U.S. Ophthalmic Handheld Surgical Instruments Market Size and Growth
The U.S. ophthalmic handheld surgical instruments market size was exhibited at USD 736.55 million in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 1,079.84 million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 3.9% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
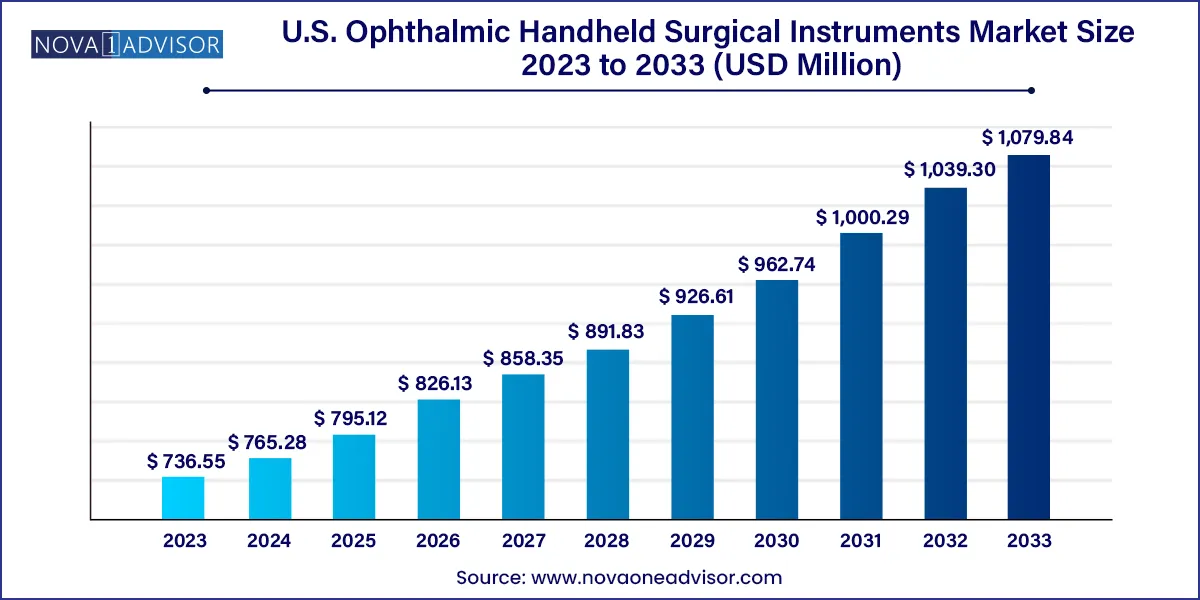
Key Takeaways:
- The ophthalmic knives segment dominated the market with the highest revenue share in 2023.
- The scissors segment is expected to undergo maximum growth over the forecast period.
- The hospitals segment held the largest market share of around 59.0% in 2023.
- The ophthalmic clinics segment accounted for a share of 29.1% in 2023 and is expected to witness the fastest growth over the forecast period.
Market Overview
The U.S. ophthalmic handheld surgical instruments market is a critical component of the broader ophthalmic devices industry, playing a pivotal role in the delivery of high-precision surgical care for ocular conditions. These instruments—ranging from forceps and scissors to ophthalmic knives and cannulas are indispensable tools in procedures such as cataract surgery, retinal detachment repair, glaucoma treatment, and corneal transplants.
The market is characterized by its close alignment with technological innovation, increasing surgical volumes, and the evolving demographics of the U.S. population. With the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reporting that more than 12 million Americans aged 40 years and older are visually impaired, the demand for advanced ophthalmic surgeries is escalating. Aging remains a core driver, as conditions such as cataracts, age-related macular degeneration (AMD), and glaucoma predominantly affect the elderly population.
Furthermore, the shift toward minimally invasive surgical techniques has increased the need for refined, ergonomic, and reusable handheld instruments capable of delivering precise incisions and manipulation within the delicate structures of the eye. A growing emphasis on outpatient and ambulatory surgical care has reinforced the demand for portable, sterilizable, and cost-effective ophthalmic tools tailored for high-efficiency procedures.
Overall, the U.S. market continues to evolve due to regulatory support, healthcare infrastructure advancements, and strong investments by both multinational corporations and specialty manufacturers. While hospitals remain key consumers, standalone ophthalmic clinics and ambulatory centers are gaining ground, driven by shorter procedural times and patient-centric care models.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Miniaturization and Precision Engineering: Instruments are becoming smaller, lighter, and more precise, enabling safer microsurgical interventions.
-
Growth of Single-use Instruments: Rising awareness of cross-contamination risks and demand for sterilization efficiency is fueling the shift to disposable tools.
-
Ergonomic Designs for Surgeon Comfort: Manufacturers are focusing on surgeon fatigue reduction through lighter instruments with improved grip control.
-
Increased Adoption of Premium Cataract Surgeries: Surgeons performing multifocal IOL implantations or femto-assisted procedures require highly specialized handheld tools.
-
Custom Instrument Sets for Specialized Procedures: Clinics are increasingly ordering customized instrument trays based on their procedural volume and focus area.
-
Integration with Digital Visualization Systems: Some instruments now come with enhanced compatibility for robotic and digital-assisted visualization platforms.
-
Rising Demand in Ambulatory Settings: Outpatient surgical centers are increasing orders for cost-efficient, reusable instruments to support growing volumes.
-
Sustainability and Green Surgery Movement: Reusable instruments and eco-conscious materials are gaining traction due to environmental concerns and healthcare sustainability goals.
Report Scope of The U.S. Ophthalmic Handheld Surgical Instruments Market
Market Driver: Rising Prevalence of Cataract Surgeries in the U.S.
One of the most potent drivers of the U.S. ophthalmic handheld surgical instruments market is the growing number of cataract surgeries performed annually. Cataracts are the leading cause of blindness worldwide and one of the most common age-related vision disorders in the United States. According to the National Eye Institute, over 24.4 million Americans aged 40 and older are affected by cataracts, and this number is expected to increase substantially as the U.S. population ages.
Cataract surgery is highly dependent on the availability of fine handheld instruments such as phaco choppers, scissors, capsulorhexis forceps, and keratomes. These tools are essential for ensuring clean incisions, lens fragmentation, and tissue manipulation. With the U.S. performing more than 3.8 million cataract surgeries per year, instrument manufacturers face a consistent and growing demand. Furthermore, the shift toward premium cataract procedures, involving intraocular lens (IOL) customization and femtosecond laser technology, has further elevated the importance of precise and durable instruments that can support intricate surgical requirements.
Market Restraint: Sterilization Challenges and Reprocessing Costs
While reusable ophthalmic instruments offer long-term cost advantages, they also introduce challenges related to sterilization and reprocessing. Infections such as Toxic Anterior Segment Syndrome (TASS) and endophthalmitis, though rare, can arise from improper instrument cleaning and handling. Given the ultra-fine structure and tight junctions of ophthalmic tools, especially cannulas and knives, ensuring consistent sterilization remains a logistical and technical challenge for surgical centers.
Moreover, the cost associated with maintaining sterility including specialized cleaning equipment, staff training, tracking systems, and compliance with FDA and CDC protocols can be prohibitive for small ophthalmic clinics. This has led to a dilemma between choosing cost-efficient reusable instruments and safer, but more expensive, single-use alternatives. As regulatory scrutiny increases, facilities must invest more resources in documentation, validation, and routine audits of instrument processing, which can slow adoption among resource-constrained practices.
5. Market Opportunity: Growth of Ambulatory Surgical Centers (ASCs)
The emergence and rapid expansion of Ambulatory Surgical Centers (ASCs) in the U.S. represents a significant market opportunity for ophthalmic handheld instrument manufacturers. ASCs offer ophthalmic procedures in cost-effective, outpatient settings, enabling high-volume surgeries such as cataract extraction, LASIK, and glaucoma interventions without the overhead costs of hospital infrastructure.
According to the Ambulatory Surgery Center Association, ophthalmology accounts for one of the highest surgical volumes in ASCs. With CMS (Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services) expanding reimbursement coverage for more eye-related surgeries in outpatient environments, ASCs are becoming preferred destinations for both patients and ophthalmologists. These facilities prefer high-quality, lightweight, and multi-functional surgical instruments that support quicker turnover and sterility compliance.
Instrument providers have an opportunity to tailor their offerings whether reusable or single-use for these environments by focusing on packaging efficiency, reduced processing time, and ergonomic functionality. Additionally, manufacturers can gain competitive advantage by offering customized instrument sets and service agreements tailored to ASC procedural needs.
U.S. Ophthalmic Handheld Surgical Instruments Market By Product Insights
Forceps emerged as the dominating product category in the U.S. ophthalmic handheld surgical instruments market due to their indispensable role in almost every ophthalmic surgical procedure. Whether in cataract extraction, retina detachment repair, or corneal transplants, forceps are used to grasp, hold, and manipulate delicate ocular tissues. Types such as capsulorhexis forceps, tying forceps, and micro-forceps are customized for anterior and posterior segment surgeries. The growing surgical caseload, coupled with increasing demand for ergonomic, titanium-made, and ultra-fine tipped forceps, has helped sustain this segment’s lead.
Ophthalmic knives are the fastest-growing product segment, driven by rising surgical complexity and demand for precise incisions. These instruments are critical in both manual small incision cataract surgery (MSICS) and phacoemulsification, where clean cuts minimize tissue trauma. Modern ophthalmic knives include crescent, slit, keratome, and MVR types, often enhanced with diamond or ceramic blades for longevity and precision. The shift toward minimally invasive incisions and premium procedures such as femtosecond laser-assisted surgeries is increasing demand for ultra-sharp, customizable knives compatible with newer techniques.
U.S. Ophthalmic Handheld Surgical Instruments Market By End-use Insights
Hospitals dominate the end-use segment due to their access to advanced ophthalmic surgical infrastructure and large surgical volumes. Tertiary care hospitals and academic medical centers routinely perform complex surgeries like retinal reattachments and pediatric strabismus corrections, which require a full suite of high-end handheld instruments. Their ability to invest in reusable surgical kits, sterilization units, and instrument tracking systems makes them top customers for manufacturers. Hospitals also benefit from integrated procurement systems and long-standing relationships with instrument vendors, enabling bulk orders and rapid restocking.

Ophthalmic clinics are the fastest-growing end-use segment, especially those offering ambulatory and outpatient surgical services. Independent eye care centers, laser eye surgery clinics, and ambulatory centers are expanding their capabilities to conduct high-volume procedures efficiently. These clinics demand lightweight, easy-to-sterilize instruments with customizable configurations to match specific procedural needs. As the number of ophthalmologists practicing outside hospitals increases and reimbursement systems become more clinic-friendly, this segment is expected to lead innovation and adoption in single-use instruments and compact surgical trays.
Country-level Analysis – United States
In the United States, the ophthalmic surgical landscape is undergoing a major transformation with a strong shift toward outpatient care and premium ophthalmic interventions. The country’s robust healthcare infrastructure, favorable reimbursement systems, and high patient awareness levels make it one of the most lucrative markets for ophthalmic surgical instruments. The aging Baby Boomer population, which is increasingly opting for elective procedures like cataract surgery, multifocal lens implantation, and glaucoma interventions, continues to propel demand for precision instruments.
Additionally, the U.S. is a global leader in ophthalmic innovation, with top-tier institutions such as the Bascom Palmer Eye Institute, Wills Eye Hospital, and Johns Hopkins leading advancements in microsurgery and tool design. Government support through the FDA’s 510(k) clearances and breakthrough device designations further accelerates commercialization. Companies operating in the U.S. also benefit from well-established distributor networks, skilled labor availability, and surgeon-led collaborations that influence instrument design.
Moreover, the rise of multi-specialty ophthalmology groups and acquisition of independent practices by private equity firms is consolidating demand, leading to standardized instrument preferences and bulk procurement agreements. This evolving business model presents new avenues for instrument makers to package their offerings with value-added services like maintenance, warranty extensions, and customization.
Some of the prominent players in the U.S. ophthalmic handheld surgical instruments market include:
- BVI
- Accutome, Inc.
- Medline Industries, Inc.
- Haag-Streit Group
- Appasamy Associates
- Millennium Surgical Corp
- Katalyst Surgical
- ASICO, LLC.
- INKA Surgical Instruments
- Surgical Holdings
Recent Developments
-
In March 2025, Bausch + Lomb introduced a new line of titanium micro-forceps with enhanced grip technology, specifically targeting high-precision vitreoretinal surgeries.
-
In January 2025, Storz Ophthalmic Instruments (BVI Medical) announced FDA clearance for its new ergonomic phaco chopper designed for use in micro-incision cataract surgeries.
-
In November 2024, Rumex International launched a single-use ophthalmic instrument tray for ASCs, optimized for high-volume cataract procedures and compliant with Joint Commission standards.
-
In August 2024, Accutome (a Halma company) unveiled a new range of diamond ophthalmic knives featuring a patented anti-glare coating to enhance visibility under operating lights.
-
In July 2024, Katena Products Inc. acquired a U.S.-based specialty tool manufacturer, expanding its portfolio of reusable instruments for glaucoma and corneal surgeries.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. ophthalmic handheld surgical instruments market
Product
- Forceps
- Scissors
- Chopper
- Ophthalmic Knives
- Cannula
- Others
End-use
- Hospitals
- Ophthalmic Clinics
- Others
Country


