Generic Injectable Market Size and Forecast 2025 to 2034
According to Nova one advisor, the global Generic Injectable Market Size was valued at USD 117.25 billion in 2024 and is predicted to be worth USD 442.36 billion by 2034, with a CAGR of 14.2% from 2025 to 2034.
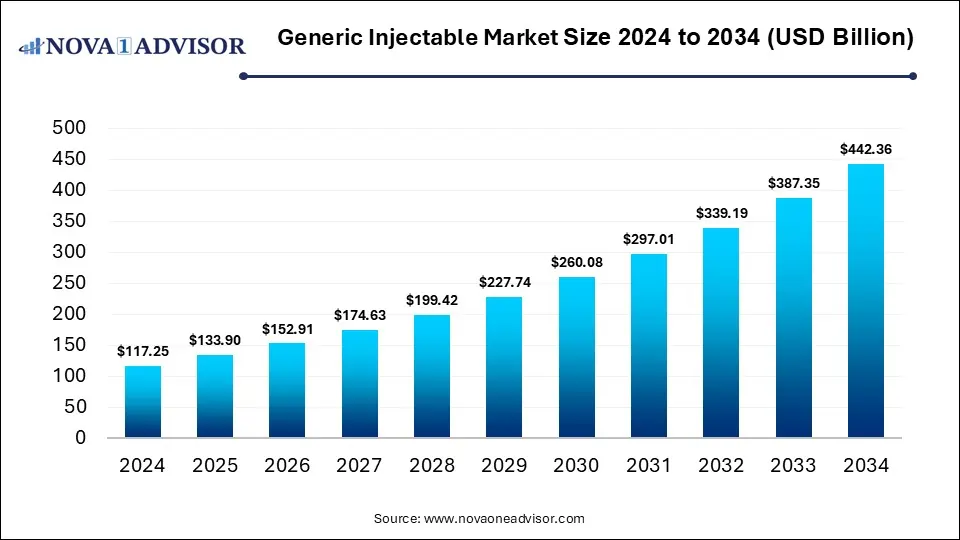
Key Takeaway:
- North America dominated the global generic injectable market with the largest market share of 46% in 2024.
- By molecule type, the large molecule segment has held a major market share of 69% in 2024.
- By molecule type, the small molecule segment hold a second largest position with a 31% of market share in 2024.
Market Overview
The global generic injectable market has emerged as one of the most vital segments in the pharmaceutical industry, bridging the gap between accessibility, affordability, and advanced treatment options. Injectable formulations are critical in modern medicine due to their fast action, high bioavailability, and ability to deliver therapies directly into systemic circulation. With patents expiring for several blockbuster biologics and chemical drugs, the market has seen a surge in the entry of generic injectable manufacturers who are offering cost-effective alternatives to branded medicines.
The increasing prevalence of chronic diseases such as cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular disorders, and infectious diseases has further accelerated the need for reliable injectable drugs. In addition, the global healthcare ecosystem has shifted toward value-based care models, where reducing costs without compromising quality is a priority. This shift positions generic injectables as a strategic solution, especially for emerging economies where healthcare budgets are constrained.
Furthermore, the COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the indispensable role of injectables, particularly in the form of vaccines, monoclonal antibodies, and supportive therapies. Manufacturers have invested in expanding production facilities, scaling supply chains, and leveraging partnerships to address growing global demand. The expansion of biosimilars and biologic-based generics has further diversified the product portfolio, transforming the competitive dynamics of the market.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Rising Adoption of Biosimilars: With biologics accounting for significant pharmaceutical spending, biosimilars are becoming an essential part of the generic injectable landscape.
-
Strategic Collaborations and Mergers: Companies are engaging in partnerships and acquisitions to strengthen their production and regulatory approval capacities.
-
Growth of Contract Manufacturing Organizations (CMOs): Pharmaceutical firms increasingly outsource production to CMOs to reduce costs and speed up time-to-market.
-
Regulatory Support for Generics: Governments across the U.S., Europe, and Asia are streamlining approval pathways for generic injectables.
-
Technological Advancements in Drug Delivery: Novel delivery mechanisms such as pre-filled syringes and auto-injectors are gaining traction.
-
Cost-Containment Initiatives by Governments and Insurers: Policies aimed at lowering healthcare expenditure are encouraging the use of generic injectables.
-
Focus on Cold-Chain Infrastructure: With biologics and vaccines requiring temperature-sensitive logistics, investment in cold-chain capabilities has grown.
Report Scope of the Generic Injectable Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 133.90 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 |
USD 442.36 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2025 to 2034 |
CAGR of 14.2% |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2034 |
| Segments Covered |
Product Type, Molecular Type, Application, Administration, and Distribution Channel |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA |
Key Market Dynamics
Driver – Rising Prevalence of Chronic Diseases
The escalating burden of chronic diseases is a primary driver for the generic injectable market. For instance, cancer cases are projected to increase substantially, with the WHO estimating nearly 30 million new cancer cases globally by 2040. Oncology treatments, which often rely on complex injectables such as chemotherapy agents and monoclonal antibodies, are witnessing growing demand. Since branded therapies are prohibitively expensive for many patients, generic injectables provide a critical, affordable alternative. Similarly, the global diabetes epidemic, with more than 500 million people affected, is pushing the demand for insulin injectables. The affordability offered by generics ensures wider patient reach, better adherence to treatment, and reduced strain on healthcare budgets.
Restraint – Stringent Manufacturing and Quality Standards
One of the significant restraints is the complexity involved in manufacturing injectable drugs. Unlike oral generics, injectables demand sterile production environments, advanced equipment, and compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). Any contamination can lead to severe patient outcomes, triggering recalls and regulatory penalties. For instance, the U.S. FDA has issued multiple warning letters to manufacturers over sterility lapses in injectable production. The high cost of maintaining sterile facilities, coupled with complex regulatory inspections, often limits new entrants and slows down approvals. This creates barriers to scaling up production in line with market demand.
Opportunity – Expansion of Biosimilar Injectables
The patent expirations of blockbuster biologics present a massive growth opportunity. Biosimilars—biologic products highly similar to approved branded drugs—are opening new revenue streams in oncology, autoimmune disorders, and cardiovascular treatments. For example, the patent expiry of trastuzumab (Herceptin) and adalimumab (Humira) has triggered a wave of biosimilar approvals worldwide. Generic injectable manufacturers are investing heavily in R&D and regulatory pathways to capture this high-value opportunity. The biosimilar segment not only drives cost savings but also enables patients to access life-saving biologic therapies at lower prices, creating a win-win for payers, providers, and patients.
Segmental Analysis
By Product Type
Chemotherapy Agents Dominated the Market
Chemotherapy agents remain the largest segment due to the global surge in cancer incidence and the widespread use of generics to reduce treatment costs. Hospitals and oncology centers increasingly prescribe generic chemotherapy formulations like doxorubicin and cisplatin to ensure accessibility. The affordability of these agents plays a pivotal role in enabling large patient populations, especially in emerging economies, to receive timely treatments. Furthermore, government initiatives that support cancer care funding indirectly encourage the adoption of generic chemotherapy injectables.
Vaccines and Monoclonal Antibodies are the Fastest Growing Segments
Vaccines, propelled by global immunization drives and the COVID-19 pandemic, have registered exponential growth. Generic versions of traditional vaccines, alongside emerging biosimilar-based monoclonal antibodies, are becoming central to market expansion. For example, biosimilar monoclonal antibodies targeting rheumatoid arthritis and cancer are gaining acceptance in Europe and Asia. These products are expected to shape the future landscape of generic injectables by addressing high-cost therapeutic areas with affordable alternatives.
By Molecular Type
Small Molecules Dominated the Market
Small molecule injectables, including antibiotics, analgesics, and cardiovascular drugs, have historically led the market due to their simpler manufacturing processes and established regulatory frameworks. Generics like ceftriaxone and morphine are widely used in hospitals worldwide, ensuring steady demand. Their stability and cost-effectiveness make them highly competitive compared to biologic-based injectables.
Large Molecules are the Fastest Growing Segment
Large molecules, or biologics, are witnessing rapid growth, primarily driven by biosimilars. Biologics such as insulin, immunoglobulins, and monoclonal antibodies have transformed chronic disease management. With patent cliffs for biologics like insulin glargine and etanercept, generic manufacturers are capitalizing on opportunities to launch affordable versions. Their adoption is growing rapidly in Europe and Asia-Pacific due to strong biosimilar-friendly regulations.
Generic Injectable Market Size By Molecular Type, 2024 to 2034 (USD Billion)
| Year |
2024 |
2025 |
2026 |
2027 |
2028 |
2029 |
2030 |
2031 |
2032 |
2033 |
2034 |
| Small Molecule |
64.49 |
73.24 |
83.18 |
94.47 |
107.29 |
121.84 |
138.36 |
157.12 |
178.41 |
202.59 |
230.03 |
| Large Molecule |
52.76 |
60.66 |
69.73 |
80.15 |
92.13 |
105.90 |
121.72 |
139.89 |
160.78 |
184.77 |
212.33 |
By Application
Oncology Dominated the Market
Oncology applications account for the largest revenue share due to the heavy reliance on injectable therapies such as chemotherapy agents, monoclonal antibodies, and supportive drugs. For instance, trastuzumab biosimilars are being used extensively in breast cancer care, significantly lowering treatment costs. With cancer prevalence continuing to rise, the demand for oncology-focused injectables is set to remain strong.
Diabetes and Infectious Diseases are the Fastest Growing Segments
Diabetes applications, particularly insulin injectables, are expanding rapidly due to the global diabetes epidemic. Biosimilar insulins are enabling wider adoption, especially in cost-sensitive markets. Meanwhile, infectious diseases like tuberculosis and COVID-19 have increased demand for injectable antibiotics and vaccines. In Africa and Asia-Pacific, programs run by WHO and UNICEF are driving access to these generics.
By Administration
Intravenous (IV) Dominated the Market
IV injectables remain the dominant route due to their widespread use in hospitals for acute conditions, oncology, and emergencies. Drugs like IV antibiotics, chemotherapy agents, and pain management injectables rely heavily on this route. The immediate bioavailability of IV injectables makes them indispensable in critical care settings.
Subcutaneous (SC) is the Fastest Growing Segment
SC administration is gaining ground due to the rise of biologics like insulin and monoclonal antibodies. Patients prefer SC injectables for their ease of self-administration, particularly in chronic conditions such as diabetes and autoimmune disorders. The growing use of pre-filled syringes and auto-injectors is also boosting adoption in this segment.
By Distribution Channel
Hospital Pharmacies Dominated the Market
Hospital pharmacies lead the distribution channel due to the extensive use of injectables in inpatient care, surgeries, and oncology treatments. Hospitals procure in bulk, ensuring consistent supply and affordability. The role of hospitals as primary centers for critical care ensures the continued dominance of this channel.
Online Pharmacies are the Fastest Growing Segment
The rise of digital healthcare platforms has fueled the growth of online pharmacies. Patients increasingly order insulin, vaccines, and chronic disease injectables online for convenience and competitive pricing. This trend accelerated during the pandemic and is expected to grow further with digital health adoption.
Regional Analysis
North America Dominated the Market
North America, led by the U.S., dominates the generic injectable market due to its robust healthcare infrastructure, strong regulatory framework, and high prevalence of chronic diseases. The FDA’s supportive initiatives for generic drug approvals have accelerated product launches. For instance, in 2023, the FDA approved multiple biosimilar injectables targeting oncology and autoimmune diseases. Large healthcare spending and insurance coverage further reinforce the dominance of North America.
Asia-Pacific is the Fastest Growing Region
Asia-Pacific is experiencing the fastest growth, driven by expanding healthcare access, growing middle-class populations, and government-backed initiatives for generic drug adoption. Countries like India and China serve as global manufacturing hubs for generic injectables, supported by cost advantages and skilled workforce availability. Additionally, rising prevalence of diabetes and infectious diseases in the region is fueling demand. Government programs, such as India’s Jan Aushadhi scheme for affordable generics, are accelerating adoption rates.
Generic Injectable Market Size By Geography, 2024 to 2034 (USD Billion)
| Year |
2024 |
2025 |
2026 |
2027 |
2028 |
2029 |
2030 |
2031 |
2032 |
2033 |
2034 |
| North America |
41.04 |
46.60 |
52.91 |
60.07 |
68.20 |
77.43 |
87.91 |
99.80 |
113.29 |
128.60 |
145.98 |
| Europe |
31.66 |
36.02 |
40.98 |
46.63 |
53.05 |
60.35 |
68.66 |
78.11 |
88.87 |
101.10 |
115.01 |
| Asia-Pacific |
29.31 |
33.88 |
39.15 |
45.23 |
52.25 |
60.35 |
69.70 |
80.49 |
92.94 |
107.30 |
123.86 |
| Latin America |
8.21 |
9.37 |
10.70 |
12.22 |
13.96 |
15.94 |
18.21 |
20.79 |
23.74 |
27.11 |
30.97 |
| Middle East & Africa (MEA) |
7.04 |
8.03 |
9.17 |
10.48 |
11.97 |
13.66 |
15.60 |
17.82 |
20.35 |
23.24 |
26.54 |
Recent Developments
-
June 2025 – Teva Pharmaceuticals expanded its biosimilar pipeline by launching a trastuzumab biosimilar in European markets.
-
May 2025 – Pfizer announced an expansion of its sterile injectable manufacturing facility in Kalamazoo, U.S., to strengthen supply chain resilience.
-
April 2025 – Viatris and Biocon Biologics gained FDA approval for a biosimilar insulin glargine, expanding options for diabetes patients.
-
February 2025 – Sandoz completed its acquisition of a biosimilar portfolio from Fresenius Kabi to strengthen its oncology injectable offerings.
-
January 2025 – Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories launched a generic version of doxorubicin hydrochloride injection in the U.S., broadening its oncology product line.
List of Top Companies
-
Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
-
Pfizer Inc.
-
Viatris Inc. (formerly Mylan)
-
Novartis AG (Sandoz Division)
-
Fresenius Kabi AG
-
Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories Ltd.
-
Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
-
Lupin Limited
-
Aurobindo Pharma Ltd.
-
Hikma Pharmaceuticals PLC
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at global, regional, and country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the global Generic Injectable market.
By Product Type
- Chemotherapy agents
- Small molecule antibiotics
- Vaccines
- Peptide antibiotics
- Blood factors
- Peptide hormone
- Insulin
- Cytokines
- Immunoglobin
- Monoclonal Antibodies
By Molecular Type
- Small Molecule
- Large Molecule
By Application
- Oncology
- Diabetes
- Infectious Diseases
- Blood Disorders
- Musculoskeletal Disorders
- Hormonal Disorders
- Pain Management
- CNS Diseases
- Cardiovascular Diseases
By Administration
- Intravenous (IV)
- Intramuscular (IM)
- Subcutaneous (SC)
By Distribution Channel
- Hospital pharmacy
- Retail pharmacy
- Drug stores
- Online pharmacy
By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa (MEA)

