Wound Closure Devices Market Size and Trends
The wound closure devices market size was exhibited at USD 14.65 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 27.79 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 6.61% during the forecast period 2024 to 2034. The growth of the wound closure devices market can be linked to the rising cases of chronic wounds, ongoing advancements in wound care technology and increase in number of surgical procedures across the globe.
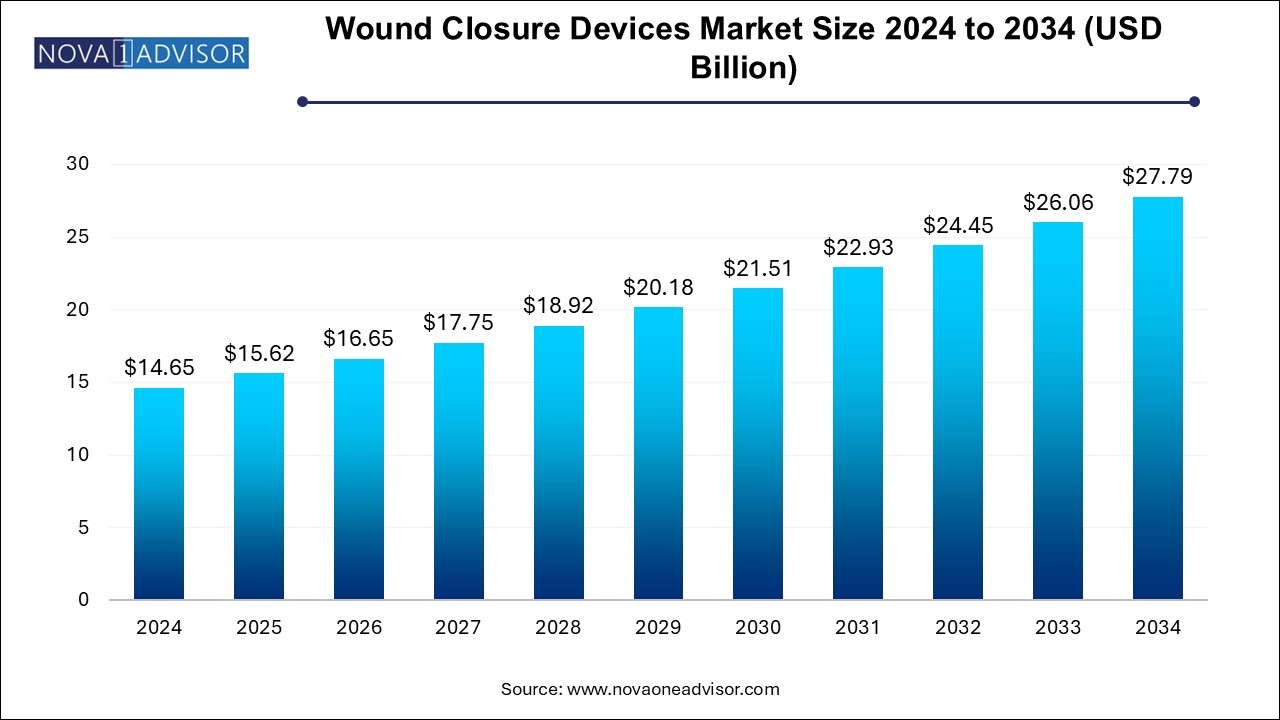
Wound Closure Devices Market Key Takeaways:
- The sutures segment dominated the market and accounted for a revenue share of 40.00% in 2024.
- The acute wounds segment dominated the market in 2024 and is expected to continue its dominance with the highest CAGR of 7.17% over the forecast period.
- The hospitals segment dominated the market and accounted for the largest revenue share of 40.0% in 2024.
- North America wound closure devices market held the largest revenue share of 38.48% in 2024.
Market Overview
The wound closure devices market represents a critical segment of the global healthcare ecosystem, providing essential tools for effective wound management and surgical recovery. These devices, which include sutures, staples, adhesives, clips, and sealants, are used to close and secure wounds across various clinical environments—from elective surgeries and trauma centers to emergency departments and outpatient care. As surgical volumes rise globally, the demand for efficient, safe, and cost-effective wound closure methods continues to accelerate.
The market is heavily influenced by advancements in materials science, minimally invasive surgical techniques, and postoperative care protocols. Modern wound closure devices are designed not only to mechanically approximate tissue but also to minimize scarring, reduce infection risk, and speed up healing. Absorbable sutures, antimicrobial-coated staples, bioactive adhesives, and tissue-compatible sealants are now commonly integrated into advanced wound management regimens.
With the growing global burden of trauma injuries, chronic wounds, and surgical procedures, wound closure devices play an indispensable role in both acute and long-term care. The elderly population, which is prone to delayed healing and post-surgical complications, is also a significant consumer segment. In addition, increasing awareness among healthcare professionals regarding optimal wound closure techniques is enhancing procedural outcomes and driving product adoption.
Market dynamics are further influenced by innovations in synthetic biomaterials, regulatory approvals for novel closure methods, and the increasing availability of outpatient procedures. Overall, the wound closure devices market is projected to experience steady growth through 2034, driven by a blend of technological innovation, expanding patient volumes, and evolving surgical standards.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Rising preference for absorbable sutures to reduce follow-up visits and eliminate the need for suture removal.
-
Growth of minimally invasive and robotic surgeries, necessitating precision closure tools with minimal tissue trauma.
-
Surging adoption of tissue adhesives and sealants for cosmetic outcomes and faster closure in dermatologic, plastic, and pediatric surgeries.
-
Advancements in synthetic biomaterials and bioabsorbable polymers, improving compatibility and healing outcomes.
-
Integration of antimicrobial coatings into sutures and staples to reduce the risk of surgical site infections (SSIs).
-
Expansion of trauma and emergency care infrastructure, particularly in developing nations, increasing demand for rapid closure devices.
-
Increased popularity of skin closure strips in outpatient settings due to ease of use and reduced scarring.
-
Growing focus on cost-effective closure solutions in low-resource settings and ambulatory surgical centers.
-
Rise in cosmetic and aesthetic procedures, boosting demand for non-invasive, scar-minimizing closure methods.
Report Scope of Wound Closure Devices Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 15.62 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 |
USD 27.79 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2034 |
CAGR of 6.61% |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2024-2034 |
| Segments Covered |
Product, Wound Type, End use, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Covered |
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, MEA |
| Key Companies Profiled |
3M, Ethicon (Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc.), Medtronic, Baxter, Smith+Nephew, Stryker, Advanced Medical Solutions Group plc, Riverpoint Medical, DermaClip, AVITA Medical, Inc., Corza Medical |
Market Driver: Increasing Global Surgical Volume
The primary driver of the wound closure devices market is the growing global volume of surgical procedures. With rising life expectancy, the prevalence of lifestyle-related conditions such as obesity, cardiovascular disease, and cancer is also increasing, leading to a surge in both elective and emergency surgeries. According to WHO, an estimated 234 million major surgical procedures are performed globally each year, a number that is expected to grow steadily through the next decade.
In every surgical procedure—whether open or laparoscopic—wound closure is a critical final step. Efficient closure ensures hemostasis, supports tissue regeneration, and reduces the risk of infection or dehiscence. Hospitals and surgical centers are adopting modern wound closure tools that minimize operative time, reduce complications, and enhance patient recovery. Additionally, as same-day surgeries and outpatient procedures become more common, the demand for faster, more reliable closure methods is accelerating.
Market Restraint: Risk of Allergic Reactions and Post-Closure Complications
A major restraint in the market is the risk of adverse reactions and complications associated with certain wound closure devices. While most devices are manufactured with biocompatible materials, some patients may experience allergic responses to specific adhesives, sutures, or sealant components. For example, cyanoacrylate-based adhesives, while effective for surface closure, may cause local irritation in sensitive individuals.
Moreover, improper closure techniques or selection of inappropriate closure devices can lead to complications such as wound dehiscence, hematoma, or hypertrophic scarring. In resource-constrained environments, reuse or substandard product quality may also elevate complication risks. These concerns necessitate careful material selection, training of medical staff, and quality control in manufacturing—all of which may add to the cost and complexity of product deployment.
Market Opportunity: Emergence of Smart and Bioactive Closure Devices
A transformative opportunity in the wound closure devices market is the development of smart and bioactive closure technologies. These include sutures and adhesives embedded with sensors, drug-release capabilities, or healing-promoting compounds. For instance, suture materials embedded with anti-inflammatory agents or antimicrobials can reduce postoperative infection rates and improve healing, particularly in immunocompromised or diabetic patients.
Startups and research institutions are also exploring electrically conductive sutures for real-time wound monitoring, as well as biodegradable clips that eliminate the need for removal. As the healthcare industry moves toward personalized and intelligent care solutions, smart closure devices offer not only clinical value but also differentiation for manufacturers. Partnerships between biotech companies, material scientists, and medical device firms are paving the way for a new generation of wound closure solutions that do more than just hold tissue together.
Wound Closure Devices Market By Product Insights
The sutures segment dominated the market and accounted for a revenue share of 40.00% in 2024. With widespread adoption in almost every surgical procedure. They are cost-effective, versatile, and available in both absorbable and non-absorbable formats, catering to a variety of clinical scenarios. Absorbable sutures are favored in internal surgeries and pediatric procedures where suture removal is undesirable, while non-absorbable types are preferred for high-tension closures or areas requiring prolonged support. Advancements in suture coatings, tensile strength, and antimicrobial properties have further reinforced their market leadership.
The adhesives segment is projected to grow at the highest CAGR, which makes it the second fastest-growing segment over the forecast period. These include fibrin-based, collagen-based, and synthetic sealants, used across surgeries such as vascular, gastrointestinal, and cosmetic procedures. Synthetic sealants offer enhanced adhesion and rapid polymerization, ideal for internal organs and bleeding control. Their ability to seal complex or irregular wounds without mechanical trauma makes them highly desirable in minimally invasive and robotic surgeries. With increasing regulatory approvals and surgeon preference, this segment is poised for robust expansion.
Wound Closure Devices Market By Wound Type Insights
The acute wounds segment dominated the market in 2024 and is expected to continue its dominance with the highest CAGR of 7.17% over the forecast period. These wounds require immediate and effective closure to restore skin integrity and prevent infection. Hospitals and trauma centers are the largest users of wound closure devices for acute wound care. Devices such as staples, sutures, and adhesives are commonly used in operating rooms and emergency departments, supported by standardized protocols and ample procedural data.
Chronic wounds are a growing focus area, particularly with the rise of diabetes, vascular diseases, and aging populations. Chronic wounds, including pressure ulcers, diabetic foot ulcers, and venous leg ulcers, pose unique challenges in closure due to delayed healing and high infection risk. Novel closure approaches, such as bioactive sealants and dressings integrated with closure functions, are gaining traction in this segment. As wound care shifts from hospitals to home and outpatient settings, demand for user-friendly closure solutions for chronic wounds is expected to increase steadily.
Wound Closure Devices Market By End Use Insights
The hospitals segment dominated the market and accounted for the largest revenue share of 40.0% in 2024, These settings handle a broad range of surgical disciplines—orthopedics, cardiovascular, general surgery—requiring reliable and diverse closure solutions. Hospital procurement systems favor clinically validated, cost-effective devices with low complication rates. In addition, most innovations in wound closure are first adopted in tertiary care hospitals before reaching smaller centers.
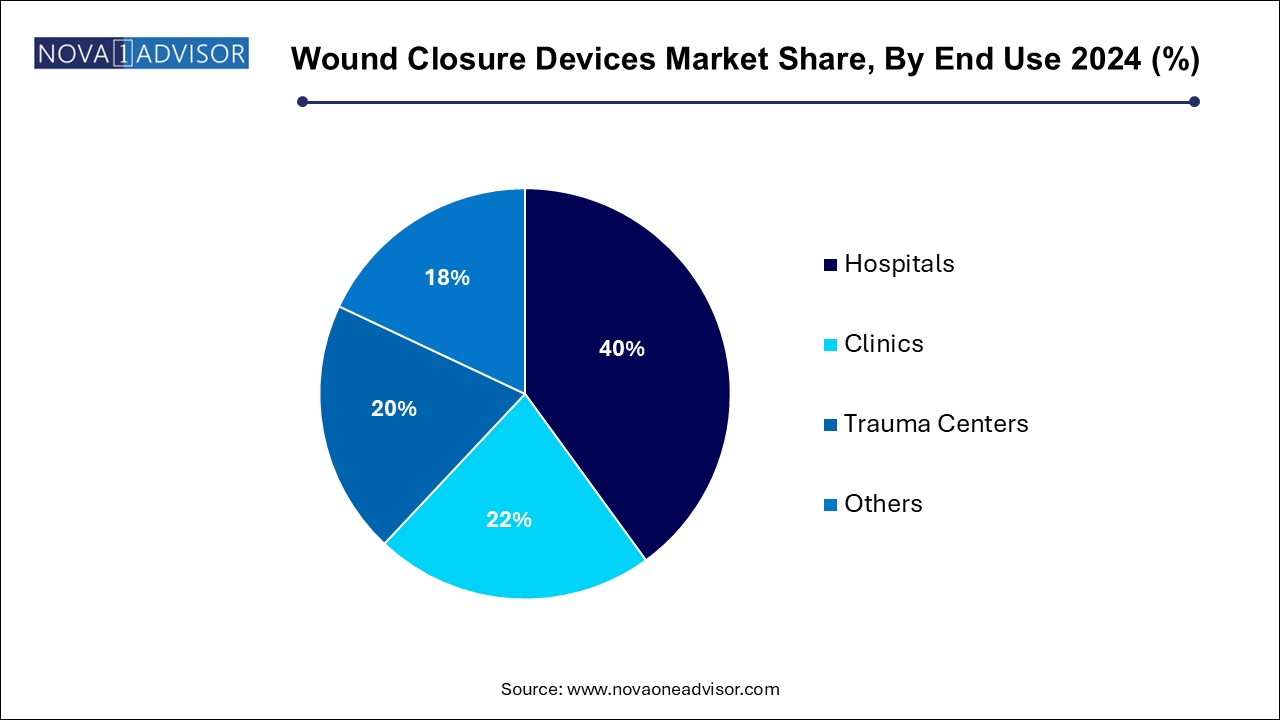
The trauma centers segment is projected to experience the fastest growth during the forecast period, These centers require rapid deployment of closure devices to manage high volumes of lacerations, penetrating injuries, and fractures. The focus is on tools that enable fast closure, minimal training, and effective hemostasis. The adoption of pre-loaded staplers, clips, and hemostatic sealants is rising in these environments. Government investments in emergency care infrastructure and mobile trauma units further support segment growth.
Wound Closure Devices Market By Regional Insights
North America wound closure devices market held the largest revenue share of 38.48% in 2024, driven by a highly developed healthcare infrastructure, strong presence of global medical device manufacturers, and a high surgical procedure rate. The U.S. alone conducts over 50 million surgeries annually, generating sustained demand for closure solutions. Advanced healthcare reimbursement systems and favorable regulatory frameworks further enable the adoption of novel wound closure technologies.
U.S. dominates the wound closure devices market in North America. The rising incidences of chronic wounds like diabetic foot ulcers and pressure ulcers, surging number of surgical procedures, ongoing advancements like bioresorbable sutures and tissue adhesives, and innovative product launches are significantly contributing to the market growth. Moreover, development of advanced materials using biomaterials and nanontechnology, smart wound closure devices, rising use of hemostatic agents, growing trend of medical tourism and implementation of personalized wound care solutions like 3D-printed skin grafts are the factors expected to drive the market growth.
Government funding research initiatives through agencies like National Institutes of Health (NIH), Department of Defense (DoD) and Depart of Veteran Affairs (VA) for advancing wound care are driving innovations in wound closure technology.
- For instance, in June 2024, BRIJ Medical, a medical device company transforming surgical incision closure, scar therapy and wound support, launched its innovative product, the Brijjit BP-75 which is specifically designed for minimizing wound complications and scarring in small and more technical surgical incisions.
Asia Pacific is the fastest growing regional market, fueled by increasing healthcare expenditure, rising surgical volumes, and expanding hospital infrastructure. Countries such as China, India, Japan, and South Korea are investing heavily in modernizing their surgical care systems. With a growing middle class and a larger elderly population, the demand for both elective and emergency surgeries is on the rise.
China is anticipated to witness lucrative growth in the Asia Pacific market. The market growth is driven by huge population base, rising number of surgical procedures, prevalence of chronic diseases like diabetes as well as government initiatives for raising awareness for wound care and advancing healthcare infrastructure.
India is significantly contributing to the expansion of wound closure devices market owing to the factors like rising incidences of accidents and trauma injuries, increased healthcare expenditure and a large population. Government initiatives like the “Make in India” program encouraging domestic manufacturing of medical devices, scheme for Strengthening of Medical Device Industry focused on reducing import dependence and established medical device clusters as well as development of medical device parks are bolstering the market growth.
Strategic Initiatives Shaping the Future of Wound Closure Devices Market
Companies in the wound closure devices market are implementing various strategic initiatives for expanding their market presence and product portfolios. Advanced bio-integrated materials and antimicrobial agents for mitigating the risk of surgical site infections (SSIs) and enhancing the biocompatibility are being explored. Sensing technologies like biosensors are incorporated for continuous wound monitoring and identification of specific biomarkers indicating infection or delayed healing. Telehealth platforms are facilitating the remote monitoring of patients. Recognizing the needs of emerging markets in various regions, manufacturers are focused on developing cost-effective and high-quality wound closure solutions. Strategic alliances among diagnostic companies, surgical instrument manufacturers and digital health platform providers are fuelling innovation.
Some of the prominent players in the wound closure devices market include:
- 3M
- Ethicon (Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc.)
- Medtronic
- Baxter
- Smith+Nephew
- Stryker
- Advanced Medical Solutions Group plc
- Riverpoint Medical
- DermaClip
- AVITA Medical, Inc.
- Corza Medical
Wound Closure Devices Market Recent Developments
- In December 2024, H.B. Fuller Company, the world’s largest pureplay adhesives company, signed agreements for the acquisition of two major medical adhesive technology companies, namely Medfill Ltd., an Irish formulator and producer of medical-grade cyanoacrylate adhesives and GEM S.r.l., a leading Italian manufacturer and provider of medical adhesives. The acquisition expands H.B. Fuller’s Medical Adhesive Technologies (MAT) business offerings in Europe.
- In August 2024, Resivant Medical, a surgical adhesive developer for closure of topical skin, received approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for its two novel products, Cutiva Topical Skin Adhesive and Cutiva PLUS Skin Closure System, combining an adhesive mesh patch with high-viscosity Cultiva liquid adhesive.
- In October 2024, BioStem Technologies Inc., a leading MedTech company developing, manufacturing and commercializing placental-based biologics for advanced wound care, declared commencement of a countrywide launch of Vendaje AC, an innovative wound care solution for patients with chronic and non-healing wounds. The launch will be initiated with Venture Medical LLC which is the exclusive sales and marketing partner of Biostem.
- In October 2024, Corza Medical, a globally leading medical technology company, launched its next-generation line of Onatec ophthalmic microsurgical sutures in Chicago at the American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO) conference.
- In October 2024, Royal Wound-X, a business unit of Royal Biologics, launched two innovative wound healing technologies, namely the ElectroFiber 3D which is a bioengineered, electrospun synthetic polymer matrix designed for accelerating healing of wounds and the Peak Powder Collagen Matrix, which is a next-generation collagen-based wound care solution for enhancing healing of surgical and non-surgical wounds.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the wound closure devices market
By Product
-
- Absorbable
- Non-Absorbable
-
- Non-Synthetic
- Collagen Based
- Synthetic
By Wound Type
- Acute Wound
- Chronic Wound
By End Use
- Hospitals
- Clinics
- Trauma Centers
- Others
By Regional
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa (MEA)


