U.S. Healthcare ERP Market Size and Research 2026 to 2035
The U.S. healthcare ERP market size was exhibited at USD 3.74 billion in 2025 and is projected to hit around USD 7.02 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 6.5% during the forecast period 2026 to 2035.
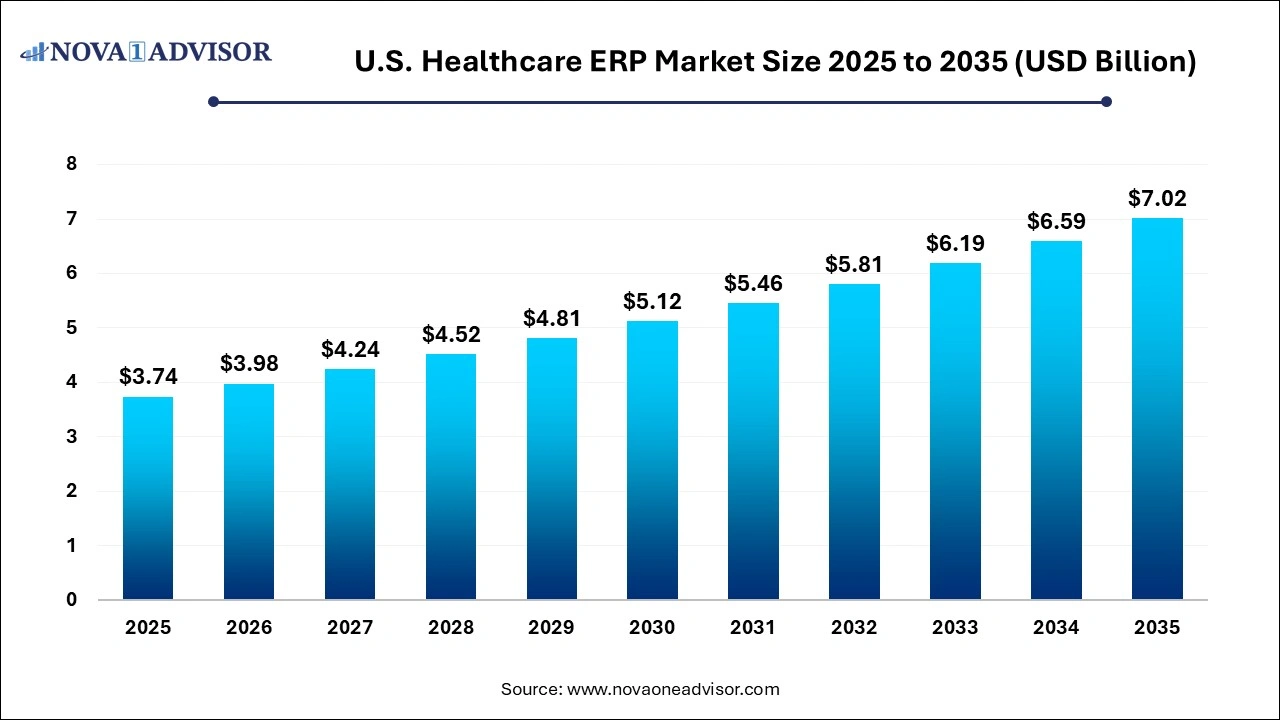
Key Takeaways:
- The finance and billing segment accounted for the largest market share of 32.3% in 2025.
- The inventory and material management segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR of 7.5% during the forecast period.
- The on-premisessegment accounted for the largest revenue share of around 74.0% in 2025.
- The cloud segment is expected to register the fastest CAGR of 9.2% over the forecast period.
U.S. Healthcare ERP Market Overview
The U.S. Healthcare Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) market is undergoing a significant transformation as healthcare providers increasingly adopt digital platforms to improve operational efficiency, enhance patient outcomes, and streamline resource utilization. Healthcare ERP systems serve as a central nervous system for hospitals, clinics, and medical institutions, integrating various business processes such as finance, procurement, supply chain, inventory, patient relationship, and workforce management into a single unified framework.
With rising operational complexities in healthcare delivery, the demand for robust, scalable, and flexible ERP solutions has intensified. Hospitals are no longer standalone facilities focused solely on patient care they are business enterprises with multiple verticals, requiring high-level coordination and analytics. This has created a fertile ground for ERP vendors to develop healthcare-specific modules that go beyond traditional enterprise applications.
According to industry observations, the shift toward value-based care, interoperability regulations, and cost containment pressures are pushing healthcare organizations to revisit their IT investments. ERP systems are increasingly seen not as an expense but as a strategic asset that enhances visibility, reduces errors, improves compliance, and ultimately boosts profitability. As organizations modernize their IT infrastructure, cloud-based ERP platforms have become especially attractive for their scalability, security, and real-time data capabilities.
Moreover, the COVID-19 pandemic exposed several inefficiencies in traditional hospital management systems, accelerating the digital shift. From managing inventory shortages of PPE to adjusting financial planning due to declining elective procedures, ERP solutions proved essential in navigating these unprecedented challenges.
Major Trends in the U.S. Healthcare ERP Market
-
Migration from On-Premise to Cloud-Based ERP Solutions: Hospitals and clinics are moving toward cloud-native platforms to benefit from lower upfront costs, ease of integration, and rapid scalability.
-
Integration with Electronic Health Records (EHRs): ERP platforms are being integrated with EHR systems to provide a unified view of clinical and administrative workflows.
-
Rise of AI and Predictive Analytics: ERP vendors are embedding AI and machine learning features to forecast demand, manage staffing, and personalize patient engagement strategies.
-
Focus on Cybersecurity and Compliance: With HIPAA and other stringent regulatory frameworks in the U.S., healthcare organizations are investing in secure ERP systems that ensure data privacy and auditability.
-
Mobile-First Interfaces and Remote Accessibility: Frontline healthcare staff and administrators require mobile ERP apps that allow access to critical functions on the go.
-
Personalized Patient Relationship Management (PRM): ERP solutions now include CRM-like functionalities to provide customized communication, billing, and service tracking for patients.
-
Vendor Collaborations and Acquisitions: ERP vendors are actively acquiring specialized healthcare IT firms to expand their product portfolios and technical capabilities.
Report Scope of The U.S. Healthcare ERP Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2026 |
USD 3.98 Billion |
| Market Size by 2035 |
USD 7.02 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2026 to 2035 |
CAGR of 6.5% |
| Base Year |
2025 |
| Forecast Period |
2026-2035 |
| Segments Covered |
Function, Deployment |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (USD Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope |
U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Epic Systems Corporation.; Cerner Corporation; McKesson Corporation; Oracle Corporation; Microsoft Corporation; Sage Software Solution; Pvt. Ltd.; QAD Inc.; Medical Information Technology, Inc.; SAP SE |
Market Driver: Demand for Operational Efficiency and Cost Reduction
One of the primary drivers propelling the U.S. Healthcare ERP market is the increasing need for operational efficiency and cost reduction in healthcare settings. Healthcare providers are under enormous pressure to deliver high-quality care while simultaneously managing shrinking reimbursements, increasing administrative burdens, and rising supply chain costs. ERP solutions provide an integrated platform that eliminates redundancies, automates manual workflows, and provides actionable insights through dashboards and analytics.
For instance, a large multi-specialty hospital may use ERP software to track inventory across departments, preventing overstocking and minimizing wastage. Similarly, centralized finance modules can provide real-time budget monitoring, payroll tracking, and expense reporting saving both time and resources. When seamlessly integrated with clinical systems, ERP platforms help align financial and patient care objectives. The cumulative effect is an efficient, agile, and data-driven healthcare organization capable of delivering better outcomes at a lower cost.
Market Restraint: High Initial Investment and Transition Complexity
Despite the potential benefits, the U.S. healthcare ERP market faces a significant restraint in the form of high initial investment and transition complexity. Implementing an ERP system involves considerable costs related to software acquisition, customization, training, infrastructure upgrades, and change management. For small- and mid-sized healthcare facilities, this can be a substantial financial burden.
Furthermore, the transition from legacy systems to a new ERP platform can be disruptive. Hospitals must address issues like data migration, integration with existing systems (like EHR and laboratory information systems), and training personnel on new workflows. Downtime during transition or failure to properly configure modules can also hamper operations. These challenges often result in delayed implementation timelines and may discourage institutions from pursuing ERP adoption despite its long-term advantages.
A notable opportunity lies in the form of government-backed incentives and policy support encouraging digital transformation across the U.S. healthcare sector. Federal and state-level programs are promoting the adoption of IT tools including ERP systems as part of broader initiatives to increase efficiency, reduce costs, and improve care quality.
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) and the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC) have introduced guidelines under the HITECH Act and 21st Century Cures Act that promote interoperability, patient access to records, and digital infrastructure upgrades. These regulations create an ecosystem where integrated ERP solutions become essential for compliance and sustainability. Vendors who tailor their offerings to meet these evolving standards will likely benefit from increased adoption among eligible healthcare providers.
Segmental Insights
By Function Insights
Finance and billing dominated the functional segment of the U.S. healthcare ERP market in 2025. As healthcare institutions face increasing scrutiny regarding financial transparency and efficiency, ERP systems with strong finance and billing capabilities are in high demand. These modules help streamline complex billing processes, automate claims management, and ensure compliance with revenue cycle management regulations. They also allow CFOs and administrators to track cash flow, monitor reimbursements, and predict financial performance with greater accuracy.
Simultaneously, Patient Relationship Management (PRM) is emerging as the fastest-growing segment, driven by the emphasis on patient-centered care. Modern ERP systems now include PRM tools that manage the entire patient journey—from appointment scheduling and personalized communication to billing and feedback collection. For example, a hospital chain in Texas implemented a PRM module integrated with their call center and mobile app, resulting in a 27% increase in patient satisfaction and reduced appointment no-show rates. This growth is further supported by the rise in consumerism in healthcare, where patients expect seamless, Amazon-like experiences when interacting with healthcare providers.
By Deployment Insights
Cloud deployment dominated the U.S. healthcare ERP market in 2025, owing to its flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and ease of maintenance. Cloud ERP systems eliminate the need for on-site servers and allow healthcare providers to access critical data and tools anytime, anywhere. This is especially beneficial for multi-location hospital networks and telemedicine providers that require real-time coordination and data exchange. Furthermore, cloud solutions enable seamless updates, lower IT staffing needs, and offer superior data backup and recovery capabilities.
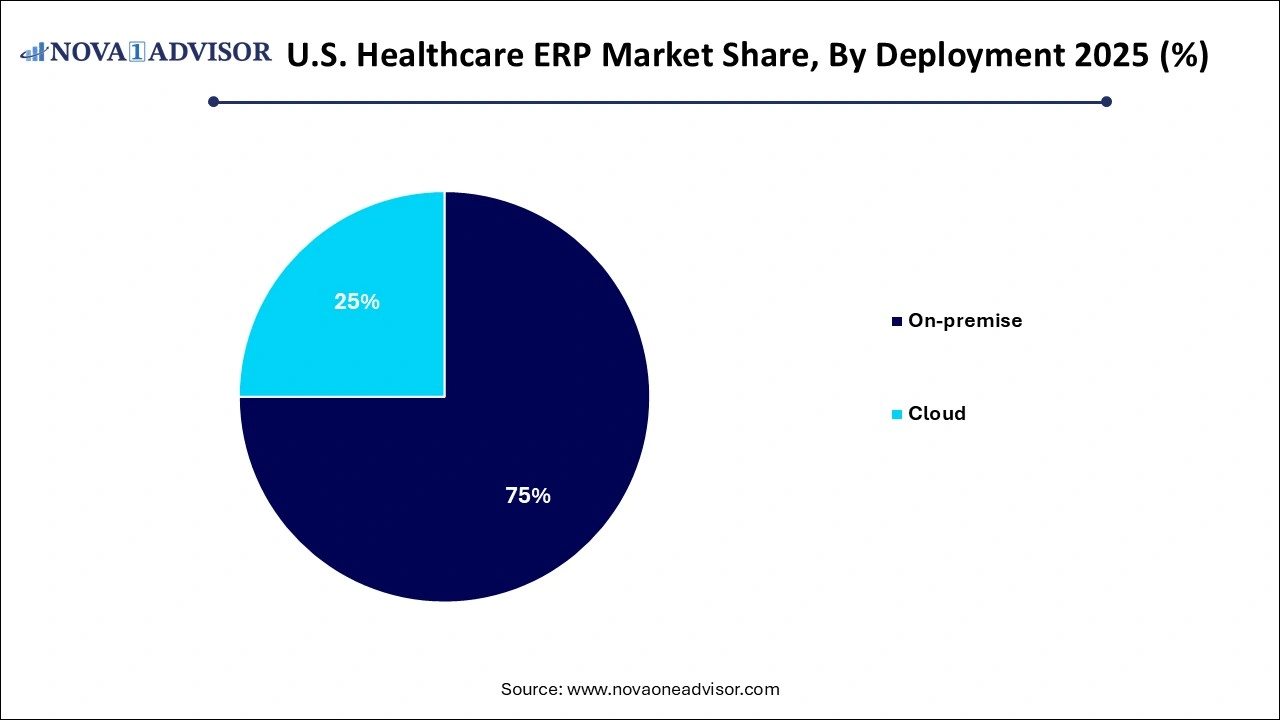
Meanwhile, on-premise deployment remains relevant for large hospitals with existing infrastructure and strict control over data security, but it is experiencing slower growth. Hospitals with complex internal systems and customized workflows often find on-premise ERP more suitable due to the degree of control and personalization it offers. However, even these entities are slowly exploring hybrid models that combine on-premise reliability with the agility of cloud access for non-critical functions. As cybersecurity in cloud platforms improves and regulations continue to evolve, the gap between on-premise and cloud adoption is expected to narrow.
Country-Level Insights United States
In the United States, the ERP adoption rate across healthcare institutions varies depending on the size and nature of the organization. Large hospital networks, such as Kaiser Permanente and HCA Healthcare, have been at the forefront of adopting comprehensive ERP systems. These organizations utilize ERP platforms to manage a wide array of functions, from workforce scheduling and payroll to inventory tracking and patient billing.
In contrast, small community hospitals and independent clinics are slower in adoption due to budget constraints and limited IT expertise. However, this is gradually changing with the rise of cloud-based solutions and government grants aimed at digital transformation. Furthermore, the U.S. healthcare landscape is seeing a surge in mergers and acquisitions, which increases the need for standardized ERP platforms that can unify operations across newly integrated facilities.
A notable trend in the U.S. is the growing use of ERP systems in ambulatory surgical centers (ASCs), specialty practices, and behavioral health facilities. These providers are seeking ERP solutions that can scale with their operations while offering healthcare-specific functionalities such as credentialing, medical billing compliance, and mobile access for field workers.
Some of the prominent players in the U.S. healthcare ERP market include:
Recent Developments
-
In January 2025, Oracle Health announced the expansion of its cloud ERP suite tailored for U.S. healthcare providers, introducing new analytics capabilities for patient experience and revenue cycle management. This comes as part of its strategy to integrate more AI-driven features across its product line.
-
In March 2025, Workday Inc. revealed its partnership with a leading midwestern health system to deploy a full-suite cloud ERP for finance and human capital management. The move is expected to standardize workflows and improve labor productivity across 20+ facilities.
-
In February 2025, Infor launched its next-gen ERP platform, specifically designed for healthcare organizations, with preconfigured templates for hospitals, ASCs, and specialty clinics. The launch emphasized speed of deployment and low-code customization for IT teams.
-
In December 2024, SAP SE enhanced its Business Technology Platform with healthcare-specific modules, allowing providers to create custom apps for inventory alerts, staff scheduling, and patient engagement within the ERP environment.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. healthcare ERP market
Function
- Inventory and material management
- Supply chain and logistics management
- Patient relationship management
- Finance and billing
- Others
Deployment


