U.S. Waste Management Market Size and Trends
The U.S. waste management market size was exhibited at USD 343.25 million in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 597.53 million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 5.7% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
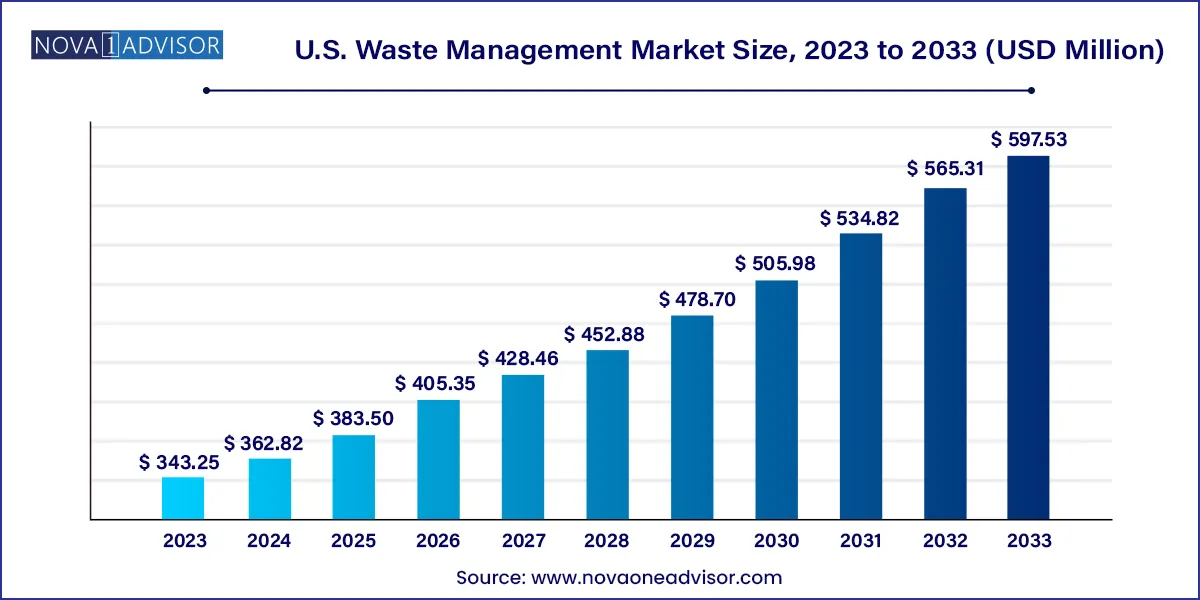
U.S. Waste Management Market Key Takeaways:
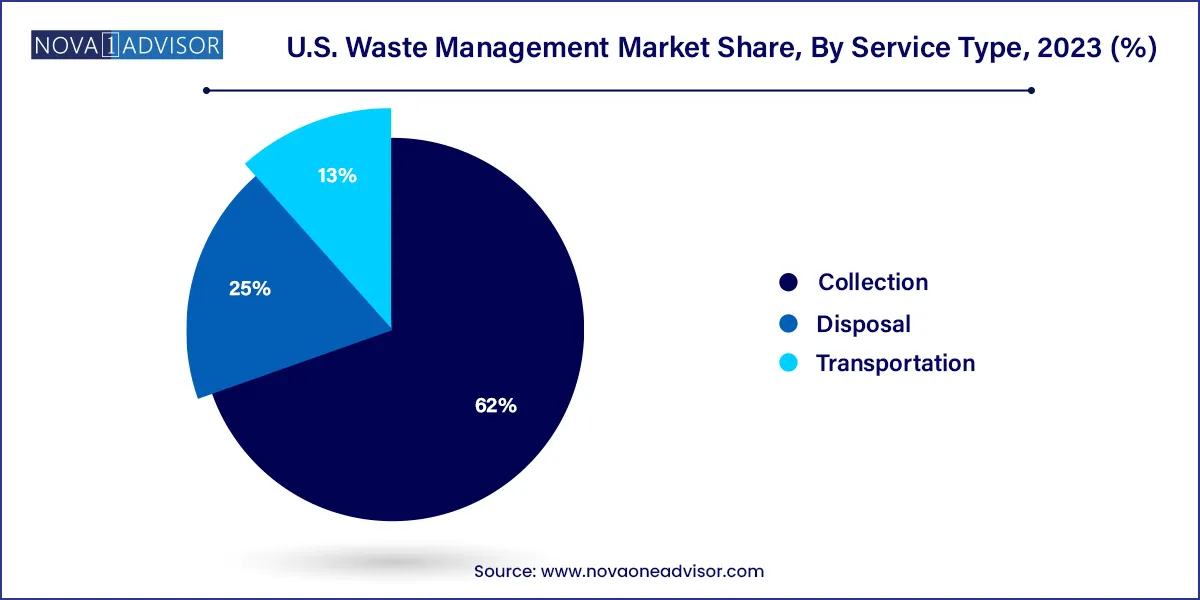
- The collection segment dominated the U.S. market in 2023 with around 62.0% revenue share.
- The disposal segment, on the other hand, was the second largest but is expected to be the fastest-growing segment with a CAGR of 5.7% from 2024-2033.
- The industrial waste segment dominated the U.S. market revenue share in 2023.
Market Overview
The U.S. waste management market stands as one of the most robust and evolving industries within the country’s infrastructure and environmental services landscape. As economic activities diversify and consumer consumption increases, so does the volume and complexity of waste produced. From household refuse and commercial waste to hazardous biomedical materials and the rapidly growing mountain of e-waste, the U.S. faces mounting challenges that demand innovative, sustainable, and scalable waste management solutions.
Traditionally reliant on landfill disposal and incineration, the market is now witnessing a paradigm shift toward more circular and resource-efficient systems. Factors such as climate change awareness, corporate sustainability mandates, and evolving state-level policies are playing a vital role in reshaping operational priorities. Additionally, urbanization, along with the rise of mega-cities, is pressuring municipalities to modernize waste collection and disposal infrastructure. Across the public and private sectors, players are increasingly embracing digital tools, automation, and alternative waste processing technologies to stay ahead of the curve.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Adoption of Circular Economy Principles
Focus is shifting from linear waste disposal to resource recovery, reuse, and recycling, promoting long-term sustainability.
-
Digitalization of Waste Logistics
Smart bins, route optimization for waste trucks, and IoT-based waste monitoring are being deployed to enhance efficiency and reduce operational costs.
-
Expansion of Waste-to-Energy Initiatives
Municipalities and private firms are exploring incineration and anaerobic digestion to convert waste into electricity and biofuels.
-
Growing Significance of E-Waste Recycling
As the U.S. consumer electronics sector expands, so does the challenge of e-waste, leading to the emergence of specialized recycling firms.
-
Stricter Environmental Regulations and Compliance Norms
Agencies at federal and state levels are tightening rules around landfill emissions, hazardous waste handling, and single-use plastics.
-
Integration of AI and Machine Learning in Sorting Facilities
Advanced AI tools are being used for high-speed sorting of recyclables, improving throughput and quality control in material recovery facilities.
-
Rise in Private-Public Partnerships (PPPs)
To fund and manage complex waste operations, governments are increasingly collaborating with private firms on infrastructure development and service delivery.
Report Scope of U.S. Waste Management Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 362.82 Million |
| Market Size by 2033 |
USD 597.53 Million |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 |
CAGR of 5.7% |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered |
Service Type, Waste Type |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Country scope |
U.S. |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Waste Management Inc, Republic Services Inc, Waste Connections Inc, Clean Harbors Inc, Casella Waste Systems, Stericycle, Covanta Holding Corporation, US Ecology Inc, Heritage Crystal Clear Inc, Recycle Track Systems |
Market Driver – Policy-Backed Push for Sustainable Urban Waste Handling
A powerful driver shaping the U.S. waste management market is the proactive policy environment that promotes sustainable waste handling practices in urban areas. Many cities have adopted zero-waste goals, emphasizing waste segregation at source, community composting, and recycling mandates. These initiatives not only aim to reduce dependency on landfills but also contribute to cleaner city environments and public health outcomes. Government-backed incentive schemes and funding programs are enabling local authorities and businesses to upgrade infrastructure, invest in greener technologies, and enhance public awareness. This systemic approach, rooted in governance and sustainability, is accelerating innovation and improving service coverage in both affluent and underserved areas.
Market Restraint – Fragmented Operational Ecosystem
Despite its advancements, the U.S. waste management industry is challenged by its highly fragmented ecosystem. Regulatory frameworks, waste processing protocols, and infrastructure quality vary widely across states and municipalities. While some cities operate with advanced material recovery facilities and AI-enabled fleet systems, others struggle with aging infrastructure and low recycling rates. This inconsistency not only creates gaps in national performance metrics but also limits the scalability of private innovations across jurisdictions. For service providers, the need to navigate diverse compliance requirements and investment expectations across geographies can lead to operational inefficiencies and cost overruns.
Market Opportunity – Growth in Medical and Biohazard Waste Solutions
The increasing scale of healthcare services in the U.S. presents a compelling opportunity in the management of medical and biohazard waste. Hospitals, outpatient clinics, veterinary services, laboratories, and even home-based healthcare setups are significant generators of infectious and regulated medical waste. Given the high health and environmental risks posed by improper disposal, this segment demands rigorous handling protocols and specialized equipment. Service providers capable of offering integrated solutions—combining on-site collection, secure transportation, sterilization, and regulatory compliance—are poised to carve a lucrative niche. Innovations such as mobile medical waste processing units and AI-based risk monitoring systems are also gaining traction in this domain.
U.S. Waste Management Market By Service Type Insights
Collection Services Continue to Dominate the Market
Waste collection remains the foundational service in the U.S. waste management value chain, acting as the first point of contact between waste producers and processors. With both public agencies and private operators offering services across residential, industrial, and commercial sectors, the collection segment holds the largest market share. Innovations in this segment revolve around route optimization, vehicle electrification, and real-time tracking. In cities with population densities on the rise, collection frequency and efficiency become crucial determinants of service quality, prompting investment in smart bin technologies and fleet management software.
In rural and semi-urban areas, decentralized collection services are gaining prominence. Companies are piloting localized solutions such as community drop-off centers and incentivized recycling stations to reduce logistics costs and improve recycling rates. While the fundamental need for waste pickup remains unchanged, evolving consumer expectations and rising service costs are pushing this segment toward modernization and customization.
Disposal Services are the Fastest Growing Segment
As environmental concerns become mainstream, disposal services are undergoing a significant transformation. Once dominated by landfilling, this segment is now diversifying into composting, thermal treatment, and biological digestion. Municipal governments are increasingly allocating budgetary resources for the establishment of sustainable disposal facilities that reduce greenhouse gas emissions and support renewable energy generation. These evolving requirements have opened avenues for both startups and large-scale operators to innovate in disposal technologies.
One of the fastest-growing niches within this segment is organic waste composting. With food waste representing a large share of total waste, composting hubs are being set up across major cities. Simultaneously, landfills are being retrofitted with systems that capture methane and convert it into usable energy. These value-added services are not just environmentally beneficial but also open doors for new revenue streams, driving rapid growth in the disposal category.
U.S. Waste Management Market By Waste Type Insights
Municipal Waste Remains the Largest Waste Stream
Municipal solid waste (MSW) forms the bulk of waste produced in the U.S., including residential refuse, street sweeping debris, and waste from offices and small businesses. It is also the most regulated and publicly visible category, directly affecting community health and aesthetics. Most municipalities follow a curbside collection model, but newer models include multi-stream separation for recyclables, compostables, and landfill waste. The growing adoption of "pay-as-you-throw" programs—where citizens are charged based on the volume of non-recyclable waste—has led to more conscious consumer behavior and greater sorting accuracy at the source.
Many cities are investing in MSW-to-energy plants and municipal recycling facilities to reduce dependency on external contractors. Simultaneously, public education initiatives are being launched to enhance citizen participation in waste segregation. Overall, the handling of MSW continues to be a policy priority and a major source of employment in the waste sector.
E-waste Management is Emerging as the Fastest Growing Segment
The rapid adoption of digital devices, home electronics, and smart appliances in the U.S. has led to a surge in electronic waste. Unlike traditional waste, e-waste contains complex composites of metals, plastics, and rare elements, some of which are hazardous if improperly handled. This category has become a focal point for specialized recyclers and tech-focused waste management firms. Extended producer responsibility laws are gradually being implemented across states, requiring manufacturers to finance the collection and recycling of their obsolete products.
Emerging businesses in this segment are deploying robotics and AI-driven sorting lines to safely extract valuable materials such as lithium, copper, and gold. Consumer-facing companies are also launching device trade-in and recycling programs in collaboration with certified recyclers. Given the high resource value and toxic potential of e-waste, this segment offers both economic and ecological rewards, making it the fastest-growing category in the market.
Country-Level Analysis
The United States, with its vast geography and economic diversity, exhibits a highly differentiated waste management ecosystem. In highly urbanized states such as California, New York, and Massachusetts, strict environmental laws and advanced infrastructure drive high recycling rates and cutting-edge waste technologies. On the other hand, many central and southern states continue to rely heavily on landfilling, primarily due to lower population densities and lower cost structures.
Federal agencies like the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) establish overarching guidelines, but actual execution is primarily the responsibility of state and local bodies. This has led to an innovative, albeit fragmented, market where some states are global leaders in waste reduction, while others lag in terms of technology and compliance. The diversity of this landscape ensures both challenges and opportunities for companies looking to scale operations across the country.
Some of the prominent players in the U.S. waste management market include:
- Waste Management Inc
- Republic Services Inc
- Waste Connections Inc
- Clean Harbors Inc
- Casella Waste Systems
- Stericycle
- Covanta Holding Corporation
- US Ecology Inc
- Heritage Crystal Clear Inc
- Recycle Track Systems
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. waste management market
Service Type
- Collection
- Transportation
- Disposal
Waste Type
- Municipal Waste
- Medical Waste
- Industrial Waste
- E-waste


