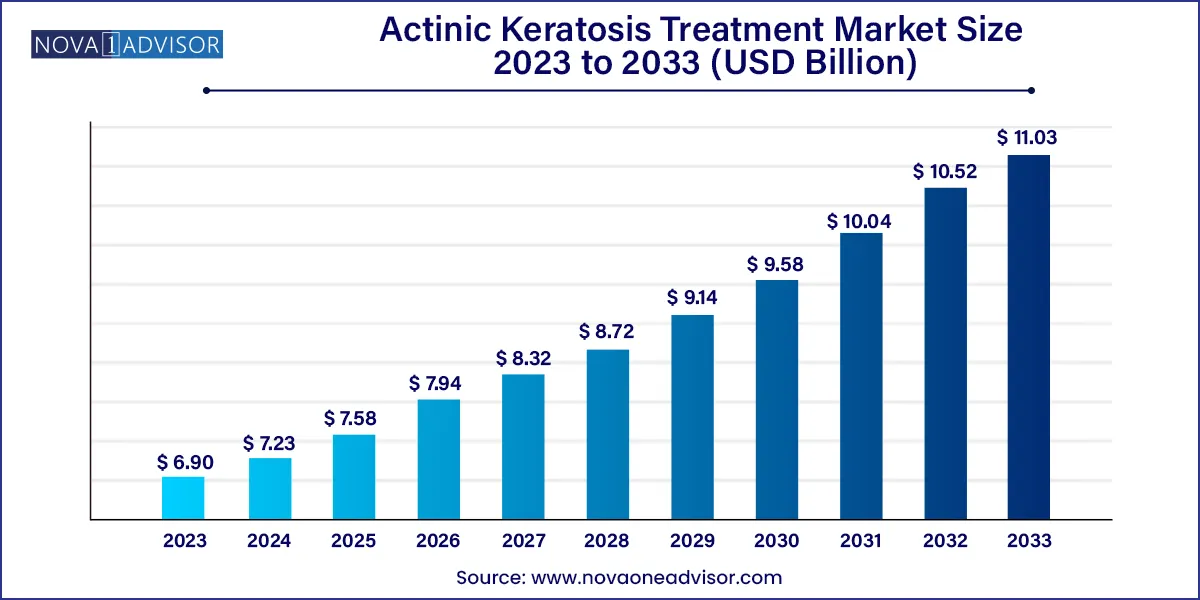
The global actinic keratosis treatment market size was exhibited at USD 6.90 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 11.03 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 4.8% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
Key Takeaways:
- North America dominated the market with the largest revenue share of 45.0% in 2023 and is anticipated to maintain its dominance over the forecast period.
- Based on therapy, the market is segmented into topical, surgery, and photodynamic therapy. Surgery held the largest revenue share of 66.0% in 2023.
- Nucleoside metabolic inhibitors held the largest revenue share of 32.4% in 2023.
- The hospitals segment held the largest share of 30.4% in 2023.
Market Overview
The Actinic Keratosis (AK) Treatment Market is a rapidly evolving domain within the broader dermatology and oncology therapeutics sector. Actinic keratosis, also known as solar keratosis, is a precancerous skin condition caused by prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds. It primarily affects fair-skinned individuals and typically manifests as rough, scaly patches on sun-exposed areas such as the face, scalp, ears, neck, and forearms. Given the increasing global awareness of skin cancer risks, early diagnosis and treatment of AK have become a critical component of skin health management.
The market for actinic keratosis treatment is driven by rising prevalence rates, particularly in aging populations and regions with high sun exposure such as Australia, the southern United States, and southern Europe. AK is one of the most commonly diagnosed skin conditions in dermatology clinics. While not all AK lesions progress to squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), the risk of malignant transformation necessitates proactive treatment.
Therapeutic approaches have evolved from traditional cryotherapy and surgical excision to more advanced topical agents, photodynamic therapy (PDT), and immune response modifiers. Recent innovations have focused on field-directed therapies, which treat both visible and subclinical lesions in a defined skin area, reducing recurrence and improving cosmetic outcomes.
Pharmaceutical companies are actively investing in R&D to improve treatment efficacy, reduce adverse effects, and develop home-use formulations for self-administered therapies. Meanwhile, healthcare providers are integrating digital dermatoscopic assessments, teledermatology, and patient education tools to enhance early detection and compliance.
With increasing dermatological focus on prevention, early intervention, and cosmetic preservation, the actinic keratosis treatment market is poised for sustained growth across both developed and emerging economies.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Shift Toward Field-Directed Therapies: Treatments targeting entire sun-damaged areas, rather than individual lesions, are gaining preference due to their efficacy in reducing recurrence.
-
Growth in Photodynamic Therapy (PDT): Non-invasive light-based treatments using photoenhancers like aminolevulinic acid are becoming popular for facial AKs with high cosmetic value.
-
Rising Adoption of Topical Immune Response Modifiers: Drugs like imiquimod and 5-fluorouracil remain first-line therapies due to their effectiveness and ease of home application.
-
Increasing Use of Digital Skin Imaging and AI Diagnostics: Dermatology clinics are integrating AI-based diagnostic tools for early detection of pre-cancerous and suspicious lesions.
-
Demand for Home-Based Treatments: Patient preference for non-invasive, self-administered options is boosting sales of prescription creams and over-the-counter therapies.
-
Combination Therapy Protocols: Dermatologists are combining cryotherapy, PDT, and topical agents for better lesion clearance rates and reduced recurrence.
-
Regulatory Support for Early Intervention: National skin cancer prevention campaigns and reimbursement programs are supporting proactive AK management, especially in high-risk populations.
Actinic Keratosis Treatment Market Report Scope
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 7.23 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 |
USD 11.03 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 |
CAGR of 4.8% |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered |
Therapy, Drug Class, End-use, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Central and South America; the Middle East and Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Almirall S.A.; LEO Pharma A/S; Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.; Novartis AG; GALDERMA; Ortho Dermatologics (Bausch Health Companies Inc.); BIOFRONTERA AG |
Market Driver: Rising Global Incidence of Actinic Keratosis and Skin Cancer Awareness
A primary driver of the actinic keratosis treatment market is the increasing incidence of UV-induced skin conditions, driven by lifestyle changes, environmental factors, and growing life expectancy. According to the Skin Cancer Foundation, over 58 million Americans have one or more actinic keratosis lesions, and more than 10% may progress to squamous cell carcinoma if untreated.
The condition is particularly prevalent among the elderly and individuals with outdoor occupations or recreational exposure to sunlight. Public health campaigns emphasizing skin cancer prevention such as Australia’s “Slip-Slop-Slap” or the American Academy of Dermatology’s Skin Cancer Awareness Month have successfully improved patient education, leading to early dermatology visits and increased treatment initiation.
Additionally, dermatologists are prioritizing full-body skin exams and lesion mapping, enabling early detection of AKs and contributing to higher demand for both in-office and home-based treatments. The emphasis on cosmetic preservation has also led many patients to seek field-directed therapies that avoid scarring and provide better aesthetic outcomes—further expanding the market.
Market Restraint: Side Effects and Low Compliance with Topical Therapies
Despite the growing availability of non-invasive treatments, the actinic keratosis treatment market faces challenges related to treatment compliance and tolerability, particularly with topical chemotherapeutics and immune response modifiers. These therapies often induce skin irritation, inflammation, peeling, and discomfort, which can discourage patients from completing the full course.
For instance, agents like 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), though highly effective, are associated with severe erythema, crusting, and pain especially when applied over large treatment areas. Similarly, imiquimod may cause local inflammatory reactions, leading to patient dropout before the therapeutic window is complete.
Moreover, the prolonged duration of topical treatment often lasting several weeks contrasts with patient expectations for fast results, particularly in cosmetically sensitive facial areas. Without proper counseling and follow-up, treatment discontinuation can reduce efficacy and increase recurrence rates.
To overcome this restraint, there is a growing focus on shorter-duration regimens, combination therapies, and formulation innovations that improve tolerability while maintaining clinical effectiveness.
Market Opportunity: Home-Based and Teledermatology-Enabled Treatment Models
A major opportunity in the actinic keratosis treatment market lies in the expansion of home-based treatment models, supported by growing access to telemedicine and remote dermatology monitoring. The COVID-19 pandemic catalyzed a shift in healthcare delivery, with patients and providers adopting virtual consultations and self-administered therapies for chronic dermatological conditions.
Topical treatments, particularly prescription creams like diclofenac sodium, fluorouracil, and imiquimod, lend themselves well to at-home use, with minimal clinician intervention required once diagnosis is confirmed. As digital dermatology platforms evolve, patients can now submit photos of lesions for remote evaluation, receive e-prescriptions, and track treatment outcomes through mobile apps.
Furthermore, advancements in photoactivated treatments and smart skin health kits are enabling patients to perform photodynamic therapy at home, expanding access for rural and underserved populations. As healthcare systems aim to reduce hospital burden and improve early intervention, the homecare segment represents a high-potential growth frontier, especially in aging societies with high AK prevalence.
Segments Insights:
By Therapy
Topical therapy dominates the therapy segment, accounting for the largest market share due to its widespread availability, ease of use, and cost-effectiveness. Agents like 5-FU, imiquimod, and diclofenac gel are extensively prescribed for both lesion-specific and field-directed treatment. Their ability to treat both visible and subclinical lesions makes them valuable in comprehensive AK management. Moreover, new formulations with shortened treatment durations and improved skin tolerability are helping expand their appeal, particularly among patients with facial or scalp lesions.
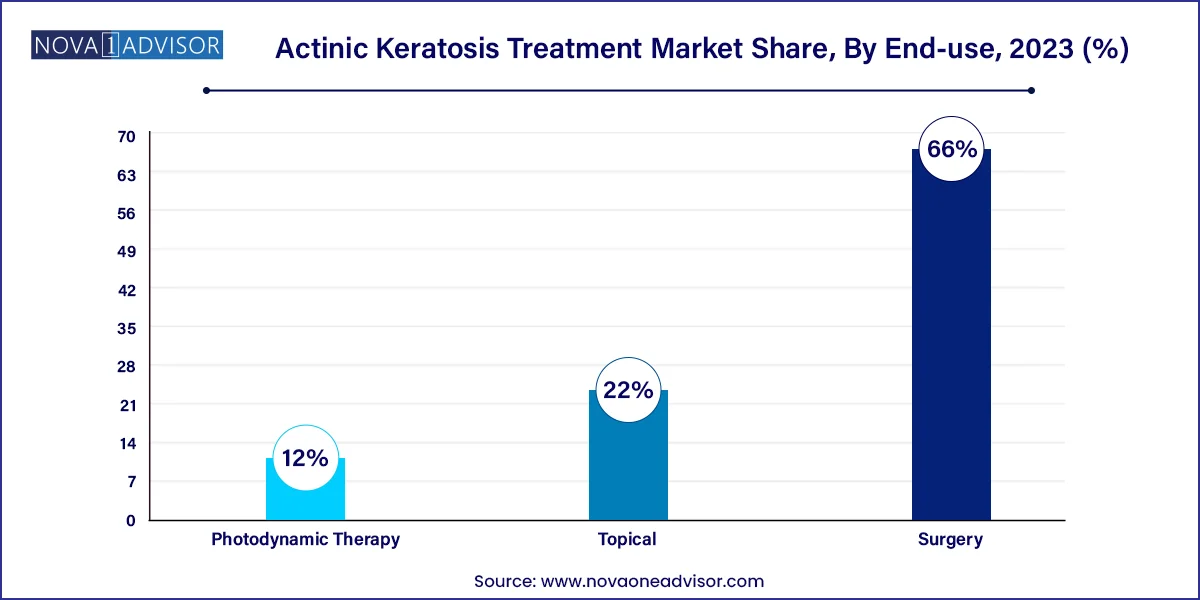
In contrast, photodynamic therapy (PDT) is the fastest-growing therapy type, especially for patients with multiple lesions or those prioritizing cosmetic outcomes. PDT involves applying a light-sensitive drug followed by activation with a specific light source, selectively destroying dysplastic cells. It offers superior cosmetic results and has shown high efficacy in treating facial and scalp AKs. With the development of home-based PDT kits and daylight PDT protocols, the procedure is becoming more accessible outside specialty dermatology clinics, further driving its growth.
By Drug Class
Nucleoside metabolic inhibitors, particularly 5-FU, lead the drug class segment, due to their established role in topical chemotherapy. These agents are well-documented in clinical guidelines and have broad regulatory approval across regions. Their ability to target rapidly dividing cells makes them effective against both AK and subclinical SCC precursors. They are widely prescribed in both monotherapy and combination protocols, ensuring continued demand in dermatology practices.
Photoenhancers are the fastest-growing drug class, aligning with the rise in photodynamic therapy. Compounds like aminolevulinic acid (ALA) and methyl aminolevulinate (MAL) are integral to light-based AK treatment, and innovations in their formulation and application protocols are improving convenience and efficacy. The expanding adoption of PDT in both high- and middle-income countries, coupled with advancements in portable light therapy devices, is accelerating the growth of this segment.
By End-use
Hospitals dominate the end-use segment, as they manage severe, complex, or recurrent AK cases. Hospitals also house the necessary infrastructure for in-office photodynamic therapy, cryotherapy, and surgical excision, especially for patients requiring histological confirmation or advanced lesion removal. In addition, hospitals serve as referral centers for high-risk patients with immune suppression or previous skin cancers, where more intensive surveillance and intervention are needed.
However, homecare is the fastest-growing end-use segment, spurred by the convenience of self-application therapies, cost-effectiveness, and the expansion of remote dermatology consultations. The availability of e-prescriptions, digital health platforms, and smart skin monitoring tools is enabling more patients to initiate and complete AK treatment from home. This trend is particularly strong in North America and Europe, where aging populations and telehealth adoption are converging to reshape dermatology care delivery.
By Regional Insights
North America leads the global actinic keratosis treatment market, owing to high awareness levels, advanced dermatology infrastructure, and a large elderly population. The United States, in particular, has one of the highest AK prevalence rates globally due to sun exposure and skin phototype demographics. Strong reimbursement policies, presence of leading dermatology companies, and proactive skin cancer screening programs further reinforce regional dominance. The U.S. also accounts for a significant share of clinical trials in topical and PDT therapies for AK.
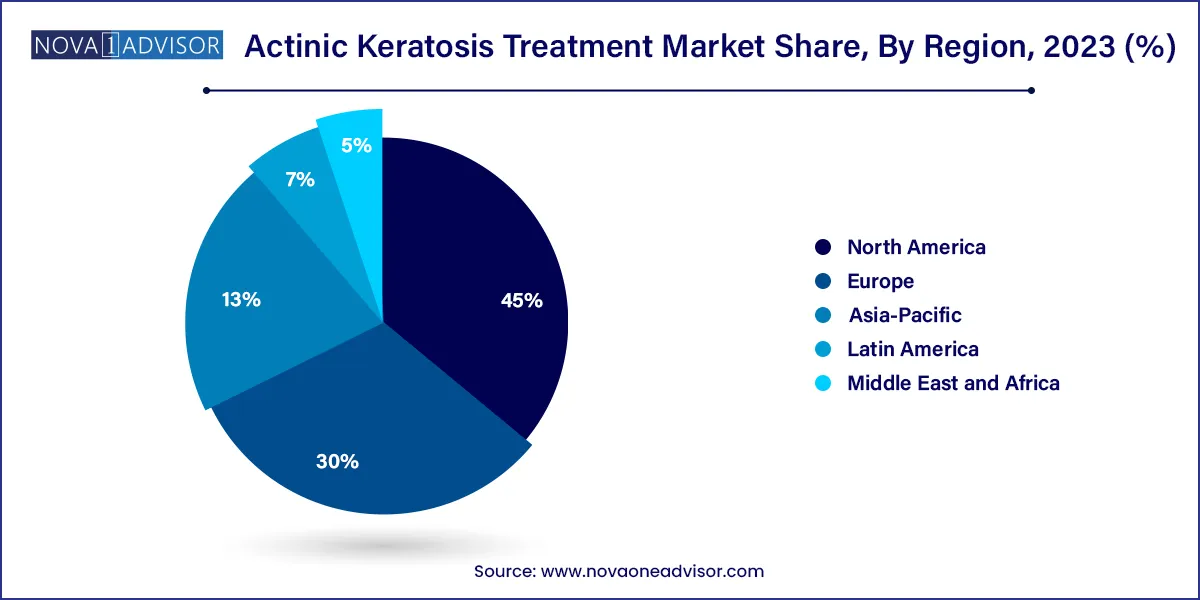
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, fueled by rising awareness, improved access to dermatological care, and changing lifestyle patterns. Countries like Australia exhibit some of the highest per capita AK incidences, while nations like Japan, China, and South Korea are investing in skin cancer awareness and early intervention programs. Urbanization, healthcare modernization, and growing demand for aesthetic outcomes are also expanding PDT and topical therapy adoption across the region.
Some of the prominent players in the Actinic keratosis treatment market include:
- Almirall S.A.
- LEO Pharma A/S
- Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
- Novartis AG
- GALDERMA
- Ortho Dermatologics (Bausch Health Companies Inc.)
- BIOFRONTERA AG
- Hill Dermaceuticals, Inc.
Recent Developments
-
February 2025 – Biofrontera AG announced the U.S. commercial rollout of Ameluz® (aminolevulinic acid) gel, for daylight photodynamic therapy in treating mild-to-moderate AKs.
-
January 2025 – Almirall S.A. received FDA approval for a shortened-duration formulation of tirbanibulin 1% ointment (Klisyri®), allowing for 3-day application with reduced skin irritation.
-
November 2024 – Sun Pharmaceutical Industries launched a generic 5-FU topical cream in emerging markets, aiming to expand affordable access to AK treatment in India and Southeast Asia.
-
September 2024 – LEO Pharma announced results from a phase 3 trial of ingenol mebutate replacement compound, showing comparable lesion clearance with improved safety profile.
-
July 2024 – Galderma launched a new digital skin assessment platform integrated with teledermatology features to support AK monitoring and patient education in Europe.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the global actinic keratosis treatment market.
Therapy
- Topical
- Photodynamic Therapy
- Surgery
Drug Class
- Nucleoside Metabolic Inhibitor
- NSAIDs
- Immune Response Modifiers
- Photoenhancers
- Others
End-use
- Hospitals
- Private Clinics
- Homecare
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)



