Genomics Market Size and Growth 2026 to 2035
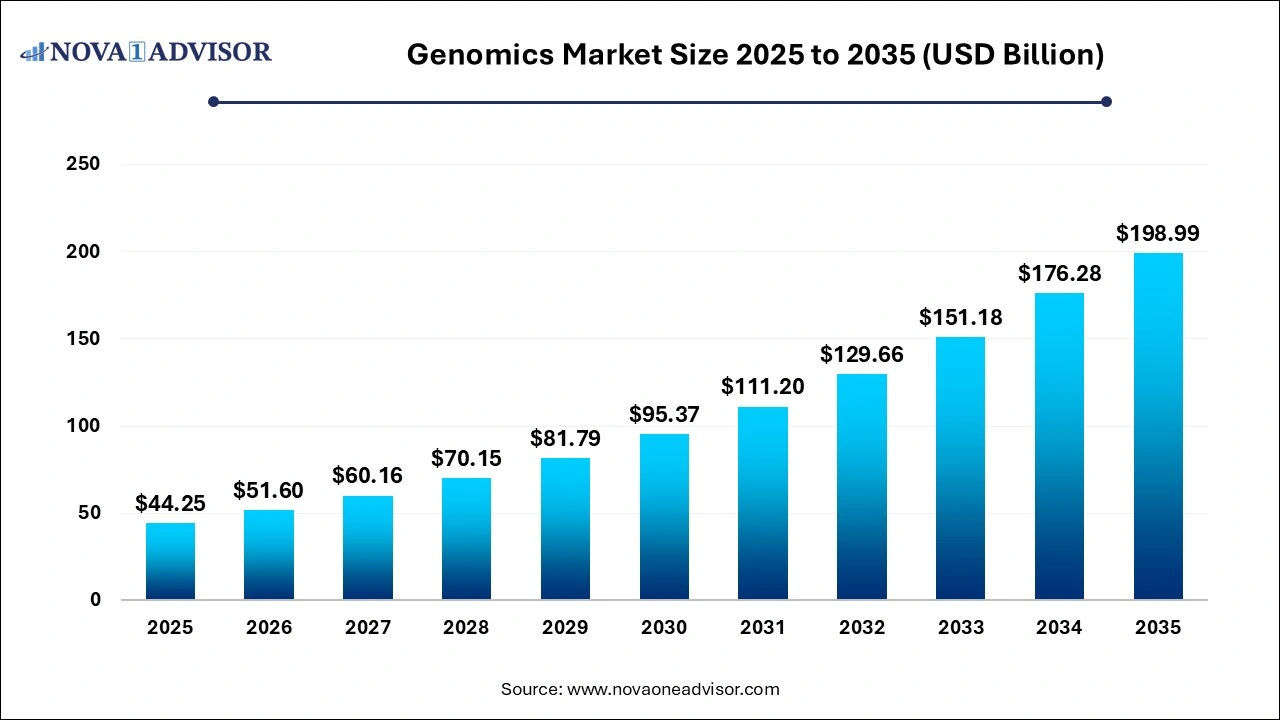
The genomics market size was exhibited at USD 44.25 billion in 2025 and is projected to hit around USD 198.99 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 16.22% during the forecast period 2026 to 2035.
Genomics Market Key Takeaways:
- The functional genomics segment dominated the overall market with the largest revenue share of 32.1% in 2025.
- The product segment dominated the market in 2025.
- The service segment is expected to register a steady CAGR by 2034.
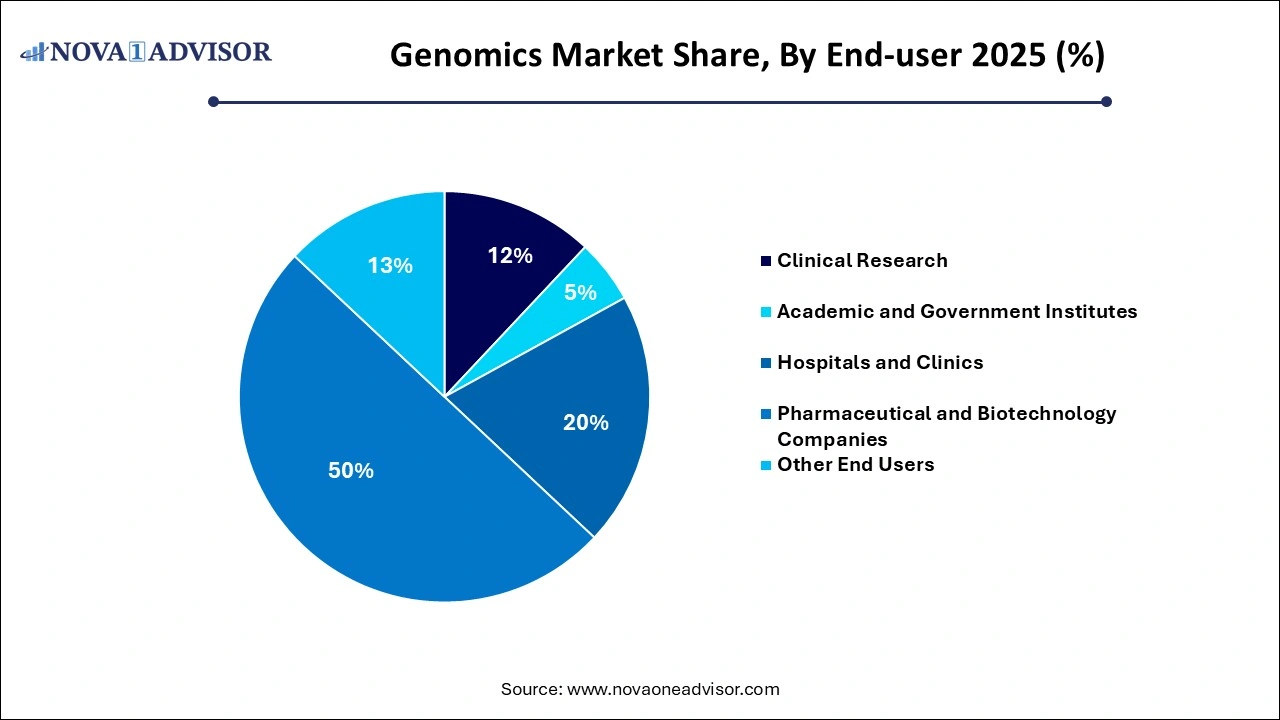
- The pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies segment led the market share 50% in 2025.
- The hospital and clinic segment is estimated to grow at a substantial pace during the forecast period.
- North America accounted for the largest market share of 43.0% in 2025.
- Asia Pacific is estimated to be the fastest-growing segment over the forecast period
- Indian market is anticipated to grow at significant growth rate over the forecast period.
Genomics Market Overview
The genomics market has grown into a transformative force in the life sciences industry, offering unprecedented insights into the structure, function, evolution, and mapping of genomes. At its core, genomics is not merely about reading DNA but interpreting complex biological systems to influence diagnostics, therapeutics, disease prevention, and personalized medicine. With the completion of the Human Genome Project in the early 2000s, the market laid its foundation for exponential growth. Today, genomics serves as a backbone for cutting-edge developments in oncology, rare genetic disorders, infectious diseases, agricultural biotechnology, and even gene-editing technologies like CRISPR.
Driven by the convergence of high-throughput sequencing technologies, bioinformatics, and precision medicine, genomics is reshaping the way we understand and treat diseases. The shift from “one-size-fits-all” healthcare to targeted, patient-specific interventions is made possible by integrating genomic insights into clinical decision-making. Furthermore, rapid reductions in sequencing costs, increasing consumer access to genomic services, and government initiatives to map population-level genomes are fueling industry momentum.
From startups offering direct-to-consumer (DTC) genetic testing to pharmaceutical giants using genomic data for drug development and diagnostics firms offering NGS-based panels, stakeholders across the ecosystem are heavily investing in genomics. In this dynamic and interdisciplinary market, data science, biology, and medicine are intersecting in ways that promise to reshape 21st-century healthcare.
Major Trends in the Genomics Market
-
Rise of Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS): The widespread adoption of NGS technologies for high-throughput, rapid, and cost-effective sequencing continues to dominate genomics workflows.
-
Integration of Artificial Intelligence in Genomic Analysis: AI and machine learning are being employed to analyze complex genomic datasets, aiding in disease gene identification, biomarker discovery, and drug response prediction.
-
Growth of Multi-omics Approaches: Combining genomics with proteomics, transcriptomics, and metabolomics is offering holistic biological insights, particularly in cancer research and personalized medicine.
-
Expanding Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Genetic Testing: Companies like 23andMe and AncestryDNA are tapping into a growing consumer base interested in ancestry, health predisposition, and lifestyle genetics.
-
Global Government-led Genomic Initiatives: Programs like the All of Us (U.S.), Genomics England, and GenomeAsia 100K are investing heavily in mapping genetic diversity to support population health research.
-
Gene Editing and CRISPR Breakthroughs: The application of CRISPR-Cas9 for targeted genome editing is driving new therapeutic strategies and ethical debates alike.
-
Clinical Adoption of Companion Diagnostics: The use of genomics to identify biomarkers and pair therapies with specific genetic profiles is transforming clinical oncology and rare disease treatment.
Report Scope of Genomics Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2026 |
USD 51.6 Billion |
| Market Size by 2035 |
USD 198.99 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2026 to 2035 |
CAGR of 16.22% |
| Base Year |
2025 |
| Forecast Period |
2026-2035 |
| Segments Covered |
Application, Technology, Deliverables, End-use, Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (USD Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Agilent Technologies; Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.; BGI Genomics; Color Genomics, Inc.; Danaher Corporation; Eppendorf AG; Eurofins Scientific; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.; GE Healthcare; Illumina Inc.; Myriad Genetics, Inc.; Oxford Nanopore Technologies; Pacific Biosciences of California, Inc.; QIAGEN N.V.; Quest Diagnostics Incorporated; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.; 23andMe, Inc. |
Genomics Market Segment Insights
By Application Insights
Functional genomics dominated the genomics market in 2025, primarily due to its foundational role in understanding gene functions, interactions, and expression patterns. Techniques such as RNA interference (RNAi), real-time PCR, and microarray analysis are widely used across oncology, neurology, and immunology research. Functional genomics enables researchers to identify the roles of specific genes in cellular pathways, thereby guiding drug discovery and genetic modification approaches. Tools like CRISPR and siRNA-based gene silencing have expanded the applicability of functional genomics, especially in disease modeling and therapeutic target validation. As a result, academic and commercial research institutions heavily invest in this segment.
Biomarker discovery is projected to be the fastest-growing application, driven by its critical role in clinical diagnostics, drug development, and personalized treatment. Techniques such as DNA sequencing, mass spectrometry, and bioinformatics-based statistical analysis are used to identify gene expressions or mutations linked to specific disease phenotypes. For example, the identification of ALK, ROS1, and EGFR mutations in lung cancer patients enables oncologists to choose appropriate targeted therapies. As pharmaceutical companies adopt a biomarker-first approach in clinical trials, demand for genomics-based biomarker discovery tools is expected to surge across oncology, cardiology, and rare diseases.
By Deliverables Insights
Products (instruments, systems, consumables, and reagents) represented the largest revenue share in 2025, as every genomic application relies on reliable hardware and standardized reagents. Sequencing platforms, PCR machines, centrifuges, and software interfaces are essential for laboratory workflows. Consumables such as sequencing kits, primers, enzymes, and chips are high-margin, recurring revenue drivers for manufacturers. Companies like Illumina, Thermo Fisher Scientific, and QIAGEN generate a substantial portion of their income from product sales.
Services, particularly NGS-based and computational genomics services, are expanding rapidly, due to increasing outsourcing of complex genomic tasks. Many smaller labs and clinical settings lack the infrastructure for advanced bioinformatics and data interpretation. Service providers fill this gap by offering variant annotation, transcriptome analysis, and data visualization tools. Additionally, contract research organizations (CROs) and diagnostic labs are leveraging cloud-based platforms to provide scalable, remote genomics services for clinical and research purposes.
By End-user Insights
Academic and government institutes were the largest end-users of genomics technologies, given their central role in conducting fundamental genomic research, disease gene mapping, and population-scale projects. Initiatives such as the UK Biobank, 1000 Genomes Project, and India’s GenomeIndia initiative underscore the importance of public-sector genomics research. These institutions are key customers for sequencing instruments, bioinformatics software, and gene editing tools, with funding from national and international grants.
Hospitals and clinics are the fastest-growing end-use segment, as genomics becomes a clinical mainstay. Applications like hereditary cancer screening, pharmacogenomics, and rapid sequencing in neonatal intensive care units (NICUs) are driving adoption. For instance, rapid whole-genome sequencing is now used to diagnose rare genetic conditions in critically ill infants. Oncology centers are also integrating genomic panels for stratifying patients into clinical trials or guiding immunotherapy. This clinical shift is accelerating the integration of genomics into routine healthcare delivery.
U.S. genomics market Size and Growth 2026 to 2035
The U.S genomics market size is evaluated at USD 12.2 billion in 2025 and is projected to be worth around USD 57.2 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 15.0% from 2026 to 2035.
.webp)
North America dominated the global genomics market in 2025, attributed to its robust research infrastructure, high healthcare expenditure, and early adoption of advanced technologies. The U.S. is home to major genomic technology providers, including Illumina, Thermo Fisher, and Pacific Biosciences. Federal initiatives like the All of Us Research Program and strong collaboration between academia and industry have fostered innovation. The region also has a favorable reimbursement landscape for genetic testing, facilitating clinical adoption. Additionally, widespread integration of genomics into drug development pipelines by biopharma companies further strengthens North America’s leadership in this domain.
Asia-Pacific is projected to be the fastest-growing region, driven by government investments in genomics, improving healthcare access, and a rising burden of chronic diseases. China’s Precision Medicine Initiative, India’s GenomeIndia project, and Japan’s investments in regenerative medicine are creating significant momentum. Local companies such as BGI Group (China), MedGenome (India), and Macrogen (South Korea) are expanding their footprints through affordable genomic services. Moreover, APAC’s genetic diversity makes it a valuable region for population-scale studies. As regulatory frameworks mature and local sequencing infrastructure strengthens, Asia-Pacific will play a key role in the future of global genomics research.
Some of the prominent players in the genomics market include:
Genomics Market Recent Development
-
March 2025 – Illumina announced the launch of NovaSeq X, a next-gen platform designed to halve the cost of whole-genome sequencing and triple data throughput, targeting large-scale genomics programs globally.
-
February 2025 – Thermo Fisher Scientific acquired Olink Proteomics, enhancing its multi-omics capabilities and expanding its biomarker discovery portfolio for clinical applications.
-
January 2025 – BGI Genomics launched a portable NGS system, MGISP-NEO, for rapid pathogen detection in rural or mobile settings, targeting developing healthcare markets.
-
December 2024 – 23andMe entered into a strategic collaboration with GSK, focusing on pharmacogenomic research to co-develop new drug targets based on genomic datasets.
-
November 2024 – Genomics England announced the sequencing of 1 million genomes, marking a major milestone in the UK’s population health and rare disease research efforts.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2026 to 20354. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the genomics market
By Application & Technology
-
- Transfection
- Real-Time PCR
- RNA Interference
- Mutational Analysis
- SNP Analysis
- Microarray Analysis
-
- Bisulfite Sequencing
- Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP & ChIP-Seq)
- Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP)
- High-Resolution Melt (HRM)
- Chromatin Accessibility Assays
- Microarray Analysis
-
- Bead-Based Analysis
- Microarray Analysis
- Real-time PCR
- Proteomics Tools (2-D PAGE; yeast 2-hybrid studies)
-
- Mass Spectrometry
- Real-time PCR
- Microarray Analysis
- Statistical Analysis
- Bioinformatics
- DNA Sequencing
By Technology
- Sequencing
- PCR
- Flow Cytometry
- Microarrays
- Other technologies
By Deliverables
-
- Instruments/Systems/Software
- Consumables & Reagents
-
- NGS-based Services
- Core Genomics Services
- Biomarker Translation Services
- Computational Services
- Others
By End-use
- Clinical Research
- Academic & Government Institutes
- Hospitals & Clinics
- Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies
- Other End Users
By Regional
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa (MEA)


.webp)