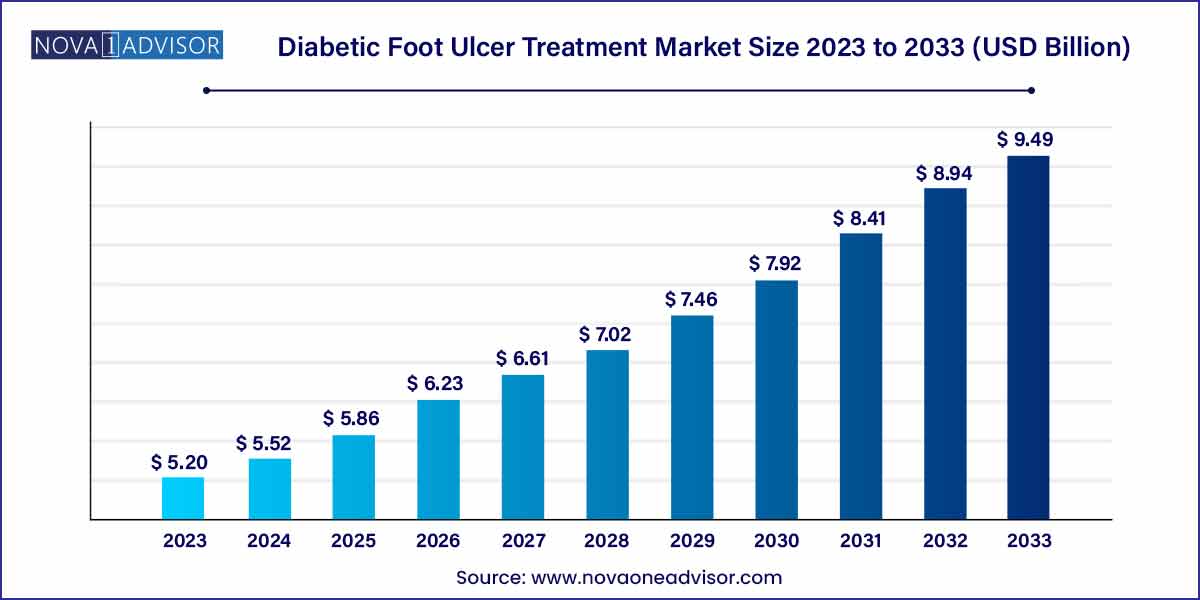
The global diabetic foot ulcer treatment market was estimated at USD 5.20 billion in 2023, is expected to surpass around USD 9.49 billion by 2033, and is poised to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.2% during the forecast period of 2024 to 2033.
Key Takeaways:
- In 2023, North America accounted for the largest share of 39.0%.
- The biologics segment dominated the industry with a share of 36.46% in 2023.
- The hospital segment accounted for a share of 34.0% in 2023.
- The homecare settings segment accounted for the largest share of 53.0% in 2023.
- The neuro-ischemic ulcers segment dominated the market in 2023 by capturing a revenue share of 53.1%.
Market Overview
The Diabetic Foot Ulcer (DFU) Treatment Market is an integral subset of the broader wound care and diabetes management industry, addressing one of the most severe complications associated with diabetes mellitus. Diabetic foot ulcers are open sores or wounds that typically develop on the bottom of the foot due to nerve damage (neuropathy), poor circulation (ischemia), or both. With the global diabetes population projected to exceed 700 million by 2045, the prevalence of DFUs continues to rise, necessitating effective treatment and prevention measures.
Globally, diabetic foot ulcers affect nearly 15% of individuals with diabetes, with a significant proportion requiring advanced intervention, including surgical procedures or limb amputation in severe cases. The management of DFUs is multifaceted, involving a combination of dressings, biologics, medications, and devices designed to accelerate healing, reduce infections, and restore tissue integrity.
As healthcare systems globally shift toward value-based care and preventative health models, there has been a growing emphasis on early diagnosis and holistic management of DFUs. This shift, combined with the increasing adoption of advanced wound care technologies and biologics, is fueling the growth of the market. Additionally, emerging economies are witnessing a surge in demand owing to increased diabetic populations, improving healthcare infrastructure, and greater awareness of diabetic complications.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Increasing Utilization of Biologic Therapies: Products like growth factors and skin substitutes are gaining traction for their regenerative properties and effectiveness in chronic wound healing.
-
Integration of AI and Telemedicine in Wound Management: Technologies that enable remote monitoring and AI-driven wound assessment tools are streamlining the management of DFUs, especially in homecare settings.
-
Rising Adoption of Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT): NPWT is being increasingly used for its ability to promote faster healing by reducing edema and increasing perfusion.
-
Personalized Wound Care Solutions: Custom-tailored treatment plans based on patient-specific factors such as wound size, depth, infection status, and comorbidities are gaining prominence.
-
Expansion in Emerging Markets: Countries like India, Brazil, and China are seeing a rapid increase in diabetic populations and an improving healthcare infrastructure, driving market demand.
-
Shifting Preference Towards Homecare: With cost pressures on hospitals and the convenience factor for patients, there is a notable shift toward managing DFUs in home settings.
-
R&D in Bioengineered Skin Substitutes: Companies are investing heavily in the development of synthetic and semi-synthetic skin grafts for superior healing outcomes.
-
Government Initiatives for Diabetes Management: Health ministries and international bodies like the WHO are launching campaigns and subsidized care programs to mitigate diabetes-related complications.
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 5.20 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 |
USD 9.49 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 |
CAGR of 6.2% |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered |
Treatment, Ulcer Type, End-Use, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Central and South America; the Middle East and Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled |
ConvaTec Group Plc; Acelity L.P. Inc.; 3M Health Care; Coloplast Corp.; Smith & Nephew Plc.; B Braun Melsungen AG; Medline Industries, LP; Molnlycke Health Care AB; Medtronic Plc. |
By Treatment Insights
Wound care dressings dominated the diabetic foot ulcer treatment market due to their widespread adoption as the first line of defense in DFU management. Among these, foam dressings and hydrocolloid dressings are extensively used for moderate to heavily exuding wounds, offering a moist environment that supports tissue regeneration. Foam dressings are particularly valued for their high absorption capacity and ability to protect from infection. Surgical and hydrogel dressings are also gaining attention, especially in hospital settings where complex ulcers require aggressive wound management.
Meanwhile, biologics are emerging as the fastest-growing treatment segment, driven by their ability to promote tissue regeneration and healing in chronic, non-healing wounds. Growth factors such as platelet-derived growth factors and skin grafts—both allografts and synthetic variants—are showing promising results in reducing healing times and improving patient outcomes. As more clinical data supports the efficacy of these therapies and regulatory pathways become clearer, biologics are expected to become a standard part of DFU treatment regimens in advanced care centers.
By End-use Insights
Hospitals dominate the end-use segment owing to their access to skilled personnel, advanced wound care infrastructure, and the ability to handle severe and complicated ulcer cases. Inpatient settings allow for better control of infection, frequent monitoring, and immediate surgical interventions if needed. Hospitals often serve as the first point of care for patients presenting with infected or gangrenous ulcers, thereby reinforcing their central role in DFU treatment.
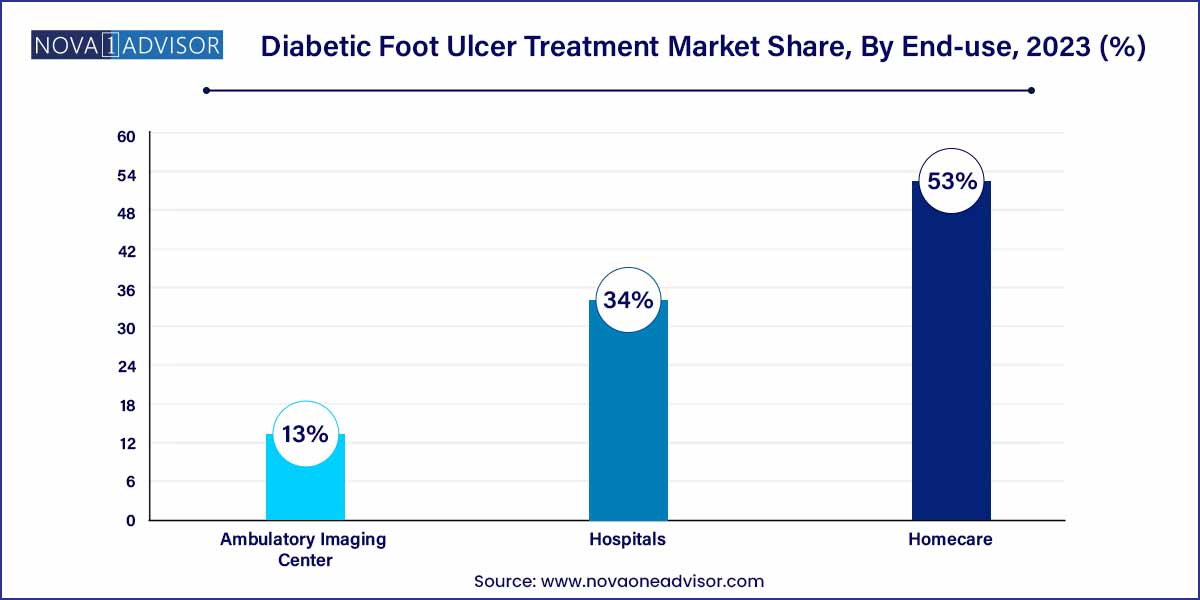
Homecare is emerging as the fastest-growing end-use segment, propelled by rising awareness, availability of portable wound care devices, and the convenience it offers to patients—particularly the elderly. The transition toward outpatient care and telehealth integration has enabled patients to manage their conditions with the support of visiting nurses and mobile health platforms. Furthermore, insurance providers are increasingly supporting homecare services to reduce hospitalization costs, further driving this trend.
By Ulcer Type Insights
Neuropathic ulcers represent the most dominant ulcer type, accounting for a large portion of DFU cases globally. These ulcers develop due to nerve damage caused by prolonged hyperglycemia and often go unnoticed due to the loss of sensation. They are commonly observed in the sole or heel area and typically require extensive debridement, regular offloading, and infection management. The dominance of this segment stems from the widespread nature of diabetic peripheral neuropathy and its close link with poor glycemic control.
Neuro-ischemic ulcers are the fastest-growing ulcer type segment, as they combine both neuropathy and ischemia, making them particularly complex and challenging to treat. These ulcers have a higher risk of infection and amputation, leading to increased demand for advanced biologics, NPWT, and surgical interventions. As clinicians move toward more nuanced categorization and personalized treatment plans, the need for robust therapies targeting neuro-ischemic ulcers is expected to surge.
By Regional Insights
North America dominates the global diabetic foot ulcer treatment market, driven by the region's high prevalence of diabetes, robust healthcare infrastructure, and early adoption of advanced wound care technologies. The United States, in particular, accounts for a significant share due to its extensive network of specialized wound care centers, widespread health insurance coverage, and presence of leading market players like Smith & Nephew, 3M, and Organogenesis. Additionally, government-backed initiatives, such as the CDC's National Diabetes Prevention Program, are raising awareness and improving care access, which positively influences treatment uptake.
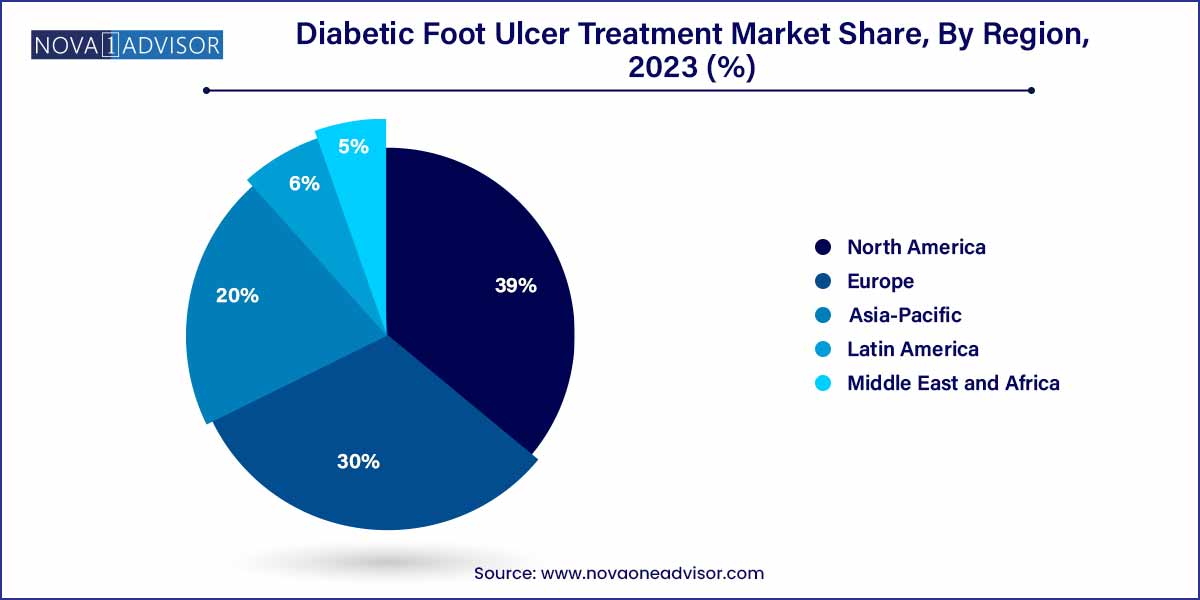
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region in the diabetic foot ulcer treatment market, owing to its rapidly expanding diabetic population and evolving healthcare ecosystems. Countries like India and China are seeing an explosion in diabetes cases, largely driven by urbanization, dietary shifts, and sedentary lifestyles. While the region still faces challenges like limited access to advanced treatments and trained wound care specialists, the tide is shifting with the entry of global players, rising healthcare expenditure, and local manufacturing of affordable wound care solutions. Governmental efforts, such as India's Ayushman Bharat health insurance scheme, are also expanding the reach of diabetic care services.
- ConvaTec, Group Plc
- Acelity L.P., Inc.
- 3M Health Care
- Coloplast Corp.
- Smith & Nephew Plc
- B Braun Melsungen AG
- Medline Industries, LP.
- Molnlycke Health Care AB
- Medtronic Plc
Recent Developments
-
March 2025: 3M Health Care Division announced the expansion of its wound care portfolio by launching a next-gen Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT) device tailored specifically for outpatient and homecare settings.
-
February 2025: Smith & Nephew partnered with an AI-driven wound assessment startup to integrate real-time image analysis into their wound care solutions, enabling faster and more accurate diagnosis of DFUs.
-
December 2024: Organogenesis Holdings Inc. published positive results from a Phase III trial for its bioengineered skin substitute, demonstrating superior healing rates in chronic DFUs compared to traditional dressings.
-
October 2024: ConvaTec Group PLC acquired a regional wound care manufacturer in Southeast Asia to strengthen its footprint in emerging markets and meet growing demand for cost-effective DFU treatment solutions.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2023 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the global diabetic foot ulcer treatment market.
Treatment
-
- Alginate Dressings
- Hydrofiber Dressings
- Foam Dressings
- Film Dressing
- Hydrocolloid Dressings
- Surgical Dressings
- Hydrogel Dressings
-
- Growth Factors
- Skin Grafts
-
- Negative Pressure Wound Therapy
- Ultrasound Therapy
- Antibiotic Medications
- Others
Ulcer Type
- Neuropathic Ulcers
- Ischemic Ulcers
- Neuro-ischemic Ulcers
End-use
- Hospitals
- Ambulatory Imaging Center
- Homecare
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)



