Biopsy Devices Market Size and Growth Forecast 2025-2034
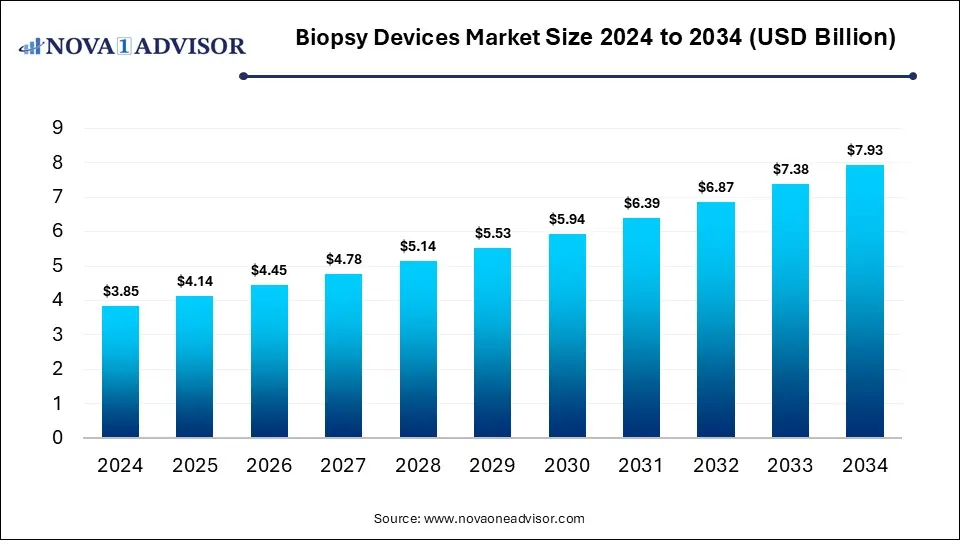
The global biopsy devices market size was valued at USD 3.85 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach around USD 7.93 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 7.5% from 2025 to 2034. The growth of the biopsy devices market is driven by the rising cancer disease burden across the globe, improvements in minimally invasive biopsy procedures, increasing awareness for early cancer detection, and innovative product launches.
Biopsy Devices Market Key Takeaways
- Needle-based biopsy guns dominated the market and accounted for the largest market share of 43.37% in 2024.
- The biopsy needle segment is expected to grow significantly over the forecast period.
- North America biopsy devices market dominated the overall global market and accounted for 43.61% of revenue share in 2024
- The U.S. biopsy devices market accounted for a 34.62% share of the global market in 2024.
- The Asia Pacific biopsy devices market is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR over the forecast period.
Market Overview
The biopsy devices market plays a pivotal role in the global healthcare diagnostics ecosystem, offering tools and technologies essential for detecting and diagnosing a wide array of diseases, primarily cancer. Biopsy involves the removal of tissue samples from the body to examine them microscopically for abnormalities. Given the increasing global burden of cancer and other chronic diseases, biopsy has become the gold standard for definitive diagnosis. Consequently, the demand for advanced, accurate, and minimally invasive biopsy tools is expanding rapidly.
Biopsy procedures today are not limited to oncology but span other specialties, including gastroenterology, pulmonology, dermatology, nephrology, and urology. Biopsy devices have evolved from simple manual forceps and needles to sophisticated, image-guided robotic systems that enhance precision and reduce patient discomfort. Market players are investing in R&D to develop devices that enable earlier, safer, and more effective sample acquisition—making real-time, point-of-care biopsies a growing possibility.
As personalized medicine continues to gain momentum, biopsy devices are increasingly being used not just for initial diagnosis but also for treatment planning, monitoring response, and guiding minimally invasive surgical interventions. The rise of liquid biopsy is also complementing tissue biopsies, but it has not replaced the need for traditional biopsy tools. Thus, the market remains strong, with promising innovations and a growing base of global patients driving future growth.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Increased Adoption of Image-Guided and Robotic Biopsy Systems: Robotics and imaging technologies are improving accuracy in complex anatomical regions.
-
Minimally Invasive and Disposable Devices on the Rise: Surge in demand for single-use, patient-safe, and cost-effective biopsy needles and forceps.
-
Growth in Vacuum-Assisted Biopsy (VAB) for Breast and Prostate Cancer: VAB offers enhanced sample yield with less trauma, supporting broader use.
-
Shift Toward Ambulatory and Outpatient Biopsy Procedures: Convenience, cost-effectiveness, and advancements in portable biopsy systems are encouraging decentralization.
-
Integration of AI in Biopsy Workflow: AI is being applied to biopsy guidance systems and pathology interpretation to improve clinical decision-making.
-
Demand for Core Needle Biopsy Over Fine Needle Aspiration: CNB offers larger, more structurally intact samples, enhancing diagnostic value.
-
Surge in Biopsy for Gastrointestinal and Lung Disorders: Increasing cases of colorectal cancer and pulmonary nodules is spurring demand for advanced endoscopic and bronchoscopic forceps.
-
Global Expansion of Cancer Screening Programs: Governments and NGOs are supporting early detection campaigns, leading to higher biopsy volumes.
How is AI Impacting the Biopsy Devices Market?
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in biopsy devices will widely impact its market growth, further enhancing their diagnostic accuracy, improving their speed and facilitating the development of personalized treatment approaches. Companies are developing AI algorithms for analyzing digitized biopsy images, further helping pathologists to identify cancerous areas, for grading tumors, and to assess tissue samples with improved speed and precision. Analysis of liquid biopsies (blood samples) for circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), exosomes, and other biomarkers, using AI-driven tools can enable early detection of cancer and also assist in monitoring treatment response. AI-powered robotic systems can assist with biopsy procedures, further reducing procedure time, improving accuracy, and potentially enhancing patient experience.
- For instance, in September 2024, Koelis SAS, a globally leading company in prostate care, declared partnership and successful initial experience with DeepHealth Prostate software for streamlining AI-powered prostate MRI interpretation and guidance in fusion biopsy with Koelis Trinity 3D Ultrasound Platform.
Biopsy Devices Market Report Scope
| Report Attribute |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 4.14 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 |
USD 7.93 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2025 to 2034 |
CAGR of 7.5% |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025 to 2034 |
| Segments Covered |
Product and Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage |
Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Cardinal Health Inc.; Hologic, Inc.; Danaher Corporation; CONMED Corporation; Cook Medical; DTR Medical; INRAD, Inc.; Devicor Medical Products Inc.; Gallini Srl; TransMed7, LLC. |
Market Driver: Growing Global Burden of Cancer and Early Detection Programs
The most significant driver behind the growth of the biopsy devices market is the rising global prevalence of cancer and the concurrent emphasis on early detection. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), cancer accounted for nearly 10 million deaths in 2023. Early detection remains the cornerstone of reducing mortality and improving outcomes, with biopsy being the most definitive method of diagnosis. Governments worldwide are launching public screening initiatives for breast, cervical, colorectal, and prostate cancers—all of which require biopsy confirmation.
Biopsy is not only a diagnostic endpoint but increasingly the first step in a personalized treatment journey. In breast cancer, for instance, biopsy determines receptor status (HER2, ER/PR), guiding hormonal or targeted therapy decisions. Similarly, lung cancer biopsies help identify actionable mutations like EGFR and ALK. These advanced molecular diagnostics can only proceed after quality tissue sampling. This demand is stimulating continual innovation and investment in biopsy tools, making them more accessible, safe, and efficient.
Market Restraint: Risk of Complications and Inadequate Sample Acquisition
Despite its clinical utility, biopsy procedures carry inherent risks and limitations that restrain broader adoption, especially in low-resource settings. Key concerns include bleeding, infection, pneumothorax (in lung biopsies), and discomfort or trauma to surrounding tissues. Inadequate sample size or sample degradation during retrieval can result in inconclusive results, leading to repeat procedures and delayed diagnosis.
This problem is particularly acute in fine needle aspiration biopsies (FNAB), where samples are smaller and more prone to artifact damage. Even in more advanced systems like VAB, operator expertise and imaging compatibility can affect the quality of sampling. For deep or hard-to-reach tumors, the risk profile is higher, deterring certain patients or facilities from performing routine biopsies. Therefore, improving training, safety mechanisms, and device ergonomics are critical to overcoming this restraint.
Market Opportunity: Integration of Robotics and AI in Biopsy Systems
A transformative opportunity lies in the convergence of robotics, imaging, and artificial intelligence (AI) within the biopsy landscape. Robotics is enabling highly precise needle placement, particularly in procedures that require millimeter-level accuracy—such as prostate, brain, and liver biopsies. Companies are developing robotic arms and navigation systems that reduce operator variability and increase the likelihood of successful sampling in a single attempt.
Meanwhile, AI is being used to optimize imaging-guided biopsies, automating the identification of lesion boundaries and predicting the most viable biopsy targets. These integrations not only improve diagnostic yield but also minimize complications and training needs. As healthcare systems move toward automation and digitalization, these intelligent biopsy solutions are expected to gain rapid adoption, particularly in advanced cancer centers and academic hospitals.
Biopsy Devices Market By Product Insights
Needle-based biopsy guns dominated the market, representing the most utilized and versatile biopsy tool category globally. Among them, core needle biopsy (CNB) devices are increasingly preferred over fine needle aspiration (FNAB) due to their ability to retrieve larger, more intact tissue samples, allowing for detailed histological and molecular analysis. CNB is commonly used for breast, prostate, liver, and kidney biopsies, providing high diagnostic yield and reduced need for repeat testing. FNAB, while still useful for thyroid nodules and superficial masses, is gradually being supplemented by CNB in critical applications. Vacuum-assisted biopsy (VAB) systems have emerged as a popular subset within this category for their minimally invasive nature and superior sample quality.
Biopsy guidance systems are the fastest-growing product segment, driven by rising adoption of image-guided and robotic-assisted procedures. Manual guidance systems integrated with ultrasound or CT offer enhanced precision, but the next leap is robotic navigation. Robotic guidance is transforming challenging biopsies, especially for prostate and lung cancers. For example, robotic-assisted bronchoscopy allows pulmonologists to access peripheral lung nodules with high accuracy, reducing false negatives and need for surgical intervention. As technology evolves, robotic guidance systems will expand into general surgery and interventional radiology, redefining the precision landscape of the biopsy market.
Biopsy Devices Market By Regional Insights
North America dominated the biopsy devices market, supported by advanced healthcare infrastructure, high cancer screening rates, and early adoption of new medical technologies. The United States, in particular, benefits from established clinical guidelines, reimbursement frameworks, and strong oncology networks. Leading hospitals routinely utilize advanced CNB and VAB systems for breast and prostate cancer diagnosis. The region is also home to key innovators such as Hologic, BD, and Boston Scientific, whose product pipelines are continuously upgraded with AI and robotics. The regulatory pathway, while rigorous, also ensures that new biopsy tools are clinically validated, increasing physician and patient trust.
- For instance, in April 2025, Labcorp, a globally leading provider of innovative and comprehensive laboratory services, expanded its precision oncology portfolio with launch of two new solutions, namely Labcorp Plasma Detect developed for clinical use to assess the risk of recurrence in stage III colon cancer patients, and the FDA-approved PGDx elio plasma focus Dx, which is the first and only kitted, pan-solid tumor liquid biopsy test for identifying patients who may benefit from targeted treatments.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, driven by increasing healthcare access, rising cancer incidence, and expanding awareness about early diagnosis. Countries such as China, India, and Japan are investing in cancer screening programs and diagnostic infrastructure. In China, for instance, lung cancer screening in smokers and urban populations has led to a spike in biopsies performed using bronchoscopic and CT-guided tools. Meanwhile, medical tourism and government-backed public health initiatives in India are supporting increased procurement of affordable biopsy systems. Regional players are entering partnerships with global companies to co-develop cost-effective solutions tailored to diverse anatomical and cultural needs.
India Biopsy Devices Market Trends
India is anticipated to witness the fastest growth in the biopsy devices market in Asia Pacific, driven by factors such as the increasing incidences of chronic diseases like cancer in the large population, rising awareness for early disease detection, supportive government initiatives for promoting cancer screening, and rising demand for minimally invasive biopsy procedures. Improvements in biopsy techniques such as advanced imaging guiding tools and minimally invasive techniques, as well as adoption of advanced techniques like liquid biopsy are boosting the market expansion.
Biopsy Devices Market Top Key Companies:
- Cardinal Health Inc.
- Hologic, Inc.
- Danaher Corporation
- CONMED Corporation
- Cook Medical
- DTR Medical
- INRAD, Inc.
- Devicor Medical Products Inc.
- Gallini Srl
- TransMed7, LLC.
Biopsy Devices Market Recent Developments
- In July 2025, Single Pass Inc., declared the launch and first enrolment in B-S.A.F.E. (Biopsy with SinglePass: Assessing Fast & Effective Tract Closure), which is a global, post-FDA market evaluation and will comprise of over 1000 unique procedures across 20 center worldwide for generating real-world evidence of the SinglePass electrocautery biopsy closure device.
- In June 2025, GeneCentric Therapeutics secured an initial $8 million through a Series C funding round. The funding will advance the launch and commercialization of GenomicsNext, which is an integrated platform developed for comprehensive liquid biopsy testing through simultaneous gene expression measurements and DNA variant detection from a single sample of circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA).
- In February 2025, Limaca Medical Ltd., commercially launched its Precision-GI endoscopic automated motorized EUS biopsy device, which is designed for obtaining improved biopsy results for patients suspected with cancer in the GI tract and adjacent organs, in the U.S. market. Limaca’s clinical trials, operational capabilities, FDA approval, and CMS Transitional Pass-Through (TPT) Payment award supported the commercialization of the device.
- In November 2024, Mammotome introduced its first automated spring-loaded core needle device, the Mammotome AutoCore Single Insertion Core Biopsy System to the market.
Biopsy Devices Market Report Segmentation
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Biopsy Devices market.
By Product
- Needle-based Biopsy Guns
- Vacuum-assisted Biopsy (VAB) Devices
- Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy (FNAB) Devices
- Core Needle Biopsy (CNB) devices
- Biopsy Guidance Systems
- Biopsy Needles
- Biopsy Forceps
- General Biopsy Forceps
- Hot Biopsy Forceps
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)

