U.S. Liver Cancer Diagnostics Market Size and Trends
The U.S. liver cancer diagnostics market size was exhibited at USD 4.00 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 6.27 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 4.6% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
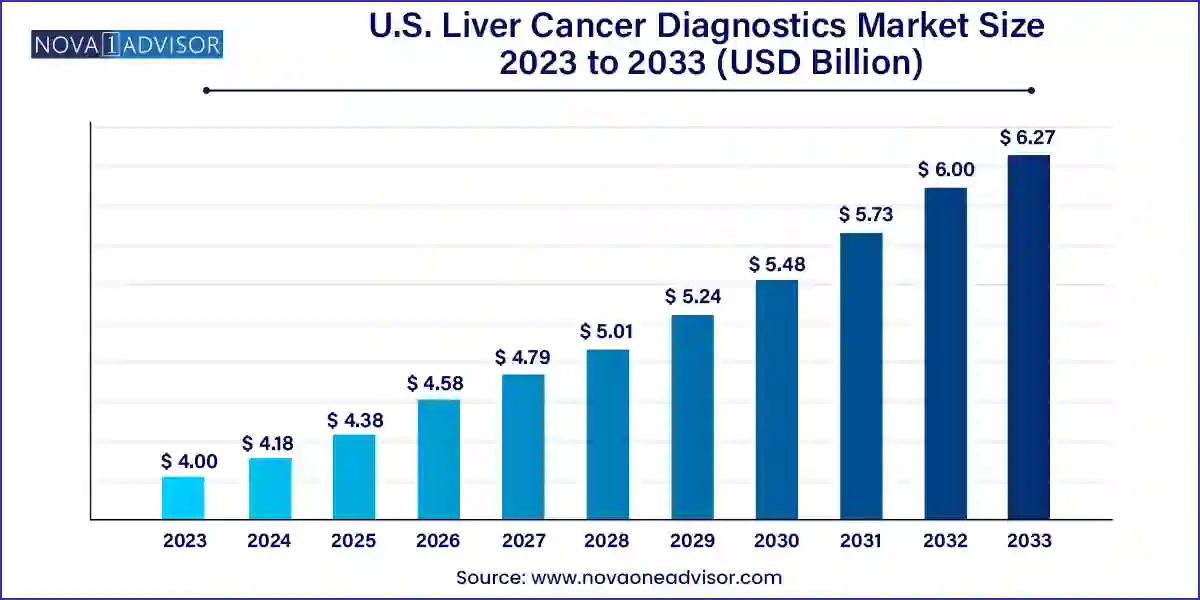
Key Takeaways:
- The laboratory tests segment accounted for the largest revenue share of around 40.15% in 2023.
- The hospitals and diagnostic laboratories segment dominated the market with a revenue share of around 50.2% in 2023.
Market Overview
The U.S. Liver Cancer Diagnostics Market is gaining significant momentum due to the rising incidence of liver cancer, growing awareness around early diagnosis, and advancements in diagnostic modalities. Liver cancer, especially hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), remains one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths in the United States. According to the American Cancer Society, approximately 41,210 new cases of liver cancer will be diagnosed in the U.S. in 2024, with over 29,380 deaths projected. This alarming trend underlines the urgent need for effective and accurate diagnostic solutions that can enable early detection, which is crucial for successful treatment outcomes.
The market encompasses a variety of test types, including laboratory tests, imaging modalities, biopsies, and endoscopic techniques, all designed to detect liver malignancies at different stages of progression. The integration of molecular diagnostics and the advent of biomarker-based tests have revolutionized liver cancer screening and diagnostics. These innovations are supported by the increasing adoption of artificial intelligence and machine learning in radiological diagnostics and pathology, enabling faster and more accurate diagnoses.
Furthermore, increased funding in research and development, along with favorable governmental policies promoting cancer screening programs, is driving the growth of this market. Institutions such as the National Cancer Institute (NCI) and other public health entities are investing in early detection programs, enhancing access to advanced diagnostic technologies across the nation.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Shift Towards Non-Invasive Diagnostics: There is a growing preference for non-invasive and minimally invasive diagnostic procedures, such as liquid biopsies and imaging techniques like MRI and CT scans.
-
Increased Adoption of Biomarker-Based Testing: Biomarkers such as alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), DCP (Des-γ-carboxy prothrombin), and newer molecular markers are increasingly utilized for early diagnosis and monitoring treatment response.
-
Artificial Intelligence Integration in Imaging: AI-powered imaging solutions are improving the precision and speed of diagnosis, aiding radiologists in detecting minute anomalies that might be missed through conventional means.
-
Point-of-Care Testing Expansion: Portable diagnostic devices and rapid testing kits are gaining traction, especially in outpatient clinics and rural healthcare settings where immediate results are critical.
-
Collaborations Between Pharma and Diagnostics Firms: Partnerships are being formed to co-develop companion diagnostics, ensuring that diagnostic solutions align with personalized treatment plans.
-
Government and Private Sector Investment in Screening Programs: Increased emphasis on liver cancer screening, especially for high-risk groups such as hepatitis B and C patients, is fostering market expansion.
-
Increased Usage of Telemedicine for Diagnostic Consultations: Telehealth platforms are being integrated with diagnostic services to offer remote access to oncologists and radiologists, facilitating earlier interventions.
Report Scope of U.S. Liver Cancer Diagnostics Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 4.18 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 |
USD 6.27 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 |
CAGR of 4.6% |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered |
Test Type, End-use, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope |
U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Abbott Laboratories; Guardant Health; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.; Illumina, Inc.; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.; Qiagen N.V.; Siemens Healthineers; Becton, Dickinson & Company; Epigenomics AG; Koninklijke Philips N.V.; and FUJIFILM Healthcare Americas Corporation. |
Market Driver: Rising Incidence of Liver Cancer in the U.S.
One of the primary drivers of the U.S. Liver Cancer Diagnostics Market is the increasing prevalence of liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma. The surge in liver cancer cases is predominantly attributed to risk factors such as chronic hepatitis B and C infections, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, and diabetes. The aging population also contributes significantly, as liver cancer incidence increases with age. As awareness grows, more patients are undergoing routine screenings, leading to a higher number of diagnoses and, consequently, a rising demand for diagnostic tools. The widespread implementation of national cancer screening programs and growing access to healthcare are also fueling market growth by encouraging early detection.
Market Restraint: High Cost of Advanced Diagnostic Technologies
While innovation is a boon for diagnostics, the cost associated with high-end diagnostic tools can act as a significant barrier, particularly for underinsured or uninsured populations. Advanced imaging techniques such as PET scans or multi-parametric MRI, and molecular diagnostic tests involving next-generation sequencing (NGS) or multi-marker panels, are often expensive and not uniformly covered by all insurance providers. Additionally, the costs associated with skilled professionals to operate these technologies and interpret results further escalate the diagnostic expenses. This cost barrier often leads to delayed diagnosis in lower-income groups, adversely affecting early treatment and market penetration.
Market Opportunity: Emergence of Liquid Biopsy as a Game-Changer
Liquid biopsy represents a transformative opportunity in the liver cancer diagnostics landscape. Unlike traditional tissue biopsies, liquid biopsies analyze circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), exosomes, or other cancer-related substances from a blood sample, offering a non-invasive and highly accurate diagnostic approach. This method enables real-time monitoring of tumor progression and treatment response. Its utility in detecting minimal residual disease (MRD) and recurrence before conventional imaging makes it a promising tool for early intervention. As research expands and validation studies confirm their efficacy, liquid biopsies are expected to see rapid adoption across U.S. healthcare facilities, unlocking significant market growth potential.
U.S. Liver Cancer Diagnostics Market By Test Type Insights
Laboratory tests dominated the U.S. liver cancer diagnostics market in 2024, particularly those focused on biomarker-based screening. Within laboratory testing, biomarkers such as alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), glypican-3 (GPC3), and des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin (DCP) are most commonly used in routine liver cancer screening. These tests are often the first-line diagnostic tools used for high-risk patients and are considered cost-effective and minimally invasive. Their accessibility and ease of use make them widely deployed in outpatient and clinical lab settings. Additionally, enzyme and isoenzyme biomarkers like alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) are used in conjunction with imaging to improve diagnostic confidence.
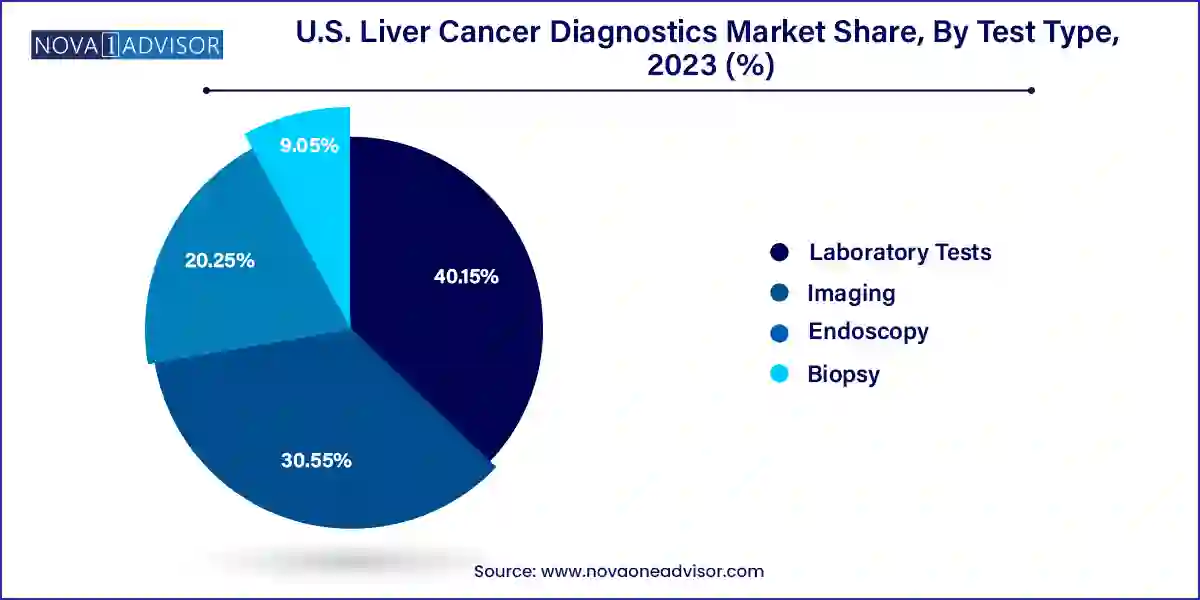
Imaging tests, particularly MRI and CT scans, are expected to be the fastest-growing segment due to technological advancements that enable higher resolution liver imaging. Enhanced imaging techniques like contrast-enhanced MRI and elastography offer detailed anatomical and functional information about liver tissues. These are especially valuable in identifying tumor margins and vascular invasion, aiding in staging and surgical planning. AI-enhanced imaging platforms are increasingly being used to reduce diagnostic turnaround times and to improve early detection rates, thereby reducing the rate of false negatives.
U.S. Liver Cancer Diagnostics Market By End-use Insights
Hospitals and diagnostic laboratories held the largest market share in 2024, due to the availability of integrated diagnostic infrastructure and specialist care. Large healthcare networks and academic medical centers in urban U.S. areas possess sophisticated imaging equipment and trained oncologists, making them preferred diagnostic centers. These institutions often handle complex liver cancer cases and also participate in clinical trials involving novel diagnostic technologies, further fueling their dominance in the segment.
Pharmaceutical and CRO laboratories are emerging as the fastest-growing end-use segment, driven by their role in biomarker discovery and clinical validation studies. The increased focus on personalized medicine has led pharmaceutical companies to collaborate with diagnostics firms for co-development of companion diagnostics. Contract Research Organizations (CROs) play a pivotal role in conducting studies that generate the real-world evidence needed for regulatory approvals and clinical utility validation. These collaborations are enhancing diagnostic accuracy and supporting the commercialization of novel liver cancer diagnostic tools.
Country-Level Analysis
The U.S. liver cancer diagnostics market is characterized by a concentration of innovation hubs and high diagnostic adoption in states such as California, New York, and Massachusetts. These states host some of the leading academic medical centers, biotech companies, and research institutions actively working on liver cancer diagnostic technologies. For example, California’s biotech corridor in the Bay Area is home to several startups focusing on liquid biopsies and digital pathology platforms.
Southern states like Texas and Florida, which have higher Hispanic populations—a demographic with increased risk for liver cancer—are also seeing targeted public health initiatives aimed at expanding early screening and detection. Meanwhile, rural and Midwestern regions still face disparities in access to high-end diagnostic technologies, leading to later-stage diagnosis and poorer outcomes. Federal policies aimed at rural healthcare infrastructure development could bridge this diagnostic gap and present new growth opportunities for diagnostic device manufacturers and service providers.
Some of the prominent players in the U.S. liver cancer diagnostics market include:
- Abbott Laboratories
- Guardant Health
- Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.
- Illumina, Inc.
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
- Qiagen N.V.
- Siemens Healthineers
- Becton, Dickinson & Company
- Epigenomics AG
- Koninklijke Philips N.V.
- FUJIFILM Healthcare Americas Corporation
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. liver cancer diagnostics market
Test Type
-
-
- Oncofetal and Glycoprotein Antigens
- Enzymes and Isoenzymes
- Growth Factors and Receptors
- Molecular Markers
- Pathological Biomarkers
- Imaging
- Endoscopy
- Biopsy
- Others
End-use
- Hospitals & Diagnostic Laboratories
- Academic & Research Institutes
- Pharmaceutical & CRO Laboratories
Regional
- West
- Midwest
- Northeast
- Southwest
- Southeast


