them ideal for outsourcing.
Given the complex and hazardous nature of oncology injectables, pharmaceutical companies prefer to partner with CMOs equipped with barrier isolators, cleanroom suites, and containment strategies for handling potent compounds. Additionally, the frequent dosing and narrow therapeutic windows of oncology drugs make quality, sterility, and batch consistency critical.
CMOs with oncology-specific infrastructure often serve multiple clients in this space, offering tailored services such as dedicated lines for high-potency APIs (HPAPIs), multi-dose vial filling, and clinical trial packaging.
Neurology and immunology applications are experiencing rapid growth, driven by the rise in chronic neurological conditions (like epilepsy and multiple sclerosis) and autoimmune diseases (like rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis). Injectable drugs in these categories such as injectable corticosteroids, monoclonal antibodies, and biologics are seeing increased demand, especially in outpatient settings.
This trend is accelerating the need for prefilled syringes, auto-injectors, and long-acting injectables, many of which require sophisticated device integration and stability studies. CMOs offering device-drug combination services and cold-chain storage are particularly well-suited to support these growing applications.
Country-Level Insights
The U.S. accounts for the entirety of this market analysis, with domestic CMOs positioned to serve both domestic and international clients under the highest regulatory scrutiny. The U.S. market is shaped by:
-
A mature regulatory environment with FDA oversight and USP <797>/<800> standards
-
A robust pharmaceutical industry with over 1,000 generic drug manufacturers
-
Favorable public health policies encouraging domestic drug production and supply chain resilience
-
A growing portfolio of biosimilars and complex generics entering the pipeline
States like New Jersey, North Carolina, California, and Massachusetts host some of the largest pharmaceutical clusters, home to CMOs specializing in sterile manufacturing, biologics, and complex injectables. These regions benefit from workforce specialization, academic partnerships, and investment incentives, making them central to U.S. market growth.
Some of the prominent players in the U.S. generic injectables pharmaceutical contract manufacturing market include:
- Hikma Pharmaceuticals plc
- Pfizer Inc.
- Fresenius Kabi
- Sandoz AG
- Jubilant Pharma Limited
- Baxter
- PCI Pharma Services
- Gland Pharma Limited (USA)
- Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories Ltd.
- Grand River Aseptic Manufacturing
Recent Developments
-
April 2025 – Samsung Biologics announced plans to open a new sterile fill-finish facility in the U.S. by 2026 to support North American biosimilar clients.
-
March 2025 – Piramal Pharma Solutions expanded its injectable manufacturing facility in Lexington, Kentucky, adding isolator-based vial and syringe filling lines.
-
February 2025 – Catalent Inc. launched an AI-powered platform for real-time batch release monitoring in its injectable manufacturing units in Indiana.
-
January 2025 – Baxter BioPharma Solutions entered a strategic partnership with a U.S. generics company to supply oncology injectables under a multi-year contract.
-
December 2024 – Lonza completed a $250 million expansion of its sterile manufacturing facility in New Hampshire, adding lyophilization capacity and automated filling systems.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2026 to 2035. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. generic injectables pharmaceutical contract manufacturing market
Molecule Type
- Small Molecule
- Large Molecule
Application
- Oncology
- Immunology
- Antidiabetic
- Neurology
- Cardiovascular
- Respiratory
- Others


