U.S. Pupillometer Market Size and Growth 2026 to 2035
The U.S. pupillometer market size was estimated at USD 114.25 million in 2025 and is expected to be worth around USD 202.68 million by 2035, poised to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.9% during the forecast period 2026 to 2035.
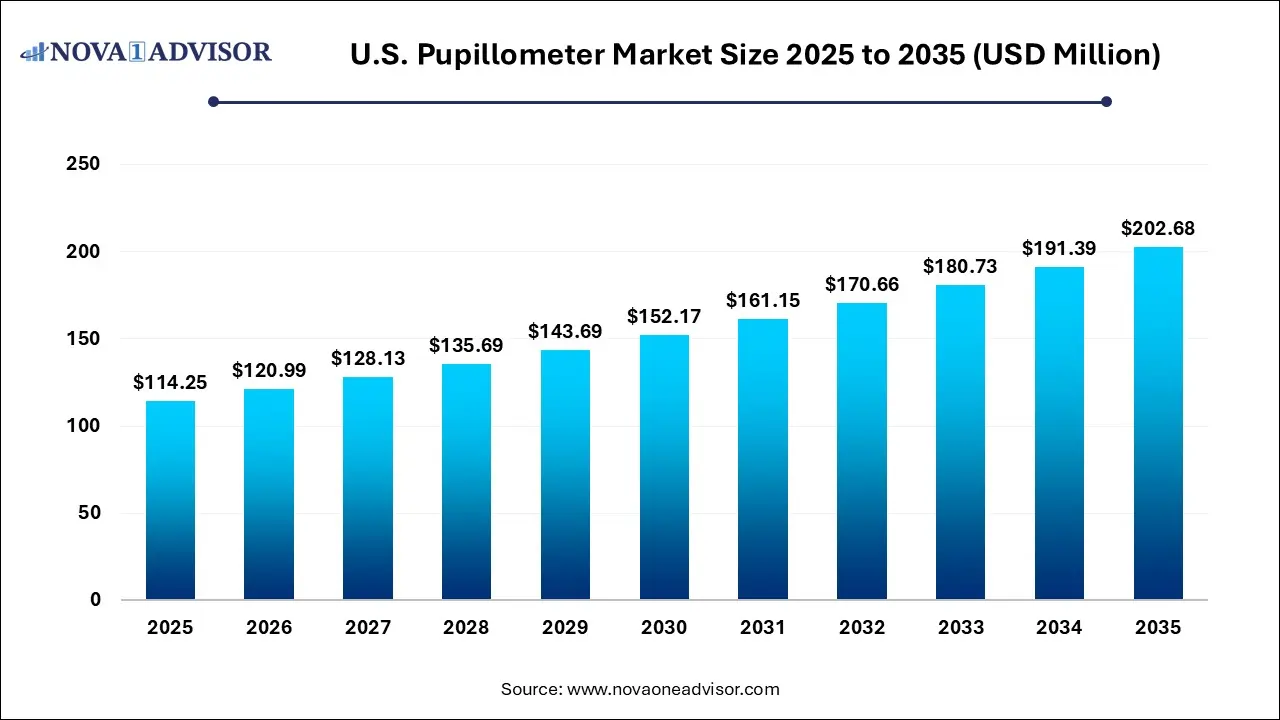
U.S. Pupillometer Market Key Takeaways
- Table-top pupillometer dominated the market and held highest revenue share of 54.21% in 2025.
- Hand-held pupillometers is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR of 5.77% during the forecast period.
- Video dominated the type segment and held the largest revenue share of 56.9% in 2025 and is expected to grow at a significant rate during the forecast period.
- Digital is expected to experience the fastest CAGR of 5.81% during the forecast period.
- Ophthalmology dominated the market and held for the largest revenue share of 50% in 2025.
- Oncology is expected to experience the fastest CAGR of 5.81% during the forecast period.
- Hospitals dominated the market and held the largest revenue share of 50% in 2025.
- Eye clinics is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR of 5.81% during the forecast period.
Market Overview
The U.S. pupillometer market is witnessing growing relevance across multiple clinical settings, with technological advancements and a shift toward objective neurological and ophthalmic assessments fueling demand. Pupillometers are medical devices used to measure the pupillary light reflex and pupil diameter, essential indicators in diagnosing and monitoring conditions related to the brain, eyes, and autonomic nervous system.
Traditional manual methods of assessing pupil size and reaction have long been a part of clinical practice, but they often suffer from observer bias, inaccuracy, and poor reproducibility. In contrast, modern digital and video pupillometers offer automated, precise, and standardized measurements. These devices are becoming critical tools in trauma units, neurology departments, ophthalmology clinics, and intensive care units (ICUs) across the United States.
The U.S. market has been especially receptive to pupillometers due to a robust healthcare system, high patient awareness, and increased incidence of conditions such as traumatic brain injuries (TBIs), glaucoma, stroke, and neurodegenerative diseases. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), approximately 223,000 TBI-related hospitalizations occurred in the U.S. in 2023 alone, creating a strong clinical demand for neurologic monitoring tools like pupillometers.
Further, the growing use of pupillometry in eye health evaluations especially for detecting afferent pupillary defects (APD), anisocoria, and early signs of glaucoma has broadened the application scope. Integration with electronic health records (EHRs), portability enhancements, and advances in pupil tracking algorithms have significantly expanded the adoption of pupillometers in outpatient and emergency settings.
Market Outlook
Market Growth Overview: The U.S. pupillometer market is expected to grow significantly between 2025 and 2034, driven by the rising neurological conditions, aging population, healthcare spending, and rising digital transformation.
Sustainability Trends: Sustainability trends involve eco-friendly manufacturing, product longevity, efficiency, and data and connectivity for efficiency.
Major Investors: Major investors in the market include NeurOptics, Inc., Johnson & Johnson Vision, Essilor Instruments USA, and Reichert Technologies.
Artificial Intelligence: The Next Growth Catalyst in U.S. Pupillometer
AI is significantly impacting the U.S. population industry by enhancing diagnostic precision and operational efficiency. AI-driven algorithms analyze complex pupillary responses in real-time, enabling earlier and more accurate detection of neurological and ophthalmological conditions like glaucoma and traumatic brain injury, which was previously a challenge with subjective methods. This technological integration is driving the development and adoption of smart, portable, and user-friendly devices, including smartphone-based pupillometers, thereby expanding market penetration into telemedicine and remote healthcare sectors.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Increased Use of Pupillometry in Neurological Assessments: Adoption is growing in neuro ICUs and emergency departments for evaluating TBIs, strokes, and brain herniation risks.
-
Shift Toward Handheld and Portable Devices: Compact, battery-operated pupillometers are gaining popularity among first responders and mobile clinics.
-
Integration with EHR and AI Algorithms: Smart pupillometers can store, compare, and analyze data using integrated software platforms.
-
Pupillometry in Oncology and Pain Management: Research is expanding into using pupillary response as a non-invasive biomarker for pain and opioid administration effects.
-
Cross-disciplinary Use Cases: Ophthalmologists, neurologists, anesthesiologists, and emergency physicians increasingly share use of these tools.
-
Rising Demand in Sports Medicine and Concussion Monitoring: Schools, colleges, and sports organizations are adopting pupillometers to track concussive injuries.
-
Expansion into Ambulatory and Primary Care: Eye clinics and general practitioners are integrating pupillometry into their diagnostic toolkits.
-
Automated Light Reflex Testing: Advances in stimulus precision and reaction timing are leading to more accurate neurological assessments.
-
Reimbursement Improvements and CPT Coding Enhancements: Insurance support for automated pupillary assessments is increasing market accessibility.
-
Increased Research on Pupil Metrics as Predictive Indicators: Studies on pupil size dynamics and autonomic response are generating new diagnostic applications.
U.S. Pupillometer Market Report Scope
| Report Attribute |
Details |
| Market Size in 2026 |
USD 120.99 Million |
| Market Size by 2035 |
USD 202.68 Million |
| Growth Rate From 2026 to 2035 |
CAGR of 5.9% |
| Base Year |
2025 |
| Forecast Period |
2026 to 2035 |
| Segments Covered |
Mobility, type, application, end-use |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage |
Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled |
NeurOptics, Inc.; Reichert Technologies; Johnson & Johnson Vision; Brightlamp, Inc.; Adaptica; Essilor Instruments USA; HAAG-STREIT GROUP; Luneau Technology Group; NIDEK CO., LTD.; SCHWIND eye-tech-solutions; US Ophthalmic; Konan Medical |
Market Driver: Growing Prevalence of Neurological and Ophthalmic Disorders
A significant driver of the U.S. pupillometer market is the rising prevalence of neurological and eye-related disorders that require accurate and real-time pupil assessments. Traumatic brain injuries (TBIs), for instance, are one of the most common causes of emergency room visits, especially among the elderly, athletes, and military personnel. Objective pupillometry is increasingly used in these scenarios to detect early signs of elevated intracranial pressure, cerebral herniation, or ischemia, conditions where rapid and accurate assessment is crucial.
Similarly, in ophthalmology, conditions like glaucoma, optic neuritis, and retinal detachment often present with pupil abnormalities. Pupillometers allow clinicians to perform afferent pupillary defect testing with high sensitivity, facilitating early diagnosis and intervention. Moreover, with a growing elderly population in the U.S. projected to reach over 80 million by 2040 the incidence of age-related eye diseases like macular degeneration and cataracts is expected to increase, thereby enhancing the need for standardized pupil evaluation tools.
Market Restraint: High Cost of Advanced Pupillometer Devices
Despite their clinical advantages, the adoption of pupillometers faces a key barrier: the relatively high cost of advanced digital and video pupillometer systems. These devices can range from several thousand dollars for basic handheld models to upwards of $10,000 or more for fully integrated video systems. For smaller practices or clinics with limited budgets, the return on investment (ROI) can be challenging to justify, especially when patient volumes are low or reimbursement is uncertain.
In addition, training staff to use and interpret pupillometer results, integrating devices with existing hospital IT systems, and maintaining calibration standards can create operational burdens. Many clinicians continue to rely on traditional penlight methods or manual pupil gauges due to these barriers, slowing the overall transition to automated systems.
Market Opportunity: Expansion into Pain Management and Critical Care Monitoring
A compelling opportunity in the U.S. pupillometer market lies in expanding applications in critical care and pain management. Research is increasingly supporting the use of pupillary reflex metrics as biomarkers for opioid efficacy, sedation depth, and pain perception. In intensive care units (ICUs), where patients are often sedated and unable to communicate, pupillometry can serve as a non-verbal, objective indicator of neurological function and analgesic effect.
Pharmacological studies have shown that pupil size and response to light stimuli can indicate a patient's nociceptive state. In anesthesia, pupillometers are being explored to fine-tune opioid dosages, assess intraoperative pain, and prevent over-sedation. As hospitals aim to improve patient outcomes and reduce adverse events from pain mismanagement or anesthesia complications, these applications offer significant clinical and market potential.
U.S. Pupillometer Market By Mobility Insights
Table-top pupillometers currently dominate the U.S. market, particularly in hospital-based neurology departments, ophthalmic centers, and academic research institutions. These devices are known for their higher resolution, stability, and extended feature sets, making them ideal for in-depth pupil diagnostics, especially when continuous monitoring and multi-modal integration are required. Table-top systems also support better integration with other ophthalmic tools, such as slit lamps and visual field analyzers, thus providing comprehensive assessments.
Hand-held pupillometers are the fastest-growing segment, driven by their portability, ease of use, and suitability for rapid neurological assessments in field settings, ambulances, sports clinics, and ICUs. The ability to deploy these devices in minutes without the need for a dedicated workstation makes them particularly attractive for trauma care, stroke assessments, and bedside exams. Furthermore, improvements in battery life, screen resolution, and wireless data transmission are fueling adoption among emergency responders and primary care physicians.
U.S. Pupillometer Market By Type Insights
Video pupillometers dominate the type segment, thanks to their superior ability to capture dynamic pupillary changes in high-resolution video formats. These systems are preferred in specialized ophthalmology and neurology clinics, where detailed analysis of light reflex latency, constriction velocity, and recovery times is critical for diagnosing complex disorders. Video-based systems also support documentation and playback, aiding in research and teaching environments.
Digital pupillometers, while slightly less comprehensive, are the fastest-growing in usage, particularly among general clinics and outpatient settings. These devices offer quick readings of pupil size and reactivity and are easier to use without significant training. Digital pupillometers are also cost-effective, making them attractive for first-time users, smaller practices, and mobile health initiatives across the country.
U.S. Pupillometer Market By Application Insights
Ophthalmology is the leading application area, as pupil measurements are a routine part of eye exams, pre-operative screenings, and glaucoma diagnostics. Eye care professionals utilize pupillometry to assess afferent defects, detect optic nerve pathologies, and monitor responses to light adaptation. The presence of dedicated eye clinics, optometric chains, and advanced ophthalmic departments in the U.S. contributes to this dominance.
Neurology is the fastest-growing application segment, especially in emergency departments and trauma centers. Conditions such as brain herniation, ischemic stroke, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and brain death require timely and accurate assessment of neurological status. Pupillometers offer quantifiable measurements for the neurological pupil index (NPi), aiding in consistent monitoring and triage decisions.
U.S. Pupillometer Market By End-use Insights
Hospitals are the dominant end-users of pupillometers, primarily due to their wide-ranging diagnostic and monitoring needs across multiple departments ICUs, neurology, trauma, and surgery. These settings require frequent and standardized pupil assessments, especially when tracking changes over time. Hospitals are also more likely to invest in advanced video pupillometry systems and staff training.
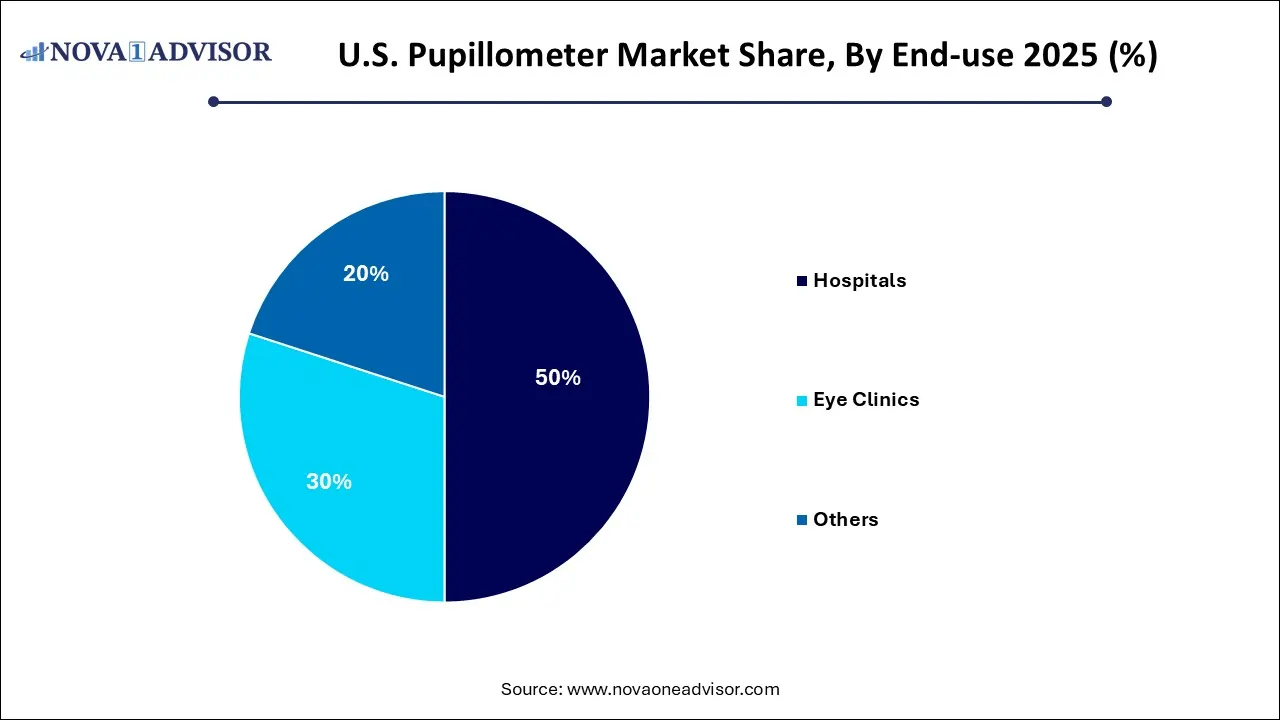
Eye clinics represent the fastest-growing end-use segment, supported by rising vision care awareness, increased prevalence of age-related eye diseases, and a shift toward preventive ophthalmology. Eye care centers are adopting digital pupillometers to enhance workflow efficiency, improve diagnostic precision, and reduce variability in assessments conducted by multiple practitioners.
Country-Level Analysis
The U.S. pupillometer market is distinguished by its clinical innovation, high adoption of medical technologies, and strong presence of specialist healthcare providers. Major academic centers, trauma hospitals, and eye care networks across the country have integrated pupillometry into routine care protocols. In neurology, standardized pupil tracking is becoming a best practice in ICUs, driven by protocols such as Brain Trauma Foundation guidelines and AAN (American Academy of Neurology) recommendations.
The expansion of mobile health units, telemedicine partnerships, and sports concussion programs is further driving demand for portable devices across states. Additionally, the U.S. leads in pupillometry-related clinical research, with multiple NIH-funded studies investigating pupil response in opioid management, Alzheimer’s detection, and concussion evaluation.
Reimbursement dynamics in the U.S. are gradually improving, with CPT codes being updated to accommodate objective pupillary assessments, making adoption financially viable for more providers. With increasing healthcare digitization and inter-device connectivity, pupillometers are becoming integral to integrated patient monitoring systems across the U.S. healthcare landscape.
Value Chain Analysis of the U.S. Pupillometer Market
- Research & Development (R&D) and Product Innovation
This initial stage involves designing and creating new, advanced pupillometer products that meet evolving clinical demands. Companies invest heavily in R&D to develop innovative features like automated data analysis, wireless charging, and integration with electronic health records (EHR).
Key Players: NeurOptics, Inc., Konan Medical USA, Inc., brightlamp, Inc., and NeuroLight Technologies Co., Ltd.
- Manufacturing and Operations
This stage involves the physical production and assembly of pupillometers using high-accuracy optics, sensors, and other components.
Key Players: HAAG-STREIT GROUP, NIDEK CO., LTD., Reichert Technologies, Essilor Instruments USA, and Johnson & Johnson Vision.
- Outbound Logistics and Distribution
Products are then stored, packaged, and transported through various channels, including direct sales, authorized distributors, and digital platforms, to reach healthcare facilities across the U.S.
Key Players: Konan Medical USA, Inc., and NeurOptics, Inc.
U.S. Pupillometer Market Companies
- NeurOptics, Inc.: Pioneers automated, objective pupillometers (like the NPi) for neurological assessment, providing critical data for brain injury monitoring and aiding in early detection of neurological disorders in critical care.
- Reichert Technologies: A major U.S. manufacturer of diagnostic eye care devices, offering reliable pupillometers for ophthalmologists and optometrists to assess ocular health and manage conditions like glaucoma.
- Johnson & Johnson Vision: A global player supporting the market with vision-focused technologies, contributing to diagnostic tools used in comprehensive eye exams and surgical planning.
- Brightlamp, Inc.: A key participant focused on innovative pupillometry, likely offering advanced solutions that integrate digital imaging for detailed analysis of pupillary responses, notes this source.
- Adaptica: Contributes specialized devices, potentially focusing on portable or integrated solutions that enhance accessibility and efficiency in various clinical settings, according to this source.
- Essilor Instruments USA: A well-known name in vision care, providing instruments that support comprehensive eye exams, including pupillometry for diagnosing and monitoring eye health issues.
- HAAG-STREIT GROUP: A leading Swiss company with a strong U.S. presence, offering high-quality diagnostic equipment, including pupillometers for precise, objective measurements in neurology and ophthalmology, notes this source.
- Luneau Technology Group: Known for advanced vision diagnostics (Visionix), they provide integrated systems that incorporate pupillometry, enhancing workflow and data analysis for eye care professionals.
U.S. Pupillometer Market Recent Developments
-
March 2025: NeurOptics, a leading U.S.-based pupillometer manufacturer, launched its new handheld NPi-300 model featuring Bluetooth integration with hospital EMR systems and improved light reflex calibration.
-
February 2025: Brightlamp Inc. announced an expansion of its mobile-based pupillometry software, Reflex Pro, into over 100 U.S. collegiate sports programs to support concussion monitoring.
-
January 2025: Neuroptics and the Mayo Clinic partnered to initiate a study evaluating the use of quantitative pupillometry in ICU pain assessment for ventilated patients.
-
December 2024: AdaptDx Pro, traditionally a dark adaptation device for macular degeneration, integrated digital pupillometry functionality in its software upgrade to expand into neuro-ophthalmic screening.
-
November 2024: EyeNetra, a Boston-based startup, received Series B funding to scale its AI-enabled mobile pupillometry platform targeting developing U.S. outpatient eye clinics.
U.S. Pupillometer Market Report Segmentation
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2035. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. Pupillometer market.
By Mobility
By Type
By Application
- Ophthalmology
- Neurology
- Oncology
- Others
By End-use
- Hospitals
- Eye Clinics
- Others


