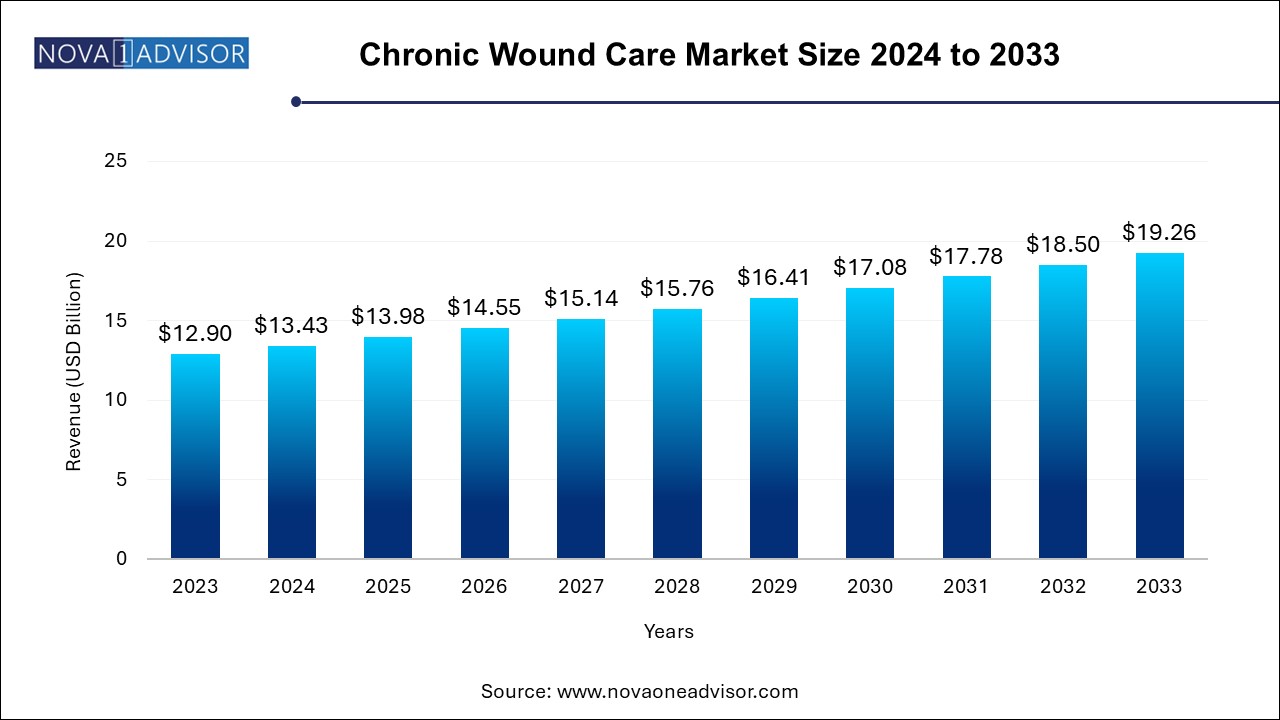
The global chronic wound care market size was exhibited at USD 12.90 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 19.26 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 4.09% during the forecast period of 2024 to 2033.Increasing incidences of sports injuries, an increasing prevalence of diabetes, and changing lifestyles are anticipated to drive market growth.
Key Takeaways:
- North America was identified as the most revenue-generating region in 2023, with over 47.0% share of the chronic wound care market.
- Advanced wound dressing dominated the product segment of the market with a market share of 35.0% in 2023
- In 2023, based on end-use, the hospital segment accounted for the maximum revenue share with around 48.00%.
- Based on application, the diabetic foot ulcers segment dominated the market in 2023 with a market share of 35.00%.
Market Overview
The chronic wound care market has evolved into a critical component of global healthcare infrastructure, responding to the increasing burden of non-healing wounds caused by diabetes, immobility, aging, vascular diseases, and trauma. Chronic wounds, defined as wounds that fail to heal through the normal repair process within 4–6 weeks, pose serious health risks including infection, amputation, and death if not managed effectively. This market encompasses a broad range of products, services, and therapeutic devices designed to accelerate wound healing, prevent complications, and improve patient quality of life.
As healthcare systems transition toward value-based models, effective wound care has gained renewed attention due to its impact on long-term patient outcomes and hospital resource utilization. A single diabetic foot ulcer, for example, can cost healthcare systems tens of thousands of dollars and lead to extended hospital stays. Chronic wounds also significantly affect elderly populations, with pressure ulcers commonly seen in long-term care facilities and immobile patients.
With the rise of advanced wound therapies such as negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT), oxygen-based treatments, and bioengineered dressings the market is now highly technology-driven and innovation-centric. The COVID-19 pandemic further emphasized the need for home-based wound care solutions, driving adoption of portable devices and digital health platforms. Governments, private insurers, and providers alike are investing in chronic wound care infrastructure as part of broader strategies to address aging populations and rising chronic disease rates.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Shift Toward Advanced and Bioactive Dressings: Hydrogel, collagen, and alginate dressings are replacing traditional gauze due to their superior healing capabilities and reduced infection risks.
-
Rise in Home-Based Wound Care and Telehealth Monitoring: Remote wound monitoring platforms are gaining traction in home healthcare settings to enable virtual consultation and reduce hospital readmissions.
-
Adoption of Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT): Portable NPWT devices are being increasingly used for diabetic foot ulcers, post-surgical wounds, and pressure injuries.
-
Integration of Artificial Intelligence in Wound Assessment: AI-driven wound analysis tools are being developed to assess healing progress and predict complications based on image recognition.
-
Increased Use of Antimicrobial and Silver-Based Products: Rising antimicrobial resistance has prompted demand for dressings with built-in infection control properties.
-
Collaborations Between MedTech and Pharma: Strategic alliances are emerging to combine wound care products with regenerative biologics and topical drug therapies.
-
Reimbursement Reforms and Bundled Payment Models: Payers are incentivizing efficient chronic wound management through bundled payments and outcome-based reimbursement structures.
Chronic Wound Care Market Report Scope
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 12.90 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 |
USD 19.26 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 |
CAGR of 4.09% |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered |
Product, Application, End-use, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Central and South America; the Middle East and Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Johnson & Johnson; Baxter International; Coloplast Corp.; 3M; Medline Industries, Inc.; ConvaTec Group PLC; Derma Sciences (Integra LifeSciences); Mölnlycke Health Care AB; Paul Hartmann AG; Smith & Nephew PLC |
Market Driver: Rising Incidence of Diabetes and Associated Complications
One of the most powerful drivers of the chronic wound care market is the growing global prevalence of diabetes, which is directly linked to an increased risk of developing diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs). According to the International Diabetes Federation, more than 530 million people globally are affected by diabetes, and roughly 15–25% of these patients will experience a foot ulcer in their lifetime. DFUs often progress to severe infections or gangrene, necessitating amputation if not treated effectively.
Chronic wound care solutions especially advanced dressings, antimicrobial therapies, and NPWT are critical in managing DFUs by promoting faster healing, reducing bacterial colonization, and improving blood flow to affected tissues. As diabetic populations expand, particularly in middle-income and aging societies, demand for cost-effective and outcome-driven wound care solutions will continue to accelerate. This driver is also fueling innovation in diagnostic platforms that enable early detection and proactive wound management strategies.
Market Restraint: High Treatment Costs and Reimbursement Challenges
Despite technological advancement, the high cost of chronic wound care and inconsistent reimbursement structures remain significant barriers to market growth, particularly in developing economies. Advanced wound care products and therapies such as collagen dressings, bioengineered skin substitutes, and NPWT devices often carry premium pricing that may be unaffordable for uninsured patients or underfunded healthcare systems.
Even in mature markets like the U.S. and Europe, coverage for some advanced wound care solutions may vary depending on the setting (hospital vs. home), provider type, and payer guidelines. Small clinics and home care providers may lack the financial resources or training to use advanced technologies, forcing them to rely on outdated and less effective treatments. Addressing these disparities requires reforming reimbursement models, increasing payer-provider collaboration, and scaling cost-effective innovations across all care levels.
Market Opportunity: Growing Demand for Wound Care in Home Healthcare Settings
The expansion of home healthcare services presents a transformative opportunity in the chronic wound care market. With a growing preference for treatment in the comfort of one’s home especially among the elderly, disabled, and post-surgical populations wound care services are shifting from hospitals to outpatient and residential settings.
Portable NPWT systems, smart dressings, telehealth wound monitoring apps, and mobile wound assessment kits are increasingly used to provide high-quality care outside of clinical environments. Home-based care is not only more convenient for patients but also reduces the risk of hospital-acquired infections and lowers the burden on acute care systems. In countries like the U.S., where hospital readmission penalties are driving efficiency mandates, home wound care solutions are becoming integral to chronic disease management plans. Companies that offer integrated, easy-to-use, and reimbursement-friendly products are likely to capture this growing market segment.
Segmental Analysis
By Product
Advanced wound dressings dominate the product segment, as they offer better outcomes in managing chronic wounds compared to traditional alternatives. Foam dressings, for example, are particularly effective in absorbing exudate and maintaining a moist environment ideal for healing venous leg ulcers and pressure ulcers. Similarly, hydrocolloid and alginate dressings conform well to wound contours and reduce the need for frequent dressing changes, enhancing patient comfort and reducing nursing time. Hospitals and specialty clinics widely use advanced dressings due to their clinical efficacy and improved healing rates.
Wound therapy devices are the fastest-growing segment, led by the increasing adoption of negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT). NPWT creates a controlled vacuum at the wound site, drawing out fluids and promoting granulation tissue formation. Portable NPWT systems are becoming standard in managing complex diabetic foot ulcers and post-operative wounds. Additionally, devices such as hyperbaric oxygen systems and electrical stimulation tools are gaining traction for treating ischemic wounds and non-healing ulcers, especially in aging and immunocompromised populations.
By Application
Diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) dominate the application segment, as they represent the most prevalent and challenging chronic wound type globally. DFUs are often complicated by peripheral neuropathy and poor circulation, making them difficult to heal without advanced care. As diabetes rates surge worldwide particularly in North America, Asia-Pacific, and the Middle East the burden of DFUs continues to grow, creating sustained demand for effective wound healing products, debridement tools, and antimicrobial dressings.
Pressure ulcers are the fastest-growing application, especially in long-term care facilities, ICUs, and among the bedridden elderly population. These ulcers arise from sustained pressure on skin and underlying tissues, and they are notoriously difficult to manage due to high infection risks and recurrence rates. Specialized foam dressings, pressure relief devices, and electric stimulation therapies are increasingly deployed in nursing homes and home healthcare environments to manage these injuries and avoid complications. The rising elderly population globally and greater emphasis on long-term care safety drive this segment’s growth.
By End-use
Hospitals dominate the end-use segment, due to their central role in acute wound management, post-surgical care, and access to specialized wound care teams. Hospitals typically use a combination of surgical wound care tools, antimicrobial dressings, NPWT devices, and adjunctive therapies to manage complex cases. They also benefit from reimbursement frameworks and bulk procurement agreements that allow for the use of premium products. Multidisciplinary wound care units are common in tertiary hospitals, enhancing their capacity to manage diabetic foot ulcers, trauma wounds, and surgical complications.
Home healthcare is the fastest-growing end-use, supported by healthcare decentralization and patient preference for at-home treatment. Portable wound care devices, disposable advanced dressings, and mobile health platforms now allow skilled nurses or caregivers to deliver effective care outside hospitals. Governments and insurers increasingly support home healthcare to reduce hospital readmissions and improve patient satisfaction. This shift is especially pronounced in North America and Western Europe, where aging demographics and payer incentives align with the trend.
Regional Analysis
North America leads the global chronic wound care market, driven by high chronic disease prevalence, robust reimbursement infrastructure, and widespread adoption of advanced technologies. The U.S. alone accounts for a significant share of the market, with over 8 million Americans living with chronic wounds. The presence of leading companies such as 3M, Smith & Nephew, and Medline alongside active government support through CMS facilitates consistent innovation and access. Additionally, the integration of EHRs, telehealth platforms, and mobile care delivery models ensures North America’s dominance.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, spurred by rapid urbanization, increasing healthcare investments, and a growing elderly population. Countries like China, India, and Japan are witnessing a sharp rise in diabetes and vascular diseases, driving demand for chronic wound care services. Regional governments are improving healthcare access, expanding insurance coverage, and funding hospital infrastructure upgrades. Moreover, local and international manufacturers are setting up production facilities and entering partnerships to meet the burgeoning demand for affordable, high-quality wound care products across the region.
Some of the prominent players in the chronic wound care market include:
- JOHNSON & JOHNSON
- BAXTER INTERNATIONAL
- Coloplast Corp.
- 3M
- Medline Industries, Inc.
- ConvaTec Group PLC
- Derma Sciences (Integra LifeSciences)
- Mölnlycke Health Care AB
- Paul Hartmann AG
- Smith & Nephew PLC
Recent Developments
-
3M Health Care (March 2025): Launched a new antimicrobial foam dressing with prolonged wear-time and integrated exudate monitoring for use in hospitals and outpatient care.
-
Smith & Nephew (February 2025): Introduced an AI-powered wound imaging system that integrates with EHRs to guide clinicians in selecting dressing types and track healing progress.
-
Mölnlycke Health Care (January 2025): Expanded its Avance Solo NPWT platform with a pediatric-friendly version targeting pressure injuries in neonatal ICUs.
-
ConvaTec Group (December 2024): Acquired a home wound care startup to strengthen its position in the rapidly expanding post-acute care market segment.
-
Medline Industries (November 2024): Announced the global rollout of a telehealth-connected dressing change protocol designed for nursing homes and home health agencies.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the global chronic wound care market.
Product
-
- Foam Dressing
- Hydrocolloid Dressing
- Film Dressing
- Alginate Dressing
- Hydrogel Dressing
- Collagen Dressing
- Other Dressing
-
- Suture & Staples
- Tissue Adhesive & Sealants
- Anti-infective Dressing
-
- Medical Tapes
- Cleansing Agents
- Others
-
- Negative Pressure Wound Therapy
- Oxygen and Hyperbaric Oxygen Equipment
- Electric Stimulation Devices
- Pressure Relief Devices
- Others
Application
- Diabetic Foot Ulcers
- Pressure Ulcers
- Venous Leg Ulcers
- Others
End-use
- Hospitals
- Specialty Clinics
- Home Healthcare
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)

