Cord Blood Banking Services Market Size and Growth
The cord blood banking services market size was exhibited at USD 27.15 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 55.96 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 7.5% during the forecast period 2024 to 2034.
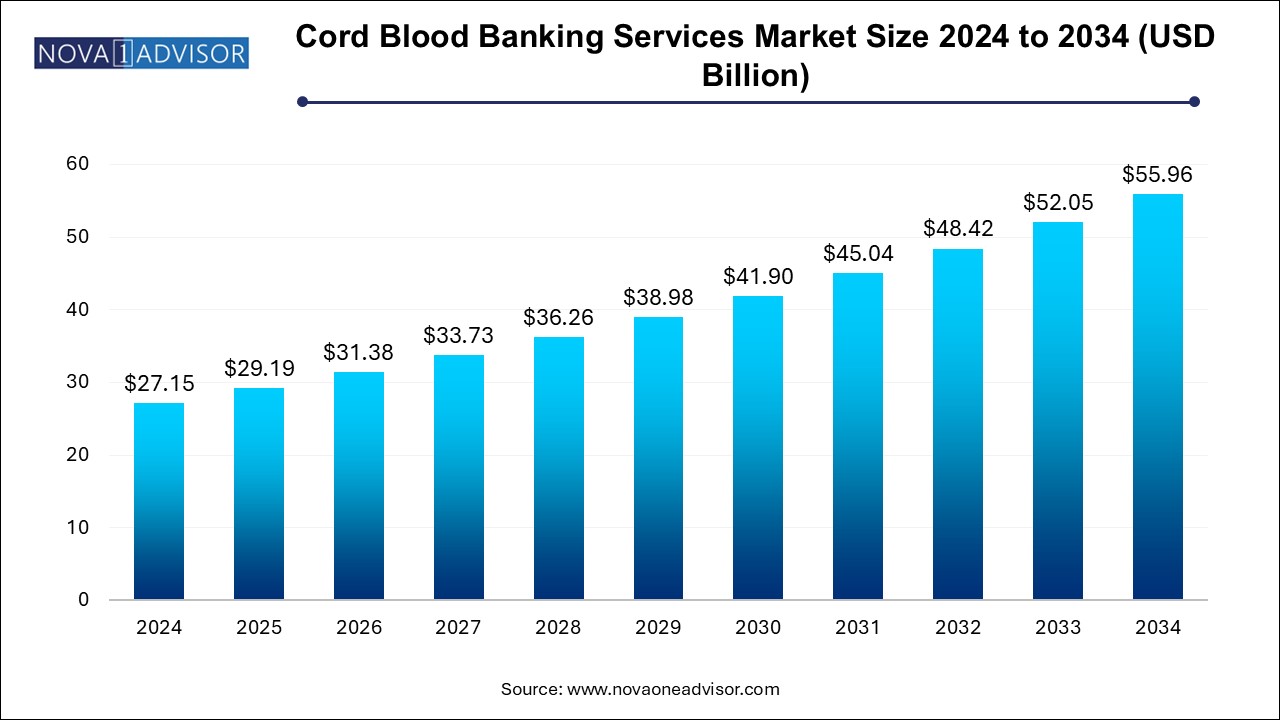
Cord Blood Banking Services Market Key Takeaways:
- The cord blood segment dominated the market in 2024.
- The cord tissue segment is expected to witness a significant growth over the forecast period.
- Cancer dominated the market and accounted for largest share in 2024.
- Blood disorder is expected to witness the fastest CAGR over the forecast period.
- Hospitals dominated the market in 2024.
- Research institutes are expected to witness the fastest CAGR during the forecast period.
- The private segment dominated the market and accounted for the largest market revenue share of 46.0% in 2024.
- The public segment is expected to witness significant growth during the forecast period.
- In 2024, North America cord blood banking services market dominated the global market with a revenue share of 42.5%.
Market Overview
The cord blood banking services market has become an increasingly vital sector within regenerative medicine and cellular therapy. Cord blood, collected from the umbilical cord and placenta after childbirth, is a rich source of hematopoietic stem cells that can be used to treat a wide array of diseases including cancers, blood disorders, genetic conditions, and immune deficiencies.
Initially dominated by a few specialized institutions, cord blood banking has now expanded globally with both public and private banking options. Public banks facilitate altruistic donations for future unrelated patients, while private banks offer personalized storage for family use, often marketed as a biological insurance policy. Furthermore, the emergence of hybrid models—combining elements of public and private banking—adds complexity and opportunity to the market.
Key drivers of the market include increasing awareness about the therapeutic potential of cord blood, rising incidence of chronic diseases treatable by stem cell transplants, advancements in stem cell processing technologies, and expanding regulatory approvals for new therapeutic indications. Additionally, the market is witnessing rapid technological innovation in storage methods, cell processing, cryopreservation techniques, and stem cell expansion, making cord blood banking more efficient and accessible than ever before.
Major Trends in the Market
-
Expansion of Indications for Cord Blood Use: Increasing applications in neurological, metabolic, and autoimmune disorders.
-
Growth of Hybrid Banking Models: Combining public donation and private family storage to optimize usage.
-
Technological Advancements in Cryopreservation: Improved viability and recovery rates after thawing.
-
Increase in Stem Cell Research Funding: Governments and private entities expanding investment in regenerative medicine.
-
Greater Consumer Awareness Campaigns: Increased efforts to educate expectant parents on the benefits of cord blood banking.
-
Emergence of Cord Tissue Banking: Growing demand for storage of mesenchymal stem cells from cord tissue for broader therapeutic use.
-
Adoption of AI in Matching Donors and Recipients: Enhancing outcomes by optimizing cell unit selection in public banks.
-
Globalization of Cord Blood Banks: Multinational partnerships expanding access to diverse genetic resources.
Report Scope of Cord Blood Banking Services Market
| Report Coverage |
Details |
| Market Size in 2025 |
USD 29.19 Billion |
| Market Size by 2034 |
USD 55.96 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2034 |
CAGR of 7.5% |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2024-2034 |
| Segments Covered |
Service, Bank, Component, Application, End-use Region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) |
Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Regional Covered |
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, MEA |
| Key Companies Profiled |
Global Cord Blood Corporation; CBR Systems Inc.; Cryo-Cell International; Cordlife Group Limited; AlphaCord LLC; CSG-BIO; California Cryobank Stem Cell Services LLC; Cord Blood Foundation (Smart Cells International); Singapore Cord Blood Bank; FamiCord; |
Key Market Driver: Rising Prevalence of Hematologic and Genetic Disorders
The main driver for the cord blood banking services market is the increasing global burden of hematologic malignancies, genetic disorders, and immune deficiencies that can be treated through hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). Diseases such as leukemia, lymphoma, sickle cell anemia, thalassemia, and severe combined immunodeficiency syndrome (SCID) are examples where cord blood transplants have demonstrated lifesaving potential.
Furthermore, cord blood offers unique advantages compared to bone marrow or peripheral blood stem cells, including lower risk of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) and less stringent human leukocyte antigen (HLA) matching requirements. These benefits are critical for patients from ethnic minority groups who often face challenges finding compatible bone marrow donors. As clinical success rates improve and new indications emerge, the demand for accessible, high-quality cord blood units is expected to grow substantially.
Key Market Restraint: High Costs Associated with Private Banking
Despite its potential, high costs associated with private cord blood banking act as a major restraint for the market. The initial collection, processing, and first-year storage fees can range from $1,500 to $3,000, with ongoing annual storage costs between $100 and $200. For many families, particularly in low- and middle-income countries, this represents a significant financial burden with uncertain future utility.
Additionally, the probability that privately stored cord blood will ever be used by the donor child or family members remains relatively low, estimated between 1 in 400 to 1 in 2,000. Without guarantees of therapeutic use, families often hesitate to invest in private banking, opting instead for public donation or foregoing storage altogether. Education efforts and cost-reduction strategies are therefore critical to expanding market penetration.
Key Market Opportunity: Advancements in Cord Tissue Banking
A promising opportunity lies in the growing adoption of cord tissue banking. While cord blood contains hematopoietic stem cells, cord tissue is rich in mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), which have broader regenerative potential, including applications in orthopedic conditions, cardiovascular repair, wound healing, and neurological disorders.
Many private banks are now offering dual packages that store both cord blood and tissue, capitalizing on the expanding scope of stem cell therapies. Research into MSC-based treatments is advancing rapidly, with several clinical trials underway for autoimmune diseases, spinal cord injuries, and even cosmetic applications. Companies that integrate cord tissue storage with robust therapeutic pipelines will be strategically positioned for future market leadership.
Cord Blood Banking Services Market By Service Insights
Collection and transportation dominate the service segment, as they are the first and most critical steps in ensuring the viability and sterility of cord blood samples. Proper collection techniques at birth, followed by secure, temperature-controlled transportation to processing facilities, are vital for maintaining cell viability and ensuring successful downstream processing and storage.
Storage services are growing fastest, driven by the cumulative effect of new enrollments and the long-term nature of storage contracts (often 20 years or more). With increasing consumer awareness and expanded clinical applications, the number of stored cord blood units is steadily rising. Innovations such as vapor-phase liquid nitrogen storage, automated inventory management systems, and enhanced thawing protocols are further fueling this segment's expansion.
Cord Blood Banking Services Market By Component Insights
Cord blood dominates the component segment, historically forming the basis of stem cell banking services. Rich in hematopoietic stem cells, cord blood is primarily used for transplant applications in oncology and hematology.
Cord tissue banking is growing rapidly, driven by increasing research demonstrating the regenerative potential of mesenchymal stem cells. Parents increasingly opt for comprehensive packages that preserve both blood and tissue, anticipating wider therapeutic applications in the coming decades. As clinical evidence and regulatory approvals for MSC-based therapies expand, this segment is poised for explosive growth.
Cord Blood Banking Services Market By Application Insights
Cancer dominates the application segment, reflecting the well-established role of cord blood transplants in treating leukemia, lymphoma, and myelodysplastic syndromes. Clinical outcomes have significantly improved over the past two decades, supported by better conditioning regimens, enhanced graft-versus-leukemia effects, and improved supportive care.
Metabolic disorders represent the fastest-growing application area, owing to emerging research into enzyme replacement therapies, lysosomal storage disorders, and inherited metabolic diseases. Cord blood stem cells are increasingly being explored for correcting enzyme deficiencies and systemic metabolic defects, opening new therapeutic horizons.
Cord Blood Banking Services Market By End-use Insights
Hospitals dominate the end-use segment, as they are the primary sites for cord blood collection during childbirth and for transplantation procedures. Many hospitals have integrated public donation programs, ensuring a steady flow of cord blood units into public banks.
Academic and research institutes are growing fastest, reflecting the surge in preclinical and clinical trials exploring new uses for cord blood and tissue-derived stem cells. Universities, medical research centers, and biotech startups are collaborating extensively to harness the regenerative potential of stem cells for diseases beyond hematologic malignancies, such as autism, cerebral palsy, and cardiovascular conditions.
Cord Blood Banking Services Market By Bank Insights
Private cord blood banks dominate the banking segment, offering personalized storage solutions for families seeking to preserve biological material for potential future use. Prominent players like Cord Blood Registry (CBR) and Cryo-Cell International have built strong brands around private banking, supported by robust marketing campaigns targeting expectant parents.
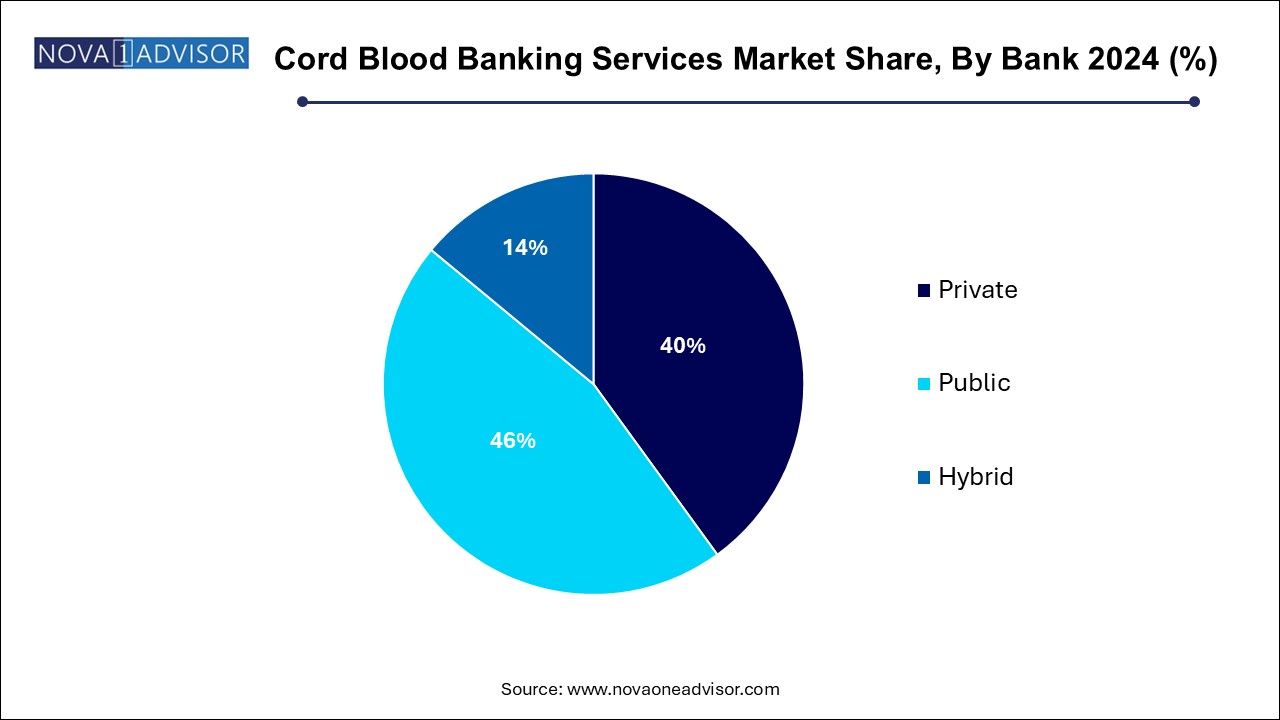
Hybrid banks are growing fastest, as they combine the advantages of public altruistic donation with the option of reserved storage for personal or family use. Hybrid models offer cost-sharing and broader access options, addressing both ethical concerns about private banking and practical concerns about access to diverse donor pools. This flexibility is particularly appealing to increasingly informed and price-sensitive consumers.
Cord Blood Banking Services Market By Regional Insights and Trends
North America dominates the global cord blood banking services market, driven by a high level of awareness, advanced healthcare infrastructure, strong regulatory frameworks, and significant private investment. The U.S. leads in both private and public banking sectors, supported by initiatives like the National Cord Blood Inventory and partnerships between hospitals and public banks.
Private banks such as Cord Blood Registry, Viacord, and Cryo-Cell International are well-established in the region. High rates of insurance coverage for childbirth procedures, proactive patient education programs, and robust support for stem cell research further contribute to North America's leadership.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, fueled by large birth cohorts, rising disposable incomes, and growing investments in healthcare modernization. Countries like China, India, Japan, and South Korea are at the forefront, with increasing numbers of public and private cord blood banks being established.
In China, regulatory reforms have stimulated the expansion of private and hybrid banking models, while Japan has made significant investments in regenerative medicine under its "Sakigake" fast-track approval program. Asia’s genetic diversity also makes its cord blood units highly valuable for global transplant registries.
Some of the prominent players in the cord blood banking services market include:
- Global Cord Blood Corporation
- CBR Systems Inc.
- Cryo-Cell International
- Cordlife Group Limited
- AlphaCord LLC
- CSG-BIO
- California Cryobank Stem Cell Services LLC
- Cord Blood Foundation (Smart Cells International)
- Singapore Cord Blood Bank
- FamiCord
Cord Blood Banking Services Market Recent Developments
-
March 2025: Cord Blood Registry (CBR) announced a partnership with a leading biotech firm to explore cord tissue-derived MSCs for neurological disease applications.
-
February 2025: Cryo-Cell International received FDA approval for a new cryopreservation protocol aimed at enhancing post-thaw stem cell viability.
-
January 2025: ViaCord launched a hybrid banking service combining personalized family storage with contributions to a national donor registry.
-
December 2024: LifeCell International expanded its network of collection centers across tier-2 and tier-3 cities in India, aiming to broaden access.
-
November 2024: StemCyte announced new clinical trial results demonstrating successful use of dual cord blood transplants in adult leukemia patients.
Segments Covered in the Report
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2034. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the cord blood banking services market
By Service
- Collection & Transportation
- Processing
- Analysis
- Storage
By Bank
By Component
By Application
- Cancer
- Genetic Disorders
- Blood Disorders
- Immune Deficiencies
- Metabolic Disorders
- Other Applications
By End-use
- Hospitals
- Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies
- Academic & Research Institutes
By Regional
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa (MEA)


