U.S. Ventral Hernia Mesh Devices Market Size and Research
The U.S. Ventral Hernia Mesh Devices Market size was exhibited at USD 356.45 million in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 790.46 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 8.29% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
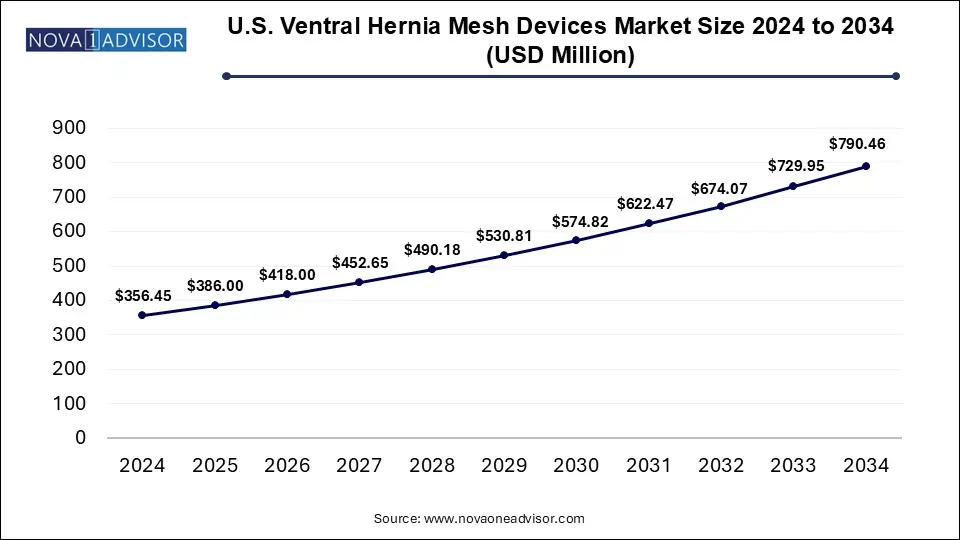
Key Takeaways:
- The non-resorbable mesh segment accounted for the largest market share of 48% in 2024.
- The incisional hernia segment accounted for the largest share of 44% in 2024.
- The open surgery segment held the largest share of 41% in 2024.
- The inpatient facilities segment held the largest share of 51% in 2024.
Market Overview
The U.S. ventral hernia mesh devices market represents a critical component of the surgical implants landscape, addressing one of the most prevalent and recurring types of hernias encountered in general surgery. Ventral hernias, including umbilical, epigastric, and incisional types, occur when tissue bulges through an opening or weak spot in the abdominal wall. The standard of care for repairing such hernias involves the use of mesh implants that reinforce the abdominal wall and reduce recurrence rates, especially in moderate to large hernias.
Over the past decade, the U.S. has witnessed a surge in ventral hernia repairs due to an aging population, increasing obesity rates, and a high prevalence of postoperative complications following abdominal surgeries. According to data from the American College of Surgeons, over 350,000 ventral hernia repairs are performed annually in the U.S., with the majority involving some form of mesh implantation. As surgical methods advance and focus shifts toward minimally invasive procedures, the demand for innovative, flexible, and biocompatible mesh devices has intensified.
Moreover, regulatory bodies such as the U.S. FDA have played a pivotal role in shaping this market through approvals, recalls, and clinical safety evaluations, encouraging manufacturers to invest in safer and more effective solutions. Technological improvements in mesh design ranging from hybrid materials and bioengineered scaffolds to antimicrobial coatings are transforming the therapeutic outcomes for patients. Additionally, increased awareness of hernia-related morbidity, especially among at-risk groups like obese individuals and manual laborers, is expected to sustain demand for mesh-based repairs across hospitals and outpatient facilities.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Growth of Hybrid and Partially Absorbable Meshes: Surgeons are increasingly opting for meshes that combine permanent and absorbable materials for better tissue integration and lower complication risks.
-
Increased Preference for Minimally Invasive Procedures: The use of laparoscopic and robotic surgeries is rising, driven by faster recovery times, less postoperative pain, and fewer wound complications.
-
Development of Antibacterial-Coated Meshes: To reduce postoperative infections, manufacturers are introducing meshes with antibacterial coatings and agents like silver or chlorhexidine.
-
Patient-Customized Mesh Designs: 3D printing and advanced polymer technologies are enabling the development of mesh devices tailored to individual anatomy.
-
Surge in Outpatient Hernia Repairs: With changes in CMS policies and payer reimbursement models, a growing number of hernia repairs are being shifted from inpatient to outpatient facilities.
-
Focus on Recurrence Prevention and Long-Term Outcomes: There is a trend toward long-term studies and real-world evidence to validate mesh durability and performance over extended periods.
-
Legal and Regulatory Scrutiny Impacting Product Development: Ongoing litigation concerning mesh-related complications has made safety, biocompatibility, and regulatory compliance top priorities for manufacturers.
Report Scope of U.S. Ventral Hernia Mesh Devices Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 386.0 Million |
| Market Size by 2034 |
USD 790.46 Million |
| Growth Rate From 2025 to 2034 |
CAGR of 8.29% |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2034 |
| Segments Covered |
Mesh type, Indication, Procedure, End use |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Medtronic plc; Becton, Dickinson and Company; Ethicon Inc. (Johnson & Johnson MedTech); Meril Life Sciences Pvt. Ltd.; Novus Scientific AB; B. Braun SE; TELA Bio, Inc.; BG Medical LLC; Integra LifeSciences Corporation; W. L. Gore & Associates, Inc.; Atrium Medical |
Market Driver: Increasing Incidence of Obesity and Post-Surgical Hernias
A major driver of the U.S. ventral hernia mesh devices market is the rising incidence of obesity and post-surgical hernias. Obesity is a well-established risk factor for the development of ventral hernias due to increased intra-abdominal pressure that weakens the abdominal wall. According to the CDC, over 42% of American adults are classified as obese, making them highly susceptible to hernia formation and recurrence post-repair. Additionally, the growing number of abdominal surgeries including bariatric procedures, cesarean sections, and laparotomies has led to a rise in incisional hernias.
For instance, approximately 15–20% of patients who undergo abdominal surgery may develop an incisional hernia, necessitating secondary repair using mesh. Surgeons increasingly prefer mesh-based reinforcement in these high-risk populations to minimize recurrence and ensure structural integrity. This trend is further supported by enhanced guidelines from surgical societies recommending mesh implantation in even primary hernia cases to reduce revision rates.
Market Restraint: Complications and Legal Risks Associated with Mesh Implants
Despite clinical advantages, the market faces considerable restraint from the complications associated with mesh implants, such as infection, adhesions, mesh migration, chronic pain, and organ perforation. These adverse outcomes have led to a significant number of product recalls and high-profile legal cases. Companies like C.R. Bard and Ethicon have faced class-action lawsuits and multi-million-dollar settlements in the U.S. over alleged mesh-related injuries.
This environment of litigation and scrutiny has heightened caution among surgeons and healthcare providers, sometimes resulting in underutilization of mesh in appropriate cases. Furthermore, the FDA’s continued monitoring of post-market safety data has led to stricter regulatory requirements and longer approval cycles, limiting the speed at which newer products can be introduced to market. Together, these challenges have increased development costs and reputational risks for mesh manufacturers.
Market Opportunity: Expansion of Robotic-Assisted Hernia Repair
An emerging opportunity in the U.S. ventral hernia mesh devices market lies in the expansion of robotic-assisted surgical platforms. Robotic surgery offers superior dexterity, 3D visualization, and enhanced precision, making it ideal for complex ventral hernia repairs where exact mesh placement and tissue manipulation are crucial. Companies like Intuitive Surgical have already partnered with hernia mesh manufacturers to co-develop instruments and meshes that are compatible with robotic systems.
This shift opens doors for specialized mesh products such as pre-shaped meshes or those with integrated fixation systems tailored to robotic applications. Hospitals and surgical centers adopting robotic programs are increasingly training their staff in robotic hernia repair, particularly for high-risk or recurrent cases. As robotic platforms become more affordable and reimbursement structures evolve, this segment is expected to grow rapidly and contribute significantly to premium mesh product sales.
Segmental Analysis
Mesh Type Outlook
The non-resorbable mesh segment dominated the market due to its durability, tensile strength, and proven track record in long-term hernia repairs. These meshes, typically made from synthetic materials like polypropylene or PTFE, are widely used in complex or recurrent hernia cases where permanent reinforcement is critical. Hospitals continue to favor these meshes for their cost-effectiveness, surgeon familiarity, and predictability in outcomes. Despite concerns regarding chronic inflammation and foreign body reactions, non-resorbable meshes remain the standard in many procedural guidelines, especially for large incisional hernias.
The fastest-growing segment is the partially absorbable mesh, which offers a hybrid solution by combining the strength of synthetic materials with the benefits of absorbable components. These meshes degrade partially over time, reducing the long-term burden on the patient’s body while supporting adequate tissue ingrowth. Clinical trials have demonstrated lower infection and adhesion rates with partially absorbable products, making them increasingly popular for laparoscopic and robotic procedures. Manufacturers are developing meshes with tailored absorption profiles to match patient-specific healing timelines, which is driving innovation and adoption in this category.
Indication Outlook
Incisional hernia emerged as the dominant indication, driven by the high incidence of post-surgical abdominal wall weaknesses. This type of hernia often requires surgical correction with mesh reinforcement due to its size and recurrence risk. Surgical societies in the U.S. recommend mesh use in over 90% of incisional hernia cases to reduce the likelihood of reherniation. Hospitals routinely stock a wide range of mesh options for these procedures, and surgeons prefer larger, high-strength meshes with fixation capabilities for secure closure.
Epigastric hernia is expected to be the fastest-growing indication, as awareness about smaller abdominal hernias and their early repair increases. Traditionally left untreated unless symptomatic, epigastric hernias are now being diagnosed and surgically repaired more frequently thanks to advancements in imaging and minimally invasive techniques. The shift toward early intervention, especially among physically active individuals or those undergoing abdominal imaging for unrelated reasons, is driving demand for small-sized, easily deployable mesh devices.
Procedure Outlook
Open surgery continues to dominate the procedure landscape for ventral hernia repairs in the U.S., especially in emergency settings and for large, complex hernias. Surgeons often prefer the tactile feedback and visibility offered by open methods, particularly when dealing with adhesions or previously failed repairs. Non-resorbable meshes are predominantly used in open procedures, and these surgeries remain more common in rural or non-specialized settings where robotic or laparoscopic equipment may not be available.
Robotic surgery is witnessing the fastest growth, reflecting its rapid integration into surgical practice across the U.S. Robotic hernia repairs offer superior ergonomics and precision, allowing for better mesh placement, reduced tension, and fewer complications. Academic centers and urban hospitals are increasingly adopting robotic platforms for hernia surgeries, and mesh manufacturers are tailoring products with flexible, low-memory properties that suit robotic deployment. As training programs and insurance coverage expand, robotic surgery is expected to capture a larger share of the procedural mix.
End Use Outlook
Inpatient facilities currently dominate the end-use segment, as many ventral hernia repairs particularly those involving incisional or recurrent hernias are performed in hospitals with access to comprehensive surgical support. These institutions handle complex cases that require longer operative times, advanced equipment, and post-operative care. Additionally, inpatient facilities benefit from established procurement channels with leading mesh suppliers, allowing for standardized mesh usage across departments.
Outpatient facilities represent the fastest-growing end-use segment, driven by the shift toward same-day surgery and cost-effective care models. Hernia repairs using laparoscopic or robotic techniques can often be completed within hours, with patients discharged the same day. Ambulatory surgical centers (ASCs) and specialized hernia clinics are embracing this trend, supported by newer mesh products that are easier to deploy and associated with shorter recovery times. Insurance reforms and bundled payment models have further encouraged outpatient adoption, making this a key growth area for mesh device sales.
Country-Level Analysis: United States
The U.S. remains the largest and most mature market for ventral hernia mesh devices globally. Factors such as a high surgical volume, advanced hospital infrastructure, and early adoption of medical innovations contribute to this position. The nation’s robust healthcare reimbursement system, coupled with a strong regulatory framework, encourages innovation while maintaining patient safety standards.
States like California, Texas, and Florida lead in surgical procedure volumes, while academic medical centers in cities like Boston, New York, and Chicago serve as hubs for clinical trials and new product testing. Furthermore, growing awareness among patients regarding elective hernia repair and minimally invasive options is fueling demand across both urban and semi-urban regions. Public health initiatives focused on obesity management, surgical quality improvement, and patient education also play a role in expanding market potential.
Some of The Prominent Players in The U.S. Ventral Hernia Mesh Devices Market Include:
- Medtronic plc
- Becton, Dickinson and Company
- Ethicon Inc. (Johnson & Johnson MedTech)
- Meril Life Sciences Pvt. Ltd.
- Novus Scientific AB
- B. Braun SE
- TELA Bio, Inc.
- BG Medical LLC
- Integra LifeSciences Corporation
- W. L. Gore & Associates, Inc.
- Atrium Medical
Recent Developments
-
March 2025 – BD (Becton, Dickinson and Company) announced the launch of the "Phasix ST Mesh with SecureFix", a resorbable mesh integrated with a new fixation system for laparoscopic and robotic ventral hernia repairs.
-
January 2025 – W.L. Gore & Associates received FDA clearance for its next-generation Gore DualMesh Plus, featuring an antibacterial coating to reduce surgical site infections.
-
November 2024 – Medtronic plc unveiled its "Symbotex L" mesh device designed specifically for robotic hernia repairs with 3D anatomical conformity and self-gripping capabilities.
-
August 2024 – Cook Medical expanded its clinical trial network for its biologic hernia mesh platform, targeting high-risk patient groups and complex hernias with poor healing profiles.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Operating room equipment market
By Mesh Type
- Resorbable Mesh
- Partially Absorbable Mesh
- Non-resorbable Mesh
By Indication
- Umbilical Hernia
- Epigastric Hernia
- Incisional Hernia
- Others
By Procedure
- Open Surgery
- Laparoscopic Surgery
- Robotic Surgery
- Others
By End Use
- Inpatient Facilities
- Outpatient Facilities

