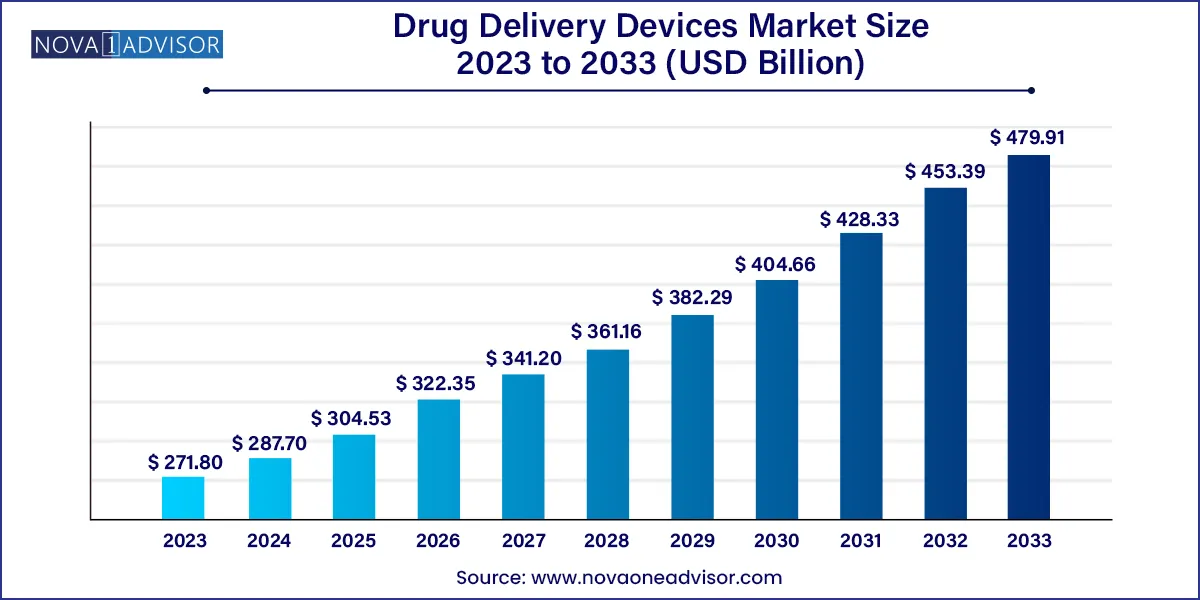
The global drug delivery devices market size was exhibited at USD 271.80 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit around USD 479.91 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 8.85% during the forecast period 2024 to 2033.
Key Takeaways:
- Based on region, North America held the largest market share of 35.0% in 2023.
- Drug delivery devices in the field of diabetes segment dominated the market in 2023 with a market share of 21.12%.
- The hospitals segment held the largest market share in 2023 with a share of 29.08%, mainly due to increasing cases of cancer, diabetes, and neurological disorders.
Market Overview
The Drug Delivery Devices Market represents a pivotal sector in the global healthcare landscape, enabling the effective, safe, and convenient administration of therapeutics. These devices are engineered to transport pharmaceutical compounds to specific body sites in controlled dosages, improving the pharmacokinetics, therapeutic efficacy, and patient adherence to medications. From insulin pens and inhalers to implantable pumps and transdermal patches, drug delivery technologies have revolutionized the way patients manage chronic and acute conditions.
This market has grown significantly due to rising prevalence of chronic diseases such as diabetes, cancer, respiratory illnesses, and cardiovascular disorders. Simultaneously, there has been a paradigm shift toward patient-centric care, emphasizing at-home drug administration and minimally invasive treatments. These changes have created robust demand for self-administration-friendly, precise, and portable drug delivery systems.
In addition, technological advancements in biosensors, nanotechnology, smart polymers, and 3D printing have led to the development of next-generation drug delivery devices, expanding the market’s potential. Coupled with regulatory support for innovation and increasing public and private investments, the drug delivery devices market is poised for significant expansion in the years ahead.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Rising Demand for Self-administration Devices: Patients increasingly prefer devices that allow independent use at home, including prefilled syringes, auto-injectors, and wearable pumps.
-
Advancements in Smart and Connected Devices: Integration of Bluetooth, IoT, and mobile apps enables dosage tracking, adherence monitoring, and remote diagnostics.
-
Growing Role of Nanotechnology: Nanoparticle-based carriers are enhancing drug solubility, targeting, and sustained release.
-
Personalized Drug Delivery: Devices are being designed to cater to patient-specific parameters such as weight, metabolism, and disease profile.
-
Expansion of Transdermal and Inhalation Routes: Non-invasive delivery methods are gaining traction, especially in pain management and respiratory care.
-
Miniaturization and Portability: Compact, wearable devices are being developed for chronic disease management like diabetes and Parkinson’s disease.
-
Regenerative Medicine and Biologics Support: Drug delivery devices are evolving to support complex biological therapies like monoclonal antibodies and cell-based products.
-
Partnerships Between Pharma and MedTech: Co-development of drug-device combination products is increasing.
-
Focus on Sustainability: Environmentally conscious designs, such as recyclable and reusable components, are emerging in device development.
-
Growth in Pediatric and Geriatric Applications: Devices tailored for vulnerable populations are being launched, addressing usability and compliance concerns.
Drug Delivery Devices Market Report Scope
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2024 |
USD 287.70 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 |
USD 479.91 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 |
CAGR of 8.85% |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Forecast Period |
2024-2033 |
| Segments Covered |
Application, Route Of Administration, End-use, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Central and South America; the Middle East and Africa |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Pfizer, Inc.; Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc.; F. Hoffmann-La Roche, Ltd.; Novartis AG; BD; Bayer AG; uniQure N.V.; Sibiono GeneTech Co. Ltd. |
Key Market Driver: Rising Burden of Chronic Diseases Globally
The most prominent driver of the drug delivery devices market is the global surge in chronic disease prevalence, especially diabetes, cancer, respiratory conditions, and cardiovascular diseases. These diseases require long-term, consistent therapy, often necessitating precise and frequent drug administration.
For example, over 537 million adults globally live with diabetes, according to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), many of whom rely on insulin delivery via pens, pumps, or injectors. Similarly, in oncology, controlled delivery of chemotherapeutics via infusion pumps or implantable devices minimizes systemic toxicity while enhancing tumor targeting.
The increasing incidence of lifestyle-related conditions, aging populations, and the need for personalized medicine all demand innovative delivery systems that improve patient adherence, therapeutic outcomes, and quality of life. As treatment regimens become more complex, especially with biologics and gene therapies, the market is expanding to meet sophisticated delivery needs across inpatient, outpatient, and home care settings.
Key Market Restraint: Stringent Regulatory and Compliance Hurdles
A critical challenge faced by the drug delivery devices market is stringent regulatory scrutiny and lengthy approval timelines. These devices must not only meet safety and efficacy standards but also demonstrate consistent performance in real-world settings. The regulatory framework includes evaluation of biocompatibility, sterility, mechanical integrity, and usability—criteria that vary between regions like the U.S. (FDA), Europe (EMA), and Japan (PMDA).
Combination products (drug + device) face added complexities, as both drug formulation and device mechanisms are assessed, often requiring dual regulatory pathways. Any changes to device design post-approval may trigger re-validation, increasing costs and development time. Furthermore, the risk of product recalls, liability claims, and adverse event reporting has led to cautious adoption, especially for emerging technologies.
These barriers can slow innovation, limit market access, and disproportionately affect small-to-medium enterprises (SMEs) with limited regulatory resources.
Key Market Opportunity: Growth in Smart and Wearable Drug Delivery Devices
A major opportunity lies in the development of smart, wearable drug delivery devices that combine sensors, wireless communication, and artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance adherence and enable real-time monitoring. Devices such as wearable insulin patches, connected inhalers, and implantable infusion pumps are transforming disease management, especially for diabetes, asthma, and oncology.
These devices not only simplify administration but also collect and transmit data to healthcare providers, enabling personalized treatment plans and early intervention. For instance, wearable injectors are being used to deliver large-volume biologics for conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn’s disease.
Startups and established medtech firms are investing heavily in AI-enabled wearable injectors, while pharmaceutical companies are collaborating to co-develop integrated therapeutic platforms. With the rise of digital health ecosystems and telemedicine, these devices are expected to become central to remote patient management and outcome-based reimbursement models.
Segments Insights:
Route of Administration Insights
Injectable drug delivery devices dominated the market in 2024. Injectable devices, including syringes, auto-injectors, insulin pens, and infusion pumps, are preferred for rapid onset and precise dosage delivery. Biologics, which often cannot be administered orally, rely heavily on subcutaneous or intravenous delivery. Auto-injectors, in particular, are gaining popularity due to their ease of use in emergency care (e.g., epinephrine for anaphylaxis) and chronic care (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis therapies).
Transdermal delivery is emerging as the fastest-growing segment. Non-invasive patches that deliver drugs through the skin are gaining traction in pain management, hormone replacement, and neurological therapies. With advancements in micro-needles, iontophoresis, and bioresponsive polymers, transdermal systems now allow more drugs—including vaccines and biologics—to be delivered painlessly and effectively. Their potential for self-administration, sustained release, and minimal systemic side effects positions them for accelerated growth.
Application Insights
Oncology applications led the market in 2024. The complexity and toxicity of cancer treatments necessitate advanced drug delivery devices that offer controlled dosing, targeted therapy, and reduced exposure to healthcare workers. Implantable pumps, port catheters, and infusion systems are extensively used in chemotherapy. As immunotherapies and ADCs (antibody-drug conjugates) rise, new delivery technologies are being developed to ensure precise targeting and patient comfort.
Diabetes is the fastest-growing application segment. The relentless rise in diabetes prevalence, particularly in Asia and Africa, is driving adoption of insulin pens, wearable glucose monitors, and closed-loop insulin pumps. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) systems, smart insulin patches, and hybrid closed-loop systems (artificial pancreas) are revolutionizing diabetes care. Personalized insulin delivery and integration with mobile apps are enhancing compliance and outcomes.
End-use Insights
Hospitals remained the largest end-user segment in 2024. Hospitals perform high-volume drug administration for both acute and chronic conditions. Devices like infusion pumps, IV catheters, and nebulizers are widely used in inpatient care. The need for sterile environments, high-throughput treatment, and clinical supervision supports sustained demand in hospital settings.
Home care settings are the fastest-growing end-use segment. Increasing patient preference for at-home treatment especially for chronic diseases has led to growing adoption of user-friendly delivery devices. Portable nebulizers, insulin pens, wearable injectors, and prefilled syringes empower patients and reduce the burden on healthcare facilities. Health systems are encouraging home-based care through remote monitoring technologies and reimbursement support, further accelerating this trend.
Regional Insights
North America held the largest share of the drug delivery devices market in 2024. The region benefits from advanced healthcare infrastructure, robust R&D investment, and the presence of major pharmaceutical and medtech firms. The U.S. leads in the adoption of biologics, smart injectors, and at-home administration solutions. Regulatory incentives like the FDA’s fast-track programs and CMS reimbursement pathways support innovation and market expansion.
The strong demand for chronic disease management tools and widespread awareness about personalized medicine further fuel regional dominance. Additionally, tech-savvy consumers in the U.S. are more likely to adopt wearable and connected delivery systems, creating favorable conditions for rapid product uptake.
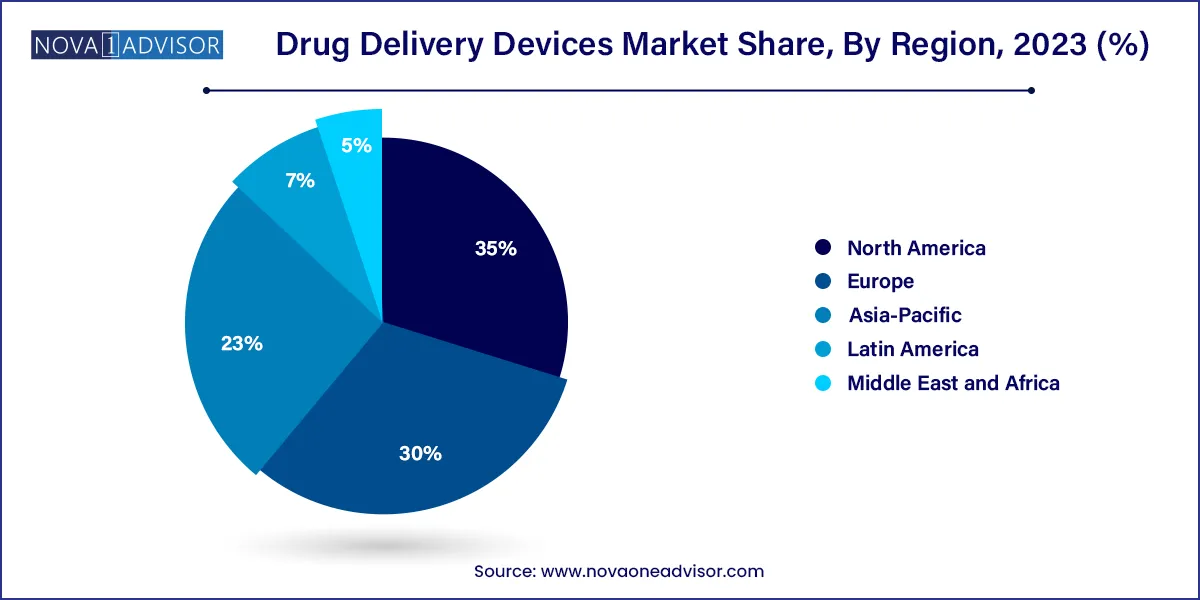
Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing market for drug delivery devices, driven by increasing healthcare access, rising chronic disease incidence, and economic development. Countries like China and India are witnessing surges in diabetes, asthma, and cancer cases, necessitating scalable and affordable drug administration technologies.
Government initiatives to expand universal healthcare, local manufacturing capabilities, and digital health infrastructure are improving access to advanced delivery devices. Partnerships between global medtech firms and regional distributors are also accelerating the availability of cutting-edge solutions in this region. Japan and South Korea, known for tech innovation, are rapidly adopting smart injectors and connected respiratory devices.
Some of the prominent players in the Drug delivery devices market include:
- Pfizer, Inc.
- Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc.
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche, Ltd.
- Novartis AG
- BD
- Bayer AG
- uniQure N.V.
- Sibiono GeneTech Co. Ltd.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the global drug delivery devices market.
Route of Administration
- Oral
- Inhalation
- Transdermal
- Injectable
- Ocular
- Nasal
- Topical
- Others
Application
- Oncology
- Infectious Diseases
- Respiratory Diseases
- Diabetes
- Cardiovascular Diseases
- Autoimmune Diseases
- Central Nervous System Disorders
- Others
End-use
- Hospitals
- Diagnostic Centers
- Ambulatory Surgery Centers/Clinics
- Home Care Settings
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)


