Adult Stem Cells Market Size and Growth
The global adult stem cells market size was valued at USD 13.19 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to reach around USD 38.48 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 11.3% from 2024 to 2033.
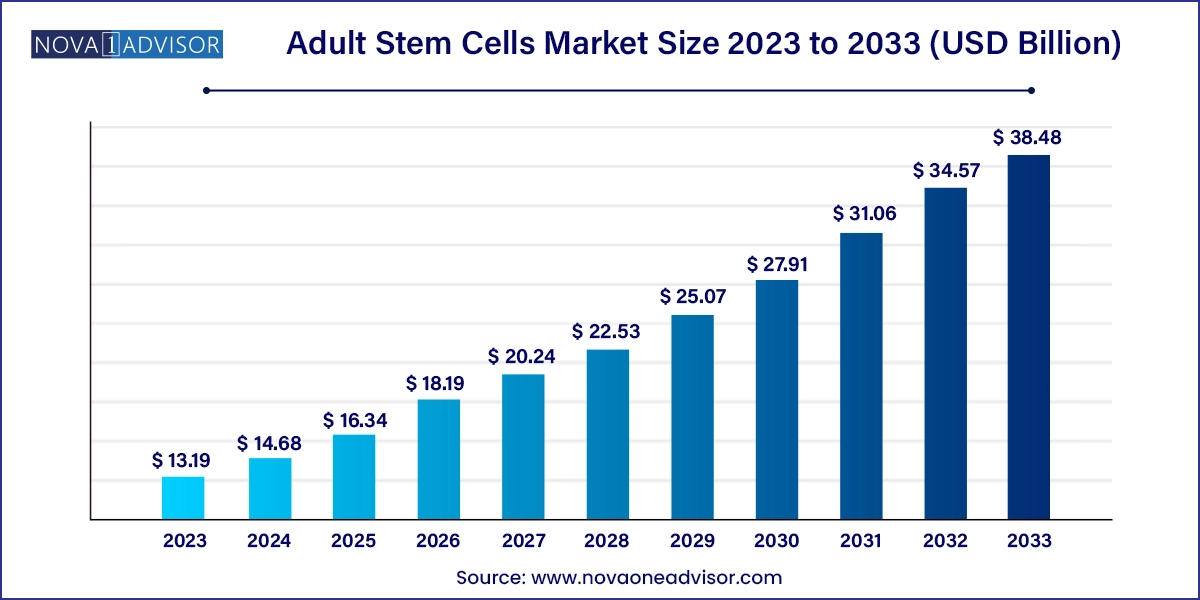
Adult Stem Cells Market Key Takeaways
- The allogeneic adult stem cells segment held the largest share of 55.78% in 2023
- The autologous adult stem cells segment is projected to grow at the fastest CAGR over the forecast period.
- The products segment dominated the market with a share of 79.59% in 2023
- The inflammatory and immunological diseases segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period
- The bone and cartilage repair segment held the largest share of 29.79% in 2023
- The disease modeling segment held the largest share of 29.63% in 2023
- The tissue engineering segment is expected to grow at a significant rate over the forecast period
- The biopharmaceutical companies segment held the largest share of 55.74% in 2023 and growing at a fastest CAGR of 11.5%,
Market Overview
The Adult Stem Cells Market is emerging as one of the most dynamic and high-potential areas within regenerative medicine, cell therapy, and biomedical research. Adult stem cells unlike embryonic stem cells are derived from developed tissues and organs and are primarily responsible for maintaining and repairing the body. Their intrinsic properties, such as self-renewal and differentiation into specific tissue types, make them an invaluable tool in clinical therapeutics, tissue engineering, and drug discovery.
Unlike their embryonic counterparts, adult stem cells bypass many ethical concerns, positioning them as a more favorable alternative for long-term application. These cells are found in a variety of tissues, including bone marrow, adipose tissue, blood, liver, and skin. Among the most widely studied and applied adult stem cell types are hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), used for blood disorders and cancers; mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), with applications in orthopedics, cardiovascular, and autoimmune conditions; and neural stem cells, gaining traction in neurodegenerative therapies.
The market is shaped by the increasing number of clinical trials, significant R&D investments, favorable regulatory changes, and growing public-private partnerships aimed at translating stem cell science into viable therapeutic platforms. As chronic diseases become increasingly prevalent and the demand for organ regeneration, immune modulation, and personalized medicine grows, adult stem cells offer a transformative solution at the intersection of biotechnology and clinical healthcare.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Shift from Research to Commercial Therapies: The transition from bench to bedside is accelerating, with adult stem cells increasingly being integrated into approved therapeutic interventions.
-
Rise of Allogeneic Therapies: Allogeneic adult stem cell therapies—where cells are sourced from a donor—are gaining favor due to their scalability and suitability for off-the-shelf treatments.
-
Expansion of Biobanking Infrastructure: Governments and private entities are heavily investing in adult stem cell biobanks, facilitating long-term storage, tracking, and commercialization.
-
Increased Focus on Adipose- and Dental Pulp-derived MSCs: Novel sources like dental pulp and adipose tissues are being explored due to easy accessibility and higher proliferation rates.
-
Technological Integration in Cell Processing: Automation, AI-powered analytics, and closed-loop bioreactors are being adopted for high-throughput stem cell expansion and differentiation.
-
Regenerative Orthopedics Boom: MSCs are being increasingly used in cartilage, ligament, and tendon repair, revolutionizing sports medicine and degenerative joint disease management.
-
Global Collaborations and Clinical Trials: Cross-border clinical partnerships are on the rise, particularly for autoimmune, neurological, and cardiovascular indications.
Adult Stem Cells Market Report Scope
| Report Attribute |
Details |
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 14.68 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 |
USD 38.48 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 |
CAGR of 11.3% |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024 to 2033 |
| Segments Covered |
Type, product & services, indication, application, end use, region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage |
Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc; STEMCELL Technologies; Osiris Therapeutics; Vericel Corporation; ZenBio, Inc.; Stempeutics Research; Fate Therapeutics, Inc.; BrainStorm Cell Therapeutics Inc.; Celgene Corporation; Stemedica Cell Technologies, Inc |
Key Market Driver: Increasing Burden of Chronic and Degenerative Diseases
A major driver fueling the adult stem cells market is the growing global burden of chronic and degenerative diseases, especially those with limited treatment options. As populations age and lifestyles become more sedentary, the incidence of conditions such as osteoarthritis, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and neurodegenerative disorders is rising dramatically. These ailments are often marked by progressive tissue damage, inflammation, or immune system dysregulation.
Adult stem cells, particularly mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), have demonstrated immense therapeutic potential in modulating immune responses, reducing inflammation, and promoting tissue regeneration. For instance, in patients with ischemic heart failure, allogeneic MSCs have shown promise in improving cardiac function and reducing scar tissue. Similarly, HSCs continue to be the gold standard for treating hematological malignancies like leukemia and lymphoma.
The ability of adult stem cells to offer non-invasive, personalized, and regenerative alternatives to traditional therapies is making them central to future treatment protocols. This is pushing hospitals, research institutions, and biotech firms to ramp up development and clinical validation efforts.
Key Market Restraint: Variability and Limited Potency Across Cell Sources
Despite their therapeutic promise, a significant challenge hampering the adult stem cell market is biological variability and limited potency compared to embryonic or induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). Adult stem cells are multipotent, meaning their differentiation potential is restricted to specific cell types. For instance, MSCs derived from adipose tissue may differ significantly in regenerative efficacy compared to bone marrow-derived MSCs.
In addition, donor age, extraction technique, culture conditions, and passage number can affect cell viability, proliferation rate, and immunomodulatory properties. This variability complicates standardization and reproducibility, especially in allogeneic or off-the-shelf applications. The lack of universal markers and characterization protocols for adult stem cells poses an additional regulatory hurdle.
While advancements in cell characterization, sorting, and expansion are underway, these scientific and technical challenges continue to limit scalability and commercial viability, particularly for large patient cohorts or multi-center clinical trials.
Key Market Opportunity: Expansion in Personalized and Precision Cell Therapy
An evolving opportunity for the adult stem cells market lies in the integration with personalized medicine and precision therapy models. As genomics and molecular diagnostics evolve, it is now possible to understand individual disease signatures at the cellular and genetic level. This has significant implications for tailoring autologous adult stem cell therapies—those derived from the patient’s own body—to minimize rejection and maximize therapeutic outcomes.
For example, personalized MSC treatments are being studied for Crohn’s disease, graft-vs-host disease (GvHD), and multiple sclerosis, where the immune system plays a central pathological role. Similarly, neural stem cells are being customized to match patient-specific neurodegenerative conditions like ALS and Parkinson’s.
Biotech companies and research institutes are investing in platforms that can extract, culture, and modify a patient’s own cells for targeted reintroduction, making therapies safer and more effective. The emergence of biomarker-driven patient selection in trials and companion diagnostics for stem cell products further enhances the market potential in this niche.
Adult Stem Cells Market By Type Insights
Autologous adult stem cells dominate the type segment, primarily due to their low risk of immunogenicity and rejection. These cells are harvested from the patient's own body, often from bone marrow or adipose tissue, and reintroduced after processing. This approach is widely used in orthopedic and cosmetic procedures, as well as in hematopoietic stem cell transplants. For instance, autologous stem cell therapy is the standard treatment for multiple myeloma, showcasing its established clinical utility.
However, allogeneic stem cells are the fastest-growing segment, thanks to the convenience of being used in off-the-shelf therapies and mass production potential. Allogeneic MSCs and HSCs are already being used in clinical trials for stroke, heart failure, and immune disorders. They offer the advantages of standardized dosing, quality control, and immediate availability, making them more attractive for emergency and chronic applications alike.
Adult Stem Cells Market By Product & Services Insights
Products dominate the market, particularly kits, media, and reagents required for stem cell isolation, expansion, and differentiation. These are essential for both therapeutic and research applications. The demand for high-performance culture media that preserve stemness while enhancing proliferation is especially high. Meanwhile, hematopoietic and mesenchymal cell lines lead the cell-based product category due to their widespread application in hematology and regenerative medicine.
Services are the fastest-growing segment, with increasing demand for stem cell banking, cell processing, and contract development services. Specialized CROs and CMOs are expanding their offerings to include GMP-grade expansion, gene modification, and quality testing for clinical-grade stem cell production. Biopharma companies and research institutes increasingly outsource these functions to accelerate development and reduce costs.
Adult Stem Cells Market By Indication Insights
Bone and cartilage repair is the largest indication, with orthopedic and sports medicine embracing MSCs for regenerative therapies. Conditions like osteoarthritis, cartilage lesions, and tendon injuries are being treated using intra-articular injections of autologous or allogeneic MSCs, offering alternatives to surgical interventions. Clinical trials have shown that MSCs can significantly reduce pain and improve joint mobility, especially in knee injuries.
Cancer and GvHD are rapidly growing indications, with hematopoietic stem cell transplants forming a cornerstone of therapy. Adult stem cells are also being explored in adjunctive roles for reducing chemotherapy-induced damage and modulating tumor microenvironments. Additionally, MSCs are being evaluated for anti-inflammatory effects in managing GvHD after bone marrow transplants, demonstrating compelling immunoregulatory outcomes.
Adult Stem Cells Market By Application Insights
Therapeutics remains the dominant application, representing the core of commercial stem cell use today. Therapies targeting musculoskeletal, hematologic, cardiac, and autoimmune conditions make up the bulk of clinical applications. The increasing number of investigational new drug (IND) applications in the U.S. and Europe further validates this trend.
On the other hand, drug development and disease modeling are growing rapidly, especially in academic and pharmaceutical R&D. Adult stem cells are used to mimic disease states in vitro and test the effects of new compounds. MSCs and neural stem cells are particularly valuable in neuroinflammation, metabolic disease, and fibrosis studies. This trend is likely to accelerate with the push toward alternatives to animal testing and high-throughput screening technologies.
Adult Stem Cells Market By End Use Insights
Biopharmaceutical companies dominate the end-use segment, accounting for significant investment in clinical trials, product development, and commercialization. These companies partner with stem cell biobanks, academic institutions, and CROs to accelerate time-to-market for regenerative therapies.
Research institutes and hospitals/clinics are rapidly expanding their roles, especially in conducting early-phase clinical trials and developing cell therapy protocols for compassionate use. Universities and academic medical centers serve as innovation hubs for adult stem cell research, while specialized hospitals increasingly offer cell-based therapies in orthopedics, neurology, and cardiology.
Adult Stem Cells Market By Regional Insights
North America leads the global adult stem cells market, driven by robust funding for stem cell research, an advanced regulatory environment, and a high concentration of biotech companies. The U.S. FDA’s Regenerative Medicine Advanced Therapy (RMAT) designation has accelerated approval pathways for promising cell therapies, encouraging clinical innovation. Major companies like Thermo Fisher Scientific, Lonza, and Mesoblast have headquarters or large operations in North America. Additionally, academic institutions such as Harvard, Stanford, and Mayo Clinic lead in clinical translation of adult stem cell therapies.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, owing to rising healthcare investments, favorable government initiatives, and expanding clinical infrastructure. Countries such as China, Japan, South Korea, and India are establishing national cell therapy guidelines and investing in stem cell banks and translational centers. Japan, through its Sakigake fast-track approval system, has emerged as a leader in regenerative medicine. Meanwhile, China’s booming biotech sector and relaxed trial environments have made it a hub for conducting early-phase stem cell research. The expanding middle class and aging population across Asia are also driving demand for cell-based treatments.
Adult Stem Cells Market Top Key Companies:
- Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc
- STEMCELL Technologies
- Osiris Therapeutics
- Vericel Corporation
- ZenBio, Inc.
- Stempeutics Research
- Fate Therapeutics, Inc.
- BrainStorm Cell Therapeutics Inc.
- Celgene Corporation
- Stemedica Cell Technologies, Inc.
Adult Stem Cells Market Recent Developments
-
In March 2025, Lonza announced an expansion of its GMP stem cell manufacturing facility in Massachusetts to support growing demand for MSC-based therapies.
-
Thermo Fisher Scientific launched a new xeno-free media for mesenchymal stem cell culture in February 2025, enhancing safety for clinical applications.
-
In January 2025, Mesoblast Ltd. received FDA clearance to begin a phase 3 trial using allogeneic MSCs for treating chronic low back pain.
-
Takeda Pharmaceuticals partnered with a Korean stem cell company in December 2024 to co-develop autologous neural stem cell therapies for Parkinson’s Disease.
-
In November 2024, BioTime Inc. (Lineage Cell Therapeutics) published promising phase 2 data on adult neural stem cells for spinal cord injury recovery.
Adult Stem Cells Market Report Segmentation
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Adult Stem Cells market.
By Type
- Autologous Adult Stem Cells
- Allogeneic Adult Stem Cells
By Product & Services
- Product
- Kits, Media, & Reagents
- Cells & cell lines
- Hematopoietic
- Mesenchymal
- Neural
- Epithelial/Skin
- Others
- Services
By Indication
- Bone and Cartilage Repair
- Cardiovascular Diseases
- Inflammatory and Immunological Diseases
- Liver diseases
- Cancer
- GvHD
- Others
By Application
- Therapeutics
- Disease Modeling
- Drug Development & Discovery
- Toxicology Studies
- Biobanking
- Tissue Engineering
- Others
By End Use
- Biopharmaceutical Companies
- Research Institutes
- Hospitals & Clinics
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)

