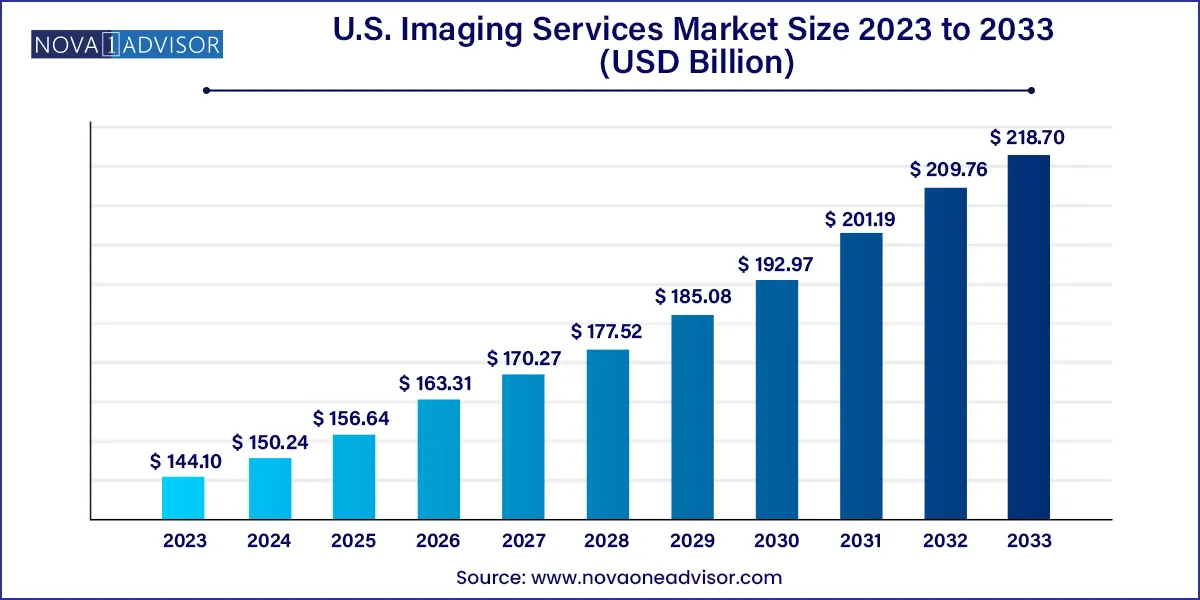
The U.S. imaging services market size was exhibited at USD 144.10 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 218.70 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 4.26% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
Key Takeaways:
- The market is segmented into X-rays, CT scans, nuclear medicine scans, MRI scans, ultrasound, and mammography. Nuclear medicine scans held the largest share of 24.29% in 2023.
- The magnetic resonance imaging segment is expected to grow at the highest CAGR of 4.59% over the forecast period.
- Hospitals held the largest share of 38.75% in 2023
- Others segment is also expected to grow at a significant CAGR during the forecast period.
Market Overview
The U.S. imaging services market forms a vital part of the country’s healthcare infrastructure, offering critical diagnostic, therapeutic, and screening capabilities across various clinical domains. These services involve the use of advanced imaging technologies such as X-rays, CT scans, MRI, ultrasound, mammography, and nuclear medicine scans to capture detailed internal visuals of the human body. Imaging supports everything from early disease detection and treatment monitoring to surgical planning and emergency intervention.
In the United States, imaging is widely adopted due to high standards in medical care, the prevalence of chronic diseases, and the growing emphasis on precision diagnostics. The market is supported by a combination of hospital radiology departments, independent diagnostic imaging centers, mobile imaging services, and ambulatory care units. Reimbursement trends, population health initiatives, and increasing awareness about preventive screenings (e.g., mammograms, coronary calcium scoring) continue to expand the demand for imaging.
Furthermore, technological advancements—such as AI-assisted image analysis, 3D and 4D imaging modalities, and low-dose radiation scanners—are redefining the quality, speed, and accessibility of imaging services. These improvements, coupled with telehealth integration and data interoperability, are enabling more efficient workflows and broader service availability in both urban and rural regions.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Increased use of AI for image interpretation and workflow automation
-
Expansion of outpatient and standalone diagnostic imaging centers
-
Rising demand for low-dose, high-resolution CT and MRI scanners
-
Surge in breast imaging awareness and mammography screenings
-
Integration of teleradiology in rural and underserved areas
-
Growth in hybrid modalities like PET/CT and PET/MRI for oncology
-
Use of portable imaging solutions in critical and home care
-
Shift toward value-based imaging tied to clinical outcomes
Report Scope of The U.S. Imaging Services Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 150.24 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 |
USD 218.70 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 |
CAGR of 4.26% |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered |
Modality, End-use |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope |
U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Radnet, Inc.; Alliance Medical; Inhealth Group; Sonic Healthcare; Dignity Health; Medica Group; Global Diagnostics; Novant Health; Concord Medical Services Holdings Limited; Center for Diagnostic Imaging, Inc.; Unilabs; Healius Limited; Simonmed Imaging |
Market Driver: Rising Chronic Disease Burden and Preventive Screening Initiatives
The escalating prevalence of chronic conditions such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, stroke, and musculoskeletal disorders is a primary driver of the U.S. imaging services market. Early and accurate imaging is essential for disease diagnosis, risk stratification, and continuous monitoring. For example, cardiac CT is now widely used for assessing coronary artery disease, while MRI is pivotal in diagnosing multiple sclerosis and spinal disorders.
Public health initiatives have further strengthened this trend. Organizations like the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) advocate for routine screenings (e.g., breast cancer, lung cancer, osteoporosis) through imaging. Widespread coverage by Medicare, Medicaid, and commercial insurers ensures that millions of patients can access these services without financial burden, reinforcing their adoption.
Market Restraint: Reimbursement Pressure and Operational Costs
Despite growing demand, imaging service providers face significant pressure from tightening reimbursement rates and increasing operational costs. The U.S. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) has introduced multiple reductions to imaging reimbursement over the past decade, especially for advanced modalities like MRI and CT. This has affected profitability and forced providers to invest in cost-efficiency strategies.
Moreover, the high capital investment required for advanced imaging equipment, radiologist salaries, maintenance, and regulatory compliance creates financial challenges, particularly for smaller or rural providers. The lack of uniformity in payer policies and coding complexities adds administrative burdens that can slow service delivery and innovation.
Market Opportunity: Integration of AI and Teleradiology
A transformative opportunity in the U.S. imaging services market lies in the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and teleradiology platforms. AI is rapidly being deployed for triaging scans, detecting anomalies, reducing interpretation times, and improving reporting accuracy. Radiology practices are using AI algorithms to streamline workflow, detect incidental findings, and ensure consistency across large imaging volumes.
Teleradiology, which enables radiologists to interpret images remotely, is addressing workforce shortages and enhancing service delivery in geographically underserved areas. It also allows for 24/7 coverage in emergency departments and night-time reporting in hospitals. As cloud platforms and secure image-sharing standards improve, these solutions will further optimize imaging turnaround and expand access to subspecialist interpretations.
U.S. Imaging Services Market By Modality Insights
X-rays remain the dominant imaging modality in the U.S. due to their widespread availability, cost-effectiveness, and application in various clinical scenarios. From fracture diagnosis to lung disease detection, X-rays are the first-line imaging tool in both emergency rooms and outpatient clinics. The advent of digital radiography (DR) has further improved image quality and speed, making X-rays even more indispensable in routine care.
MRI scans are the fastest-growing modality, especially for neurological, musculoskeletal, and oncological applications. MRI's superior contrast resolution and lack of ionizing radiation make it ideal for soft tissue evaluation. Technological advancements in 3T and 7T scanners, faster scan protocols, and noise reduction techniques have improved the patient experience and diagnostic yield. Increasing referrals for complex conditions and the expanding role of functional MRI (fMRI) are contributing to its rapid growth.
CT scans also play a significant role, particularly in trauma, cardiac, and abdominal imaging. With innovations in low-dose radiation, dual-energy scanning, and AI-based reconstruction, CT has become safer and faster, expanding its use in both acute and preventive care settings.
U.S. Imaging Services Market By End-use Insights
Hospitals dominate the imaging services market, leveraging their integrated systems, multidisciplinary teams, and access to the latest imaging infrastructure. Hospitals routinely perform a wide spectrum of imaging procedures, from emergency trauma scans to inpatient follow-ups and pre-surgical planning. Academic medical centers and tertiary care hospitals are also driving research and clinical trials in advanced imaging techniques.
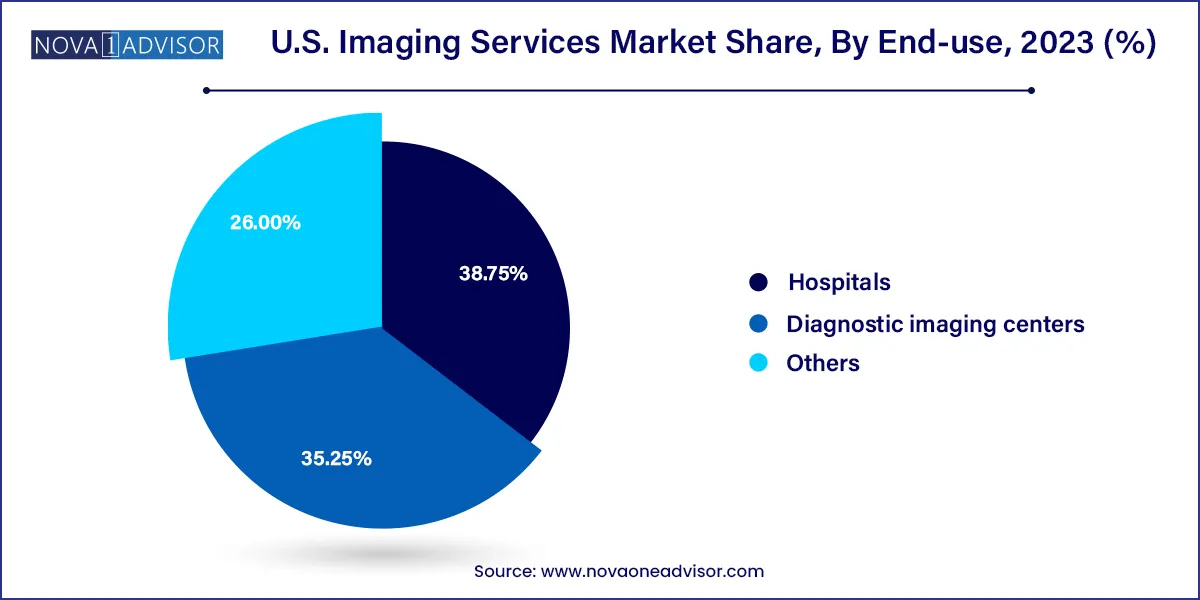
Diagnostic imaging centers are the fastest-growing end-use segment, reflecting the trend toward outpatient care and cost containment. These centers offer same-day appointments, shorter wait times, and specialized imaging services, attracting patients seeking convenience and efficiency. With payer incentives encouraging site-of-care shifts, more non-urgent imaging is being redirected from hospitals to freestanding centers. Mobile imaging services and joint ventures with physician groups are accelerating this shift.
Country-Level Analysis: United States
The U.S. imaging services market is characterized by high per capita imaging utilization, driven by robust infrastructure, broad insurance coverage, and an emphasis on diagnostic precision. The country leads in adoption of advanced modalities, AI-driven imaging platforms, and integrated radiology information systems (RIS) and PACS.
Public and private healthcare systems are investing heavily in imaging upgrades, particularly in underserved communities where portable imaging and teleradiology have emerged as vital tools. Preventive health initiatives under the Affordable Care Act and ongoing CMS reforms continue to incentivize timely imaging. Moreover, the proliferation of value-based care models is shifting imaging from volume-based metrics to quality and appropriateness benchmarks.
Recent Development
-
In April 2025, RadNet launched an AI-powered breast imaging analytics suite to improve early detection in mammography screenings.
-
In February 2025, GE HealthCare introduced its SIGNA Prime 1.5T MRI system designed for mid-tier and community hospitals.
-
In January 2025, Akumin Inc. expanded its partnership with a national hospital system to provide outsourced imaging services at 25 new sites.
-
In November 2024, Hologic gained FDA clearance for its 3DQuorum imaging platform, reducing scan times while maintaining resolution.
-
In September 2024, Canon Medical Systems USA announced a new AI-integrated CT system with enhanced lung screening capabilities.
Some of the prominent players in the U.S. imaging services market include:
- Radnet, Inc.
- Alliance Medical
- Inhealth Group
- Sonic Healthcare
- Dignity Health
- Medica Group
- Global Diagnostics
- Novant Health
- Concord Medical Services Holdings Limited
- Center for Diagnostic Imaging, Inc.
- Unilabs
- Healius Limited
- Simonmed Imaging
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. imaging services market.
Modality
- X-rays
- CT scans
- Nuclear medicine scans
- MRI scans
- Ultrasound
- Mammography
End-use
- Hospitals
- Diagnostic imaging centers
- Others


