AI Voice Agents In Healthcare Market Size and Research
The AI Voice Agents In Healthcare Market size was exhibited at USD 468.25 million in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 11,568.71 million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 37.87% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
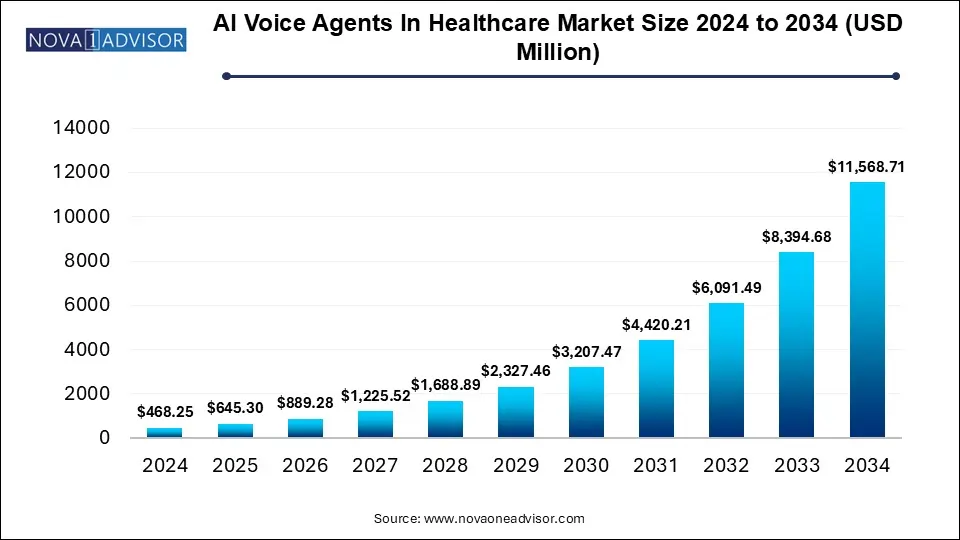
Key Takeaways:
- Among applications, clinical documentation accounted for the highest portion of market revenue in 2024, contributing 18% to the overall share.
- In terms of deployment mode, cloud-based solutions held a commanding position in the market, representing 86% of the total revenue in 2024.
- With respect to technology, NLP-powered conversational agents emerged as the leading segment, generating 33% of the global revenue in 2024.
- By end use, hospitals and health systems stood out as the primary adopters, securing a 42% share of the market revenue in 2024.
- Regionally, North America led the global AI voice agents in healthcare market, capturing 55% of the total revenue in 2024.
Market Overview
The global AI voice agents in healthcare market is poised at the forefront of a transformative shift in how healthcare providers, patients, and payers interact and communicate. These intelligent, conversational systems are reshaping everything from front-desk appointment scheduling to chronic disease monitoring, delivering timely, consistent, and scalable engagement across healthcare touchpoints. As natural language processing (NLP), speech recognition, and machine learning algorithms mature, AI voice agents are transitioning from rudimentary chatbots to empathetic, multilingual, emotionally responsive companions capable of understanding context and nuance in medical conversations.
The surge in virtual care, post-pandemic digital transformation, and the push for operational efficiency are compelling hospitals, clinics, and insurance companies to integrate voice AI into their ecosystems. With administrative burdens mounting and healthcare workforces under strain, AI voice agents offer a 24/7 support mechanism that reduces clinician burnout, enhances patient satisfaction, and optimizes workflows. As of 2024, healthcare AI voice systems are estimated to have reached thousands of deployments globally, from small physician practices to enterprise-level hospital systems, and the trajectory is only accelerating.
Notable applications include AI-driven virtual triage assistants in emergency departments, voice-activated documentation for physicians, mental health bots providing companionship and crisis support, and multilingual insurance agents explaining policies in layman’s terms. The blend of conversational AI with healthcare domain expertise is creating new value streams and redefining what patient-centric care truly means.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Rising Adoption of Multilingual Agents: To address diverse patient populations, healthcare providers are deploying voice agents capable of operating in multiple languages.
-
Emotionally Intelligent Voice AI: Systems are being trained to detect emotional cues like stress, confusion, or depression through tone analysis and respond with appropriate empathy.
-
EHR Integration and Automation: Voice agents are increasingly integrated with electronic health records (EHRs) to facilitate real-time updates, appointment reminders, and charting.
-
Voice AI for Mental Health Support: Companion bots and mental wellness agents are seeing adoption in telepsychology and eldercare settings.
-
Cloud-Based Deployments on the Rise: Scalable, cost-effective cloud-based models are overtaking on-premise installations due to lower IT overhead.
-
Healthcare-Specific NLP Training: Vendors are investing in industry-specific datasets to train AI models for better accuracy in medical terminology and clinical conversations.
-
Voice Agent Interoperability Across Devices: AI voice platforms are now designed to work seamlessly across mobile phones, smart speakers, kiosks, and hospital systems.
Report Scope of AI Voice Agents In Healthcare Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 645.30 Million |
| Market Size by 2034 |
USD 11,568.71 Million |
| Growth Rate From 2025 to 2034 |
CAGR of 37.87% |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2034 |
| Segments Covered |
Application, Deployment Mode, Technology, End use, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Zocdoc; eHealth, Inc.; Assort Health; RevSpring; Innovacer; Parakeet Health, Inc.; Cedar Cares, Inc.; Infinitus Systems; VOCADS; In Touch Now |
Market Driver: Workforce Shortages and Administrative Overload
A leading driver propelling the AI voice agents market in healthcare is the severe shortage of medical professionals, particularly administrative and nursing staff. Hospitals and clinics are grappling with a growing burden of non-clinical tasks, from appointment coordination to documentation and insurance verification. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), a projected shortfall of 10 million healthcare workers is anticipated by 2030, predominantly in low- and middle-income countries. AI voice agents fill these gaps by automating routine and repetitive tasks, freeing up clinicians to focus on critical care. For example, AI-powered assistants now handle over 60% of inbound scheduling calls at some U.S. hospitals, leading to substantial reductions in wait times and staffing costs.
Market Restraint: Data Privacy and Ethical Concerns
Despite the benefits, one of the key restraints hindering adoption is the concern surrounding data privacy, ethical usage, and regulatory compliance. AI voice agents process sensitive patient information, and any breach or misuse can result in severe consequences, both legal and reputational. The complexity of healthcare regulations such as HIPAA in the U.S., GDPR in Europe, and other localized standards makes deployment a legal minefield. Patients may also feel uncomfortable or skeptical about sharing intimate health details with automated agents. Moreover, there's an ongoing debate about whether AI systems can truly offer empathetic care in scenarios like mental health support or end-of-life discussions. These ethical dilemmas must be addressed through transparency, consent protocols, and robust security frameworks.
Market Opportunity: Voice-Driven Home Healthcare and Remote Monitoring
A major opportunity lies in expanding AI voice agents to the domain of home healthcare and remote patient monitoring (RPM). With the elderly population rising globally and chronic diseases becoming more prevalent, voice agents can serve as at-home caregivers reminding patients to take medication, logging symptoms, and alerting clinicians when anomalies are detected. This is particularly impactful in rural or underserved areas where access to care is limited. Startups and health-tech giants alike are developing ambient voice agents that function hands-free through smart speakers or IoT devices. For example, an AI voice companion might track a heart failure patient's weight and breathlessness daily, flagging deterioration to a remote cardiologist. Such innovations align with the broader trend toward decentralized and preventive care models.
Segmental Analysis
Application Outlook
Appointment Scheduling emerged as the leading application segment, driven by high call volumes and the need for 24/7 accessibility. AI voice agents now handle scheduling, rescheduling, and cancellations with natural dialogue capabilities. Hospitals are saving thousands of hours annually by automating these transactions, ensuring quicker patient access to care and better resource planning. The convenience of confirming appointments via voice bots integrated with patient calendars is also boosting patient adherence and clinic efficiency.
Mental Health & Companion Bots are the fastest-growing application, reflecting increased awareness of mental health and the need for scalable solutions in this space. These bots are designed to detect mood patterns, initiate supportive conversations, and escalate to human therapists when needed. Particularly among elderly patients and individuals with anxiety or depression, voice-based interactions offer non-judgmental companionship and continuity of care. Startups like Wysa and Woebot are advancing conversational AI agents capable of engaging in therapeutic dialogue and emotional support, with partnerships emerging with health systems globally.
Deployment Mode Outlook
Cloud-based deployments lead the segment, thanks to their scalability, faster updates, and cost-efficiency. Healthcare systems prefer cloud solutions that can be rolled out across multiple sites without the need for complex infrastructure. Vendors offer secure, HIPAA-compliant cloud environments with remote management capabilities. Furthermore, cloud platforms enable real-time analytics and user behavior insights, helping healthcare providers fine-tune their service delivery.
On-premise solutions are growing in specialty clinics and sensitive data environments, where providers require direct control over data flow and security. Though limited in scalability, on-premise deployments appeal to organizations with existing IT capacity and stringent data governance protocols, such as large academic medical centers or government hospitals.
Technology Outlook
NLP-Powered Conversational Agents dominate the technology segment, as these systems offer superior natural language understanding and contextual dialogue. They are capable of handling multi-turn conversations, switching topics as needed, and interpreting patient intent. Their usage spans from symptom triage to post-discharge follow-up, with AI adapting to different patient dialects and vocabulary.
Emotionally Aware AI Agents are experiencing the fastest growth, leveraging sentiment analysis to interpret emotional tone and respond empathetically. These agents are critical in mental health and pediatric care, where tone recognition adds a layer of trust and engagement. AI developers are investing in affective computing, enabling bots to adjust conversation pace, offer supportive language, and even detect distress signals during crisis calls.
End Use Outlook
Hospitals and Health Systems are the primary end users, accounting for the majority share due to the complexity and scale of operations. Large hospitals deploy AI voice agents for everything from patient onboarding to discharge follow-ups. These agents support multi-departmental workflows, ensuring streamlined communication between patients and administrative staff, while improving response times.
Home Healthcare Providers represent the fastest-growing segment, as voice agents become integral to aging-in-place initiatives and chronic disease management. Voice assistants are being used for patient reminders, symptom reporting, and even virtual companionship. The convenience and accessibility of voice-based interfaces make them ideal for older adults and people with disabilities who may struggle with traditional apps or devices.
Regional Analysis
North America leads the AI voice agents in healthcare market, fueled by a mature digital health ecosystem, strong investment from tech giants, and supportive regulatory structures. The U.S., in particular, boasts a thriving startup ecosystem and healthcare systems willing to pilot and scale AI initiatives. Providers like Mayo Clinic, Cleveland Clinic, and Kaiser Permanente are early adopters of voice AI for triage, EHR navigation, and patient communication. Moreover, U.S. insurers are increasingly backing voice-driven health tech as part of population health and value-based care models.
Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing region, driven by its vast, aging population, rising chronic disease burden, and accelerated digital adoption post-COVID. Countries like Japan, China, and India are integrating voice agents into public health helplines, hospital systems, and eldercare services. Language diversity and rural access challenges make voice-based solutions particularly attractive. For example, Indian health-tech startup MFine launched a multilingual voice bot to support COVID triage, marking a broader trend toward vernacular digital health tools.
Some of The Prominent Players in The AI Voice Agents In Healthcare Market Include:
- Zocdoc
- eHealth, Inc.
- Assort Health
- RevSpring
- Innovacer
- Parakeet Health, Inc.
- Cedar Cares, Inc.
- Infinitus Systems
- VOCADS
- In Touch Now
Recent Developments
-
January 2025: Nuance Communications, a Microsoft company, unveiled a voice-enabled ambient clinical documentation tool tailored for primary care physicians, reducing note-taking burden.
-
February 2025: Wysa announced integration with the UK’s National Health Service (NHS) to provide voice-guided mental wellness support across English-speaking regions.
-
March 2025: Babylon Health launched a multilingual AI voice agent for triaging symptoms in rural areas of India and Bangladesh through a partnership with local telecoms.
-
April 2025: Amazon Web Services (AWS) introduced healthcare-specific enhancements to its Amazon Lex platform, improving the capabilities of voice bots in medical settings.
-
May 2025: Cerner and GYANT entered into a strategic partnership to embed voice AI into EHR workflows for outpatient clinics, enabling intelligent patient intake and post-visit summaries.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Operating room equipment market
By Application
- Appointment Scheduling
- Clinical Documentation
- Patient Triage & Symptom Checking
- Patient Engagement
- Remote Monitoring
- Mental Health & Companion Bots
- Billing & Insurance Support
- Others
By Deployment Mode
By Technology
- Rule-based Voice Assistants
- NLP-Powered Conversational Agents
- Emotionally Aware AI Agents
- Multilingual Voice Agents
- Others
By End Use
- Hospitals and Health Systems
- Outpatient Clinics and Physician Offices
- Home Healthcare Providers
- Patients
- Payers and Insurance Firms
- Others
By Regional
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa (MEA)

