U.S. Health Sensors Market Size and Research
The U.S. health sensors market size was exhibited at USD 12.25 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 63.57 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 17.9% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
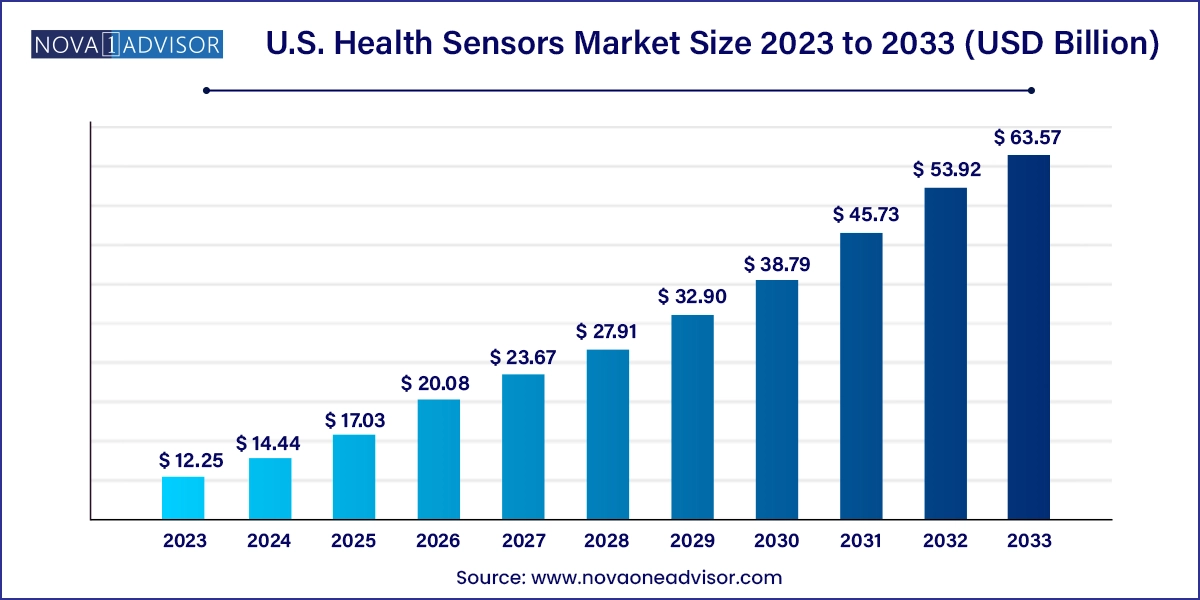
U.S. Health Sensors Market Key Takeaways:
- Based on product, wearable sensors segment accounted for a substantial market share of 35.15% in 2023.
- The implantable/ingestiblesensors segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period
- Based on application, chronic illness & at risk-monitoring accounted for the largest revenue share in 2023.
- The segment is also expected to grow at the fastest CAGR in the forecast period
Market Overview
The U.S. health sensors market represents a rapidly evolving segment at the intersection of healthcare, consumer technology, and digital health innovation. Health sensors are pivotal components in the collection, monitoring, and transmission of physiological data in real time or near real-time. These devices are integrated into wearables, handheld diagnostic tools, implantable systems, and ingestible sensors that enable everything from chronic disease monitoring and wellness tracking to hospital patient triage and post-acute care management.
The adoption of health sensors in the U.S. has surged, driven by an aging population, increasing prevalence of chronic conditions such as diabetes and cardiovascular diseases, growing emphasis on home-based healthcare, and the expansion of value-based care models. The COVID-19 pandemic further accelerated the demand for remote health monitoring solutions, leading to widespread acceptance of telemedicine and continuous health monitoring technologies.
Today’s health sensors range from simple wearable pulse oximeters to advanced biosensors capable of measuring multiple biomarkers such as glucose, heart rate variability, respiratory patterns, hydration levels, and even neurological signals. Many of these devices are now equipped with Bluetooth and Wi-Fi connectivity, allowing seamless integration with smartphones, electronic health records (EHRs), and cloud analytics platforms. Innovations in miniaturization, biocompatibility, and data encryption are further enabling sensors to be embedded in smartwatches, patches, ingestible pills, and implantable chips.
The U.S., with its robust technological ecosystem, healthcare spending, and digital infrastructure, remains one of the most dynamic markets for health sensor development and commercialization. As healthcare providers and technology companies increasingly collaborate, the focus is shifting toward preventive, proactive, and personalized healthcare delivery, making health sensors indispensable tools in 21st-century medicine.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Integration of AI and Predictive Analytics in Sensor Platforms: Smart health sensors are increasingly incorporating AI to detect anomalies and trigger real-time alerts.
-
Rising Popularity of Non-invasive Monitoring: Wearables and remote sensors capable of monitoring without skin penetration are driving user adoption.
-
Expansion of Home-Based Monitoring Programs: Insurers and providers are deploying sensor-enabled devices for chronic disease management at home.
-
Increased Use of Disposable Sensors for Infection Control: Especially in post-acute care and hospital settings, disposable sensors are reducing contamination risks.
-
Adoption of Ingestible and Implantable Sensors for Advanced Diagnostics: Gastrointestinal and cardiac implants now support remote telemetry and patient-specific analytics.
-
Consumerization of Health Monitoring: Devices like smart rings, fitness trackers, and biosensor-enabled clothing are blurring the line between clinical and consumer health.
-
Blockchain and Encrypted Data Transmission for Sensor Security: As health sensors become data-intensive, securing transmission and interoperability is becoming a priority.
Report Scope of U.S. Health Sensors Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 14.44 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 |
USD 63.57 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 |
CAGR of 17.9% |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered |
Product, Application, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope |
U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Analog Devices, Inc; Avago Technologies Ltd.; Danaher Corporation; First Sensors AG; GE Healthcare; Honeywell International Inc.; Koninklijke Philips N.V.; Medtronic; OMNIVISION; Proteus Digital Health; Sensirion AG; Smith’s Medical Inc. (ICU Medical) |
U.S. Health Sensors Market By Product Insights
Wearable sensors dominated the U.S. health sensors market, driven by their wide applicability across both clinical and consumer health applications. Within this category, non-disposable wearable sensors—such as smartwatches, fitness bands, and medical-grade monitors—are extensively used in wellness monitoring, chronic illness management, and clinical trials. Apple, Fitbit, and Garmin have introduced devices with FDA-cleared capabilities such as ECG monitoring and fall detection, while medical-grade wearables are being used in cardiac rehab and arrhythmia tracking.
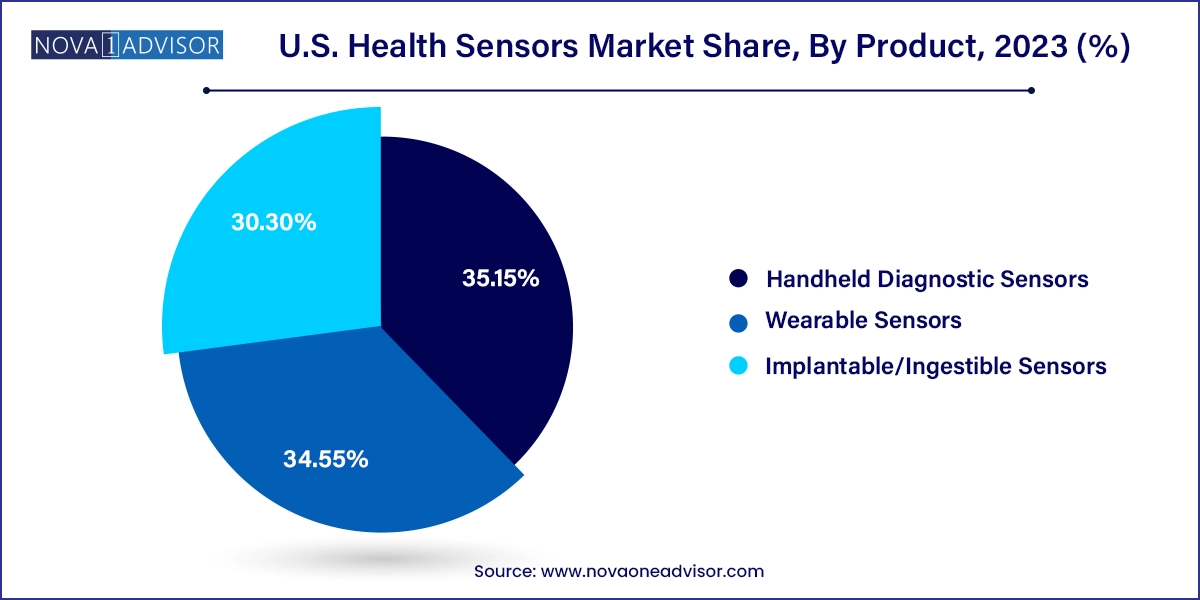
Disposable wearable sensors are the fastest-growing sub-segment, particularly for post-acute care and infectious disease monitoring. These include patches for ECG, temperature, and oxygen tracking, designed for single-use to reduce infection risk. Hospitals and home health agencies favor these sensors for short-term monitoring during transitions of care, and startups like BioIntelliSense are innovating in this space with FDA-cleared solutions such as BioButton.
Implantable/Ingestible sensors, while currently niche, are expanding rapidly in sensor therapeutics and hospital clinical monitoring. These include cardiac implantable sensors, ingestible temperature or pH sensors, and neural activity monitors. Advances in bioelectronics, energy harvesting, and material science are enabling sensors that can remain in the body for weeks or even months, wirelessly transmitting vital signals to care teams.
U.S. Health Sensors Market By Application Insights
Chronic illness and at-risk monitoring emerged as the largest application segment, primarily due to the growing aging population and prevalence of conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and COPD. Patients with multiple comorbidities often require continuous assessment of vitals, and wearable sensors allow clinicians to adjust medications, diet, and therapy based on real-time data. Remote patient monitoring programs reimbursed under Medicare Part B further validate this segment’s dominance.
Sensor therapeutics is the fastest-growing application, enabled by implantable and ingestible technologies that go beyond passive monitoring to include feedback-driven drug delivery and physiologic modulation. For example, sensors embedded in drug capsules can track adherence and digestion. In neurology, implantable vagus nerve stimulators with sensor feedback are being explored for epilepsy and depression. The convergence of sensing, actuation, and AI is opening new frontiers in personalized treatment.
Country-Level Analysis
In the United States, regional differences in adoption of health sensors are influenced by population density, healthcare infrastructure, reimbursement environments, and technology penetration.
The Northeast region dominates the market, driven by high urbanization, well-established academic medical centers, and early adoption of telehealth. Institutions like Massachusetts General Hospital, Mount Sinai, and UPenn Health are leading clinical studies in sensor validation, integrating health sensors into both acute care and longitudinal studies.
However, the Southwest region, particularly Texas and Arizona, is the fastest-growing market. Here, a combination of rural populations, rising chronic disease prevalence, and investment in home health infrastructure is creating a fertile environment for sensor deployment. Texas-based hospitals and health plans are increasingly partnering with sensor startups to deliver value-based care to remote and underserved areas, leveraging cloud platforms and remote nursing.
Some of the prominent players in the U.S. health sensors market include:
- Analog Devices, Inc
- Avago Technologies Ltd.
- Danaher Corporation
- First Sensors AG
- GE Healthcare
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Koninklijke Philips N.V.
- Medtronic
- OMNIVISION
- Proteus Digital Health
- Sensirion AG
- Smith’s Medical Inc. (ICU Medical)
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. health sensors market
Product
- Handheld Diagnostic Sensors
-
- Chronic Illness & At Risk-Monitoring
- Patient Admission Triage
- Logistical Tracking
- In Hospital Clinical Monitoring
- Post-acute Care Monitoring
-
- Disposable Wearable Sensors
- Non-disposable Wearable Sensors
-
-
- Wellness Monitoring
- Chronic Illness & At Risk-Monitoring
- Patient Admission Triage
- Logistical Tracking
- In Hospital Clinical Monitoring
- Sensor Therapeutics
- Post-acute Care Monitoring
- Implantable/Ingestible Sensors
-
- Wellness Monitoring
- Chronic Illness & At Risk-Monitoring
- Patient Admission Triage
- In Hospital Clinical Monitoring
- Sensor Therapeutics
- Post-acute Care Monitoring
Application
- Chronic Illness & At Risk-Monitoring
- Wellness Monitoring
- Patient Admission Triage
- Logistical Tracking
- In Hospital Clinical Monitoring
- Sensor Therapeutics
- Post-acute Care Monitoring
- Home-based
- Others
Regional
- West
- Midwest
- Northeast
- Southwest
- Southeast


